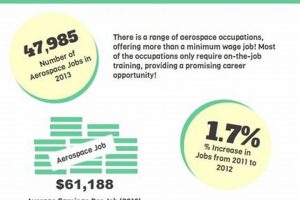
Employment opportunities within the aeronautics and space industry located in the Golden State are a significant segment of the state’s economy. These positions encompass a wide range of technical and administrative roles directly related to the design, development, manufacturing, and maintenance of aircraft, spacecraft, and related systems. For instance, a mechanical engineer designing a satellite component or a quality control inspector verifying the integrity of an aircraft wing would both hold such a position.
The concentration of these roles in California stems from a long history of aerospace innovation and a robust network of educational institutions and research facilities. Benefits derived from this sector include substantial economic contributions through job creation, technological advancements that ripple through other industries, and the establishment of California as a leader in cutting-edge engineering and scientific endeavors. The sector’s growth has been fueled by both government contracts and private sector investment, solidifying its importance to the state’s financial health.
The following sections will delve into specific types of careers available, required skills and education, leading employers, and emerging trends shaping the future of this dynamic employment landscape. Further discussion will also cover regional variations in job availability and resources for individuals seeking to enter or advance within this field.
Securing a position within the aerospace sector in California requires a strategic approach, given the competitive nature of the industry and the specialized skills demanded.
Tip 1: Target Specific Companies: Research leading aerospace firms and identify those whose missions and values align with individual career aspirations. Tailor applications to each company’s specific needs, highlighting relevant experience and skills.
Tip 2: Emphasize Technical Skills: Proficiency in relevant software, programming languages, and engineering principles is paramount. Continuously update technical expertise to remain competitive in a rapidly evolving field. Consider pursuing certifications relevant to specific roles.
Tip 3: Network Strategically: Attend industry conferences, career fairs, and networking events to connect with professionals and potential employers. Building relationships can provide valuable insights into unadvertised openings and industry trends.
Tip 4: Obtain Relevant Education and Training: A degree in aerospace engineering, mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, or a related field is generally required. Consider advanced degrees or specialized certifications to enhance qualifications. Research institutions in California known for their aerospace programs.
Tip 5: Develop a Strong Portfolio: Showcase relevant projects, research, and accomplishments in a well-structured portfolio. This provides tangible evidence of skills and abilities to potential employers. Include examples of problem-solving and innovation.
Tip 6: Tailor Resumes and Cover Letters: Customize resumes and cover letters to match the specific requirements of each job posting. Highlight relevant experience and skills, using keywords from the job description. Proofread carefully for errors.
Tip 7: Prepare for Technical Interviews: Technical interviews often involve problem-solving exercises and in-depth discussions of engineering principles. Practice answering common technical questions and be prepared to explain technical concepts clearly and concisely.
Adhering to these guidelines increases the probability of successfully navigating the competitive landscape and securing a desirable position.
The subsequent sections will explore the current demands in the specified field and future outlooks for job seekers.
1. Engineering Design
Engineering design is a core component within the spectrum of employment opportunities in the aeronautics and space industry located in California. It encompasses a range of specialized disciplines focused on conceiving, developing, and refining aerospace systems and components. The strength and innovation within this design sector directly influence the competitiveness and advancement of the state’s aerospace enterprises.
- Aerodynamics and Fluid Dynamics
This facet concerns the study of air and fluid flow around aircraft and spacecraft. Engineers specializing in this area design airfoils, control surfaces, and propulsion systems to optimize performance and stability. For example, computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations are used to analyze airflow over a wing, predicting lift and drag forces. These skills are crucial for improving fuel efficiency and maneuverability in both commercial and military aircraft, driving demand for specialized engineering talent in California.
- Structural Design and Analysis
Structural engineers are responsible for ensuring the integrity and safety of aerospace vehicles under various stress conditions. They analyze material properties, conduct stress tests, and design structures capable of withstanding extreme loads and temperatures. For instance, finite element analysis (FEA) is employed to simulate the structural response of an aircraft fuselage during flight. This specialization is critical for creating lightweight, durable, and safe aerospace components, necessitating expertise in advanced materials and structural mechanics within California’s job market.
