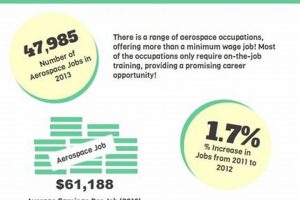
Opportunities within the aircraft and spacecraft industries situated in the state’s most populous city are the subject of this exploration. These positions encompass a broad range of roles, from engineering and design to manufacturing and support, all contributing to the advancement of flight and space technology within a specific geographic area.
The concentration of aerospace related employment in this major metropolitan area offers several advantages. Proximity to academic institutions facilitates research and development, while the availability of a skilled workforce enhances productivity. Furthermore, historical connections to aviation and technological innovation provide a strong foundation for continued growth in the sector. The presence of major transportation hubs further facilitates efficient logistics and supply chain management.
The subsequent discussion will delve into the specific sectors contributing to this employment landscape, the required skills and qualifications for these roles, and the overall outlook for the industry within the designated region.
Securing a position related to flight and space technology within New York requires a focused and strategic approach. The following points provide guidance for individuals seeking such employment.
Tip 1: Enhance Technical Skills: Focus on developing specialized knowledge in areas such as aerodynamics, propulsion systems, or avionics. Certification and advanced degrees can significantly improve competitiveness.
Tip 2: Network Strategically: Attend industry events, join professional organizations, and connect with individuals working in the sector. Networking can provide valuable insights and potential job leads.
Tip 3: Tailor Resume and Cover Letter: Highlight relevant experience and skills that align with the specific requirements of each position. Generic applications are less likely to succeed.
Tip 4: Research Companies Thoroughly: Understand the company’s projects, products, and culture before applying. Demonstrate this knowledge during the interview process.
Tip 5: Prepare for Technical Interviews: Be prepared to answer technical questions related to engineering principles, design methodologies, and problem-solving skills. Practice common interview questions and scenarios.
Tip 6: Consider Internship Opportunities: Internships provide valuable hands-on experience and exposure to the industry. They can also lead to full-time employment opportunities.
Tip 7: Explore Government Positions: Investigate opportunities with government agencies involved in aerospace research, development, and regulation. These positions often offer stability and career advancement potential.
Tip 8: Maintain Awareness of Industry Trends: Stay informed about the latest advancements in aerospace technology, such as electric propulsion, autonomous systems, and sustainable aviation. This knowledge demonstrates a commitment to professional development.
Adhering to these recommendations increases the probability of success when pursuing career opportunities related to aircraft and spacecraft technology in New York.
The subsequent section will address the future prospects and evolving nature of the industry within the specified locale.
1. Engineering Design
Engineering design forms a cornerstone of opportunities relating to flight and space technology within the New York metropolitan area. These roles involve conceiving, developing, and refining aircraft and spacecraft components, systems, and overall architecture. The availability of such positions is directly correlated with the presence of aerospace manufacturers, research institutions, and related businesses in and around New York. Failure to prioritize engineering design would significantly impede the advancement of related technologies. For example, a local firm specializing in advanced materials might employ engineering designers to optimize the structural integrity and weight of aircraft wings, directly affecting fuel efficiency and performance.
The practical significance of understanding this connection lies in workforce development and strategic resource allocation. Educational institutions can tailor curricula to meet the specific needs of local aerospace companies, ensuring a pipeline of qualified engineering graduates. Similarly, government agencies can incentivize research and development projects that promote innovation in engineering design, thereby attracting further investment in the sector. This could involve funding for the design of more efficient rotor systems for urban air mobility vehicles, a growing area of interest within the city.
In summary, engineering design is an essential component of opportunities in the aerospace domain in New York. Recognizing its importance enables stakeholders to foster innovation, support workforce development, and drive economic growth. Challenges may include competition from other regions with established aerospace hubs and the need to adapt to rapidly evolving technological landscapes. However, focused efforts to strengthen engineering design capabilities can secure New York’s position as a contributor to the broader aerospace industry.
2. Manufacturing
Manufacturing is a critical, albeit often understated, component of opportunities related to flight and space technology within New York. Although New York City itself is not typically associated with large-scale aerospace manufacturing plants, its surrounding areas and the broader state do contribute through specialized component production and related services. These activities generate a spectrum of positions, from skilled machinists and technicians to quality control specialists and production managers. For instance, a facility outside the city specializing in precision-engineered aircraft parts directly creates employment opportunities for individuals with expertise in computer numerical control (CNC) machining and materials science. The absence of this manufacturing capability would render the design and development efforts in the region incomplete and ultimately unsustainable.
The practical significance of understanding this relationship extends to economic development and workforce planning. State and local governments can attract aerospace-related manufacturers by offering incentives such as tax breaks, infrastructure improvements, and workforce training programs. Furthermore, community colleges and technical schools can align their curricula with the specific needs of these manufacturers, ensuring a steady supply of qualified personnel. An example of practical application includes the establishment of advanced manufacturing centers focused on aerospace technologies, fostering collaboration between industry, academia, and government to accelerate innovation and create jobs. Also, the manufacture of unmanned aerial vehicles or UAVs, (drones), is expanding, driving manufacturing jobs.
