Finite element analysis applied to the design and analysis of aircraft and spacecraft represents a crucial aspect of modern aerospace development. This computational method discretizes a complex structure into smaller, simpler elements, allowing engineers to predict its behavior under various conditions such as stress, strain, and temperature. For example, simulating airflow over a wing section or determining the structural integrity of a satellite component during launch are typical applications of this methodology.
The utilization of this type of analysis offers significant advantages in terms of cost reduction, improved performance, and enhanced safety. By identifying potential design flaws early in the development process, costly physical prototypes and testing can be minimized. Furthermore, optimization techniques enabled by simulation can lead to lighter, more efficient designs, contributing to improved fuel economy and payload capacity. Historically, this approach has evolved alongside advancements in computing power and numerical algorithms, becoming an indispensable tool for aerospace engineers.
The following sections will delve into specific aspects, including the types of elements used, the software employed, and the challenges associated with accurately modeling complex aerospace structures. Further exploration will highlight practical applications, current research trends, and future directions in this dynamic field.
Tips in Finite Element Analysis for Aerospace Engineering
The following outlines key considerations for effective employment of finite element analysis within the aerospace engineering domain. Adherence to these guidelines can significantly improve the accuracy and reliability of simulation results.
Tip 1: Select Appropriate Element Types: The choice of element type (e.g., beam, shell, solid) is critical for accurate representation of the structure. For thin-walled structures like aircraft skins, shell elements are generally preferred over solid elements due to their computational efficiency. Beam elements are suitable for slender structural members like spars and ribs.
Tip 2: Validate Material Properties: Inputting accurate material properties (e.g., Young’s modulus, Poisson’s ratio) is paramount. Consult reputable material databases and consider experimental testing to verify material characteristics, particularly for composite materials that exhibit anisotropic behavior.
Tip 3: Refine Mesh Density Strategically: A finer mesh generally leads to more accurate results, but it also increases computational cost. Focus mesh refinement on areas of high stress gradients or geometric complexity. Employ adaptive meshing techniques to automatically refine the mesh based on error estimates.
Tip 4: Apply Realistic Boundary Conditions: Accurately representing boundary conditions (e.g., fixed supports, applied loads) is crucial for realistic simulation. Consider the effects of joint flexibility and load distribution when defining boundary conditions.
Tip 5: Verify Solution Convergence: Ensure that the solution converges by progressively refining the mesh and monitoring key results (e.g., maximum stress, displacement). A converged solution indicates that further mesh refinement will not significantly alter the results.
Tip 6: Validate Simulation Results: Whenever possible, validate simulation results against experimental data or analytical solutions. This step helps to identify potential errors in the model or assumptions.
Tip 7: Account for Manufacturing Tolerances: Consider the impact of manufacturing tolerances on structural performance. Incorporate variations in geometry and material properties into the simulation to assess their effects on stress concentrations and structural stability.
Effective application requires meticulous attention to detail and a thorough understanding of both the theoretical foundations and the practical limitations. By following these suggestions, engineers can leverage the power of computational simulation to design safer, more efficient, and more reliable aerospace structures.
The subsequent sections will provide further insights into advanced modeling techniques and best practices for in various analysis contexts.
1. Structural Integrity
Structural integrity within the realm of aerospace engineering is inextricably linked to finite element analysis. The computational simulation provides a vital means of predicting a structure’s behavior under various loading conditions, thereby enabling assessment of its ability to withstand operational stresses without failure. This connection is characterized by a cause-and-effect relationship: applied loads induce stresses and strains within the structure, and simulation quantitatively predicts these effects, informing design decisions to ensure sufficient strength and stiffness. Structural integrity is, therefore, not merely a consideration but a core component of its methodology, directly influencing design choices and safety margins. A practical example includes the analysis of an aircraft wing subjected to aerodynamic forces during flight. Engineers employ simulation to identify areas of high stress concentration, enabling reinforcement or redesign to prevent crack initiation and propagation.
The practical significance of understanding the interrelation lies in optimizing structural design for both performance and safety. Simulation allows for the exploration of different material combinations, geometric configurations, and loading scenarios, identifying the most efficient designs that meet stringent structural requirements. Consider the design of a spacecraft heat shield, where simulation is used to predict thermal stresses arising from atmospheric reentry. Accurate prediction enables the selection of appropriate materials and thermal protection strategies, ensuring the spacecraft’s survival. Furthermore, this predictive capability is essential for evaluating the impact of potential damage, such as that from bird strikes or foreign object debris, allowing for the development of damage-tolerant designs that maintain structural integrity even in the presence of localized damage.