- Systems Engineering
Systems engineers focus on the integration of various subsystems within an aircraft or spacecraft, ensuring that all components function harmoniously. They define system requirements, manage interfaces, and conduct trade studies to optimize overall performance. For example, a systems engineer might be responsible for integrating the navigation, communication, and sensor systems within a satellite. This holistic approach is essential for developing complex aerospace systems, creating a demand for engineers with broad technical knowledge and project management skills in California.
- Propulsion Systems Design
This area involves the design and development of engines and propulsion systems for aircraft and spacecraft. Engineers specializing in this field work on improving engine efficiency, reducing emissions, and developing new propulsion technologies. For instance, they might design a new turbine blade for a jet engine or develop a hybrid rocket engine for space launch vehicles. Innovation in propulsion is vital for advancing aerospace capabilities, leading to a need for highly specialized engineers with expertise in thermodynamics, combustion, and materials science in California.
These facets collectively represent the critical role of engineering design within the Californian landscape. The state’s leading aerospace companies actively seek professionals skilled in these areas to maintain their competitive edge and drive future innovation. The demand for specialized engineering design expertise continues to shape the career paths and educational opportunities available within California’s aerospace sector.
2. Manufacturing Processes
Manufacturing processes are intrinsically linked to the availability and nature of aeronautics and space-related employment within California. The efficiency, precision, and innovation inherent in these processes directly influence the competitive advantage and productivity of the state’s aerospace industry, thereby shaping the demand for specialized labor and expertise.
- Advanced Materials Fabrication
The aerospace sector increasingly relies on advanced materials such as composites, alloys, and ceramics to achieve weight reduction, improved performance, and enhanced durability. Manufacturing processes involving these materials, including automated fiber placement, resin transfer molding, and powder metallurgy, require highly skilled technicians, engineers, and quality control specialists. For example, the production of carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) wing structures necessitates expertise in material handling, tooling design, and non-destructive testing, creating specialized employment opportunities in California.
- Precision Machining and Manufacturing
The production of aerospace components demands extremely tight tolerances and high levels of precision. Manufacturing processes such as CNC machining, laser cutting, and electrical discharge machining (EDM) are critical for creating complex geometries and achieving the required surface finishes. These processes necessitate skilled machinists, programmers, and metrologists who can operate and maintain advanced manufacturing equipment. For instance, the manufacturing of turbine blades for jet engines requires micron-level precision to ensure optimal aerodynamic performance, driving the demand for highly skilled precision machinists in California.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing technologies are increasingly used in the aerospace industry to produce complex parts with reduced lead times and material waste. Processes such as selective laser melting (SLM), fused deposition modeling (FDM), and stereolithography (SLA) enable the creation of customized components with intricate designs. The implementation of additive manufacturing requires skilled engineers, technicians, and designers who can operate 3D printers, optimize part designs for additive manufacturing, and perform post-processing operations. The growing adoption of 3D printing in California’s aerospace sector is generating new employment opportunities in this rapidly evolving field.
- Assembly and Integration
The assembly and integration of aerospace systems involves the meticulous joining of individual components into functional units, such as aircraft wings, engine modules, and satellite payloads. These processes require skilled technicians and engineers who can follow detailed assembly procedures, perform electrical and mechanical connections, and conduct functional testing. For example, the integration of avionics systems within an aircraft cockpit necessitates expertise in wiring harness assembly, software configuration, and system validation, leading to demand for skilled technicians and engineers with expertise in aerospace electronics in California.
These facets illustrate the critical role of manufacturing processes in shaping the nature and availability of aerospace-related employment in California. The state’s commitment to technological innovation and advanced manufacturing continues to drive demand for skilled professionals who can operate, maintain, and improve these complex manufacturing processes, thereby solidifying California’s position as a leader in the aerospace industry.
3. Research and Development
Research and Development (R&D) is a fundamental driver shaping the landscape of employment opportunities within the aeronautics and space sector in California. The state’s robust R&D ecosystem, encompassing both public and private institutions, fuels innovation, technological advancements, and the creation of high-skilled jobs. This section explores specific facets of R&D and their direct connection to career prospects within California’s aerospace industry.