In summary, manufacturing plays a vital supporting role in the New York aerospace landscape, even if its presence is less prominent than in other states. Recognizing its importance enables stakeholders to cultivate a supportive ecosystem for aerospace-related businesses, enhance workforce skills, and promote economic diversification. The challenge lies in competing with regions that have already established themselves as major manufacturing hubs. However, by focusing on niche capabilities, investing in advanced manufacturing technologies, and fostering strong partnerships between industry and education, New York can solidify its position as a contributor to the aerospace manufacturing supply chain.
3. Research
The pursuit of knowledge and innovation constitutes an essential driver of opportunities related to flight and space technology within New York City. Research activities, typically conducted at universities, research institutions, and within corporate research and development departments, generate a demand for scientists, engineers, and technicians. This creates specialized opportunities in areas such as aerodynamics, materials science, propulsion systems, and avionics. For instance, a university laboratory investigating novel composite materials for aircraft structures directly translates into employment for research scientists and postdoctoral fellows. Without consistent research endeavors, advancements in aerospace technologies would stagnate, thereby limiting the sector’s growth potential and associated employment prospects.
The practical implications of this connection extend to technology transfer and economic competitiveness. Research breakthroughs originating in New Yorks institutions can lead to the creation of new aerospace companies and products, boosting economic activity and creating high-skilled jobs. Government funding for research grants, coupled with industry partnerships, fosters an environment conducive to innovation. As an example, the development of more efficient drone technologies through university research could lead to the establishment of drone-based delivery or inspection services within the city, generating new business opportunities and employment. Furthermore, the creation of research parks around universities helps to encourage collaboration and generate opportunities for new companies to settle near major research hubs.
In summary, research is a critical catalyst for career pathways and advancements in flight and space technology. Recognizing this strong interconnection enables stakeholders to prioritize investments in research infrastructure, support academic-industry collaborations, and attract top talent to the region. Challenges might include competition for research funding and the need to translate research findings into commercially viable products. However, by fostering a vibrant research ecosystem, New York can secure a leading position in certain segments of the aerospace sector, enhancing its overall competitiveness and creating opportunities.
4. Regulations
The regulatory framework governing flight and space technologies exerts a considerable influence on the employment landscape within New York. Compliance with federal, state, and local mandates generates a demand for specialized professionals and shapes the operational practices of aerospace-related businesses.
- Compliance Officers and Legal Counsel
Aerospace companies require individuals with expertise in aviation law, environmental regulations, and safety standards. These professionals ensure adherence to relevant mandates and mitigate potential legal liabilities, affecting staffing levels and skill requirements in legal and compliance departments. Examples include ensuring compliance with FAA regulations for drone operations in urban environments, or international regulations for parts manufacturing and sales.
- Safety Inspectors and Auditors
Regulatory agencies, such as the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), employ inspectors and auditors to oversee the operations of airlines, maintenance facilities, and other aerospace-related entities. These roles contribute to the overall safety and security of the aviation system, increasing needs for qualified and trained inspectors. Furthermore, some positions may involve oversight of manufacturing processes and compliance with national and international regulations.
- Certification Specialists
The certification of aircraft, components, and personnel is a critical regulatory function. Certification specialists evaluate compliance with established standards and issue the necessary approvals. The need for these specialists is likely to increase with technological advancements and the introduction of new types of aircraft, driving demand for these expert positions.
- Environmental Compliance Managers
Growing environmental concerns have led to stricter regulations on aircraft emissions, noise pollution, and waste disposal. Aerospace companies must employ environmental compliance managers to develop and implement strategies to minimize their environmental footprint. As environmental standards tighten, there is a corresponding increase in the demand for qualified managers.
In summary, regulations directly and indirectly impact the number and types of opportunities in New York. Adherence to these rules necessitates dedicated personnel and compliance departments, making the regulatory aspect a vital force within the sector and a defining element of employment dynamics.
5. Maintenance
Aircraft maintenance is integral to safe and efficient air operations and contributes significantly to opportunities related to flight and space technology within the New York metropolitan area. This field encompasses a wide range of activities, from routine inspections and repairs to complex overhauls and modifications, ensuring the continued airworthiness and performance of aircraft.
- Aircraft Mechanics and Technicians
Aircraft mechanics and technicians conduct scheduled maintenance, troubleshoot malfunctions, and perform repairs on aircraft systems, including engines, airframes, and avionics. The presence of major airports such as JFK and LaGuardia directly correlates with the demand for these skilled professionals. For example, a technician might specialize in the repair of a specific engine type, ensuring the reliability and safety of aircraft operating in and out of New York.
- Avionics Technicians
Avionics technicians specialize in the maintenance, repair, and installation of aircraft electronic systems, including navigation, communication, and flight control systems. As aircraft become increasingly reliant on sophisticated avionics, the demand for qualified technicians continues to grow. This can also include the new installations of new equipment and complete re-wiring of electrical systems.
