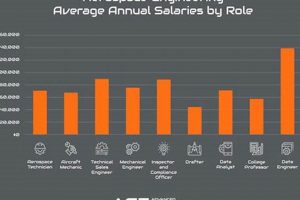
Opportunities in aviation and space technology located in and around a specific Swiss city represent a niche segment of the international employment market. These positions span various roles, from engineering and design to manufacturing, maintenance, and management, all contributing to the advancement of flight and space exploration. As an example, individuals might find opportunities as aerospace engineers, technicians, or project managers within companies operating in this sector.
This localized professional sphere benefits from Switzerland’s strong economy, its reputation for precision manufacturing, and its central location within Europe, facilitating international collaboration and innovation. Historically, the region has attracted skilled professionals due to its high quality of life and the presence of reputable research institutions and international organizations that contribute to the growth and development of related industries. This contributes significantly to local and national economic prosperity and technological advancement.
The following sections will delve into the specific types of positions available, the necessary qualifications and skills, the leading companies in the region, and resources for individuals seeking to pursue a career in this specialized area. Information regarding training programs and the overall outlook for career advancement will also be addressed, providing a comprehensive overview for prospective employees.
The following insights aim to provide guidance for individuals seeking roles within the aviation and space industries located in and around a prominent Swiss city. These recommendations focus on strategic approaches for career advancement and successful job acquisition.
Tip 1: Conduct Thorough Company Research: Before applying to any position, invest significant time in understanding the specific activities, projects, and culture of the organizations operating in the region. This enables a tailored application that demonstrates genuine interest and knowledge.
Tip 2: Highlight Relevant Skills and Experience: Emphasize skills and experience directly related to the aerospace sector, such as knowledge of aviation regulations, proficiency in CAD software, or experience with composite materials. Provide concrete examples of how these skills have contributed to previous successes.
Tip 3: Network Strategically: Attend industry events, conferences, and workshops in the Geneva area to connect with professionals in the field. Building relationships with individuals working in aerospace can provide valuable insights and potential opportunities.
Tip 4: Tailor Applications to Specific Roles: Avoid generic applications. Each application should be specifically tailored to the requirements outlined in the job description, highlighting how the candidate’s qualifications align with the employer’s needs.
Tip 5: Obtain Relevant Certifications and Training: Consider obtaining certifications or completing training courses that are recognized and valued within the aviation and space industries. Examples include certifications in project management, quality assurance, or specific engineering disciplines.
Tip 6: Demonstrate Understanding of the Swiss Aerospace Landscape: Research the specific challenges and opportunities within the Swiss aerospace industry, such as its focus on precision engineering and sustainable aviation technologies. Articulating this understanding during interviews demonstrates a proactive and informed approach.
Tip 7: Prepare for Technical Interviews: Expect rigorous technical interviews that assess in-depth knowledge of relevant engineering principles, software, and industry standards. Practice solving technical problems and clearly articulating technical concepts.
These guidelines aim to increase the likelihood of securing employment within the competitive aviation and space sectors in the area. Diligent research, strategic networking, and targeted skill development are essential for success.
The subsequent sections will explore specific companies, required qualifications, and resources available to support career development in the field.
1. Engineering Specializations
The aerospace sector near Geneva demands a highly specialized engineering workforce to support its diverse activities. These specializations are crucial for maintaining competitiveness and driving innovation in this demanding industry.
- Avionics Engineering
Avionics engineers design, develop, and maintain the electronic systems used in aircraft and spacecraft. This includes navigation systems, communication systems, and flight control systems. For professionals in the Geneva area, proficiency in these areas is essential for roles in aircraft manufacturing, maintenance, and modification.
- Aerodynamics Engineering
Aerodynamics engineers focus on the study of air flow around aircraft and spacecraft, optimizing designs for efficiency and stability. This is particularly relevant in the Geneva area, where companies are involved in the design and testing of new aircraft components and systems. An understanding of computational fluid dynamics and wind tunnel testing is highly valued.
- Propulsion Engineering
Propulsion engineers specialize in the design, development, and testing of engines and propulsion systems for aircraft and spacecraft. Geneva’s aerospace industry includes companies involved in the maintenance and overhaul of aircraft engines, creating opportunities for propulsion engineers with expertise in turbine technology and combustion systems.
