Compensation for professionals involved in the application, development, and management of specialized surface treatments for aircraft and spacecraft components within a global context is a multifaceted subject. This remuneration reflects the technical expertise, experience level, and geographic location of the individual, as well as the specific demands and complexity of the role.
Understanding the financial rewards associated with this sector provides valuable insights into its growth, the demand for skilled personnel, and the economic factors influencing the aerospace industry. It also reflects the critical role these specialized treatments play in aircraft safety, performance, and longevity, and the premium placed on expertise in this field. Historically, compensation has been influenced by the overall health of the aviation sector and technological advancements in coating materials and application techniques.
This discussion will delve into the factors that influence earnings, exploring the range of salaries across different roles and geographical locations, while also considering the impact of experience and specialized skills on earning potential.
This section offers guidance to individuals seeking to understand and potentially enhance their earning potential within the international aerospace coatings field.
Tip 1: Emphasize Specialized Certifications: Pursue and obtain certifications specific to aerospace coatings application, quality control, and inspection. Examples include Nadcap accreditation or manufacturer-specific training. Demonstrated competence in these areas directly correlates with higher earning potential.
Tip 2: Gain Expertise in Advanced Coating Technologies: Familiarize oneself with emerging coating technologies such as plasma spraying, vapor deposition, and nanotechnology-enhanced coatings. Proficiency in these advanced techniques positions individuals as valuable assets, commanding premium compensation.
Tip 3: Seek International Experience: Opportunities exist in various countries with thriving aerospace industries. Working abroad, even for a limited time, can significantly boost one’s resume and increase marketability, leading to improved compensation packages.
Tip 4: Develop Strong Communication and Project Management Skills: Technical expertise alone is insufficient. The ability to effectively communicate complex information to colleagues, clients, and regulatory bodies, coupled with demonstrable project management capabilities, is highly valued and rewarded.
Tip 5: Network Actively within the Industry: Attend industry conferences, join professional organizations, and cultivate relationships with individuals in leadership positions. Networking provides access to unadvertised job opportunities and valuable insights into compensation trends.
Tip 6: Understand Regional Market Variations: Research the prevailing compensation structures in different geographic regions. Factors such as cost of living, demand for specific skillsets, and government regulations can influence salary levels. Tailoring one’s career aspirations to these market conditions is crucial.
Tip 7: Document and Quantify Achievements: Maintain a detailed record of accomplishments, including quantifiable results such as cost savings, process improvements, or defect reduction rates. Presenting a compelling narrative of impact during salary negotiations strengthens one’s position.
By focusing on specialization, continuous learning, and strategic career planning, individuals can effectively navigate the global market and maximize their earning potential.
The next section will explore the long-term career outlook and potential for growth within this specialized field.
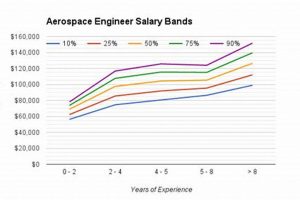
1. Experience Level
Experience level serves as a primary determinant of compensation within the international aerospace coatings sector. Increased practical experience directly translates to enhanced skill sets, deeper understanding of complex processes, and improved problem-solving abilities, all of which contribute to higher earning potential.
- Entry-Level Positions (0-3 years)
Positions at this level typically involve assisting experienced technicians or engineers in coating application, preparation, or inspection. Roles include coating applicators, quality control assistants, and junior technicians. Compensation reflects the limited independent responsibility and focus on foundational skill development. Examples include assisting in surface preparation, mixing coatings, and performing basic inspections under supervision. These positions offer a pathway to higher salaries as experience is gained.
- Mid-Level Positions (3-7 years)
Professionals in this category possess a solid understanding of coating processes and are capable of performing tasks with minimal supervision. Roles may include coating technicians, quality control inspectors, and process engineers. Compensation increases due to increased autonomy, specialized knowledge, and ability to troubleshoot common issues. Example: Performing non-destructive testing, conducting failure analysis, and managing small-scale coating projects.
- Senior-Level Positions (7-10+ years)
Individuals at this level possess extensive knowledge and experience in aerospace coatings, often specializing in a particular area such as research and development, process optimization, or regulatory compliance. Roles can include senior engineers, technical specialists, and team leaders. Compensation reflects advanced expertise, project leadership capabilities, and the ability to contribute to strategic decision-making. Examples include leading coating research projects, developing new coating application techniques, and ensuring compliance with international aerospace standards.
- Management/Executive Positions (10+ years)
These positions require a deep understanding of all aspects of the aerospace coatings industry, along with strong leadership and management skills. Roles include engineering managers, program managers, and directors of operations. Compensation is significantly higher due to strategic responsibilities, financial oversight, and overall impact on company performance. Examples include overseeing large-scale coating projects, managing budgets and resources, and developing long-term coating strategies for the organization.