In summary, structural integrity within aerospace systems is inherently dependent on finite element analysis. It allows for the predictive evaluation of structural performance, informing design decisions to optimize strength, stiffness, and damage tolerance. A persistent challenge lies in accurately representing complex material behavior and loading conditions within the simulation. Overcoming this challenge requires continuous improvement in computational methods, material characterization techniques, and validation strategies, further solidifying its role as a cornerstone of structural design within the aerospace sector.
2. Aerodynamic Performance
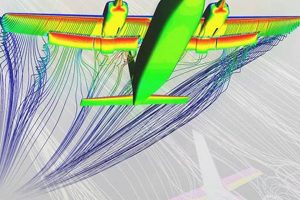
Aerodynamic performance, encompassing lift, drag, and stability characteristics, is fundamentally intertwined with finite element analysis applied within the aerospace sector. Computational simulation provides the quantitative means to predict aerodynamic forces and their effects on aircraft and spacecraft structures. Aerodynamic loads induce pressure distributions across external surfaces, causing structural deformation, and simulation allows for the iterative refinement of designs to optimize aerodynamic efficiency and minimize structural stress. The accurate prediction of aerodynamic performance is not merely a desirable outcome; it is a critical component of its proper application, influencing decisions related to airfoil design, control surface effectiveness, and overall vehicle stability. For instance, analyzing airflow around a wing section allows engineers to predict lift and drag coefficients, enabling the optimization of airfoil shapes for specific flight conditions.
The practical significance of understanding this interrelation lies in the ability to optimize aircraft and spacecraft designs for improved fuel efficiency, increased payload capacity, and enhanced maneuverability. Simulation facilitates the exploration of different aerodynamic configurations, enabling the identification of designs that minimize drag and maximize lift. Consider the design of a supersonic aircraft where wave drag becomes a dominant factor. Computational fluid dynamics simulations, coupled with structural analysis, enable engineers to optimize the vehicle’s shape to reduce wave drag and improve fuel efficiency. Furthermore, the method is essential for predicting stability derivatives, which are critical for designing effective control systems and ensuring safe flight characteristics. Understanding these dynamic interactions allows engineers to account for aeroelastic effects, where structural deformation influences aerodynamic performance, and vice versa, preventing phenomena such as flutter.
In summary, aerodynamic performance in aerospace applications is inextricably linked to finite element analysis, which allows for the predictive evaluation of aerodynamic characteristics and their impact on structural behavior. A persistent challenge lies in accurately modeling complex flow phenomena, such as turbulence and flow separation. Overcoming this requires continuous advancement in computational methods, turbulence modeling techniques, and validation strategies, further solidifying its role in aerodynamic design within the aerospace sector. The integration of computational fluid dynamics and structural analysis facilitates the development of lighter, more efficient, and more stable aircraft and spacecraft.
3. Material Behavior
The accurate characterization of material behavior is paramount to the effective utilization of finite element analysis within aerospace engineering. The fidelity of simulation results hinges on the correct representation of material properties and their response to various environmental and loading conditions. Inaccurate material models lead to erroneous predictions, potentially compromising structural integrity and performance.
- Constitutive Modeling
Constitutive models define the mathematical relationship between stress and strain for a given material. Selecting an appropriate constitutive model, accounting for factors such as plasticity, viscoelasticity, and creep, is essential for accurately simulating material response under complex loading scenarios. For example, simulating the behavior of a titanium alloy in a jet engine turbine blade requires a model that captures high-temperature creep and fatigue characteristics. The model’s ability to replicate these behaviors dictates the reliability of the stress and strain predictions.
- Anisotropic Material Properties
Aerospace structures often incorporate composite materials, which exhibit anisotropic properties, meaning their mechanical behavior varies with direction. Accurately representing these anisotropic properties in simulation requires detailed material characterization and the use of specialized finite elements capable of handling directional dependencies. For example, the stiffness and strength of a carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) wing structure are significantly different along the fiber direction compared to the transverse direction. Accurate modeling of these differences is crucial for predicting the wing’s response to aerodynamic loads.
- Temperature Dependence
Material properties are often sensitive to temperature variations, particularly in aerospace applications involving extreme thermal environments. Finite element models must account for the temperature dependence of material properties such as Young’s modulus, thermal expansion coefficient, and yield strength. For example, simulating the behavior of a hypersonic vehicle’s leading edge requires consideration of the significant temperature gradients and their effect on the material’s mechanical properties. Failure to account for temperature dependence can lead to inaccurate stress predictions and potentially catastrophic structural failure.
