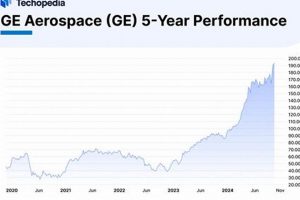
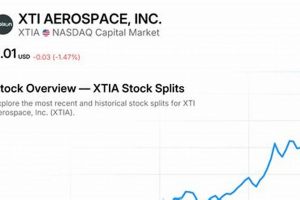
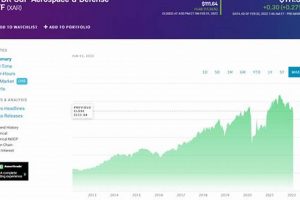
The leading publicly traded companies involved in the development, manufacturing, and sales of products and services related to air and space travel, as well as national security, are central to this discussion. These entities operate in a highly specialized sector, contributing to both civilian and military applications. A prime example is a major manufacturer of commercial aircraft and a significant supplier to global defense agencies.
Investment in this sector provides exposure to industries with substantial technological innovation and often, long-term government contracts. This can provide a degree of stability and growth potential not always found in other markets. Historically, performance has been influenced by geopolitical events, governmental spending policies, and global economic conditions, making it a sector warranting careful consideration.
The following sections will delve into the key factors that influence these organizations, analyze current market trends, and examine the financial metrics used to assess their performance and potential as investment opportunities. This exploration aims to provide a comprehensive overview of this dynamic and significant area of the global economy.
Evaluating Premier Aerospace and Defense Investments
Prudent investment in leading aerospace and defense companies requires a comprehensive assessment of multiple factors. Due diligence is paramount.
Tip 1: Understand Government Contracts: A significant portion of revenue is derived from government contracts. Analyze contract backlogs, renewal probabilities, and the potential impact of changes in government spending policies. For example, a shift in national defense priorities can significantly alter the revenue stream of a major defense contractor.
Tip 2: Assess Technological Innovation: The sector is driven by technological advancements. Evaluate research and development investments, patent portfolios, and the company’s ability to adapt to emerging technologies such as unmanned aerial vehicles or advanced cybersecurity solutions. Consider the competitive landscape regarding the adoption of these technologies.
Tip 3: Monitor Geopolitical Events: Global instability and international conflicts directly influence demand. Track geopolitical developments, defense budgets of key nations, and potential arms agreements. An increase in global tensions often leads to heightened defense spending, benefiting related companies.
Tip 4: Analyze Financial Health: Examine key financial metrics such as revenue growth, profit margins, debt-to-equity ratio, and cash flow. A healthy balance sheet and consistent profitability are indicators of a stable and reliable investment.
Tip 5: Evaluate Supply Chain Resilience: The global supply chain is crucial. Assess the company’s supply chain vulnerabilities, diversification strategies, and ability to mitigate disruptions from geopolitical events or economic downturns. A robust and diversified supply chain minimizes operational risks.
Tip 6: Consider Diversification Within the Sector: Diversifying investments across different segments within the aerospace and defense industry can mitigate risk. This might include investing in companies focused on commercial aviation, defense electronics, or space exploration.
Tip 7: Stay Informed on Regulatory Changes: The aerospace and defense sector is heavily regulated. Monitor changes in export controls, environmental regulations, and international trade agreements, as these can significantly impact operations and profitability.
In summary, successful investment necessitates a thorough understanding of governmental influences, technological advancement, and financial stability. Diligence and informed decision-making are key.
The concluding section will provide a final perspective on the aerospace and defense market’s investment potential.
1. Government Contracts
Government contracts are a foundational element for many entities considered to be premier aerospace and defense investments. These agreements, primarily with national defense agencies, represent a significant, and often the largest, source of revenue for these companies. The stability and predictability afforded by long-term government contracts allows for sustained research and development, infrastructure investment, and consistent dividend payouts to shareholders. The cyclical nature of the commercial aerospace sector makes government contracts a vital buffer against economic downturns. For example, Boeing’s defense division consistently provides revenue even when commercial aircraft orders fluctuate.