In summary, the connection between experience level and compensation is undeniable within the international aerospace coatings field. As individuals progress through their careers and gain specialized expertise, their earning potential increases significantly, reflecting the value placed on their skills and knowledge. Continuous professional development and pursuit of advanced certifications further enhance earning potential at each experience level.
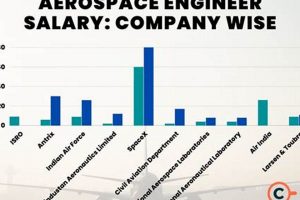
2. Geographic Location
Geographic location exerts a significant influence on compensation levels within the international aerospace coatings sector. This correlation arises due to variations in regional economic conditions, the concentration of aerospace industries, the cost of living, and differing regulatory environments. Regions with a high demand for skilled aerospace professionals, coupled with a relatively high cost of living, typically offer more competitive compensation packages to attract and retain talent. Conversely, areas with a lower demand or a lower cost of living may offer comparatively lower salaries for similar roles.
For example, positions in aerospace manufacturing hubs like Seattle, Washington, or Toulouse, France, often command higher salaries than those in regions with less concentrated aerospace activity. These hubs benefit from the presence of major aerospace manufacturers and suppliers, creating a competitive labor market that drives up compensation. Furthermore, government regulations and labor laws pertaining to benefits, overtime, and worker protections vary across countries and regions, impacting the overall compensation package offered to employees. The presence of strong labor unions in certain locations can also influence salary negotiations and benefits packages.
In summary, understanding the geographic nuances of the aerospace coatings market is crucial for both employers seeking to establish competitive compensation structures and employees seeking to maximize their earning potential. Location-specific factors, including industry concentration, economic conditions, and regulatory environments, collectively shape the compensation landscape and should be carefully considered when evaluating employment opportunities or establishing salary benchmarks. Failure to account for these variations can lead to misaligned expectations and hinder the ability to attract and retain skilled professionals in this specialized field.
3. Skill Specialization
A direct correlation exists between specialized skillsets and enhanced compensation within the international aerospace coatings sector. The increasing complexity of aircraft design and the stringent performance requirements for coatings necessitate expertise in specific areas. Mastery of niche skills, such as advanced surface preparation techniques, specialized application methods (e.g., plasma spraying or vapor deposition), or proficiency in non-destructive testing, translates to a greater demand for these individuals, thereby driving up their earning potential. For instance, engineers with specialized knowledge in corrosion-resistant coatings for specific aircraft components are often highly sought after and command premium salaries due to the critical role their expertise plays in ensuring aircraft safety and longevity.
Furthermore, expertise in regulatory compliance, particularly concerning environmental regulations governing the use of certain coating materials, is increasingly valuable. Professionals who can navigate complex international regulations and ensure adherence to environmental standards are critical for aerospace companies operating globally. Similarly, those possessing in-depth knowledge of specific coating performance characteristics, such as thermal barrier coatings for turbine blades, are essential for optimizing engine efficiency and durability. The ability to apply these specialized skills in a practical setting, such as troubleshooting coating failures or developing innovative coating solutions, further enhances an individual’s market value and earning capacity.
In conclusion, cultivating specialized skills is a strategic approach to maximizing compensation within the international aerospace coatings industry. The demand for professionals with niche expertise is expected to continue growing as the aerospace sector advances and regulatory requirements become more stringent. Individuals who invest in developing advanced skills and obtaining relevant certifications will be well-positioned to capitalize on these trends and achieve significant career advancement and increased earnings.
4. Certifications Held
The acquisition and maintenance of relevant certifications have a demonstrable positive impact on compensation within the international aerospace coatings sector. These certifications serve as tangible evidence of an individual’s competence and adherence to industry standards, making them a valuable asset to employers and increasing earning potential. The relationship between certifications and remuneration is underpinned by the assurance that certified professionals possess a validated skill set and a commitment to maintaining industry best practices. For example, individuals holding Nadcap accreditation, a widely recognized standard for aerospace manufacturing processes, often command higher salaries due to the rigorous training and evaluation required to obtain and maintain this certification. This is because Nadcap-certified personnel demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of coatings processes and the ability to consistently meet stringent quality requirements.
Furthermore, certifications specific to coating application techniques, such as those offered by coating manufacturers or professional organizations, enhance an individual’s value in the labor market. These certifications validate proficiency in the application of specific coating types, ensuring consistent and reliable results. For example, a technician certified in the application of thermal barrier coatings for turbine blades would be highly sought after by aerospace engine manufacturers and maintenance providers, leading to increased salary prospects. The practical significance of this understanding lies in the ability for both employers and employees to make informed decisions about training, skill development, and compensation. Companies can prioritize hiring certified professionals and incentivize certification attainment among existing staff, while individuals can strategically invest in certifications that will demonstrably increase their earning potential.