- Failure Criteria
Predicting material failure is a critical aspect of structural analysis. Finite element models must incorporate appropriate failure criteria, such as maximum stress, maximum strain, or damage mechanics models, to predict the onset of cracking, delamination, or other failure modes. For example, simulating the impact of a bird strike on an aircraft fuselage requires a failure criterion that accurately predicts the initiation and propagation of damage within the composite structure. Accurate failure prediction allows engineers to design structures with improved damage tolerance and enhanced safety margins.
The interplay between material behavior and finite element analysis is fundamental to ensuring the safety and performance of aerospace structures. Accurate material characterization, appropriate constitutive modeling, and the incorporation of temperature dependence and failure criteria are essential for generating reliable simulation results. Continued advancements in material science and computational methods will further enhance the accuracy and predictive capabilities of simulation in this critical engineering discipline.
4. Thermal Management
Thermal management is a critical engineering discipline within the broader context of aerospace development, intricately linked to the application of finite element analysis. Maintaining operational temperature ranges for various components and systems is essential for ensuring performance, reliability, and safety. Simulation, a key tool in this area, enables the prediction and mitigation of thermal stresses, heat transfer inefficiencies, and potential thermal runaway scenarios.
- Conduction Analysis
Conduction, the transfer of heat through a solid material, is a fundamental aspect of thermal management. Finite element analysis allows for the precise modeling of heat flow within structures, accounting for material properties, geometric complexities, and contact resistances. For example, modeling the thermal conductivity of a heat sink attached to a power amplifier in a satellite payload ensures that the amplifier operates within its specified temperature limits. The analysis helps to optimize heat sink geometry and material selection to maximize heat dissipation.
- Convection Analysis
Convection, the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids, is crucial for managing heat dissipation in systems exposed to airflow or liquid cooling. Simulation enables the prediction of convective heat transfer coefficients and temperature distributions in these environments. Consider the analysis of airflow around an aircraft engine nacelle. Simulation helps to optimize the nacelle’s shape to minimize drag and maximize heat transfer from the engine components, preventing overheating.
- Radiation Analysis
Radiation, the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves, is particularly important in space applications where conduction and convection are limited. Simulation allows for the modeling of radiative heat exchange between surfaces, accounting for surface emissivities, view factors, and solar radiation. For example, analyzing the thermal radiation from a satellite’s solar panels to its internal components helps to design effective thermal insulation and cooling systems to maintain stable operating temperatures. This type of analysis informs the placement of multi-layer insulation (MLI) and radiator panels to optimize thermal performance.
- Thermo-Structural Analysis
Thermo-structural analysis combines thermal and structural analysis to assess the impact of thermal loads on structural integrity. Temperature gradients can induce thermal stresses that, if not properly managed, can lead to structural deformation or failure. For example, simulating the thermal stresses in a spacecraft heat shield during atmospheric reentry is critical for ensuring its structural integrity under extreme thermal conditions. The analysis informs the selection of appropriate materials and structural designs to withstand the combined effects of heat and mechanical loads.
These facets of thermal management, facilitated by finite element analysis, are crucial for the successful design and operation of aerospace systems. Accurately predicting and mitigating thermal effects enhances performance, extends component lifespan, and ensures the overall safety and reliability of aircraft and spacecraft. The ongoing development of advanced simulation techniques and material models continues to improve the effectiveness of in addressing complex thermal challenges in the aerospace industry.
5. Vibration Analysis
Vibration analysis is an indispensable component of structural design within the aerospace engineering sector. Its application, often reliant on methodologies, focuses on predicting the dynamic response of aircraft and spacecraft structures to various excitation sources. These analyses are critical for ensuring structural integrity, preventing fatigue failures, and optimizing system performance in the operational environment.
- Modal Analysis
Modal analysis identifies the natural frequencies and mode shapes of a structure, which are intrinsic properties determining its response to dynamic loading. For example, in aircraft wing design, modal analysis is employed to ensure that natural frequencies are sufficiently separated from engine excitation frequencies and aerodynamic buffet frequencies to prevent resonance. The mode shapes provide insights into the deformation patterns of the structure at each natural frequency, informing the placement of damping devices and structural reinforcements.
- Harmonic Response Analysis
Harmonic response analysis predicts the steady-state response of a structure subjected to sinusoidal excitation. This type of analysis is particularly useful in evaluating the effects of engine vibrations on aircraft fuselage structures or the response of satellite components to sinusoidal vibrations during launch. The results of harmonic response analysis enable engineers to assess stress levels and displacement amplitudes, ensuring that they remain within acceptable limits.