The nature and terms of government contracts dictate the financial health and operational capabilities. These contracts are complex, encompassing stringent performance standards, regulatory compliance, and cost controls. Winning and executing these contracts effectively requires a deep understanding of governmental procurement processes and the ability to navigate bureaucratic hurdles. Furthermore, companies must adhere to strict ethical guidelines to maintain their eligibility for future contracts, a crucial aspect for continued success. Failure to meet contractual obligations can lead to penalties, reputational damage, and ultimately, a loss of future opportunities. Lockheed Martin’s success, for instance, is largely attributed to its ability to consistently deliver on complex defense programs within budget and on schedule.
In conclusion, the relationship between government contracts and leading aerospace and defense investments is symbiotic and critical. A thorough analysis of a company’s contract portfolio, its success rate in securing new contracts, and its track record in fulfilling obligations, is essential for any investment decision in this sector. Understanding this connection allows investors to better assess the long-term viability and growth potential of these companies, while also recognizing the inherent risks associated with reliance on governmental spending priorities.
2. Technological Advancement
Technological advancement forms the bedrock upon which the enduring value of entities within the aerospace and defense sector is built. Companies that consistently innovate secure a competitive advantage, attract lucrative contracts, and maintain their position among leading investments. This relationship is causal: investment in research and development (R&D) precipitates technological breakthroughs, which in turn, drive revenue and enhance shareholder value. A prime example is Raytheon Technologies’ focus on advanced radar systems; this dedication has translated into significant contracts for its defense segment and enhanced its overall financial standing. Without sustained technological progress, these organizations risk obsolescence and decline.
The practical significance of understanding this connection lies in its application to investment decisions. Investors need to scrutinize a company’s commitment to R&D, its patent portfolio, and its track record of bringing innovative solutions to market. Furthermore, the ability to anticipate future technological trends, such as the proliferation of autonomous systems or the integration of artificial intelligence, is critical. Consider the transformative effect of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs); companies that invested early in this technology now dominate the market and enjoy substantial returns. Monitoring these developments allows for better risk assessment and informed investment decisions.
In summary, a company’s capacity for technological advancement is inextricably linked to its long-term viability as a leading aerospace and defense investment. While geopolitical events and government spending policies exert influence, sustained innovation is the cornerstone of success. Investors should focus on companies that prioritize R&D, foster a culture of innovation, and demonstrate a clear vision for the future of aerospace and defense technology. Failing to do so exposes investors to the risk of backing companies that are ultimately unable to adapt to the ever-evolving technological landscape.
3. Geopolitical Landscape
The geopolitical landscape exerts a significant influence on leading aerospace and defense organizations. Global tensions, international conflicts, and shifting alliances directly impact demand and profitability for these entities.
- Defense Spending and Budget Allocations
National defense budgets are directly influenced by the prevailing geopolitical climate. Increased threats or perceived instability often lead to expanded military spending, directly benefiting defense contractors. For example, heightened tensions in Eastern Europe have prompted many NATO member states to increase their defense budgets, boosting demand for military hardware and services provided by major defense companies.
- International Arms Trade and Export Policies
Geopolitical dynamics shape international arms trade agreements and export policies. These policies dictate which countries can purchase military equipment and from whom, directly impacting the sales and revenue streams of leading aerospace and defense firms. Political sanctions or shifts in diplomatic relations can significantly alter trade patterns, requiring these companies to adapt their market strategies. An example is the impact of sanctions on Russia, which has re-oriented its defense procurement toward domestic sources.
- Regional Conflicts and Military Engagements
Ongoing regional conflicts and military engagements create immediate demand for military equipment, intelligence, and logistical support. These situations can lead to increased orders for weapons systems, surveillance technology, and related services. The ongoing conflicts in the Middle East, for example, have sustained demand for various defense technologies and services provided by global aerospace and defense firms.
- Cybersecurity Threats and Information Warfare
The rise of cyber warfare and digital espionage has created a growing market for cybersecurity solutions and intelligence gathering capabilities. As nations increasingly engage in cyber operations, the demand for cybersecurity technologies provided by aerospace and defense companies rises. The increasing sophistication of cyber threats from state-sponsored actors compels governments to invest heavily in cybersecurity infrastructure and expertise.
In conclusion, the geopolitical landscape is a key determinant of success for leading aerospace and defense organizations. These companies must navigate complex international relations, adapt to changing defense priorities, and anticipate potential conflicts to maintain their competitive edge and secure long-term growth. An understanding of these dynamics is essential for any investor seeking to assess the viability and potential of these investments.