- Materials Engineering
Materials engineers research and develop new materials for use in aircraft and spacecraft, focusing on properties such as strength, weight, and resistance to extreme temperatures. Geneva benefits from proximity to research institutions engaged in advanced materials research, providing opportunities for materials engineers to contribute to the development of lighter, stronger, and more durable aerospace components.
These engineering specializations are fundamental to the success of the aerospace sector in the Geneva region. Companies seek professionals with specialized skills and knowledge to drive innovation, ensure safety, and maintain a competitive edge in the global market. Continued investment in education and training in these areas is essential for supporting the growth of the industry.
2. Regulatory Compliance
The nexus between regulatory compliance and aerospace employment in the Geneva area is significant. Strict adherence to international and national aviation regulations is a prerequisite for all activities within the sector. This creates a demand for professionals with expertise in navigating and implementing these regulations. Non-compliance can result in severe penalties, including operational restrictions and financial repercussions for companies. For instance, companies involved in aircraft maintenance must comply with European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) regulations to ensure airworthiness standards are maintained. Failure to meet these standards can lead to the grounding of aircraft and damage to a company’s reputation.
The need for compliance specialists extends across various roles. Engineers must design aircraft components and systems in accordance with safety regulations. Manufacturing personnel must adhere to quality control standards and documentation requirements. Project managers must ensure that projects are executed in compliance with environmental regulations and safety protocols. A specific example is the implementation of the Single European Sky ATM Research (SESAR) project, which requires compliance with new air traffic management regulations. Professionals involved in this project need to understand and implement these regulations to improve air traffic efficiency and safety.
In summary, regulatory compliance is not merely a procedural requirement but a fundamental aspect of aerospace employment in the Geneva area. It influences job roles, skill requirements, and operational practices across the sector. The growing complexity of aviation regulations requires a workforce that is knowledgeable, adaptable, and committed to maintaining the highest standards of safety and compliance. This demand presents both challenges and opportunities for individuals seeking to advance their careers in the area.
3. International Collaboration
Aviation and space activities located near Geneva are intrinsically linked to international collaboration due to the global nature of the industry and Switzerland’s position as a hub for international organizations. Numerous companies in the region participate in joint ventures, partnerships, and research projects with entities from Europe, North America, and Asia. This interconnectedness necessitates a workforce skilled in cross-cultural communication, international regulations, and collaborative project management. For example, a local engineering firm might collaborate with a European consortium on developing a new aircraft component, requiring employees to navigate different engineering standards, communication protocols, and legal frameworks.
The benefits of international collaboration are multifaceted. It allows companies to access specialized expertise, share resources, and reduce development costs. It also fosters innovation by bringing together diverse perspectives and approaches. Airbus, for instance, represents a prime example of international collaboration in the aerospace industry, and Swiss-based companies often supply components or services to Airbus programs. This participation necessitates employees who are familiar with international supply chains, quality control standards, and project management methodologies. Furthermore, the presence of international organizations such as the International Air Transport Association (IATA) in Geneva further emphasizes the importance of understanding global aviation standards and practices.
In summary, international collaboration is not merely an added benefit but a fundamental aspect of the aviation and space job market near Geneva. It requires a workforce that is adaptable, culturally sensitive, and proficient in navigating the complexities of global partnerships. Successfully engaging in international collaboration enhances the competitiveness of local companies and provides professionals with opportunities to work on cutting-edge projects and expand their global networks. Challenges such as language barriers, differing work cultures, and regulatory variations must be addressed to fully realize the benefits of this interconnected approach.
4. Research and Development
Research and Development (R&D) forms a cornerstone of advancement and competitiveness, significantly influencing the nature and availability of “geneva aerospace jobs”. Investment in R&D drives innovation, creates demand for specialized skills, and ultimately shapes the trajectory of the sector in the region. The following points elaborate on key aspects of this relationship.
- Fundamental Research in Aerospace Materials
This facet involves investigating novel materials and composites with enhanced strength-to-weight ratios, thermal resistance, and durability. For example, research into carbon fiber reinforced polymers (CFRP) can lead to the development of lighter aircraft structures, reducing fuel consumption and improving performance. “geneva aerospace jobs” in this area might include materials scientists, engineers, and technicians involved in the design, testing, and manufacturing of these advanced materials.
