Compensation for professionals in the field of aircraft and spacecraft design, development, and testing at a prominent European aircraft manufacturer is a key consideration for those pursuing careers in this sector. The remuneration packages can vary significantly based on factors such as experience, location, specialization, and the specific role within the organization. For example, a junior engineer focusing on structural analysis may receive a different starting remuneration than a senior specialist in propulsion systems.
Understanding the potential earnings associated with these specialized roles provides valuable insights for career planning and negotiation. These figures reflect not only the demand for skilled personnel in the aerospace industry but also the economic landscape and cost of living in the regions where Airbus operates. Historical trends show an increase in these figures parallel to technological advancements and the growing global demand for air travel and space exploration.
The following discussion will delve into the various factors influencing remuneration, explore the typical range, compare compensation across different experience levels and locations, and highlight potential career advancement opportunities within the organization that may impact financial rewards.
Understanding and effectively negotiating remuneration in the aerospace engineering sector, particularly at a major corporation, requires careful preparation and a strategic approach. The following tips offer guidance for individuals seeking employment or advancement within such an organization.
Tip 1: Research Industry Benchmarks: Thoroughly investigate average compensation figures for similar roles, experience levels, and locations. Websites like Glassdoor, Salary.com, and professional engineering associations can provide valuable data. This allows for a grounded understanding of realistic earning potential.
Tip 2: Highlight Relevant Skills and Experience: Emphasize qualifications, technical skills, and project experience that directly align with the specific requirements of the position. Quantify achievements whenever possible, demonstrating the tangible value brought to previous roles. For instance, specify efficiency improvements or cost reductions achieved through engineering solutions.
Tip 3: Consider Total Compensation: Evaluate the entire compensation package, including benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, stock options, paid time off, and professional development opportunities. These benefits can significantly impact the overall value of the employment offer.
Tip 4: Understand Regional Cost of Living: Factor in the cost of living in the specific location where the position is based. Remuneration may vary based on regional differences in expenses such as housing, transportation, and taxes. Adjust expectations accordingly to ensure financial stability.
Tip 5: Demonstrate a Long-Term Perspective: Convey a commitment to professional growth and development within the organization. Highlight a desire to contribute to long-term projects and innovation, indicating an understanding of the company’s strategic objectives. This can strengthen the negotiation position by signaling a valuable investment.
Tip 6: Practice Negotiation Skills: Prepare to articulate the value brought to the role and the reasons for seeking a specific remuneration level. Practice negotiating strategies and be prepared to compromise while advocating for fair and competitive compensation.
Employing these strategies can lead to a more informed and effective negotiation process, resulting in a remuneration package that accurately reflects experience, skills, and the value contributed to the organization.
The following section will provide a comparison across different experience levels and locations.
1. Experience Level
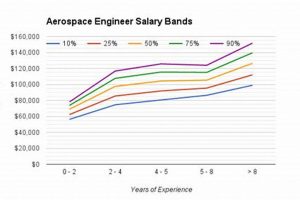
Experience level is a primary determinant of compensation for aerospace engineers at Airbus. As engineers accrue practical experience and demonstrate increasing proficiency, their earning potential typically increases commensurately. This correlation is underpinned by the enhanced value experienced engineers bring to the organization through accumulated knowledge, skills, and proven problem-solving abilities.
- Entry-Level Engineers
Entry-level positions, typically occupied by recent graduates or those with limited industry experience (0-3 years), represent the starting point for aerospace engineering careers at Airbus. Compensation at this level reflects foundational knowledge and the potential for growth. These engineers often work under supervision, contributing to design, analysis, or testing tasks. Remuneration is generally lower than that of more experienced colleagues, serving as an investment in future expertise. For example, a recent graduate working on structural analysis of aircraft wings would likely earn a starting that is lower than other people.
- Mid-Level Engineers
Mid-level engineers (3-7 years of experience) possess a more refined skillset and a track record of successful project contributions. They often take on more complex tasks, leading small teams or specialized projects. Their remuneration reflects their growing expertise and increased responsibility. These engineers may be involved in tasks such as designing aircraft systems, optimizing performance, or troubleshooting technical issues. Their work experience would be higher salary package.
- Senior Engineers
Senior engineers (7+ years of experience) are recognized experts in their respective fields. They possess extensive knowledge, advanced technical skills, and a proven ability to lead large-scale projects. Their remuneration reflects their expertise and leadership capabilities. Senior engineers may be responsible for developing new technologies, overseeing complex engineering projects, or providing technical guidance to junior engineers. Their role is often more strategic, involving long-term planning and decision-making.