4. Financial Performance
Financial performance serves as a critical indicator for evaluating the investment quality of leading aerospace and defense organizations. Sustained profitability, efficient capital management, and a robust balance sheet often correlate with long-term success and shareholder value in this sector. Key indicators provide insights into a company’s operational efficiency, strategic positioning, and ability to generate returns.
- Revenue Growth and Diversification
Consistent revenue growth, both organically and through acquisitions, signals a company’s ability to capture market share and adapt to changing industry dynamics. Diversification across various segments (commercial aviation, military, space) mitigates risk associated with fluctuations in any single market. For instance, a company with substantial revenue from both government contracts and commercial aircraft sales is generally more resilient to economic downturns affecting either sector.
- Profit Margins and Operational Efficiency
Profit margins, including gross margin, operating margin, and net profit margin, reflect a company’s ability to control costs and effectively manage its operations. Higher margins indicate greater efficiency and a stronger competitive position. Comparing these margins to industry averages provides context for assessing a company’s relative performance. For example, a firm with consistently higher operating margins than its peers likely possesses superior cost management practices or a more favorable product mix.
- Cash Flow Generation and Capital Allocation
Strong cash flow generation provides a company with the financial flexibility to invest in R&D, pursue acquisitions, and return capital to shareholders through dividends and share repurchases. Prudent capital allocation decisions, such as strategic investments in new technologies or accretive acquisitions, demonstrate management’s ability to generate long-term value. A company with a history of generating strong free cash flow and effectively allocating capital is generally viewed favorably by investors.
- Debt Management and Balance Sheet Strength
A healthy balance sheet, characterized by manageable debt levels and a strong equity base, enhances a company’s financial stability and resilience. Companies with excessive debt are more vulnerable to economic shocks and may have limited capacity to invest in future growth. Key metrics include debt-to-equity ratio, interest coverage ratio, and credit ratings. Lower debt levels and higher credit ratings generally indicate a more financially sound company.
In summary, a comprehensive analysis of financial performance metrics is essential for identifying promising investment opportunities within the aerospace and defense sector. Strong revenue growth, healthy profit margins, robust cash flow generation, and prudent debt management are all indicators of a company’s ability to create value for shareholders and maintain a leading position in this dynamic industry. These factors should be considered in conjunction with geopolitical trends and technological advancements to form a well-rounded investment thesis.
5. Supply Chain Security
The integrity and resilience of supply chains are paramount to the sustained operational capabilities of premier aerospace and defense firms. Disruptions within these chains can have significant ramifications, affecting production schedules, technological advancements, and ultimately, national security.
- Component Sourcing and Vendor Diversification
Reliance on single-source suppliers for critical components creates vulnerabilities within the supply chain. Strategic diversification of vendors, across multiple geographic regions, mitigates the risk of disruptions due to geopolitical instability, natural disasters, or supplier insolvency. For example, major aerospace manufacturers often maintain relationships with several suppliers for essential parts like semiconductors, reducing their dependency on any single entity. This strategy adds complexity but enhances overall supply chain security.
- Counterfeit Parts Detection and Prevention
The infiltration of counterfeit parts into the supply chain poses a significant threat. These substandard components can compromise system performance, reliability, and safety, leading to potentially catastrophic consequences. Robust detection and prevention measures, including rigorous testing, supplier audits, and traceability systems, are essential. Government regulations and industry standards often mandate stringent quality control processes to minimize the risk of counterfeit parts entering the defense supply chain.
- Cybersecurity and Data Protection
Supply chains are increasingly vulnerable to cyberattacks and data breaches. Cybercriminals can target suppliers to gain access to sensitive information, intellectual property, or critical infrastructure. Robust cybersecurity measures, including encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits, are necessary to protect the integrity of the supply chain. Collaboration and information sharing among suppliers and prime contractors are also critical for identifying and mitigating cyber threats.
- Geopolitical Risks and Trade Compliance
Geopolitical instability and shifting trade policies can significantly impact supply chain security. Export controls, sanctions, and trade disputes can disrupt the flow of goods and materials, leading to delays and increased costs. Aerospace and defense companies must closely monitor geopolitical developments and ensure compliance with all applicable trade regulations. Diversifying sourcing locations and establishing contingency plans can help mitigate the risks associated with geopolitical instability.
