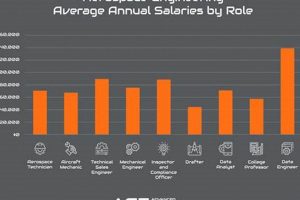
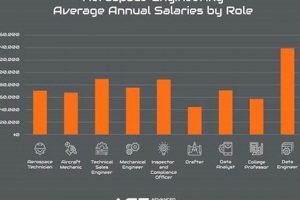
Employment opportunities within the aerospace sector located in Idaho represent a segment of the state’s economy focused on the design, development, manufacturing, and maintenance of aircraft, spacecraft, and related systems. These positions can range from engineering and technical roles to manufacturing and administrative support. As an example, a mechanical engineer in Idaho might work on designing components for unmanned aerial vehicles, or a technician could be involved in the repair and maintenance of aircraft engines.
The availability of these specific career paths in Idaho contributes to the state’s technological advancement and economic diversification. Historically, Idaho’s aerospace industry has been linked to government contracts and private sector innovation, providing skilled individuals with opportunities to contribute to national defense, scientific research, and commercial aviation. This sector fosters innovation and attracts specialized talent, thereby enhancing the state’s overall competitiveness.
The following sections will provide an overview of specific companies involved, required skills and education, and the overall job market outlook for individuals seeking to pursue a career in this field within the state. Subsequent analysis will also examine relevant resources for job seekers and highlight potential future trends shaping this industry in Idaho.
The pursuit of a career in Idaho’s aerospace field requires a strategic approach. Success hinges on careful preparation and informed decision-making. The following tips are designed to guide prospective candidates through the process.
Tip 1: Acquire Relevant Education and Certifications: Pursue a degree in aerospace engineering, mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, or a related field. Certifications such as FAA Airframe and Powerplant (A&P) licenses are often essential for maintenance roles.
Tip 2: Develop Technical Skills: Proficiency in CAD software (e.g., SolidWorks, AutoCAD), programming languages (e.g., Python, MATLAB), and simulation tools is highly valued. Practical experience through internships or projects enhances employability.
Tip 3: Network Within the Industry: Attend industry conferences, join professional organizations (e.g., AIAA), and connect with professionals on platforms like LinkedIn. Networking expands awareness of opportunities and provides valuable insights.
Tip 4: Research Idaho-Based Aerospace Companies: Identify companies operating in Idaho that align with career interests. Thoroughly understand their products, services, and company culture to tailor applications effectively. Examples include companies specializing in unmanned aerial systems (UAS) or those supporting government contracts.
Tip 5: Tailor Resumes and Cover Letters: Customize application materials to highlight relevant skills and experience specific to each position. Emphasize quantifiable achievements and demonstrate a clear understanding of the role’s requirements.
Tip 6: Prepare for Technical Interviews: Anticipate technical questions related to engineering principles, design processes, and specific software or hardware. Practice problem-solving and clearly articulate technical concepts.
Tip 7: Consider Government Contracting Opportunities: Idaho’s aerospace sector is often influenced by government contracts. Familiarize oneself with the application processes and security clearance requirements associated with these positions.
Following these guidelines will significantly enhance prospects within the Idaho aerospace job market. Diligence and strategic planning are critical for securing a rewarding career in this dynamic field.
The next section will provide valuable resources and potential trends in Idaho’s aerospace scene.
1. Engineering Design
Engineering design serves as a foundational pillar for the availability and nature of aerospace jobs in Idaho. The demand for engineers specializing in aerospace, mechanical, electrical, and related disciplines directly drives the creation of these employment opportunities. Without engineering design capabilities, there would be a limited scope for manufacturing, research, and development activities within the state’s aerospace sector. For instance, companies designing new unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) require engineers to conceptualize, model, and test these systems, translating into direct job creation for design engineers, simulation specialists, and testing personnel.