- Principal Engineers and Technical Specialists
At the pinnacle of the engineering career path are principal engineers and technical specialists. These individuals possess exceptional expertise, often recognized as industry leaders in their fields. Their remuneration is commensurate with their specialized knowledge, strategic contributions, and ability to drive innovation. They typically lead research and development efforts, mentor junior engineers, and represent the company at industry conferences and events. Their expertise helps the company and improve product quality.
In essence, the correlation between experience level and compensation at Airbus underscores the value placed on accumulated knowledge, proven skills, and leadership capabilities. As engineers progress through their careers, their remuneration reflects their growing contributions to the organization’s success.
2. Geographic Location
Geographic location exerts a significant influence on remuneration for aerospace engineers at Airbus, reflecting regional economic conditions, cost of living variations, and the presence of specialized aerospace hubs. Compensation packages are adjusted to account for these factors, ensuring competitive salaries within specific regions while reflecting the overall economic landscape.
- Cost of Living Adjustments
Airbus adjusts remuneration to reflect the cost of living in different locations. For example, engineers working in cities with higher living costs, such as Munich or Paris, typically receive higher salaries compared to those in regions with lower expenses, like Seville. These adjustments ensure that employees maintain a comparable standard of living regardless of their work location. This ensures the employee living standard and improve productivity.
- Regional Economic Conditions
Economic conditions in the region where an Airbus facility is located impact remuneration levels. Areas with robust economic growth and strong demand for skilled engineers may offer higher salaries to attract and retain talent. Conversely, regions with slower economic growth may see lower salary levels due to reduced competition for skilled workers. The country economy growth is really important.
- Aerospace Industry Clusters
Locations with established aerospace industry clusters, such as Toulouse, France, or Hamburg, Germany, often offer competitive remuneration packages. These clusters attract a concentration of aerospace companies and related industries, creating a competitive job market that drives up salaries. The presence of research institutions and specialized training facilities in these clusters further contributes to higher earning potential for aerospace engineers.
- Government Incentives and Regulations
Government incentives and regulations can indirectly influence remuneration levels in certain regions. Tax breaks, subsidies, or other incentives designed to attract aerospace companies may lead to increased investment and job creation, potentially driving up salaries for skilled engineers. Similarly, regulations related to labor standards and minimum wage requirements can impact the overall compensation landscape.
In summary, geographic location serves as a crucial factor in determining remuneration for aerospace engineers at Airbus, reflecting the interplay of cost of living, regional economic conditions, industry clusters, and government policies. Understanding these geographic nuances is essential for both job seekers and employers in the aerospace industry.
3. Specific Expertise
Remuneration for aerospace engineers at Airbus is intrinsically linked to their specific area of expertise. Certain specialized skill sets are in higher demand due to technological advancements, industry trends, and project requirements, thus commanding a premium in the labor market. For example, engineers specializing in advanced composite materials, artificial intelligence applications for aerospace, or sustainable aviation technologies often receive higher salaries than those with more general skills. This reflects the criticality of their knowledge to Airbus’s strategic objectives and competitive advantage. The direct impact of specialized skill sets on project success and innovation drives the demand for, and consequently, the compensation of these experts.
To illustrate, an engineer proficient in the design and optimization of electric propulsion systemsa burgeoning field in aviationis likely to be highly valued and compensated accordingly, given the industry’s push towards more sustainable practices. Similarly, specialists in cybersecurity for aircraft systems are in increasing demand as aviation becomes more interconnected, and their expertise is vital for protecting against potential threats. These examples demonstrate how specific expertise directly correlates with an engineer’s ability to contribute to cutting-edge projects, thereby justifying a higher remuneration. Also, certification can make salary become increase.
The relationship between specialized skills and remuneration serves as a key incentive for engineers to pursue advanced training and certifications in high-demand areas. Furthermore, Airbus utilizes this compensation model to attract and retain talent in critical domains, ensuring it maintains a competitive edge in innovation and technological advancement. Understanding this connection is vital for engineers seeking to maximize their earning potential and for Airbus in effectively allocating resources to foster a skilled and specialized workforce.
4. Education & Certifications
The level of education and possession of relevant certifications demonstrably influences compensation for aerospace engineers at Airbus. A direct correlation exists between advanced degrees, specialized training, and recognized certifications and the earning potential within the organization. Engineers holding a Master’s degree or a Ph.D., especially in specialized fields such as aerodynamics, propulsion, or structural mechanics, are typically compensated at a higher rate than those with only a Bachelor’s degree. This reflects the advanced knowledge and research capabilities that these degrees signify. For instance, an engineer with a doctorate in composite materials could command a higher salary due to their expertise being crucial for developing lighter and more fuel-efficient aircraft components. Moreover, specific certifications that validate expertise in industry-standard software or regulatory compliance can also result in increased compensation. Examples include certifications in finite element analysis (FEA) software or airworthiness regulations, signifying competency and immediate value to Airbus.