In summary, ensuring supply chain security is crucial for premier aerospace and defense firms to maintain operational readiness, technological superiority, and financial stability. Vigilant monitoring, strategic diversification, and robust security measures are essential for mitigating the risks associated with a complex and interconnected global supply chain. Companies that prioritize supply chain security are better positioned to navigate disruptions and sustain their competitive advantage in this critical sector.
6. Market Position
Market position is a critical determinant of success and investor confidence among the top aerospace and defense stocks. A dominant market position often translates to pricing power, larger contract wins, and greater influence on industry standards. This position is earned through a combination of technological innovation, successful product development, and strategic acquisitions that consolidate market share. For example, a company that holds a leading share in the military aircraft engine market is likely to secure lucrative long-term maintenance and upgrade contracts, resulting in predictable revenue streams and enhanced financial stability. Market leadership, therefore, serves as a powerful indicator of a company’s resilience and long-term growth potential.
Maintaining a strong market position requires continuous adaptation to evolving industry dynamics. Leading entities allocate significant resources to research and development to stay ahead of competitors and anticipate future technological trends. Furthermore, strategic partnerships and collaborations can enhance market reach and allow access to new technologies or customer segments. Consider the impact of mergers and acquisitions in the defense sector; they often result in a more consolidated market structure, with the acquiring company strengthening its market position and potentially realizing cost synergies. The practical significance of understanding this dynamic lies in identifying companies with the ability to both defend their existing market share and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Ultimately, a company’s market position is a reflection of its competitive advantages and its ability to create value for customers and shareholders. Challenges to this position can arise from disruptive technologies, increased competition from emerging players, or shifts in government procurement policies. Companies that proactively address these challenges and continue to invest in innovation and customer satisfaction are more likely to sustain their market leadership and deliver superior returns for investors. Therefore, market position serves as a bellwether for evaluating the long-term prospects of aerospace and defense stocks, highlighting those poised for continued success in this demanding industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses commonly held inquiries related to this sector, providing insights into investment considerations and industry characteristics.
Question 1: What fundamental factors influence the performance of this collection of businesses?
Government spending policies, geopolitical events, technological advancements, and macroeconomic conditions are primary determinants. Budgetary shifts, international tensions, innovation cycles, and overall economic health exert considerable influence.
Question 2: What are the primary risks associated with investing in these types of equities?
Reliance on government contracts introduces political and budgetary risk. Technological obsolescence poses a threat to companies failing to innovate. Geopolitical instability can lead to unpredictable shifts in demand. Economic downturns may reduce both commercial and defense spending.
Question 3: How is profitability typically measured in this segment?
Key metrics include revenue growth, operating margin, net profit margin, and return on invested capital (ROIC). Consistent profitability and efficient capital allocation are essential indicators.
Question 4: What role does technological innovation play in this area?
Technological leadership is crucial for securing contracts and maintaining competitiveness. Companies that invest heavily in R&D and successfully bring innovative solutions to market tend to outperform their peers. Examples include companies who are at the forefront in autonomous systems, advanced materials, or cybersecurity.
Question 5: How should geopolitical risks be factored into investment decisions?
Assessment of geopolitical risks requires careful monitoring of international relations, defense spending trends, and potential conflict zones. Increased geopolitical instability often leads to higher defense budgets, benefiting related companies.
Question 6: What is the significance of a company’s contract backlog in this segment?
A large contract backlog provides a degree of revenue visibility and stability. It represents the value of future revenue to be recognized from existing contracts. However, the backlog also requires analysis to determine funding certainty and execution risks.
In conclusion, understanding the various factors affecting leading organizations is critical for effective investment decisions. Government influence, innovation, and global affairs all shape this arena.
This concludes the discussion on commonly asked questions. The subsequent section summarizes the key takeaways and offers final recommendations.
Concluding Remarks
This exploration has provided an overview of the key elements influencing the performance of leading aerospace and defense stocks. Government contracts, technological innovation, the geopolitical landscape, financial performance, supply chain security, and market position are identified as critical factors. Analysis of these areas offers a more informed perspective on potential investment strategies.
Investment within this sector requires diligence and awareness of its unique characteristics. Prospective investors must rigorously assess the factors outlined to make informed decisions. Continued monitoring of market dynamics and sector-specific trends is essential for maintaining a well-informed investment approach in the complex realm of top aerospace and defense stocks.