The skill set required for engineering design in Idaho’s aerospace companies often includes proficiency in computer-aided design (CAD) software, computational fluid dynamics (CFD), finite element analysis (FEA), and other simulation tools. Furthermore, knowledge of materials science, aerodynamics, and control systems is critical. The practical application of engineering design principles is evident in the development of advanced aircraft components, satellite systems, and propulsion technologies. These applications not only require skilled engineers but also lead to the development of new technologies, further fueling job growth and innovation within Idaho’s aerospace ecosystem.
In summary, the connection between engineering design and aerospace jobs in Idaho is causal and indispensable. A robust engineering design sector acts as a catalyst for manufacturing, research, and overall industry growth. Challenges in this domain include attracting and retaining qualified engineers, particularly those with specialized expertise. However, continued investment in education, research, and development will strengthen Idaho’s position in the aerospace industry and foster a greater number of highly skilled jobs.
2. Manufacturing Roles
Manufacturing roles are a crucial element of the “aerospace jobs in idaho” landscape. These positions are directly responsible for translating engineering designs and prototypes into tangible aerospace components and systems. The presence of robust manufacturing capabilities within the state directly determines the volume and variety of aerospace employment opportunities. Without these roles, the engineering and design efforts would remain theoretical, lacking the practical application necessary for the aerospace sector to thrive. For instance, if an Idaho-based company designs a new composite wing for a light aircraft, manufacturing personnel are needed to fabricate the mold, lay up the composite material, cure the structure, and perform quality control checks. This specific activity creates multiple job positions, including composite technicians, quality assurance inspectors, and machine operators.
The types of manufacturing roles prevalent in Idaho’s aerospace sector often include machinists, welders, assemblers, quality control specialists, and production managers. These positions require specific skills and certifications depending on the nature of the manufacturing process. CNC machining, precision welding, and non-destructive testing are common techniques employed. The importance of these manufacturing roles extends beyond simply producing parts. They also contribute to process improvement, cost reduction, and overall product quality. For example, a manufacturing engineer might analyze the production line to identify bottlenecks and implement lean manufacturing principles to increase efficiency, thereby improving the company’s competitiveness and potentially leading to further job creation.
In conclusion, the relationship between manufacturing roles and aerospace jobs in Idaho is fundamentally causal. A strong manufacturing base fosters innovation, attracts investment, and sustains the industry’s growth. Challenges in this area include maintaining a skilled workforce capable of adapting to advanced manufacturing techniques and competing with lower-cost manufacturing regions. However, investing in workforce training programs and supporting local manufacturing initiatives will ensure Idaho’s continued success in the aerospace sector and the creation of more high-quality manufacturing positions.
3. Maintenance Personnel
The demand for maintenance personnel directly influences the scope and stability of aerospace jobs in Idaho. Individuals in these roles are responsible for the inspection, repair, and overhaul of aircraft and related systems. The continued airworthiness of aircraft, a critical safety and regulatory requirement, necessitates a skilled maintenance workforce. Without qualified technicians, aircraft cannot operate, thus impacting the entire aerospace ecosystem. As a practical example, consider an Idaho-based aviation company operating a fleet of aircraft for cargo transport. Maintenance personnel would be responsible for performing routine inspections, troubleshooting mechanical issues, and replacing worn or damaged components. These actions ensure the aircraft’s safe and reliable operation, enabling the company to fulfill its transportation obligations and sustain its business activities, subsequently supporting other roles within the company.
The specific tasks performed by maintenance personnel in Idaho vary depending on the type of aircraft and the nature of the operation. General aviation aircraft require regular inspections and maintenance to comply with Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) regulations. Commercial airlines demand highly skilled technicians to perform complex repairs and overhauls. Furthermore, military installations may employ specialized maintenance personnel to service military aircraft. The skills required range from basic mechanical knowledge to advanced troubleshooting abilities, often necessitating FAA Airframe and Powerplant (A&P) licenses. These certifications demonstrate a level of competency recognized by the industry and regulatory bodies. Continuous training and education are essential to keep up with evolving aircraft technologies and maintenance procedures. The presence of skilled maintenance personnel contributes significantly to the safety and efficiency of aerospace operations, thereby enhancing the attractiveness of Idaho as a location for aerospace businesses.
