Positions within the air and space industry located in Northern Ireland represent opportunities for individuals with a diverse range of skills. These roles encompass engineering, manufacturing, research, and support functions necessary for the design, production, and maintenance of aircraft and related technologies. For example, an engineer might work on developing lighter and more efficient aircraft components, while a technician could be involved in the assembly of these parts.
The availability of employment in this sector is crucial for regional economic growth, driving innovation, and fostering technological advancement. Historically, the presence of these opportunities has attracted skilled workers, encouraged investment in training programs, and positioned Northern Ireland as a contributor to the global aerospace market. These positions offer competitive salaries, opportunities for professional development, and the chance to work on cutting-edge projects.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific types of roles, the qualifications required, and the companies that are actively recruiting in this field. Further analysis will examine the future outlook for employment, including projected growth and emerging skill demands.
This section provides actionable guidance for individuals seeking employment within the air and space sector in Northern Ireland. These suggestions are designed to enhance prospects and facilitate successful career progression.
Tip 1: Target Specific Skill Development: Identify areas of expertise that are in high demand within the regional air and space industry. Examples include advanced composite materials, avionics engineering, or precision manufacturing. Acquire relevant certifications or experience to demonstrate competency.
Tip 2: Research Regional Employers: Thoroughly investigate companies operating in Northern Ireland that specialize in air and space technology. Understand their specific areas of focus, recent projects, and future growth plans. Tailor applications to align with their individual requirements.
Tip 3: Network Professionally: Attend industry events, conferences, and workshops to connect with professionals in the field. Utilize platforms such as LinkedIn to expand networks and engage in relevant discussions. Building relationships can provide access to unadvertised opportunities.
Tip 4: Leverage Educational Resources: Explore the educational and training programs offered by local universities and colleges that are tailored to the air and space sector. Participating in internships or research projects can provide valuable practical experience and industry contacts.
Tip 5: Emphasize Relevant Experience: When applying for roles, highlight previous experience that is directly applicable to the air and space industry, even if it comes from seemingly unrelated fields. Demonstrate transferable skills such as problem-solving, technical proficiency, and project management.
Tip 6: Monitor Industry Trends: Stay informed about the latest technological advancements, regulatory changes, and market developments within the air and space sector. This knowledge will enable candidates to adapt their skills and position themselves as forward-thinking professionals.
Tip 7: Prepare for Technical Assessments: Anticipate the inclusion of technical assessments as part of the application process. Practice problem-solving skills and review fundamental concepts related to air and space engineering, manufacturing, or maintenance. A strong performance on these assessments can significantly enhance candidacy.
Following these recommendations will increase the likelihood of securing and advancing within positions in the air and space sector of Northern Ireland. Diligence, preparation, and continuous learning are key to success.
The next section will summarize the key takeaways from this analysis and offer final insights.
1. Engineering Design
Engineering design is a core element of the air and space sector in Northern Ireland, driving innovation, efficiency, and safety across all areas of development and production. Opportunities in this area are essential for the continued growth and competitiveness of the regional industry.
- Conceptual Design and Analysis
This involves the initial phase of creating air and space systems, including aircraft, spacecraft, and related equipment. Engineers in this role conceptualize and model potential designs, conduct simulations to evaluate performance, and assess feasibility. These positions are fundamental for establishing the groundwork for subsequent phases of development and ensuring that designs meet stringent performance criteria.
- Structural Engineering
Structural engineers are responsible for the design, analysis, and testing of air and space vehicle structures. They ensure that these structures can withstand extreme stresses, temperatures, and pressures while maintaining integrity and safety. Their work directly impacts the safety and reliability of aircraft and spacecraft, requiring a deep understanding of materials science, mechanics, and computational modeling. These roles often demand advanced degrees and specialized certifications.
- Systems Integration
Positions focused on systems integration involve coordinating and integrating various engineering disciplines, such as electrical, mechanical, and software engineering, to create cohesive air and space systems. These engineers oversee the compatibility and functionality of different components and subsystems, ensuring seamless operation of the final product. Effective communication and collaboration are crucial for success in these roles.
