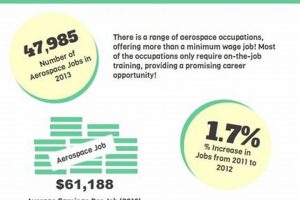
Positions focused on designing, developing, testing, and producing aircraft, spacecraft, satellites, and related systems within the state of California represent a significant sector of employment. These roles often require a strong foundation in mathematics, physics, and computer science, and may involve specializations in areas such as aerodynamics, propulsion, materials science, and structural analysis. An example includes a structural engineer designing the load-bearing components of a new commercial airplane in Southern California.
The prevalence of these specialized technical roles in California is due to a confluence of factors, including the presence of major aerospace companies, research institutions, and government facilities like NASA’s Ames Research Center and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. This concentration creates a beneficial ecosystem fostering innovation, driving economic growth, and contributing to advancements in air and space exploration. Historically, California has been a hub for aerospace activity since the early 20th century, playing a critical role in both military and commercial aviation development.
The remainder of this discussion will explore the various aspects of this professional landscape, including prominent employers, required qualifications, salary expectations, and key geographic areas within the state where these opportunities are most abundant. Future trends influencing the job market and resources for career advancement will also be considered.
The pursuit of a career within California’s aerospace sector requires strategic planning and diligent preparation. The following guidelines offer practical advice for individuals seeking opportunities in this competitive field.
Tip 1: Focus Academic Training: Prioritize advanced coursework in relevant engineering disciplines, such as mechanical, electrical, or aerospace engineering. Specific concentrations like propulsion systems, control systems, or materials science enhance competitiveness. For example, a graduate degree with a focus on computational fluid dynamics can significantly improve prospects for roles involving aerodynamic design.
Tip 2: Seek Internship Experience: Secure internships with established aerospace firms or research institutions. Hands-on experience working on real-world projects is invaluable. An internship at a company like Boeing or Northrop Grumman provides exposure to industry practices and technologies.
Tip 3: Develop Technical Proficiency: Master industry-standard software and tools. Proficiency in CAD software like CATIA or SolidWorks, simulation tools like ANSYS, and programming languages like MATLAB or Python is essential. Documented experience with these tools should be highlighted in application materials.
Tip 4: Cultivate a Strong Network: Attend industry conferences and networking events to connect with professionals in the field. Building relationships with individuals at target companies can provide valuable insights and potential career leads. Active participation in professional organizations like the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA) facilitates networking opportunities.
Tip 5: Tailor Application Materials: Customize resumes and cover letters to align with the specific requirements of each position. Highlight relevant skills and experiences that demonstrate a clear understanding of the target role. Quantify achievements whenever possible, such as “improved aerodynamic efficiency by 15%.”
Tip 6: Obtain Relevant Certifications: Pursue professional certifications that validate specialized skills and knowledge. Certifications in areas such as project management or systems engineering can enhance credibility. Examples include the Project Management Professional (PMP) certification or the Certified Systems Engineering Professional (CSEP) designation.
Tip 7: Consider Geographic Factors: Focus search efforts on regions within California with a high concentration of aerospace activity. Southern California, particularly the Los Angeles and San Diego areas, offers numerous opportunities due to the presence of major aerospace companies and research facilities.
These guidelines, when implemented effectively, significantly increase the likelihood of securing a successful career within California’s dynamic aerospace industry. A proactive and strategic approach is paramount in this highly competitive environment.
The following sections will further examine specific company profiles and emerging technologies shaping the future of opportunities within this sector.
1. Location
Geographic location is a primary determinant in the availability and nature of aerospace engineering positions within California. The distribution of these jobs is not uniform across the state; rather, it is heavily concentrated in specific regions due to the presence of established aerospace companies, research institutions, and related infrastructure. For example, Southern California, encompassing Los Angeles, Orange, and San Diego counties, hosts a significant proportion of opportunities due to the historical presence of major aerospace manufacturers and government research facilities. The proximity to suppliers, skilled labor pools, and testing ranges creates a synergistic effect, attracting further investment and employment in the region.
Conversely, Northern California, while a hub for technology companies, has a relatively smaller concentration of traditional aerospace roles. However, the Bay Area does house NASA Ames Research Center and some companies focused on newer space technologies, such as commercial spaceflight and satellite development. This illustrates a variation in the type of roles available depending on the specific region within the state. Understanding this geographic concentration is crucial for job seekers aiming to maximize their prospects and for companies seeking to establish or expand operations.
In summary, the relationship between location and aerospace engineering opportunities in California is direct and consequential. The historical development and ongoing concentration of aerospace activity in Southern California makes it the dominant region for such employment. While other areas, such as the Bay Area, offer opportunities, the scale and nature of these positions differ significantly. Understanding this geographical landscape allows for informed decision-making for both individuals and organizations operating within or entering this industry.
