Compensation provided to individuals employed by the mentioned aerospace manufacturer constitutes a significant factor in attracting and retaining skilled professionals. This remuneration typically includes a base wage or annual salary, and may encompass benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and performance-based bonuses.
The level of earnings within this sector often reflects the complexity and specialization of the roles. Factors influencing compensation include experience, education, and specific job responsibilities. Historically, competitive wages and comprehensive benefits packages have played a crucial role in sustaining a qualified workforce within this industry, contributing to innovation and operational efficiency.
The following sections will delve into aspects of compensation structure, factors that influence earning potential, and typical salary ranges across different job functions within the specified aerospace company.
Tips Regarding Compensation at the Aerospace Manufacturer
Understanding factors influencing potential income can be beneficial for individuals seeking employment or advancement within this specific organization.
Tip 1: Research Specific Roles: Investigate typical compensation ranges for desired positions before applying. Utilize online resources, industry reports, and professional networking to gather accurate data.
Tip 2: Highlight Relevant Skills and Experience: Emphasize qualifications and experience directly related to the job requirements. Provide quantifiable examples of past achievements to demonstrate value.
Tip 3: Consider Location: Compensation often varies depending on geographic location. Research the cost of living and average earnings in the specific location of the manufacturing facility or office.
Tip 4: Network Strategically: Connect with current or former employees to gain insights into company culture and compensation practices. Attend industry events and career fairs to expand your network.
Tip 5: Negotiate Effectively: Understand the market value of your skills and experience. Be prepared to negotiate your initial offer, presenting a well-reasoned counter-proposal based on research and industry standards.
Tip 6: Factor in Benefits: Evaluate the entire compensation package, including health insurance, retirement plans, and other benefits. These benefits can significantly impact total compensation value.
Understanding market value, carefully showcasing expertise, and strategic negotiation are crucial elements for maximizing earning potential within this industry.
The following sections will provide further detailed insights into the various components of employee remuneration at the organization.
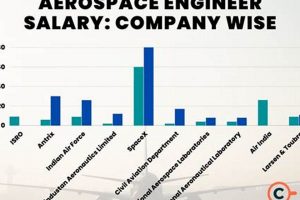
1. Role Specialization
The degree of specialization inherent in a particular role within the aerospace manufacturer’s operations significantly influences the associated compensation. More specialized roles typically require advanced skills, extensive training, and a higher level of expertise, thereby commanding a greater remuneration.
- Avionics Engineer
This specialized engineering role focuses on the design, development, and testing of aircraft electronic systems. This requires in-depth knowledge of electrical engineering, software development, and aerospace regulations. Due to the complexity and critical nature of avionics systems, individuals in this role generally receive a higher compensation compared to more general engineering positions. The safety and reliability of aircraft heavily depend on the avionics, making this role highly valued.
- Aerodynamics Specialist
Aerodynamics specialists analyze air flow and its impact on aircraft performance. This requires expertise in fluid dynamics, computational modeling, and wind tunnel testing. Their contributions directly affect fuel efficiency, stability, and overall aircraft design. The specialized knowledge and skills required for this position result in a substantial contribution and a corresponding higher earnings bracket.
- Stress Analysis Engineer
This role involves evaluating the structural integrity of aircraft components under various stress conditions. This requires a strong understanding of materials science, finite element analysis, and aerospace design principles. Given the importance of ensuring aircraft safety and preventing structural failures, these engineers are typically compensated at a premium. Accurate stress analysis is critical for maintaining airworthiness.
- Manufacturing Process Engineer (Composites)
This engineer specializes in the manufacturing processes related to composite materials, which are increasingly used in modern aircraft. This involves expertise in materials science, tooling design, and automated manufacturing techniques. The specialized knowledge of composite manufacturing, which requires significant training and experience, typically leads to a higher level of compensation compared to general manufacturing engineering roles. Composites play a vital role in reducing aircraft weight and improving fuel efficiency.