The impact of education and certifications on remuneration is further amplified by their influence on career progression. Engineers with advanced qualifications often have access to more specialized and leadership-oriented roles, which naturally come with increased financial rewards. Furthermore, Airbus may provide financial support or incentives for engineers to pursue relevant certifications, recognizing their value in enhancing the company’s overall expertise and competitiveness. This proactive approach demonstrates the practical significance of continuous learning and skill development in maximizing earning potential within the organization. The company might even do partnerships with universities to give its employees education about the aerospace engineering.
In conclusion, education and certifications serve as critical components of an aerospace engineer’s compensation package at Airbus. Higher levels of education and specialized certifications signify increased expertise, which translates into higher demand and, consequently, higher salaries. While practical experience remains crucial, a strong educational foundation and relevant certifications provide a competitive edge, facilitating career advancement and improved earning potential. These factors must be considered by both aspiring and current aerospace engineers aiming to optimize their remuneration and career trajectory within Airbus.
5. Role Complexity
Role complexity significantly influences remuneration for aerospace engineers at Airbus. Compensation structures within the organization recognize and reward engineers who undertake tasks demanding a higher degree of cognitive skill, problem-solving ability, and responsibility. An engineer engaged in designing a novel aircraft wing structure, involving intricate aerodynamic calculations and advanced materials, commands a higher remuneration compared to an engineer performing routine maintenance checks on existing systems. The heightened responsibility associated with complex roles, where errors could have significant financial or safety repercussions, justifies a premium in pay. Therefore, the degree of difficulty and the scope of impact directly correlate with the compensation package.
Consider the practical example of two engineers with comparable years of experience: one specializing in computational fluid dynamics (CFD) for optimizing wing designs and another focusing on component testing. The CFD specialist tackles a more complex role, requiring advanced mathematical modeling, extensive computational resources, and the ability to interpret complex simulation results. Their work directly influences aircraft performance and fuel efficiency, aligning with strategic company objectives. This heightened complexity translates into higher market value and, consequently, greater compensation. The component testing engineer, while vital for ensuring structural integrity, operates within a more defined scope and established procedures, resulting in a different level of remuneration. Likewise, an engineer tasked with leading a multi-national team to develop a new avionics system faces a much higher level of complexity due to dealing with regulations, team management, project and technical. These different tasks have a huge different salary too.
In summary, the degree of complexity inherent in an aerospace engineer’s role is a critical determinant of compensation at Airbus. It encompasses the level of technical expertise required, the scope of responsibility, and the potential impact of the work. Recognizing and rewarding role complexity ensures that the organization attracts and retains talent capable of tackling the most challenging engineering tasks, driving innovation, and maintaining a competitive edge in the aerospace industry.
6. Company Performance
The overall financial health and strategic achievements of Airbus exert a tangible influence on the compensation packages offered to its aerospace engineers. When the company demonstrates strong profitability, successful product launches, and significant market share, it often translates into increased opportunities for employee bonuses, salary adjustments, and other performance-based incentives. This direct correlation stems from the recognition that engineers contribute significantly to the company’s success through their design, development, and innovation efforts. For instance, a year marked by record aircraft deliveries and substantial contract wins might result in higher-than-average bonus payouts for engineers involved in those specific projects or contributing to overall production efficiency. The company’s earnings help workers have compensation, whether its benefits or bonus.
Conversely, periods of economic downturn or instances of significant project delays can negatively impact the financial rewards available to engineers. If Airbus experiences reduced profitability due to decreased aircraft orders, production bottlenecks, or unforeseen market challenges, the allocation of resources for employee compensation may be constrained. This could manifest as smaller bonus pools, delayed salary increases, or even workforce reductions in certain areas. The relationship is not always linear, however. Airbus may prioritize retaining key engineering talent even during challenging times, recognizing the long-term strategic value of their expertise. This could involve offering non-monetary benefits, such as enhanced professional development opportunities or increased job security, to compensate for potential limitations on salary growth.
In conclusion, the financial performance of Airbus serves as a significant determinant of aerospace engineer compensation, shaping both immediate rewards and long-term career prospects. While individual contributions and expertise remain vital, the company’s overall success provides the financial foundation for competitive salaries and performance-based incentives. Engineers are therefore encouraged to understand the broader business context in which they operate, recognizing that their efforts are inextricably linked to Airbus’s financial health and, ultimately, their own compensation.