- Design for Manufacturing (DFM)
DFM engineers optimize designs for efficient and cost-effective manufacturing processes. They work closely with manufacturing teams to ensure that designs are practical, scalable, and aligned with available production capabilities. This role requires a comprehensive understanding of manufacturing techniques, materials, and assembly processes. Optimizing DFM can significantly reduce production costs and improve product quality.
These diverse aspects of engineering design collectively shape the trajectory of the air and space industry in Northern Ireland. Engineers in these fields are at the forefront of technological advancement, contributing to safer, more efficient, and more sustainable air and space travel. The availability of such roles underscores the region’s commitment to innovation and its capacity to support the future of air and space exploration.
2. Manufacturing Expertise
Manufacturing expertise is a critical determinant of the quantity and quality of positions within the air and space sector of Northern Ireland. Specialized skills and knowledge are essential for producing high-precision components and systems, ensuring the industry’s continued success and global competitiveness.
- Precision Machining
This involves the fabrication of intricate air and space components using advanced machining techniques. Examples include computer numerical control (CNC) milling, turning, and grinding. The skills required are highly specialized, demanding expertise in materials science, tool selection, and quality control. Increased demand for lightweight and durable materials directly translates to a need for skilled machinists and programmers within the air and space sector.
- Composite Materials Manufacturing
The utilization of composite materials, such as carbon fiber reinforced polymers, is increasing in air and space applications due to their strength-to-weight ratio. Manufacturing expertise in this area includes processes like layup, resin transfer molding (RTM), and automated fiber placement (AFP). Professionals with knowledge in composite material properties, curing techniques, and non-destructive testing are essential for producing reliable and high-performance components.
- Assembly and Integration
This facet focuses on the precise assembly and integration of various air and space system components. This includes the installation of avionics, electrical systems, and mechanical linkages. Expertise in reading technical drawings, using specialized tooling, and adhering to strict quality control procedures is paramount. Demand for skilled assembly technicians is driven by the increasing complexity of air and space systems and the need for meticulous integration processes.
- Quality Assurance and Inspection
Rigorous quality assurance and inspection processes are integral to air and space manufacturing. This involves using advanced metrology equipment, such as coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) and non-destructive testing (NDT) methods, to verify component dimensions and integrity. Professionals in this area require in-depth knowledge of quality standards, inspection techniques, and data analysis. Their work is essential for ensuring the safety and reliability of air and space systems.
The possession of robust manufacturing expertise is indispensable for Northern Ireland’s air and space industry. The demand for professionals skilled in these disciplines creates a diverse range of career opportunities, contributing significantly to the region’s economic growth and technological advancement. These jobs are vital in maintaining the high standards of safety, performance, and reliability required in air and space operations.
3. Avionics Integration
Avionics integration represents a crucial aspect of aerospace engineering, involving the seamless combination of electronic systems within aircraft. This integration is not merely a physical assembly, but a complex interaction of hardware and software that requires specialized skills. The availability of qualified professionals in avionics integration significantly influences the landscape of opportunities within the aerospace sector in Northern Ireland.
- Systems Architecture Design
This facet concerns the development of comprehensive system architectures for avionics suites. This involves determining the optimal arrangement of sensors, displays, control systems, and communication networks within an aircraft. For example, designing an integrated flight management system that effectively combines navigation, weather data, and traffic avoidance information. The ability to design robust and efficient architectures directly impacts the availability of senior engineering roles within Northern Ireland’s aerospace firms.
- Hardware/Software Interface Development
The successful integration of avionics systems hinges on the creation of efficient and reliable interfaces between hardware components and software applications. This includes developing communication protocols, data processing algorithms, and control logic. As an illustration, developing a secure and responsive interface between a radar system and a flight control computer. The demand for professionals skilled in this area is driven by the increasing sophistication of avionics systems and the necessity for seamless data exchange.
- Testing and Validation
Stringent testing and validation procedures are essential to ensure the proper functioning and safety of integrated avionics systems. This involves conducting laboratory simulations, flight tests, and certification processes. For instance, performing electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing to verify that avionics systems do not interfere with each other. The need for qualified test engineers and certification specialists is critical for maintaining airworthiness standards and supporting continued aerospace operations in Northern Ireland.