- Transient Response Analysis
Transient response analysis evaluates the dynamic behavior of a structure subjected to time-varying loads, such as those encountered during landing, takeoff, or atmospheric turbulence. This analysis type is essential for understanding the short-duration, high-amplitude responses of critical components, enabling the design of robust structures capable of withstanding these transient events. For instance, simulating the impact of landing gear on the runway allows engineers to optimize the landing gear design and assess the stresses induced in the airframe.
- Random Vibration Analysis
Random vibration analysis predicts the response of a structure to broadband random excitation, such as that caused by acoustic noise or turbulent flow. This analysis is crucial for evaluating the fatigue life of components subjected to sustained vibration environments, particularly in aerospace applications. Examples include assessing the fatigue damage accumulation in electronic equipment mounted within an aircraft fuselage subjected to engine noise or predicting the response of a satellite structure to the random vibrations experienced during launch.
The results derived from vibration analyses directly influence design decisions in several ways. By accurately predicting structural response to dynamic loads, engineers can optimize structural designs to minimize vibration levels, reduce stress concentrations, and extend component lifespan. The interplay between vibration analysis and overall structural integrity is therefore a critical consideration in aerospace engineering applications. Ongoing research focuses on developing advanced computational methods and experimental techniques to enhance the accuracy and reliability of vibration predictions, thereby contributing to safer and more efficient aerospace systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common queries regarding the application of computational simulation within the aerospace engineering domain. The information presented aims to clarify prevalent misunderstandings and provide concise explanations of essential concepts.
Question 1: What is the fundamental purpose of applying finite element analysis in aerospace engineering?
The primary objective is to predict the structural, thermal, and dynamic behavior of aircraft and spacecraft components under various operational conditions. This predictive capability informs design optimization, reduces the need for physical prototypes, and enhances overall system safety.
Question 2: What types of software are commonly employed for in the aerospace industry?
Several commercial software packages are widely used, including but not limited to ANSYS, ABAQUS, and NASTRAN. The selection of a specific software often depends on the complexity of the analysis, the specific physics being modeled, and the organization’s existing infrastructure.
Question 3: How is the accuracy of simulations validated within the aerospace context?
Validation typically involves comparing simulation results with experimental data obtained from physical testing. This process can include static load testing, modal surveys, and thermal vacuum tests. Discrepancies between simulation and experimental results necessitate refinement of the model, boundary conditions, or material properties.
Question 4: What are the primary challenges associated with modeling composite materials in aerospace simulations?
Composite materials exhibit anisotropic behavior, requiring accurate characterization of material properties in multiple directions. Furthermore, predicting failure mechanisms in composites, such as delamination and fiber breakage, necessitates the use of advanced material models and computational techniques.
Question 5: How does address the issue of computational cost for large-scale aerospace structures?
Strategies for mitigating computational cost include mesh optimization, model order reduction techniques, and the utilization of high-performance computing resources. These approaches allow for efficient simulation of complex structures without compromising accuracy.
Question 6: What role does play in the certification process for new aircraft designs?
Simulation provides critical evidence of structural integrity and compliance with regulatory requirements. Regulatory agencies often require extensive validation of simulation methodologies to ensure their reliability in predicting structural performance under critical loading scenarios.
This FAQ section has addressed some common points. The accuracy and reliability of simulations are paramount for informed decision-making in this sector.
Further exploration into the advancements and future trends is warranted for a deeper understanding.
Conclusion
The application of finite element analysis within aerospace engineering has been extensively explored, highlighting its crucial role in structural design, performance optimization, and safety assurance. The discussion encompassed fundamental concepts, including structural integrity, aerodynamic performance, material behavior, thermal management, and vibration analysis, emphasizing the predictive capabilities afforded by this computational methodology. The importance of accurate material characterization, appropriate element selection, and rigorous validation procedures were underscored as essential for generating reliable simulation results.
The continued advancement of computational techniques, coupled with increasing computational power, promises to further expand the capabilities of finite element analysis within the aerospace sector. Ongoing research into advanced material models, multiscale simulation methods, and uncertainty quantification will contribute to more accurate and robust predictions, facilitating the design of safer, more efficient, and more reliable aircraft and spacecraft. A commitment to rigorous validation and continuous improvement remains paramount for realizing the full potential in addressing the complex engineering challenges of the future.





![Top UC Berkeley Aerospace Engineering Masters Programs [Rankings] Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions Top UC Berkeley Aerospace Engineering Masters Programs [Rankings] | Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-647-300x200.jpg)