- Advanced Materials Research
Research into novel materials with enhanced strength-to-weight ratios, temperature resistance, and other critical properties is essential for improving the performance and efficiency of aerospace vehicles. This research often involves the development of new alloys, composites, and coatings, demanding skilled material scientists, engineers, and technicians. For instance, research on ceramic matrix composites for high-temperature engine components directly contributes to the development of more efficient jet engines, creating jobs for materials specialists in California.
- Autonomous Systems Development
The development of autonomous systems, including unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and autonomous spacecraft, is a rapidly growing area of research in the aerospace industry. This research involves the integration of advanced sensors, control algorithms, and artificial intelligence to enable vehicles to operate without human intervention. The development of autonomous flight control systems or self-navigating spacecraft requires engineers and scientists with expertise in robotics, computer vision, and machine learning, creating significant employment opportunities in California’s technology-driven aerospace sector.
- Next-Generation Propulsion Technologies
Research into advanced propulsion technologies, such as electric propulsion, hypersonic propulsion, and fusion propulsion, is crucial for enabling future space exploration and air transportation. This research involves the development of innovative engine designs, propellant systems, and energy sources. The exploration of new rocket engine concepts or advanced fuel formulations necessitates engineers, physicists, and chemists with expertise in combustion, thermodynamics, and plasma physics. California’s research institutions and aerospace companies are at the forefront of propulsion research, generating high-paying jobs for specialized scientists and engineers.
- Space Exploration Technologies
Research into technologies that support space exploration, such as life support systems, radiation shielding, and in-situ resource utilization (ISRU), is vital for enabling long-duration space missions and the establishment of human settlements on other planets. This research involves the development of closed-loop environmental control systems, advanced shielding materials, and techniques for extracting resources from extraterrestrial environments. Scientists and engineers working on these technologies require expertise in biology, chemistry, and environmental engineering. The ongoing investment in space exploration research creates a diverse range of aerospace jobs in California, spanning various scientific and engineering disciplines.
These facets collectively demonstrate the significant impact of R&D on the creation and evolution of employment opportunities within the aeronautics and space industry in California. The state’s ongoing investment in R&D ensures a steady stream of innovation, technological advancements, and high-skilled jobs, solidifying California’s position as a global leader in the aerospace sector.
4. Testing and Validation
Testing and validation are indispensable components of the aerospace industry, exerting a significant influence on the availability and nature of related employment in California. Rigorous testing protocols are mandated to ensure the safety, reliability, and performance of aircraft, spacecraft, and associated systems. This demand for stringent evaluation directly translates into a need for specialized personnel capable of designing, executing, and analyzing test procedures, thereby shaping the occupational landscape.
The repercussions of inadequate testing can be catastrophic, as demonstrated by historical incidents involving aircraft failures due to undetected flaws. Consequently, aerospace organizations invest heavily in comprehensive testing regimes that encompass component-level assessments, system-level integration tests, and flight simulations. These processes necessitate a diverse range of expertise, including test engineers, instrumentation technicians, data analysts, and quality assurance specialists. For example, a structural test engineer might oversee the physical testing of an aircraft wing to verify its ability to withstand specified load conditions, while a software validation engineer might ensure the integrity of flight control system code through rigorous simulation and hardware-in-the-loop testing. The complexity and criticality of these roles underscore the importance of specialized skills and training within the industry.
In conclusion, the rigorous demands of testing and validation within the aeronautics and space sector are a primary driver for the creation of specialized career opportunities in California. While the sector faces ongoing challenges in maintaining a skilled workforce and adapting to evolving regulatory requirements, the emphasis on safety and reliability ensures that testing and validation will remain a critical function, sustaining demand for qualified professionals in the foreseeable future. This emphasis reinforces California’s position as a hub for aerospace innovation and employment.
5. Regulatory Compliance
The complex and stringent regulatory landscape governing the aeronautics and space sector directly influences the types and availability of employment opportunities in California. Adherence to federal regulations, particularly those promulgated by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and other agencies, necessitates specialized expertise throughout the lifecycle of aerospace products, from design and manufacturing to operation and maintenance. For example, compliance with FAA Part 21, which governs the certification of aircraft and related products, requires manufacturers to employ personnel dedicated to quality assurance, conformity inspection, and documentation control. The presence of these regulatory requirements directly drives the demand for skilled professionals proficient in navigating and implementing complex compliance protocols.