In summary, compensation within the specified aerospace company is directly correlated with the level of specialization required for each role. These specializations demand specific skillsets, extensive knowledge, and significant expertise, contributing directly to product quality, innovation, and adherence to stringent aerospace regulations. The higher compensation associated with these roles reflects the value and demand for specialized skills within the competitive aerospace industry.
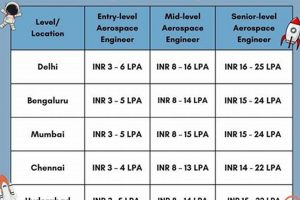
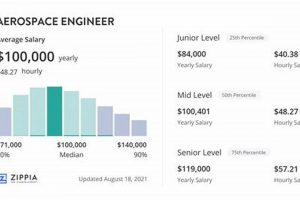
2. Experience Level
The correlation between professional experience and compensation within the mentioned aerospace company represents a fundamental aspect of its remuneration structure. Increased experience typically translates to enhanced skills, deeper knowledge, and a proven track record, directly impacting earning potential.
- Entry-Level Positions
Individuals in entry-level roles, such as recent graduates or those with limited prior experience, typically receive a base salary commensurate with their initial skills and qualifications. These positions often serve as a training ground, providing opportunities to develop fundamental skills and gain industry knowledge. Initial compensation reflects the learning curve and the limited ability to independently manage complex tasks.
- Mid-Level Positions
With several years of experience, professionals transition to mid-level positions, assuming greater responsibilities and contributing more directly to project outcomes. Compensation at this level reflects the increased value provided through accumulated skills, independent problem-solving abilities, and mentorship potential for junior colleagues. Demonstrated success in previous projects significantly impacts earning potential during this stage.
- Senior-Level Positions
Senior-level roles demand extensive experience, deep expertise, and the ability to lead teams, manage complex projects, and make strategic decisions. Compensation for senior-level professionals recognizes their contributions to innovation, operational efficiency, and overall organizational success. These individuals often possess specialized certifications, advanced degrees, and a proven history of leadership, all of which directly influence their earning power.
- Leadership and Executive Positions
At the highest levels of the organization, leadership and executive roles require extensive industry experience, proven leadership capabilities, and a strategic vision. Compensation for these positions reflects the responsibility for guiding the company’s direction, managing significant resources, and driving business growth. These individuals are accountable for high-level decisions and are therefore commensurately compensated.
In summation, experience level serves as a primary determinant of the compensation structure within this aerospace context. As individuals progress through their careers, acquiring new skills, demonstrating increasing competence, and assuming greater responsibilities, their earning potential increases accordingly. This progression incentivizes continuous professional development and rewards expertise, fostering a skilled and motivated workforce.
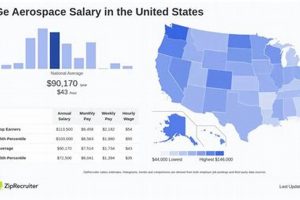
3. Geographic Location
Geographic location exerts a considerable influence on compensation levels within the specified aerospace manufacturing context. Variations in cost of living, regional economic factors, and the concentration of industry expertise contribute to disparities in salaries across different locations where the company operates.
- Cost of Living Adjustments
Compensation packages are frequently adjusted to reflect the cost of living in a specific area. Cities or regions with higher costs of housing, transportation, and general expenses necessitate higher wages to maintain a comparable standard of living. Employees working in areas with inflated living costs may receive location-based pay differentials to offset these expenses. Failure to account for cost-of-living differences can impact employee morale and retention.
- Regional Economic Conditions
Economic factors, such as unemployment rates, regional growth, and the strength of the local economy, can affect salary levels. Regions with robust economic activity and high demand for skilled labor often command higher wages to attract and retain qualified professionals. Locations experiencing economic downturns may see reduced salary growth or even wage stagnation. Government incentives and tax policies in specific regions can also influence overall compensation packages.
