Opportunities within the field relating to design, development, testing, and manufacturing of aircraft, spacecraft, and related systems located within the state of Michigan constitute a specific segment of the employment market. These positions involve the application of engineering principles to solve problems in atmospheric and space flight, and can range from entry-level roles to senior management positions. An example would be a position at a company specializing in the production of components for commercial or military aircraft located in the Detroit metropolitan area.
The presence of these roles is vital to the state’s economy, fostering innovation and technological advancement, and creating high-skill, high-paying jobs. Historically, Michigan has been a significant player in the automotive industry, and this established engineering base has facilitated the growth of related sectors, including the aforementioned field. This concentration of expertise translates into a competitive advantage, attracting companies and talent to the region.
The following sections will elaborate on the specific industries and companies in Michigan that offer these employment prospects, the required skills and qualifications, and the expected career paths for individuals pursuing such vocations.
Securing Opportunities in Michigan’s Aerospace Sector
The pursuit of roles involving the design, development, and maintenance of aerospace systems within the state of Michigan necessitates a strategic approach. The following guidelines are intended to enhance the likelihood of success in this competitive field.
Tip 1: Emphasize Relevant Academic Background: A strong foundation in aerospace, mechanical, or electrical engineering is essential. Curricula should include coursework in aerodynamics, propulsion, control systems, and materials science. For instance, a Master’s degree specializing in computational fluid dynamics can be highly advantageous.
Tip 2: Cultivate Practical Experience: Internships or co-op positions with aerospace companies or research institutions provide invaluable hands-on experience. Contributions to projects involving design, testing, or data analysis demonstrate a candidate’s ability to apply theoretical knowledge.
Tip 3: Develop Specialized Skills: Proficiency in industry-standard software such as CAD/CAM, MATLAB, and finite element analysis (FEA) tools is crucial. Additionally, familiarity with aerospace-specific regulations and standards, such as those issued by the FAA, is highly valued.
Tip 4: Network Strategically: Attend industry conferences, career fairs, and workshops to connect with professionals in the aerospace sector. Building relationships with recruiters and engineers can provide insights into unadvertised openings and company cultures.
Tip 5: Highlight Problem-Solving Abilities: Aerospace engineering demands creative solutions to complex challenges. Applicants should be prepared to articulate their approach to problem-solving, providing specific examples of how they have overcome technical obstacles in past projects.
Tip 6: Tailor Applications: Customize resumes and cover letters to match the specific requirements of each position. Highlight skills and experiences that directly address the employer’s needs, demonstrating a clear understanding of the role and the company’s mission.
Tip 7: Research Target Companies: A thorough understanding of a company’s products, services, and market position is crucial. Demonstrate an informed interest in their work during interviews, showcasing initiative and a commitment to contributing to their success.
Adhering to these guidelines will significantly improve the prospects of securing desired roles within the thriving aerospace ecosystem in Michigan, leading to a rewarding and impactful career.
The subsequent sections will provide a detailed overview of the key employers, emerging trends, and long-term career trajectory for those seeking opportunities in Michigan’s aerospace arena.
1. Manufacturing and Production
The manufacturing and production segment forms a critical component of Michigan’s aerospace engineering jobs landscape. The presence of advanced manufacturing facilities directly correlates with the demand for skilled aerospace engineers to oversee processes, optimize production lines, and ensure adherence to stringent industry standards. These engineers are instrumental in the fabrication of airframe components, engine parts, and electronic systems integral to aircraft and spacecraft.
The automotive industry’s historical presence in Michigan has fostered a culture of high-volume manufacturing and precision engineering, providing a foundation for aerospace production. Companies leverage existing infrastructure and expertise to produce components for both commercial and defense applications. For instance, a Michigan-based company might specialize in the machining of turbine blades for jet engines, requiring aerospace engineers to develop manufacturing processes, select appropriate materials, and implement quality control measures. Another practical application may include the production of composite materials crucial for reducing aircraft weight, increasing fuel efficiency and range.