2. Skills
The acquisition and mastery of specific technical and soft skills directly influence an individual’s prospects for securing opportunities. In the field of aerospace engineering in California, a robust skillset functions as a primary determinant of employability and professional advancement. The absence of required expertise inevitably limits access to various positions, emphasizing the critical connection between these attributes and career success. This dynamic underscores the necessity for continuous professional development and strategic skill enhancement.
Technical skills, such as proficiency in CAD/CAM software (e.g., CATIA, SolidWorks), finite element analysis (FEA) tools (e.g., ANSYS, Abaqus), and programming languages (e.g., MATLAB, Python), are foundational requirements for many roles. For example, a structural engineer designing aircraft components must possess comprehensive knowledge of FEA to simulate stress and strain under various loading conditions. Moreover, strong analytical and problem-solving abilities are essential for troubleshooting complex engineering challenges. Equally important, communication and teamwork capabilities enable effective collaboration within multidisciplinary project teams. A team working on a new satellite launch system, for instance, requires members with diverse expertise to communicate and coordinate effectively.
The correlation between specific abilities and opportunities within the California aerospace industry is evident. Job postings consistently highlight required expertise, and candidates possessing a demonstrable mastery of relevant technical and soft skills often have a competitive advantage. Therefore, a proactive approach to skill development, aligned with industry demands, is paramount for individuals seeking to establish or advance their careers. Further, understanding this nexus enables educational institutions to tailor curricula to better equip graduates with the necessary tools for success.
3. Salary
Compensation for aerospace engineering positions in California is influenced by several factors, including education, experience, specialization, and employer. The state’s high cost of living typically translates into higher salaries compared to national averages for similar roles. Consequently, the monetary aspect is a significant element when considering career options. For example, a recent graduate with a bachelor’s degree might start at a lower salary compared to an engineer with a master’s degree and five years of experience specializing in propulsion systems. The financial implications of this career path extend to considerations of location within California, as areas with higher demand and living costs often offer more competitive packages. Therefore, prospective employees must evaluate potential earnings against their personal financial needs and career aspirations.
Industry-specific benchmarks provide further insight into salary ranges for particular positions. Data from sources such as the Bureau of Labor Statistics and industry surveys reveals disparities between different sub-disciplines within aerospace engineering. For instance, roles requiring advanced expertise in areas like spacecraft design or satellite communications may command higher salaries than more generalist positions. The size and profitability of the employing organization can also exert a significant influence. Major corporations often provide greater financial incentives than smaller firms or startups. Similarly, jobs requiring security clearances or involving sensitive technologies are frequently accompanied by enhanced compensation packages. Therefore, the relationship between salary and specific aerospace engineering positions is complex, involving a multitude of interdependent variables.
In conclusion, salary is a crucial variable influencing both the attractiveness and feasibility of different aerospace engineering careers. The economic considerations, combined with the intellectual challenges and potential for innovation, form the core of the value proposition for prospective employees. Understanding the interplay of contributing factors is thus essential for informed decision-making. While competitive pay can be a significant motivator, the associated challenges of demanding workloads and specialized skill requirements must also be carefully considered for long-term career satisfaction and success within the California aerospace engineering job market.
4. Companies
The presence and activities of aerospace companies form the bedrock of aerospace engineering jobs in California. These organizations, ranging from multinational corporations to specialized startups, directly generate the demand for engineers through their research, development, manufacturing, and operational activities. Without these entities, the prospect of finding employment in this specific field within the state would be severely limited. The sheer number of available positions, the variety of specializations, and the opportunities for career advancement are all directly proportional to the health and activity of these companies. For example, Lockheed Martin’s operations in Palmdale contribute significantly to the demand for aerospace engineers specializing in aircraft design and testing. Similarly, SpaceX’s presence in Hawthorne creates roles related to rocket propulsion and space vehicle engineering. The specific requirements and skill sets demanded by each company shape the overall technical landscape of the labor market.
The geographical distribution of aerospace companies within California further impacts the concentration and accessibility of opportunities. As previously noted, Southern California hosts a significant cluster of these organizations, making it the primary hub for aerospace engineering jobs. This concentration fosters a competitive environment, attracting skilled engineers and creating a dynamic ecosystem of innovation and technological advancement. Government contracts and funding play a critical role in sustaining many of these companies, driving both job creation and technological progress. The constant pursuit of cutting-edge technologies, particularly in areas like advanced materials, autonomous systems, and electric propulsion, necessitates a continuous influx of highly skilled engineers. Understanding the strategic priorities and ongoing projects of these companies allows job seekers to tailor their skills and application materials accordingly.