7. Negotiation Skills
Negotiation skills exert a direct influence on the final remuneration package secured by aerospace engineers at Airbus. The ability to articulate one’s value proposition, understand market benchmarks, and effectively advocate for fair compensation is crucial in securing a salary that reflects expertise and experience. Engineers who possess strong negotiation acumen are better equipped to present their qualifications persuasively, justify desired compensation levels based on industry standards and individual contributions, and navigate the offer process to achieve favorable outcomes. This ability is especially relevant during initial hiring and subsequent performance review cycles, where adjustments to compensation are often negotiated.
The application of negotiation skills extends beyond simply asking for a higher figure. It involves demonstrating a clear understanding of the role’s responsibilities, the company’s needs, and the engineer’s specific expertise in addressing those needs. For example, an aerospace engineer with demonstrable experience in successfully implementing cost-saving measures on previous projects can leverage this track record during negotiations, quantifying the potential financial benefits to Airbus. Similarly, proficiency in emerging technologies or specialized software packages can be presented as a valuable asset, justifying a higher salary than the initial offer. Effective negotiation also involves understanding the total compensation package, including benefits, stock options, and professional development opportunities, and strategically prioritizing certain aspects to maximize overall value.
In summary, negotiation skills represent a critical component in determining the final compensation of aerospace engineers at Airbus. The ability to articulate one’s value, understand market dynamics, and effectively advocate for fair remuneration is instrumental in securing a salary that reflects expertise and experience. Furthermore, this skill fosters a proactive approach to career management, empowering engineers to actively shape their financial trajectory within the organization.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding remuneration for aerospace engineers at Airbus, offering clarity on various aspects influencing compensation packages.
Question 1: What is the typical starting for an entry-level aerospace engineer at Airbus?
The initial remuneration for entry-level aerospace engineers at Airbus varies based on factors such as location, academic qualifications, and specific role requirements. While precise figures are subject to change, compensation generally aligns with industry standards for similar positions in the respective region.
Question 2: How does geographic location affect the Airbus aerospace engineer salary?
Geographic location exerts a significant influence on remuneration. Engineers working in locations with higher costs of living or strong aerospace industry clusters typically receive higher salaries to offset expenses and remain competitive in the local market.
Question 3: What educational qualifications lead to increased Airbus aerospace engineer salary?
Advanced degrees, such as Master’s degrees or Ph.D.s in specialized fields like aerodynamics or propulsion, often result in increased compensation. Relevant certifications also demonstrate expertise and can positively influence remuneration.
Question 4: Are performance-based bonuses a common component of aerospace engineer compensation at Airbus?
Performance-based bonuses are frequently incorporated into compensation packages, rewarding engineers for exceeding expectations, contributing to successful projects, and aligning with company objectives. These bonuses are contingent upon individual and company performance.
Question 5: How can an aerospace engineer at Airbus negotiate a higher salary?
Effective negotiation skills involve demonstrating a clear understanding of the role’s requirements, quantifying the engineer’s value proposition, and researching industry benchmarks for similar positions. Proactive communication and a thorough understanding of the total compensation package are crucial.
Question 6: Does company performance affect aerospace engineer salaries at Airbus?
Company performance directly impacts the financial rewards available to engineers. Periods of strong profitability and successful project outcomes often translate into increased opportunities for bonuses and salary adjustments, while economic downturns may result in constrained compensation.
In summary, compensation for aerospace engineers at Airbus is determined by a multifaceted interplay of experience, location, qualifications, performance, and negotiation skills. Understanding these factors is essential for both job seekers and current employees.
The next section will present actionable advice for enhancing career prospects within the aerospace engineering domain.
Airbus Aerospace Engineer Salary
The examination of “airbus aerospace engineer salary” reveals a complex interplay of factors influencing compensation. Experience, geographic location, education, role complexity, company performance, and negotiation skills collectively shape the remuneration landscape for these professionals. A thorough understanding of these elements is crucial for career planning and financial strategizing within the aerospace industry. Furthermore, the correlation between specialized skills and earning potential underscores the importance of continuous learning and professional development.
Prospective and current aerospace engineers should leverage this knowledge to navigate the compensation process effectively. Continued diligence in skill enhancement, coupled with a strong understanding of industry trends and market demands, will prove invaluable in securing competitive remuneration and fostering long-term career success. The data presented herein serves as a foundation for informed decision-making and strategic career advancement within Airbus and the broader aerospace sector.



![Aerospace Engineer Salary: CS vs Aero Eng? [2024] Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions Aerospace Engineer Salary: CS vs Aero Eng? [2024] | Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-71-300x200.jpg)
![[Guide] Bennett Aerospace Salaries: What to Expect (2024) Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions [Guide] Bennett Aerospace Salaries: What to Expect (2024) | Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-52-300x200.jpg)