In summary, manufacturing and production jobs are integral to the state’s aerospace engineering sector. These positions require a specialized skill set, demanding expertise in manufacturing processes, materials science, and quality control. The close proximity to automotive suppliers and technological know-how has fostered a thriving aerospace production environment. Addressing workforce development challenges, such as a need for engineers with specialized manufacturing expertise, will be critical to sustained growth in this sector.
2. Research and Development
Research and Development (R&D) forms a crucial element within Michigan’s landscape of aerospace engineering roles. This component drives innovation, technological advancement, and the long-term competitiveness of the sector. The presence of robust R&D activities directly correlates with the creation of high-skill, high-paying positions for engineers specializing in areas such as advanced materials, propulsion systems, and autonomous flight control. For example, a project focused on developing lighter, more durable composite materials for aircraft structures relies heavily on the expertise of aerospace engineers involved in materials science, stress analysis, and manufacturing processes. The success of such projects translates into new job opportunities and strengthens Michigan’s position as a hub for aerospace innovation.
The practical significance of R&D extends beyond immediate job creation. It contributes to the development of cutting-edge technologies that can be commercialized, attracting further investment and fostering a cycle of innovation. University-based research programs, often in collaboration with industry partners, play a vital role in this process. Examples include the development of more efficient engine designs, advanced sensor technologies for aircraft monitoring, and novel methods for reducing aircraft noise. These advancements not only enhance the performance and safety of aircraft but also contribute to broader societal benefits, such as reduced fuel consumption and environmental impact.
In conclusion, a strong commitment to R&D is essential for sustaining and expanding opportunities within the Michigan aerospace engineering sector. Addressing challenges such as securing funding for research initiatives and fostering collaboration between academia and industry will be critical to unlocking the full potential of this domain. Continued investment in R&D will ensure that Michigan remains at the forefront of aerospace innovation, driving economic growth and creating high-value employment for generations to come.
3. System Design Expertise
System design expertise is a fundamental requirement for many roles within the Michigan aerospace engineering job market. These roles involve the holistic integration of various components and subsystems to create functional and efficient aerospace vehicles and systems. The ability to conceptualize, model, and optimize complex systems is highly valued by employers in this sector.
- Requirements Definition and Management
Defining and managing system requirements is crucial to the design process. Aerospace engineers in Michigan must translate high-level objectives into specific, verifiable requirements for each system component. This process involves collaboration with stakeholders, analysis of trade-offs, and documentation of requirements using industry-standard tools and methodologies. For example, in designing a new unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), engineers must define requirements for payload capacity, range, endurance, and operational environment, ensuring that all components integrate seamlessly to meet these specifications.
- Modeling and Simulation
The use of modeling and simulation tools is essential for predicting system performance and identifying potential design flaws early in the development cycle. Aerospace engineers in Michigan employ software such as MATLAB, Simulink, and finite element analysis (FEA) tools to create virtual prototypes of aerospace systems. These models are used to simulate flight dynamics, structural behavior, and thermal performance, allowing engineers to optimize designs and reduce the risk of costly failures. An engineer designing a new aircraft wing, for example, might use FEA software to simulate the wing’s response to aerodynamic loads, ensuring that it can withstand the stresses of flight without exceeding its structural limits.
- Integration and Testing
Integrating individual components into a cohesive system and thoroughly testing its performance are critical steps in the aerospace engineering process. Michigan engineers are involved in designing and implementing test plans, conducting simulations, and analyzing test data to verify that the system meets its requirements. This might involve testing a new engine control system in a simulated flight environment or conducting wind tunnel tests to validate the aerodynamic performance of a new aircraft design. The integration and testing phase ensures that all components work together effectively and that the final product meets or exceeds expectations.
- Verification and Validation
Verification and validation (V&V) activities are critical steps in aerospace system design, ensuring that the system meets both its specified requirements (verification) and the intended operational needs (validation). Michigan aerospace engineers are responsible for developing and executing V&V plans, conducting analyses, and generating reports to demonstrate compliance. This process might involve performing flight tests to validate the performance of an autopilot system or conducting safety analyses to demonstrate that the system meets regulatory requirements. Effective V&V ensures the reliability, safety, and effectiveness of aerospace systems.