- System Maintenance and Upgrades
The long-term reliability and performance of avionics systems require ongoing maintenance and upgrades. This includes troubleshooting technical issues, implementing software updates, and retrofitting new technologies into existing aircraft. An example includes diagnosing and resolving intermittent failures in a flight control system or installing new communication equipment to meet evolving regulatory requirements. The provision of these services creates long-term employment opportunities for technicians and engineers in Northern Ireland’s aerospace maintenance sector.
These diverse elements of avionics integration collectively shape the nature of technical roles within the aerospace industry of Northern Ireland. The demand for professionals skilled in these areas will continue to grow, reflecting the ongoing need for safe, efficient, and technologically advanced air transportation.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Strict adherence to regulatory frameworks is paramount within the air and space sector, directly influencing the types and availability of positions. These frameworks, established by bodies such as the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) or the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), mandate specific procedures and standards for design, manufacturing, maintenance, and operation. The consequence of non-compliance is significant, potentially leading to grounding of aircraft, financial penalties, and reputational damage for involved organizations. This creates a sustained demand for professionals specializing in navigating and ensuring adherence to these complex regulations.
The presence of qualified personnel is not merely a matter of avoiding penalties, but also of ensuring the safety and reliability of air and space operations. For example, design engineers must ensure that new aircraft components meet stringent airworthiness directives. Similarly, maintenance technicians must adhere to prescribed procedures when performing repairs, documenting each step meticulously to comply with traceability requirements. This necessitates specialized training and certification, creating distinct career paths for individuals specializing in compliance-related functions. Air and space companies actively seek individuals with expertise in areas such as quality assurance, safety management systems (SMS), and auditing, positions that are critical for maintaining operational certifications.
The increasing complexity of air and space regulations, coupled with growing scrutiny from regulatory bodies, reinforces the importance of these compliance roles. The regulatory environment is not static, with continuous updates and amendments requiring ongoing professional development and adaptation. The need for skilled professionals who can interpret, implement, and maintain compliance within air and space operations contributes directly to the overall strength and stability of positions in Northern Ireland. In conclusion, effective regulatory compliance is not simply a cost of doing business, but a vital component of the sector, supporting a wide range of specialized jobs and fostering a culture of safety and responsibility.
5. Research and Development
Activities focused on discovering and applying new knowledge represent a crucial catalyst for the availability and nature of positions within the aerospace sector in Northern Ireland. Investment in investigation directly fuels technological advancement, leading to the creation of innovative products and processes. As a consequence, demand arises for skilled professionals capable of conducting investigations, developing prototypes, and implementing cutting-edge technologies. For instance, government funding allocated to research into sustainable aviation fuels has led to the establishment of research teams within Northern Ireland universities and private firms, generating new employment opportunities for scientists, engineers, and technicians.
This link is not unidirectional; the presence of a skilled workforce in Northern Ireland also attracts further investigation investments. Companies recognize the value of locating research facilities in regions with a strong talent pool, creating a positive feedback loop. A practical example is the establishment of advanced engineering centers by global aerospace corporations in Northern Ireland, drawn by the availability of graduates from local universities with expertise in areas such as composite materials and computational fluid dynamics. These centers, in turn, generate further employment opportunities for researchers and engineers, contributing to the growth of the regional economy and enhancing Northern Ireland’s reputation as a hub for aerospace innovation.
In summary, there is a symbiotic relationship between activities focused on discovering and applying new knowledge and the creation of sustainable, high-value positions within the aerospace sector of Northern Ireland. Continued investment in investigation, coupled with a strategic focus on developing relevant skills, is essential for ensuring the long-term competitiveness and prosperity of the region’s industry and the associated workforce. Challenges remain in securing consistent funding and attracting top talent, but addressing these challenges will yield significant economic and societal benefits.
6. Economic Impact
The presence and prosperity of the aerospace sector in Northern Ireland exert a significant influence on the regional economy. This impact is directly correlated with the availability and quality of positions within the industry. Employment in aerospace contributes to economic activity through various channels, including wages paid to employees, taxes generated, and spending on goods and services within the local economy. As the sector expands, demand for skilled workers increases, creating new opportunities and driving economic growth. This growth, in turn, attracts further investment, establishing a positive feedback loop that amplifies the benefits to the region. For example, the establishment of a new aircraft component manufacturing facility generates jobs not only within the facility itself but also in supporting industries such as logistics, engineering services, and training providers.