- Development of Advanced Propulsion Systems
R&D efforts focused on propulsion systems aim to improve efficiency, reduce emissions, and explore alternative fuels. Examples include research into hybrid-electric propulsion, alternative fuel combustion, and advanced turbine technologies. “geneva aerospace jobs” related to propulsion systems may encompass mechanical engineers, aerospace engineers specializing in propulsion, and researchers developing and testing new engine designs.
- Avionics and Flight Control System Innovation
This area concentrates on developing advanced avionics systems, autonomous flight control technologies, and enhanced sensor capabilities. Innovation can lead to improved flight safety, reduced pilot workload, and increased operational efficiency. “geneva aerospace jobs” in avionics and flight control systems may involve electrical engineers, software engineers, and systems engineers responsible for designing, integrating, and testing these advanced systems.
- Sustainable Aviation Technologies
R&D focuses on reducing the environmental impact of air travel. This includes the development of more fuel-efficient aircraft, alternative fuels (biofuels, synthetic fuels, hydrogen), and electric propulsion systems. “geneva aerospace jobs” in sustainable aviation includes scientists, engineers and technicians testing aircraft structure with bio-based composites to reduce CO2 emmisions in the long run.
In conclusion, R&D plays a pivotal role in shaping the “geneva aerospace jobs” market. It not only drives technological advancements but also creates demand for highly skilled professionals across a range of disciplines. Continued investment in R&D is essential for maintaining competitiveness and fostering sustainable growth in the sector.
5. Maintenance Operations
Maintenance operations are an integral component of the aviation sector, significantly influencing the scope and nature of “geneva aerospace jobs”. The continuous upkeep and repair of aircraft, engines, and associated systems necessitate a skilled workforce and represent a substantial portion of activity in the area’s aerospace industry. Without effective maintenance, the safety, reliability, and operational efficiency of aircraft would be compromised.
- Aircraft Maintenance Technicians
Aircraft maintenance technicians conduct routine inspections, perform repairs, and replace defective components on aircraft. Their role is critical for ensuring airworthiness and adherence to safety standards. In the context of “geneva aerospace jobs”, these positions require specialized training and certifications, such as EASA Part-66 licenses. Technicians may work on various aircraft types, from commercial airliners to business jets, depending on the maintenance facilities in the region. A practical example involves technicians performing scheduled maintenance checks on engines, replacing worn parts, and conducting functional tests to ensure optimal performance.
- Engine Overhaul Specialists
Engine overhaul specialists focus on the complete disassembly, inspection, repair, and reassembly of aircraft engines. This complex process demands a high level of expertise and precision. “geneva aerospace jobs” in this area often involve working with turbine engines, performing non-destructive testing, and adhering to strict quality control procedures. For instance, specialists might overhaul a CFM56 engine, replacing turbine blades, bearings, and seals, and then conducting performance tests to ensure the engine meets manufacturer specifications.
- Avionics Maintenance Personnel
Avionics maintenance personnel specialize in the repair and maintenance of aircraft electronic systems, including navigation, communication, and flight control systems. These positions require expertise in digital electronics, software, and troubleshooting techniques. “geneva aerospace jobs” for avionics specialists involve diagnosing and repairing complex electronic faults, calibrating instruments, and updating software. For example, personnel may troubleshoot a malfunctioning autopilot system, replacing faulty sensors, and reprogramming the control computer.
- Maintenance Planning and Management
Maintenance planning and management roles involve coordinating and scheduling maintenance activities, ensuring compliance with regulations, and managing resources effectively. These positions require strong organizational and analytical skills, as well as a thorough understanding of aircraft maintenance procedures. “geneva aerospace jobs” in this area may include maintenance planners, supervisors, and managers who oversee the entire maintenance process, from scheduling inspections to managing spare parts inventory. A typical task involves creating a maintenance schedule for a fleet of aircraft, optimizing resource allocation, and ensuring compliance with EASA regulations.
The demand for skilled maintenance personnel near Geneva reflects the importance of these operations to the aviation industry. The various roles described above all contribute to the safety and efficiency of air travel, showcasing how maintenance operations represent a significant segment of “geneva aerospace jobs”, demanding specialized skills, adherence to rigorous standards, and continuous professional development.