- Industry Cluster Concentration
The presence of other aerospace companies and related industries within a geographic area creates a competitive labor market, impacting salaries. Areas with a high concentration of aerospace activity, such as regions with major aerospace hubs, tend to offer more competitive compensation packages to attract experienced professionals from a wider pool of talent. The presence of universities with strong aerospace programs also contributes to a qualified talent pool, influencing wage structures.
- Tax Implications and Government Regulations
State and local tax laws can have a direct impact on an employee’s take-home pay, thereby influencing the gross salary required to achieve a desired net income. Regions with lower state income taxes may offer slightly lower gross salaries, as employees retain a larger portion of their earnings. Government regulations related to minimum wage, overtime pay, and benefits mandates can also affect compensation standards across different locations.
The influence of geographic location on compensation is multifactorial. Cost of living adjustments, regional economic conditions, the presence of industry clusters, and varying tax implications all contribute to salary differentials across different operational sites. A comprehensive compensation strategy must consider these factors to ensure competitive wages and attract top talent across diverse geographical regions.
4. Benefits Package
A comprehensive benefits package constitutes an integral component of the overall remuneration offered by the aerospace manufacturer, supplementing the base salary and contributing significantly to employee well-being and financial security. Its value is a key consideration for prospective and current employees evaluating total compensation.
- Health Insurance Coverage
Health insurance, encompassing medical, dental, and vision care, represents a substantial portion of the total benefits package. The extent of coverage, including premiums, deductibles, and co-pays, directly impacts an employee’s out-of-pocket healthcare expenses. Comprehensive health plans can attract and retain talent, particularly in competitive labor markets. The value of health benefits is often factored into salary negotiations and comparisons with other companies.
- Retirement Savings Plans
Retirement savings plans, such as 401(k) or pension plans, provide employees with opportunities to save for retirement and secure their financial future. Employer contributions, matching programs, and investment options significantly influence the long-term value of these plans. Strong retirement benefits can enhance employee loyalty and reduce financial stress, positively affecting productivity and job satisfaction. The structure and generosity of these plans directly influence the perceived value of the total compensation package.
- Paid Time Off (PTO) and Leave Policies
Paid time off, including vacation, sick leave, and holidays, offers employees the opportunity to rest, recharge, and attend to personal matters. Generous PTO policies contribute to work-life balance and reduce burnout. Extended leave options, such as parental leave or family leave, provide support during critical life events. The amount and flexibility of PTO are often considered a significant component of overall job satisfaction and can influence an employee’s willingness to accept a particular salary offer.
- Life and Disability Insurance
Life and disability insurance provide financial protection to employees and their families in the event of unforeseen circumstances. Life insurance offers a death benefit to beneficiaries, while disability insurance provides income replacement in case of temporary or permanent disability. These benefits offer peace of mind and financial security, enhancing the overall value of the compensation package. The availability and level of coverage are important considerations for employees, especially those with dependents.
The benefits package offered significantly enhances the overall attractiveness of employment by the organization. By providing comprehensive health coverage, retirement savings options, paid time off, and financial protection, the company aims to attract and retain top talent in the competitive aerospace industry, thereby influencing its reputation as an employer of choice and ultimately, ensuring a skilled and stable workforce.
5. Performance Bonuses
Performance bonuses represent a variable component of total compensation offered by the specified aerospace manufacturer, directly linking employee earnings to individual, team, or company-wide achievements. Their design and implementation are crucial for incentivizing desired behaviors and driving organizational success.
- Individual Performance Metrics
Individual performance bonuses are often tied to pre-defined metrics related to an employee’s specific role and responsibilities. Examples include achieving project milestones, exceeding sales targets, or demonstrating significant improvements in efficiency or quality. The monetary value of the bonus is typically calculated based on a percentage of the employee’s base salary, providing a direct financial incentive for high achievement. The system aims to reward and motivate employees to exceed expectations and contribute to the company’s objectives.