In summary, maintenance personnel are an indispensable component of the aerospace job sector in Idaho. Their expertise ensures the safe and reliable operation of aircraft, supporting the broader industry and facilitating economic activity. The challenges associated with maintaining a skilled maintenance workforce include the need for ongoing training, competitive compensation, and a commitment to safety. Addressing these challenges through investment in education, apprenticeship programs, and robust safety protocols will strengthen Idaho’s aerospace industry and ensure the continued availability of quality aerospace jobs.
4. Government Contracts
The presence and scope of government contracts wield a significant influence on the availability and nature of aerospace jobs in Idaho. These contracts, typically awarded by federal agencies such as the Department of Defense or NASA, provide financial resources and project mandates that directly translate into employment opportunities within the state’s aerospace sector.
- Funding Stability and Job Creation
Government contracts offer a degree of financial stability that is often lacking in purely commercial ventures. This stability allows aerospace companies in Idaho to hire and retain personnel, particularly engineers, technicians, and program managers. For instance, if an Idaho-based firm secures a contract to develop and test advanced sensor systems for unmanned aerial vehicles, it would likely need to expand its workforce to meet the project’s demands. This expansion directly creates jobs in design, manufacturing, testing, and support.
- Technological Advancement and Skill Development
Many government contracts involve cutting-edge research and development, requiring aerospace companies to employ individuals with specialized skills and expertise. These projects often drive technological advancements and foster skill development within the Idaho aerospace workforce. An example is a contract to develop new propulsion systems for small satellites, which would necessitate hiring engineers with expertise in propulsion, materials science, and control systems. The project would not only create jobs but also enhance the overall skill level of the workforce.
- Compliance and Regulatory Expertise
Government contracts invariably come with strict compliance requirements and regulatory oversight. This necessitates the employment of personnel with expertise in areas such as quality assurance, security protocols, and environmental regulations. Companies must adhere to rigorous standards and documentation procedures to maintain compliance. For example, a firm working on a military contract must employ personnel familiar with defense acquisition regulations and security clearance procedures. The need for compliance expertise adds a layer of specialized job opportunities to the aerospace sector.
- Economic Impact and Supply Chain Effects
The economic impact of government contracts extends beyond the direct creation of jobs within the contracting company. These contracts often generate ripple effects throughout the supply chain, creating additional employment opportunities for subcontractors and suppliers in Idaho. For example, a prime contractor working on a government project may source components from local manufacturers, creating jobs in those manufacturing facilities. Government contracts thereby contribute to a broader economic ecosystem that supports aerospace employment across the state.
In summary, the presence of government contracts acts as a significant driver for aerospace jobs in Idaho, fostering financial stability, technological advancement, regulatory compliance, and broader economic growth. The specific nature and scope of these contracts directly shape the types of jobs available and the skills required within the state’s aerospace sector.
5. Research & Development
Research and Development (R&D) serves as a significant catalyst for the creation and evolution of aerospace jobs in Idaho. The investments channeled into R&D activities directly influence the demand for specialized skills and the development of cutting-edge technologies within the state’s aerospace sector. Idaho companies engaged in R&D often require highly skilled engineers, scientists, and technicians to conduct experiments, develop new prototypes, and analyze data. For example, if an Idaho-based aerospace firm receives funding to research and develop new materials for aircraft construction, this directly generates jobs for materials scientists, mechanical engineers, and technicians involved in testing and fabrication. These positions, in turn, require advanced education and training, further strengthening the overall skill base within the Idaho workforce.
The practical significance of R&D extends beyond immediate job creation. Successful R&D projects can lead to the development of innovative aerospace products and services, resulting in the expansion of existing companies or the establishment of new ventures within Idaho. Consider the development of a novel drone technology through R&D efforts. If this technology proves commercially viable, it can stimulate demand for additional roles in manufacturing, marketing, and customer support, thereby amplifying the initial impact of R&D on aerospace jobs. Moreover, a thriving R&D sector attracts external investment and fosters a culture of innovation, enhancing Idaho’s reputation as a hub for aerospace activities. These opportunities translate into long-term economic benefits and create a sustainable ecosystem for aerospace employment.