These facets of system design expertise are essential for engineers seeking roles in Michigan’s aerospace sector. A strong understanding of requirements management, modeling and simulation, integration and testing, and verification and validation is highly valued by employers and is crucial for contributing to the development of innovative and reliable aerospace systems.
4. Quality Assurance Roles
Quality assurance constitutes a non-negotiable aspect within the aerospace engineering jobs landscape in Michigan. The inherently safety-critical nature of aerospace systems necessitates rigorous quality control measures throughout the design, manufacturing, and testing phases. Positions dedicated to quality assurance ensure adherence to stringent industry standards, regulatory requirements, and customer specifications.
- Inspection and Testing
Aerospace engineers in quality assurance roles are responsible for developing and implementing inspection and testing protocols to identify defects and ensure compliance with established standards. This may involve visual inspections, non-destructive testing methods (e.g., radiography, ultrasonic testing), and functional testing of components and systems. For instance, an engineer might oversee the inspection of turbine blades for microscopic cracks or oversee the testing of an aircraft’s hydraulic system to verify its performance under extreme conditions. The integrity of parts produced relies heavily on the application of meticulous quality control, ensuring both performance and safety.
- Process Auditing
Process auditing involves systematically evaluating manufacturing processes to identify areas for improvement and ensure adherence to quality management systems. Aerospace engineers in Michigan conduct audits of production lines, assembly processes, and supplier facilities to verify compliance with industry standards such as AS9100. An audit might uncover inconsistencies in welding procedures or identify a lack of proper documentation, leading to corrective actions that enhance overall quality and reduce the risk of defects.
- Statistical Process Control (SPC)
Statistical process control is a method for monitoring and controlling manufacturing processes using statistical techniques. Aerospace engineers in quality assurance roles utilize SPC to track key process parameters, identify trends, and detect deviations from established control limits. This allows for early detection of potential problems and proactive implementation of corrective measures. For example, SPC might be used to monitor the dimensions of machined parts, identifying any gradual shifts in the process that could lead to out-of-tolerance components.
- Root Cause Analysis
When defects or failures occur, aerospace engineers in quality assurance roles conduct root cause analyses to determine the underlying causes of the problem. This involves a systematic investigation to identify the factors that contributed to the failure, such as design flaws, manufacturing errors, or material defects. By identifying the root cause, engineers can implement corrective actions to prevent similar failures from occurring in the future. A root cause analysis might reveal that a material failure was due to improper heat treatment, leading to revised manufacturing procedures and improved quality control measures.
The emphasis on these interconnected facets within quality assurance underscores the crucial role it plays in safeguarding the reliability and performance of aerospace systems within Michigan’s industry. By ensuring adherence to rigorous standards and proactively identifying and addressing potential problems, quality assurance professionals contribute significantly to the safety and success of aerospace endeavors.
5. Governmental Opportunities
The connection between governmental opportunities and the broader range of aerospace engineering positions in Michigan is significant. Government agencies, both federal and state, directly and indirectly influence the scope, nature, and availability of such positions. Direct influence manifests through employment at agencies such as the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), the Department of Defense (DoD), and related regulatory bodies. These entities employ aerospace engineers for research, development, testing, and oversight of aerospace programs and technologies. Indirectly, government contracts awarded to private companies operating within Michigan’s aerospace sector drive demand for engineering expertise, leading to the creation of jobs at the contractor level. For example, a Department of Defense contract awarded to a Michigan-based company for the development of advanced aerospace materials translates into a need for engineers specializing in materials science, structural analysis, and manufacturing processes.
The importance of governmental opportunities stems from several factors. Government-funded research initiatives often push the boundaries of aerospace technology, creating opportunities for engineers to work on cutting-edge projects. Furthermore, government regulations and standards shape the design and development of aerospace systems, requiring engineers to possess a thorough understanding of these requirements. The practical significance of this understanding lies in the ability to navigate the complex regulatory landscape and ensure compliance with all applicable standards. Failure to adhere to these standards can result in significant delays, cost overruns, and even project cancellations. Finally, governmental roles can offer unique career paths, including opportunities for leadership, policy development, and public service.