6. Manufacturing Processes
The specialized techniques and procedures used to create aircraft components, systems, and complete aircraft directly influence the availability, nature, and skill requirements of “geneva aerospace jobs”. Expertise in these processes is essential for maintaining safety, quality, and efficiency within the sector. The following explores key facets of manufacturing and their impact on the employment landscape.
- Precision Machining
Precision machining involves the use of computer numerical control (CNC) machines to create intricate parts with extremely tight tolerances. This process is crucial for manufacturing engine components, landing gear parts, and structural elements. “geneva aerospace jobs” related to precision machining require skilled machinists, CNC programmers, and quality control inspectors with expertise in materials science and metrology. An example is the manufacturing of turbine blades, which demands extreme precision to ensure aerodynamic efficiency and structural integrity.
- Composite Manufacturing
Composite manufacturing involves the creation of components from materials such as carbon fiber reinforced polymers (CFRP), which offer high strength-to-weight ratios. These materials are used extensively in aircraft fuselages, wings, and control surfaces. “geneva aerospace jobs” in composite manufacturing require technicians, engineers, and quality assurance personnel with expertise in lay-up techniques, curing processes, and non-destructive testing methods. An example involves the production of a composite wing section, which requires precise layering of carbon fiber sheets and careful monitoring of the curing process to achieve optimal strength and durability.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, involves building components layer by layer from materials such as titanium, aluminum, and polymers. This technology allows for the creation of complex geometries and customized parts, reducing material waste and lead times. “geneva aerospace jobs” in additive manufacturing require engineers, technicians, and designers with expertise in 3D modeling, material selection, and process optimization. An example is the production of lightweight interior components or customized brackets using additive manufacturing techniques.
- Assembly and Integration
Assembly and integration processes involve the joining of individual components to create larger subassemblies and ultimately complete aircraft. This requires skilled technicians, assemblers, and quality control inspectors with expertise in mechanical assembly, electrical wiring, and hydraulic systems. “geneva aerospace jobs” in assembly and integration require strict adherence to engineering drawings, safety procedures, and quality standards. An example involves the assembly of an aircraft fuselage, which requires precise alignment and fastening of numerous components to ensure structural integrity and aerodynamic performance.
These manufacturing processes collectively shape the demand for specialized skills in the “geneva aerospace jobs” market. Expertise in precision machining, composite manufacturing, additive manufacturing, and assembly processes is essential for ensuring the safety, quality, and performance of aircraft and their components. Continued advancements in manufacturing technologies will further influence the nature and requirements of these positions, emphasizing the need for ongoing training and professional development.
7. Project Management
Effective project management is critical to the success of aviation and space endeavors, directly shaping the scope, efficiency, and outcomes of “geneva aerospace jobs”. The complexity and scale of aerospace projects necessitate structured approaches to planning, execution, and control. Professionals skilled in project management are essential for ensuring projects are completed on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards.
- Project Planning and Scheduling
This facet involves defining project scope, objectives, and deliverables, as well as creating detailed schedules and resource allocation plans. Project managers utilize tools such as Gantt charts and critical path method (CPM) to ensure projects stay on track. For instance, in the development of a new aircraft component, project managers must plan the entire process, from design and prototyping to testing and certification. Failure to plan effectively can lead to delays, cost overruns, and compromised quality. “geneva aerospace jobs” in project management often involve the creation of detailed work breakdown structures and the identification of critical milestones.
- Risk Management
Risk management involves identifying potential risks, assessing their impact, and developing mitigation strategies. Aerospace projects are inherently risky due to the complexity of the technology and the stringent safety requirements. Project managers must anticipate potential challenges, such as supply chain disruptions, technical failures, and regulatory hurdles. An example is the management of risks associated with the integration of new avionics systems, where software glitches or hardware malfunctions can have serious consequences. “geneva aerospace jobs” focused on risk management require analytical skills and the ability to develop contingency plans.
- Stakeholder Management
Stakeholder management involves identifying and engaging with all parties who have an interest in the project, including customers, suppliers, regulatory agencies, and internal teams. Effective communication and collaboration are essential for ensuring that all stakeholders are aligned and informed. An example is the management of relationships with regulatory agencies during the certification process for a new aircraft engine, where compliance with safety standards is paramount. “geneva aerospace jobs” in stakeholder management require strong interpersonal skills and the ability to negotiate and resolve conflicts.