In summary, R&D represents a vital component of the aerospace job market in Idaho, driving innovation, creating high-skilled positions, and stimulating economic growth. While challenges such as securing funding and attracting talent remain, the strategic importance of R&D in shaping the future of aerospace employment in Idaho cannot be overstated. Continued investment in R&D initiatives and the cultivation of a supportive innovation environment are essential to ensuring the continued prosperity of the state’s aerospace sector and maintaining a competitive edge in the global aerospace market.
6. Unmanned Systems
The burgeoning field of unmanned systems, encompassing both aerial (drones) and ground-based robotic technologies, significantly impacts the composition and availability of aerospace jobs in Idaho. This sector’s growth has fostered demand for specialized skills and created unique employment opportunities within the state’s aerospace landscape.
- Design and Development Engineering
The design and development of unmanned systems necessitate a skilled engineering workforce. Roles include aerospace engineers specializing in aerodynamics and flight control, electrical engineers focusing on power systems and communication, and mechanical engineers designing structural components and payload integration. Real-world examples include the development of precision agriculture drones for crop monitoring or the creation of unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) for infrastructure inspection. This facet directly translates into jobs in Idaho for engineers with specialized knowledge in unmanned systems design.
- Manufacturing and Assembly
The manufacturing and assembly of unmanned systems components also generates employment opportunities. These positions require skilled technicians and assemblers capable of working with intricate electronic components, composite materials, and precision instruments. Examples include the production of drone frames, the integration of sensors and cameras, and the assembly of robotic platforms. As unmanned systems production scales up, the demand for skilled manufacturing personnel in Idaho increases accordingly, creating more aerospace-related jobs.
- Software Development and Data Analysis
Unmanned systems rely heavily on software for navigation, control, and data processing. This dependency creates demand for software developers proficient in programming languages like Python and C++, as well as data analysts skilled in extracting insights from sensor data. Examples include the development of autonomous navigation algorithms, the creation of image processing software for aerial surveillance, and the analysis of sensor data collected by unmanned environmental monitoring systems. The growing reliance on software and data analysis amplifies the need for skilled professionals in these areas within Idaho’s aerospace sector.
- Operations and Maintenance
The operation and maintenance of unmanned systems create a need for trained technicians and pilots. These roles involve conducting pre-flight checks, piloting unmanned aircraft, troubleshooting technical issues, and performing routine maintenance. Examples include the operation of drones for infrastructure inspection, the piloting of UGVs for security patrol, and the maintenance of robotic equipment used in hazardous environments. As the adoption of unmanned systems increases, the demand for qualified operators and maintenance personnel in Idaho’s aerospace sector expands proportionally.
Collectively, these facets demonstrate the multifaceted influence of unmanned systems on aerospace jobs in Idaho. The demand for skilled professionals in design, manufacturing, software development, and operations underscores the importance of investing in education and training programs to support the continued growth of this sector and ensure that Idaho remains a competitive player in the unmanned systems market.
7. Education Requirements
The relationship between education requirements and aerospace jobs in Idaho is direct and causal. The specific educational background and qualifications demanded for various positions within the aerospace sector directly determine the pool of eligible candidates and influence the overall skill level of the workforce. The aerospace industry, characterized by complex technologies and stringent safety standards, necessitates a highly educated workforce. Without a sufficient supply of qualified individuals, Idaho’s aerospace sector may face limitations in its ability to innovate, compete, and attract new businesses. For example, engineering positions typically require a bachelor’s or master’s degree in aerospace, mechanical, electrical, or a related engineering field. Technician roles often require associate degrees or specialized certifications from accredited technical schools. These educational prerequisites are essential for ensuring that employees possess the technical knowledge and skills necessary to perform their duties effectively and safely.