In summary, the possession of relevant certifications within the international aerospace coatings industry serves as a key determinant of compensation. These credentials provide validation of skills, knowledge, and adherence to industry standards, thereby increasing an individual’s marketability and earning potential. Investing in recognized certifications represents a strategic approach for professionals seeking to advance their careers and maximize their compensation in this highly specialized field.
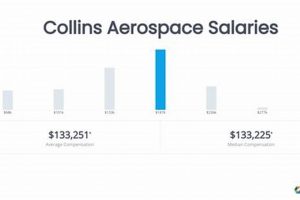
5. Company Size
Company size exerts a discernible influence on compensation within the international aerospace coatings sector. Larger organizations, characterized by greater revenue streams, more extensive project portfolios, and often, a broader geographic footprint, typically offer higher salaries compared to smaller enterprises. This disparity is attributable to several factors. Larger companies possess the financial capacity to invest in attracting and retaining highly skilled personnel, offering more competitive compensation packages, comprehensive benefits, and opportunities for professional development. Furthermore, larger projects undertaken by these organizations often demand a higher level of expertise and specialization, commanding a premium in terms of remuneration. For instance, a senior coatings engineer working on the development of advanced thermal barrier coatings for a multinational aerospace manufacturer is likely to receive a significantly higher salary than an engineer performing similar tasks for a smaller, regional coatings supplier. This difference is also reflective of the complexity and scale of the challenges presented by larger organizations, requiring more sophisticated problem-solving and strategic thinking.
The impact of company size extends beyond base salary, influencing benefits packages, bonus structures, and long-term incentive plans. Larger companies often provide more comprehensive health insurance, retirement plans, and stock options, contributing to a more attractive overall compensation package. Moreover, the potential for career advancement within larger organizations tends to be greater, offering employees opportunities to progress into management or leadership roles, which in turn lead to higher salaries. Conversely, smaller companies may offer a more intimate work environment and greater autonomy but may lack the resources to match the compensation levels of their larger counterparts. However, this isn’t uniformly true; some smaller specialized companies with unique technologies or market niches can offer competitive salaries to attract key talent. One example could be a boutique firm specializing in highly customized coatings for niche applications within the space exploration sector, where specialized skills are highly valued.
In summary, company size serves as a significant, although not sole, determinant of compensation within the international aerospace coatings sector. Larger organizations generally possess the financial resources to offer more competitive salaries and benefits packages, while smaller companies may offer different advantages, such as a more personalized work environment or specialized expertise in specific market segments. Understanding the compensation landscape within different size companies is essential for both employers seeking to attract talent and employees aiming to maximize their earning potential and career prospects. A comprehensive assessment of compensation packages, encompassing salary, benefits, and career advancement opportunities, is critical when evaluating employment opportunities within this dynamic industry.
6. Economic Climate
The overall economic climate significantly impacts remuneration trends within the international aerospace coatings sector. Fluctuations in economic indicators, such as GDP growth, inflation rates, and global trade volumes, influence both the demand for aerospace products and the financial capacity of companies to offer competitive salaries. A stable and expanding economy typically fosters increased aircraft production, maintenance activities, and research and development investments, all of which contribute to a positive outlook for compensation in this field.
- Aerospace Industry Performance
The financial health of the aerospace industry itself is a primary driver. Increased aircraft orders, driven by growing passenger traffic or defense spending, lead to higher production rates and consequently, a greater demand for coatings professionals. Conversely, economic downturns often result in reduced aircraft orders, layoffs, and salary freezes. For example, the COVID-19 pandemic severely impacted the aviation industry, leading to widespread salary reductions and hiring freezes in the aerospace coatings sector globally. As travel demand rebounded, so did the opportunities and compensation levels for these professionals.
- Government Regulations and Trade Policies
Government policies, including tariffs, trade agreements, and environmental regulations, influence the costs of materials, production, and compliance within the aerospace coatings industry. Stringent environmental regulations may necessitate the adoption of more expensive, eco-friendly coatings, impacting manufacturing costs and potentially affecting wages. Tax incentives and government subsidies for aerospace manufacturing can boost industry profitability and allow companies to offer more competitive salaries. Trade wars or protectionist policies can disrupt supply chains and increase costs, potentially leading to downward pressure on wages.