In summary, the relationship between aerospace companies and the availability of aerospace engineering jobs in California is one of direct cause and effect. The strategic decisions, operational requirements, and technological investments made by these companies collectively define the shape and scope of the employment landscape. Awareness of the key players, their areas of focus, and their hiring practices is essential for navigating this competitive job market and maximizing the chances of securing a fulfilling and impactful career. Challenges remain in maintaining a stable and growing aerospace sector, particularly in the face of global competition and fluctuating economic conditions. However, California’s strong foundation in aerospace, combined with ongoing investment in innovation, positions the state to remain a leading center for aerospace engineering employment for the foreseeable future.
5. Education
The acquisition of a formal education serves as a primary gateway into the field of aerospace engineering in California. A bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering, or a closely related field such as mechanical or electrical engineering, is generally considered a minimum requirement for entry-level positions. The curriculum typically encompasses a rigorous foundation in mathematics, physics, and engineering principles, providing candidates with the fundamental knowledge necessary to address complex technical challenges. For instance, the design of an aircraft wing requires a thorough understanding of aerodynamics, structural mechanics, and materials science, all of which are typically covered in undergraduate coursework. Furthermore, practical experience gained through laboratory exercises, design projects, and internships enhances theoretical knowledge and prepares graduates for real-world engineering applications.
Advanced degrees, such as master’s or doctoral degrees, often lead to more specialized roles and higher earning potential. Specific areas of specialization, such as propulsion systems, control systems, or composite materials, can significantly enhance a candidate’s competitiveness in specific segments of the industry. For example, a master’s degree with a focus on computational fluid dynamics can be highly advantageous for positions involving aerodynamic design and analysis. Furthermore, research experience gained during graduate studies often equips candidates with the skills necessary for innovation and problem-solving in a rapidly evolving technological landscape. Many California universities maintain close partnerships with aerospace companies, facilitating research collaborations and providing students with valuable networking opportunities. These connections often translate into internships or full-time employment upon graduation.
In conclusion, education plays a critical role in shaping the career prospects of aerospace engineers in California. A strong academic foundation, coupled with practical experience and specialized knowledge, is essential for success in this demanding field. Continuous professional development and lifelong learning are also crucial for staying abreast of technological advancements and maintaining a competitive edge. While talent and drive are important, formal education provides the necessary tools to create, build, and advance complex Aerospace engineering systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding career opportunities within the aerospace engineering sector in California. The information provided is intended to offer clarity and guidance to prospective job seekers.
Question 1: What are the primary qualifications required for entry-level positions?
A bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering or a closely related field is generally expected. Strong academic performance in mathematics, physics, and relevant engineering coursework is crucial. Internship experience is highly valued, demonstrating practical application of theoretical knowledge.
Question 2: Which regions of California offer the most abundant aerospace engineering employment opportunities?
Southern California, particularly Los Angeles and San Diego counties, maintains the highest concentration of aerospace companies and related job openings. The San Francisco Bay Area also presents opportunities, especially within companies focusing on newer space technologies.
Question 3: What is the typical salary range for an aerospace engineer in California?
Salaries vary based on experience, education, and specialization. Entry-level positions may offer lower salaries, while experienced engineers with advanced degrees and specialized expertise command higher compensation. Cost of living adjustments should be factored into salary considerations.
Question 4: Which skills are most in-demand among aerospace engineering employers in California?
Proficiency in CAD/CAM software (e.g., CATIA, SolidWorks), finite element analysis tools (e.g., ANSYS), and programming languages (e.g., MATLAB, Python) is highly valued. Strong communication, teamwork, and problem-solving skills are also essential.
Question 5: How can an individual increase their chances of securing an aerospace engineering job in California?
Focus on building a strong academic foundation, gaining relevant internship experience, developing in-demand technical skills, and networking with industry professionals. Tailor resumes and cover letters to match specific job requirements. Obtain professional certifications where applicable.
Question 6: What are some emerging trends shaping the future of aerospace engineering in California?
The development of advanced materials, autonomous systems, electric propulsion, and commercial spaceflight are driving new opportunities. Companies focused on these areas are likely to experience growth and increased hiring activity.
In summary, securing a position in aerospace engineering demands preparation, skill development, and strategic planning. While challenges exist, the California job market offers robust opportunities for qualified and motivated individuals.
The following section will summarize findings and conclude this report.
Conclusion
This discussion has provided a comprehensive overview of opportunities in California. Key aspects, including location, necessary skills, compensation levels, major employers, and educational requirements, have been examined. The concentration of these positions in Southern California, the importance of advanced technical abilities, and the influence of both company size and economic factors on earning potential have been emphasized. Furthermore, the foundational role of education and the value of continuous professional development have been underscored.
The dynamic nature of the aerospace industry necessitates constant adaptation and skill enhancement. Professionals seeking to advance their careers within this field should remain informed about emerging technologies and industry trends. The pursuit of such knowledge, coupled with strategic career planning, is essential for sustained success. Further research into specific company profiles and specialized areas of aerospace engineering is encouraged.