In conclusion, governmental opportunities are an integral part of the aerospace engineering ecosystem in Michigan. They provide direct employment, drive innovation through research funding, and shape the regulatory environment in which the industry operates. Addressing challenges such as navigating the complexities of government procurement processes and securing funding for aerospace programs will be critical to maximizing the benefits of this connection for both engineers and the broader Michigan aerospace sector.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding career opportunities in the aerospace engineering sector within the state of Michigan. The information presented is intended to provide clarity and guidance for individuals seeking employment in this field.
Question 1: What are the primary industries employing aerospace engineers in Michigan?
The primary industries include aerospace manufacturing, defense contracting, automotive suppliers involved in aerospace components, and research institutions. Opportunities can be found in both large corporations and smaller, specialized firms.
Question 2: What educational qualifications are typically required for entry-level positions?
A Bachelor of Science degree in aerospace engineering, mechanical engineering, or a closely related field is generally required. Advanced degrees, such as a Master of Science or Ph.D., may be necessary for research-oriented or specialized roles.
Question 3: Are there specific skills or software proficiencies that are highly sought after by employers?
Proficiency in CAD/CAM software (e.g., CATIA, NX), finite element analysis (FEA) tools (e.g., ANSYS, Abaqus), and programming languages such as MATLAB is highly desirable. Knowledge of aerospace-specific regulations and standards is also beneficial.
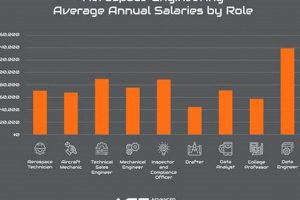
Question 4: What is the typical salary range for aerospace engineers in Michigan?
Salary ranges vary depending on experience, education, and the specific role. However, entry-level positions typically offer competitive salaries, with experienced engineers earning significantly more. Resources such as the Bureau of Labor Statistics can provide more specific salary data.
Question 5: Are there internship or co-op opportunities available for students pursuing aerospace engineering degrees in Michigan?
Yes, many companies and research institutions in Michigan offer internship and co-op programs for students. These opportunities provide valuable hands-on experience and can often lead to full-time employment after graduation.
Question 6: How does Michigan’s automotive industry influence its aerospace sector?
Michigan’s strong automotive engineering base has fostered a culture of manufacturing excellence and technological innovation that benefits the aerospace sector. Automotive suppliers with expertise in areas such as materials science, manufacturing processes, and electronics often contribute to the aerospace supply chain.
In summary, the aerospace engineering sector in Michigan offers diverse opportunities for qualified individuals. A strong educational foundation, relevant skills, and a proactive approach to networking are essential for success in this competitive field.
The subsequent section will explore potential career paths and long-term growth prospects for aerospace engineers in Michigan.
Concluding Remarks on Opportunities in Michigan’s Aerospace Sector
This exposition has illuminated critical facets of opportunities in Michigan related to air and space vehicle engineering. Key points encompass the vital role of manufacturing, the importance of research and development, the necessity of system design and quality assurance expertise, and the influence of governmental agencies. The diverse nature of available roles, ranging from entry-level positions to advanced research and leadership roles, offers a dynamic career landscape.
The sustained growth and continued innovation within Michigan’s air and space sector hinge upon strategic investments in education, research, and infrastructure. As technology advances and demand for skilled aerospace professionals increases, individuals and organizations are encouraged to pursue and foster excellence in this critical engineering domain. The future success of Michigan’s presence in the industry depends on collaborative efforts and a steadfast commitment to advancement.


![Top States: Best States for Aerospace Jobs in [Year] Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions Top States: Best States for Aerospace Jobs in [Year] | Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-441-300x200.jpg)

![Find Indeed Aerospace Jobs: Your [Area] Career Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions Find Indeed Aerospace Jobs: Your [Area] Career | Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-431-300x200.jpg)