- Inflation and Cost of Living
Inflation erodes purchasing power and can prompt employees to demand higher salaries to maintain their standard of living. In regions experiencing high inflation rates, aerospace coatings companies must adjust compensation packages to remain competitive and retain skilled personnel. The cost of living, which varies significantly across different geographic locations, also plays a crucial role. Companies operating in high-cost-of-living areas typically offer higher salaries to offset the increased expenses faced by employees.
- Technological Advancements
Technological advancements in coating materials and application techniques can impact the demand for specific skill sets and, consequently, compensation levels. For instance, the development of automated coating systems may reduce the need for manual labor in some areas, while simultaneously increasing the demand for technicians skilled in operating and maintaining these systems. Professionals with expertise in emerging coating technologies, such as nanotechnology-enhanced coatings or self-healing coatings, are often highly sought after and command premium salaries.
In conclusion, the economic climate serves as a fundamental contextual factor influencing salary levels and employment opportunities in the international aerospace coatings industry. Understanding these economic forces is essential for both employers seeking to attract and retain skilled personnel and employees seeking to maximize their earning potential. A comprehensive assessment of economic indicators, industry trends, and government policies is crucial for navigating the complexities of the global aerospace coatings market and making informed career decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries related to compensation within the international aerospace coatings sector, providing clarity on factors influencing salary ranges and career progression.
Question 1: What is the typical salary range for an entry-level aerospace coatings technician in Europe?
The salary range for entry-level technicians in Europe can vary depending on the specific country and the company’s financial performance. Generally, one might expect a starting salary between 25,000 and 35,000 per annum. Factors influencing this range include the cost of living in the specific region and the demand for skilled technicians.
Question 2: How does holding a Nadcap certification affect an aerospace coatings inspector’s salary in North America?
Possessing Nadcap accreditation typically results in a higher salary for aerospace coatings inspectors in North America. The accreditation demonstrates adherence to industry standards and competency in inspection procedures. Expect a salary increase of approximately 5% to 15% compared to non-certified inspectors, depending on experience and the specific role.
Question 3: What are the salary expectations for a senior coatings engineer with ten years of experience in Asia, specializing in thermal barrier coatings?
Senior coatings engineers with extensive experience in thermal barrier coatings can command a premium salary in Asia. With ten years of experience, one might anticipate an annual salary ranging from $80,000 to $150,000 USD. This range is influenced by the engineer’s expertise, the specific location within Asia, and the size and profitability of the employing organization.
Question 4: How does the size of an aerospace company impact the salary offered to a coatings research and development scientist?
Larger aerospace companies generally offer higher salaries to coatings research and development scientists compared to smaller firms. These larger organizations possess greater financial resources and are often involved in more complex and demanding projects. Expect a salary difference of potentially 20% to 30% or more when comparing similar roles in a large multinational corporation versus a smaller, specialized coatings supplier.
Question 5: What is the typical compensation package for an aerospace coatings sales representative with international responsibilities?
Aerospace coatings sales representatives with international responsibilities often receive a base salary plus commission structure. The base salary can range from $60,000 to $100,000 USD, with potential for significant commission earnings based on sales performance. The overall compensation package may also include benefits such as travel expenses, health insurance, and retirement contributions.
Question 6: How does economic recession impact compensation adjustments within the international aerospace coatings market?
Economic recession typically leads to decreased demand for aerospace products and services, resulting in cost-cutting measures within the industry. This can manifest in salary freezes, reduced bonuses, and, in some cases, layoffs. Compensation adjustments during economic downturns often prioritize maintaining employment levels over significant salary increases. However, highly skilled professionals with critical expertise may still be able to negotiate favorable terms, depending on their value to the organization.
In conclusion, compensation within the aerospace coatings sector is influenced by numerous factors, including experience, certification, geographic location, company size, and the prevailing economic climate. Understanding these dynamics is essential for both employers and employees seeking to navigate the complexities of the global labor market.
The following section will delve into future trends and evolving technologies that will shape the international aerospace coatings job market.
Conclusion
This exploration has illuminated the multifaceted nature of compensation within the international aerospace coatings sector. It has identified key determinants such as experience, geographic location, skill specialization, certifications, company size, and the broader economic climate. A comprehensive understanding of these factors is essential for both employers seeking to attract and retain talent and professionals aiming to maximize their earning potential within this specialized field.
The aerospace industry continues to evolve, demanding increasingly sophisticated coating solutions and expertise. A proactive approach to continuous learning, skill development, and strategic career planning remains crucial for sustained success and optimized earnings within the dynamic international aerospace coatings market. Individuals and organizations that prioritize these elements will be best positioned to thrive in the years to come.


![Unlock: Aerospace Scientist Salary [2024 Guide] Insights Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions Unlock: Aerospace Scientist Salary [2024 Guide] Insights | Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-220-300x200.jpg)