- Quality Assurance and Control
Quality assurance and control involve implementing processes and procedures to ensure that project deliverables meet the required quality standards. Aerospace projects demand rigorous quality control due to the critical nature of the applications. Project managers must establish quality metrics, conduct inspections, and implement corrective actions to address any defects or deviations. For instance, in the manufacturing of aircraft structural components, quality control inspectors must verify that the materials and processes meet stringent specifications. “geneva aerospace jobs” related to quality assurance and control require attention to detail and a commitment to maintaining high standards.
The effective application of project management principles is essential for the success of aerospace projects and directly impacts the demand for skilled professionals in “geneva aerospace jobs”. The roles discussed highlight the importance of planning, risk management, stakeholder engagement, and quality control in ensuring projects are completed safely, efficiently, and to the required standards. Continual development of project management skills is crucial for individuals seeking to advance their careers in this dynamic sector.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding employment prospects, required qualifications, and key aspects of the aviation and space industries located in the specified region.
Question 1: What types of “geneva aerospace jobs” are commonly available?
Common positions include aerospace engineers specializing in avionics, propulsion, or structures; aircraft maintenance technicians with EASA certifications; project managers overseeing aircraft development or modification projects; and regulatory compliance specialists ensuring adherence to international aviation standards. Opportunities also exist in research and development, focusing on advanced materials, sustainable aviation technologies, and new avionics systems.
Question 2: What qualifications are typically required for “geneva aerospace jobs”?
Educational requirements often include a bachelor’s or master’s degree in aerospace engineering, mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, or a related field. Specific certifications, such as EASA Part-66 for aircraft maintenance technicians, are frequently required. Professional experience in the aviation or space industry is highly valued, as is knowledge of relevant software and design tools (e.g., CAD, CAM, MATLAB).
Question 3: Which companies are major employers for “geneva aerospace jobs”?
Key employers in the region include companies specializing in aircraft maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) services; manufacturers of aircraft components and systems; research institutions involved in aerospace technology development; and international organizations related to aviation regulation and standardization. Specific company names can be obtained through online job boards, industry directories, and professional networking platforms.
Question 4: What is the salary range for “geneva aerospace jobs”?
Salary ranges vary significantly depending on the position, level of experience, and the size and type of employer. Entry-level positions may command lower salaries compared to senior engineering or management roles. Generally, the compensation reflects the high cost of living in Switzerland and the specialized skills required for these positions. Precise salary data can be found on salary benchmarking websites and through direct inquiries with potential employers.
Question 5: Are there opportunities for international candidates seeking “geneva aerospace jobs”?
Opportunities exist for international candidates, but a valid work permit is generally required. Switzerland has specific immigration policies that prioritize skilled workers who meet certain criteria. Proficiency in English is often essential, and knowledge of French or German can be advantageous. International candidates should research visa requirements and be prepared to demonstrate their qualifications and experience to potential employers.
Question 6: How can individuals find available “geneva aerospace jobs”?
Available positions are typically advertised on online job boards, company websites, and professional networking platforms such as LinkedIn. Attending industry events and career fairs can also provide valuable networking opportunities. Additionally, specialized recruitment agencies focusing on the aerospace sector may be helpful in identifying suitable positions.
These FAQs provide a foundational understanding of the career landscape in the aviation and space industries near Geneva. Further research and networking are recommended for individuals pursuing opportunities in this specialized field.
The subsequent sections will present additional resources and insights for career development in the sector.
Geneva Aerospace Jobs
This exploration has delineated the multifaceted nature of employment within the aviation and space sectors situated near the prominent Swiss city. Key areas such as engineering specializations, regulatory compliance, international collaboration, research and development, maintenance operations, manufacturing processes, and project management have been examined to provide a comprehensive overview of the opportunities and requirements present in this localized industry. The analysis also addressed common inquiries regarding necessary qualifications, leading employers, and avenues for job searching.
The sustained demand for skilled professionals in these domains underscores the ongoing importance of aviation and space technologies to the regional and global economy. Individuals seeking careers should prioritize acquiring specialized knowledge, relevant certifications, and a proactive approach to professional development. Ultimately, the continued growth and innovation within this sector depend on a workforce committed to excellence and adaptability in the face of evolving challenges and opportunities. Further, the pursuit of “geneva aerospace jobs” often requires a dedication to continuous learning, reflecting the ever-changing landscape of these complex technologies.