The practical significance of understanding education requirements extends to both job seekers and educational institutions. Prospective employees must be aware of the specific qualifications sought by employers to tailor their education and training accordingly. This might involve pursuing specific degrees, obtaining relevant certifications, or gaining practical experience through internships or co-op programs. Educational institutions, in turn, must ensure that their curricula align with the needs of the aerospace industry, providing students with the knowledge and skills demanded by employers. Partnerships between educational institutions and aerospace companies can help bridge the gap between academic training and industry practice, providing students with valuable hands-on experience and ensuring that graduates are well-prepared for careers in the aerospace sector. Furthermore, certain specialized roles may require advanced degrees or specialized training in areas such as avionics, propulsion systems, or composite materials. Therefore, the education requirements vary depending on the specific nature of the job and the complexity of the tasks involved.
In summary, the level of education in Idaho is an enabler for the advancement of technology. Investment in STEM education and specialized training programs are essential for fostering a skilled workforce capable of supporting the continued growth and success of Idaho’s aerospace sector. Failure to address these educational needs could hinder the state’s ability to attract and retain aerospace businesses and could limit its competitiveness in the global aerospace market. Meeting these needs also entails overcoming challenges in attracting and retaining qualified instructors, providing access to state-of-the-art equipment, and ensuring that educational programs remain relevant and responsive to the evolving needs of the aerospace industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries concerning career opportunities within the aerospace sector in Idaho. The following questions and answers provide insights into various aspects of this industry within the state.
Question 1: What are the primary types of aerospace companies operating in Idaho?
Aerospace firms in Idaho encompass a diverse range, including those focused on unmanned aerial systems (UAS), aircraft maintenance and repair, component manufacturing, and engineering services. Government contractors are also prevalent, contributing to research and development efforts.
Question 2: What educational qualifications are typically required for aerospace positions in Idaho?
Educational requirements vary depending on the role. Engineering positions generally necessitate a bachelor’s or master’s degree in aerospace, mechanical, or electrical engineering. Technician roles often require an associate’s degree or specialized certifications, such as an FAA Airframe and Powerplant (A&P) license.
Question 3: Are there specific skill sets that are highly valued by aerospace employers in Idaho?
Proficiency in CAD software (e.g., SolidWorks, AutoCAD), programming languages (e.g., Python, MATLAB), and simulation tools is often highly valued. Knowledge of materials science, aerodynamics, and control systems is also advantageous.
Question 4: What is the general outlook for the aerospace job market in Idaho?
The outlook for the aerospace job market in Idaho is generally positive, driven by factors such as government contracts, technological advancements, and the growth of the UAS sector. However, specific opportunities may fluctuate depending on economic conditions and industry trends.
Question 5: Are security clearances typically required for aerospace positions in Idaho?
Security clearances may be required for positions involving government contracts or access to sensitive information. The level of clearance required depends on the specific responsibilities and the nature of the work performed.
Question 6: What resources are available for individuals seeking aerospace jobs in Idaho?
Resources include online job boards (e.g., Indeed, LinkedIn), company websites, professional organizations (e.g., AIAA), and career services offered by universities and technical colleges. Networking with industry professionals is also a valuable strategy.
This overview of frequently asked questions offers a foundation for understanding the nuances of the aerospace employment scene in Idaho. Further research and networking are encouraged for those pursuing careers in this dynamic field.
The next section provides a concise summary of the key elements discussed throughout this examination of aerospace employment prospects within Idaho.
Aerospace Jobs in Idaho
This examination has explored the multifaceted landscape of aerospace jobs in Idaho, encompassing engineering design, manufacturing, maintenance, government contracts, research and development, unmanned systems, and educational requirements. The availability and nature of these positions are intricately linked to the state’s economic and technological environment. Government contracts provide stability and drive innovation, while the growth of unmanned systems creates demand for specialized skills. Educational institutions play a critical role in preparing a qualified workforce to meet the evolving needs of the industry.
Continued investment in education, research, and infrastructure is essential for sustaining and expanding opportunities for aerospace jobs in Idaho. Addressing challenges such as attracting and retaining skilled workers and adapting to technological advancements will be crucial for maintaining competitiveness in the global aerospace market. As the aerospace sector continues to evolve, a proactive approach to workforce development and strategic partnerships between industry, government, and educational institutions will be key to realizing the full potential of aerospace employment opportunities within the state.