- Team-Based Incentives
In situations where collaboration and teamwork are critical, team-based incentives may be implemented. These bonuses are awarded based on the collective performance of a team in achieving shared goals, such as completing a complex project on time and within budget. The bonus amount is then distributed among team members based on predefined criteria or peer evaluations. This approach encourages cooperation and shared accountability, incentivizing team members to support each other and work together towards a common objective.
- Company-Wide Performance Goals
Company-wide performance bonuses are typically linked to the achievement of overall organizational objectives, such as revenue growth, profitability targets, or successful product launches. These bonuses are often distributed to all eligible employees, regardless of their specific role, creating a sense of shared ownership and aligning individual interests with the company’s strategic goals. Eligibility criteria and bonus amounts are usually determined by senior management and communicated to employees transparently, fostering a sense of fairness and motivating employees to contribute to the company’s overall success.
- Alignment with Strategic Objectives
Effective performance bonus programs are carefully aligned with the company’s strategic objectives, ensuring that incentivized behaviors directly contribute to the organization’s long-term success. The metrics used to determine bonus payouts should be measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART), providing clear expectations and facilitating performance tracking. Regular review and adjustments to the bonus program are essential to maintain its effectiveness and ensure alignment with evolving business priorities.
Performance bonuses, when designed and implemented strategically, represent a powerful tool for driving employee engagement, improving performance, and aligning individual interests with organizational goals within the aerospace manufacturing company. They represent a key variable component affecting the earnings, and the overall attractiveness of compensation packages offered.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Compensation
The following questions address common inquiries related to remuneration within the specific aerospace manufacturing environment. These answers aim to provide clarity and factual information to prospective and current employees.
Question 1: What is the typical starting compensation for an entry-level engineer?
Entry-level engineering salaries are influenced by factors such as degree level, academic performance, and specialized coursework. While specific figures vary, typical starting compensation aligns with industry standards for similar roles within the geographic location of the facility.
Question 2: How frequently are salary adjustments implemented?
Salary adjustments are typically reviewed annually, contingent upon individual performance, company performance, and market conditions. Merit-based increases are awarded based on performance evaluations and contributions to organizational objectives.
Question 3: What benefits are included in the standard compensation package?
The standard benefits package generally encompasses health insurance (medical, dental, vision), retirement savings plans (such as 401(k) with company match), paid time off (vacation, sick leave), life insurance, and disability insurance. Specific details regarding coverage levels and eligibility criteria are outlined in the employee handbook.
Question 4: Are performance bonuses a standard component of compensation?
Performance bonuses are awarded based on individual, team, or company-wide achievement of predetermined goals. Eligibility and bonus amounts are dependent on performance against established metrics and adherence to company policies. Bonus structures vary by role and department.
Question 5: Does geographic location influence compensation levels?
Yes, geographic location is a significant factor in determining compensation. Salaries are adjusted to reflect differences in cost of living and prevailing wage rates within specific regions where the company operates.
Question 6: How can employees negotiate their salary offers?
Candidates are encouraged to research industry standards and demonstrate the value they bring to the organization. Negotiation should be based on objective factors such as skills, experience, and market rates. Justifications for desired compensation should be supported by verifiable data and a clear articulation of contributions.
This FAQ section provides a general overview of compensation practices. Specific details are subject to change and are outlined in official company policies and employment agreements.
The subsequent sections will present resources for exploring earnings at the manufacturer.
Conclusion
This exploration has provided a comprehensive overview of the factors influencing compensation at the specified aerospace manufacturer. Examination of role specialization, experience level, geographic location, benefits packages, and performance bonuses reveals the complexities inherent in determining individual earnings. A thorough understanding of these elements is crucial for individuals seeking employment or advancement within the organization.
The data and insights presented serve as a valuable resource for informed decision-making. Continued vigilance regarding industry trends and company performance is essential for navigating career opportunities and maximizing earning potential within the aerospace sector. Responsible financial planning and a commitment to professional development will serve individuals well in achieving their career aspirations.