- Quality Control Inspectors
Quality control inspectors ensure that maintenance work is performed to the highest standards and in accordance with regulatory requirements. They conduct inspections, review maintenance records, and verify the airworthiness of aircraft before they are returned to service. The presence of major maintenance repair and overhaul MRO facilities contributes substantially to the volume of open positions.
- Maintenance Planners and Managers
Maintenance planners and managers coordinate and schedule maintenance activities, manage resources, and ensure that maintenance operations are conducted efficiently and effectively. These individuals play a critical role in optimizing maintenance schedules, minimizing downtime, and controlling costs, affecting the productivity of maintenance operations and aircraft availability.
The maintenance sector is a consistent source of opportunity. Proximity to major transportation hubs, the presence of maintenance facilities, and ongoing technological advancements contribute to demand. As aircraft fleets age and new technologies are introduced, the need for qualified maintenance professionals will continue to grow, securing a position within the industry and ensuring the safety and reliability of air travel.
6. Innovation
Advancements are a critical determinant of opportunities pertaining to flight and space technology within the New York metropolitan area. It encompasses the development of new technologies, processes, and business models that drive progress and enhance competitiveness in this sector. The capacity for inventive solutions directly influences the emergence of new roles, requiring specialized expertise and skills. For example, the development of novel urban air mobility (UAM) vehicles sparks demand for engineers specializing in electric propulsion, autonomous flight control systems, and advanced materials. Without a robust commitment to creating new and better technologies, the local aerospace sector faces stagnation and struggles to attract investment.
The practical significance of comprehending this lies in its impact on economic development and workforce adaptation. New York can position itself as a hub for cutting-edge developments by fostering collaborations between universities, research institutions, and private companies. This ecosystem attracts talent, generates intellectual property, and stimulates entrepreneurial activity. One clear example is the establishment of incubators and accelerator programs focused on aerospace startups, which provide resources, mentorship, and funding to help these ventures succeed. The existence of these entities encourages inventors and technological creators to establish their operations in New York.
In conclusion, technological advances are intrinsically linked to the viability and expansion of flight and space-related employment in New York. Prioritizing investment in research and development, promoting collaborations, and supporting aerospace entrepreneurship are vital strategies for ensuring the sustained growth and competitiveness of this field. While challenges such as regulatory hurdles and capital constraints exist, a proactive approach to fostering a culture of discovery unlocks opportunities and positions New York as a notable player in the future of flight and space technology.
Frequently Asked Questions about Aerospace Jobs in New York
The following addresses common inquiries regarding employment within the aircraft and spacecraft industries located in the state’s most populous city. These questions aim to provide clarity and guidance for individuals seeking to enter or advance within this sector.
Question 1: What types of qualifications are typically required for opportunities related to flight and space technology within New York?
Educational backgrounds in engineering (aerospace, mechanical, electrical), computer science, or related fields are frequently expected. Specific positions may require advanced degrees, certifications, or specialized training relevant to the industry.
Question 2: Are there specific industries or sectors within the region that offer a greater concentration of opportunities related to flight and space technology?
Component manufacturing, maintenance and repair operations (MROs) located near major airports, and research institutions often represent a significant source of employment. Opportunities may also exist with government agencies involved in air traffic control or aerospace regulation.
Question 3: What is the general outlook for the industry within New York, and are there any expected trends or growth areas?
The outlook is generally stable, with potential for growth in niche areas such as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), urban air mobility (UAM), and advanced materials. Innovation and technological advancements are expected to drive future employment prospects.
Question 4: What are some common challenges faced by individuals seeking opportunities related to flight and space technology in New York?
Competition for available positions, the need for specialized skills and experience, and the high cost of living in the New York metropolitan area represent significant challenges.
Question 5: Are there any specific resources or organizations that can assist individuals in their job search?
Professional organizations such as the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA), industry associations, online job boards, and networking events can provide valuable resources and support.
Question 6: How does the state’s geographic location and infrastructure contribute to the viability of the region?
Proximity to major transportation hubs, access to a skilled workforce, and the presence of academic institutions contribute to its viability as a location for aerospace-related activities.
This section has addressed fundamental concerns and provided direction for navigating opportunities related to flight and space technology in New York.
The subsequent part contains concluding remarks and a summary of critical points.
Conclusion
This discussion has examined opportunities within the aircraft and spacecraft industries in New York City, with particular attention paid to positions related to engineering, manufacturing, research, regulations, maintenance, and innovation. The analysis revealed a multifaceted sector influenced by technological advancements, regulatory frameworks, and economic factors.
The future trajectory of aerospace jobs new york depends on sustained investment in research and development, strategic workforce development initiatives, and the ability of local businesses to adapt to evolving technological landscapes. Continued vigilance and proactive measures are necessary to maintain competitiveness and fully leverage the potential of this critical industry.