The sector’s economic influence extends beyond direct employment. The high-tech nature of aerospace positions fosters innovation and technological advancement, benefiting other sectors of the economy. The development of new materials, manufacturing processes, and software solutions often finds applications in industries such as automotive, healthcare, and energy. Furthermore, the presence of a thriving aerospace industry enhances Northern Ireland’s reputation as a hub for innovation and attracts foreign direct investment. The influx of investment creates more employment opportunities, particularly for highly skilled workers. For instance, the development of a regional center specializing in composite materials for aircraft has attracted international researchers and engineers, boosting the local economy and improving the skills base of the workforce.
In conclusion, the economic impact is a critical component of the viability and sustainability of the aerospace sector in Northern Ireland. Investment in workforce development, infrastructure, and support for innovation is essential for maximizing the economic benefits generated by the industry. Although challenges remain, such as global competition and economic uncertainty, strategic planning and collaboration between government, industry, and educational institutions can ensure that the aerospace sector continues to be a significant driver of economic growth and prosperity in Northern Ireland. This positive cycle fosters more positions, better economic outcomes, and further advancements in the region.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding career prospects within the air and space sector of Northern Ireland. Information is presented to provide a clear and concise understanding of the regional industry.
Question 1: What qualifications are generally required for engineering positions in the aerospace sector?
Typically, a bachelor’s or master’s degree in aerospace engineering, mechanical engineering, or a related field is required. Specific roles may necessitate specialized certifications or licenses, depending on the area of expertise.
Question 2: Which companies are the primary employers in Northern Ireland’s air and space industry?
Several prominent companies operate within the region, including those specializing in aircraft component manufacturing, engineering design services, and maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) activities. Specific company names can be found through industry directories and online job boards.
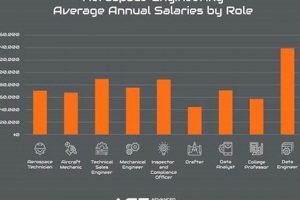
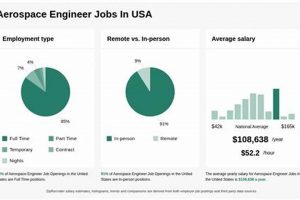
Question 3: What is the typical salary range for professionals in Northern Irelands air and space sector?
Salary levels vary significantly based on experience, qualifications, and the specific role. Entry-level positions may command lower salaries, while senior engineering or management roles offer higher compensation. Detailed salary data is available from industry surveys and recruitment agencies.
Question 4: Are there specific skills that are particularly in demand within the regional aerospace industry?
Currently, expertise in areas such as composite materials manufacturing, avionics integration, and precision machining is highly valued. Proficiency in computer-aided design (CAD) software and finite element analysis (FEA) is also frequently sought after.
Question 5: How can individuals with non-aerospace backgrounds transition into the industry?
Transferable skills from fields such as mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, or manufacturing can be valuable. Targeted training programs and professional certifications can also enhance prospects for individuals seeking to change careers.
Question 6: What is the future outlook for employment in the air and space sector in Northern Ireland?
The sector is generally expected to experience continued growth, driven by factors such as increasing demand for air travel and ongoing investment in aerospace technology. However, the specific rate of growth may be influenced by global economic conditions and regulatory changes.
The information provided above offers a general overview of opportunities in Northern Irelands air and space industry. Further research and networking are recommended for individuals seeking to pursue a career in this field.
The subsequent section will summarize the key findings of this analysis and offer concluding thoughts.
Aerospace Jobs NI
The preceding analysis has presented a multifaceted overview of the employment landscape within the air and space sector of Northern Ireland. Key findings emphasize the importance of engineering design, manufacturing expertise, avionics integration, regulatory compliance, and research and development as critical drivers of job creation and economic growth. The availability of skilled professionals in these domains directly influences the region’s competitiveness and ability to attract investment.
The sustained success of the air and space sector in Northern Ireland hinges on a continued commitment to workforce development, strategic investment in research and innovation, and proactive engagement with evolving regulatory requirements. Stakeholders must actively collaborate to address challenges such as global competition and skills gaps to ensure the long-term prosperity of the industry. The future of aerospace jobs NI depends on decisive action taken today to foster a robust and sustainable ecosystem for technological advancement and economic growth.