The practical significance of regulatory compliance extends beyond mere adherence to legal mandates; it fundamentally impacts safety, operational efficiency, and market access. Aerospace companies operating in California must demonstrate compliance to secure certifications, approvals, and permits necessary to conduct business. This creates a continuous need for regulatory affairs specialists, compliance managers, and auditors who can ensure that all aspects of the organization’s operations align with applicable regulations. Furthermore, the evolving nature of regulations, driven by technological advancements and emerging safety concerns, requires ongoing training and development of personnel to maintain compliance expertise. A real-world example is the implementation of new cybersecurity regulations for aircraft systems, which has led to increased demand for cybersecurity engineers and compliance officers within the aerospace industry. These individuals are responsible for assessing and mitigating cybersecurity risks, developing security protocols, and ensuring that aircraft systems are protected from cyber threats, thereby safeguarding the safety and integrity of air travel.
In summary, regulatory compliance is not merely an ancillary function but a core component shaping the demand for specialized skills and expertise within the aeronautics and space job market in California. The state’s position as a leading aerospace hub is inextricably linked to its ability to navigate and adhere to complex regulatory requirements. While the cost of compliance can be substantial, the benefits, in terms of enhanced safety, reliability, and market access, far outweigh the challenges. Looking ahead, the demand for regulatory compliance professionals in California’s aerospace sector is expected to remain strong, driven by ongoing regulatory changes and the increasing complexity of aerospace systems.
6. Location Clusters
The concentration of aerospace jobs in California is not uniformly distributed across the state; rather, it is heavily influenced by the phenomenon of location clusters. These clusters, characterized by a geographic concentration of interconnected companies, specialized suppliers, service providers, and associated institutions in a particular field, create a synergistic environment that fosters innovation, attracts talent, and drives economic growth. The presence of these clusters is a significant determinant of where aerospace employment opportunities are most abundant within California. The causes are multifaceted, often including proximity to major research universities, historical government investment in aerospace programs, and a skilled labor pool cultivated over decades.
Southern California, particularly Los Angeles and Orange counties, represents a prominent aerospace cluster. Its roots trace back to the early days of aviation and the subsequent expansion of the aerospace industry during the Cold War. The presence of major aerospace companies, such as Boeing, Northrop Grumman, and SpaceX, has created a dense network of suppliers, subcontractors, and specialized service providers, all benefiting from proximity to these industry leaders. The effect is a self-reinforcing cycle: as companies locate or expand within the cluster, they attract skilled workers, which further enhances the region’s attractiveness to other aerospace firms. A similar, though smaller, cluster exists in the San Francisco Bay Area, with a focus on space technology and satellite communication, driven by companies like Lockheed Martin Space and numerous innovative startups. These geographical concentrations facilitate the efficient exchange of knowledge, ideas, and resources, contributing to the overall competitiveness of California’s aerospace sector.
Understanding the role of location clusters is of practical significance for individuals seeking aerospace employment in California. It allows job seekers to focus their search efforts on specific regions where their skills are most in demand. Furthermore, it enables companies to strategically locate their operations to maximize access to talent, suppliers, and research infrastructure. While challenges exist, such as high housing costs in these clustered areas, the benefits of proximity to industry leaders and a specialized labor pool often outweigh these disadvantages. The link between location clusters and aerospace jobs is integral to the vitality of the broader aerospace industry in California, shaping its trajectory and competitiveness on a global scale.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding employment opportunities within the aeronautics and space sector in California. The information provided aims to offer clarity and guidance for individuals considering or pursuing careers in this field.
Question 1: What educational qualifications are typically required for positions in California’s aerospace industry?
A bachelor’s degree in a relevant engineering discipline (e.g., aerospace, mechanical, electrical) is generally considered a minimum requirement. Many advanced positions necessitate a master’s or doctoral degree, particularly those involving research and development or specialized engineering tasks. Furthermore, certain roles may require specific certifications or licenses.
Question 2: Which areas of specialization within aerospace engineering are currently experiencing high demand in California?
Several areas are experiencing robust demand, including systems engineering, propulsion systems, avionics, and advanced materials. Expertise in software engineering and cybersecurity is also highly sought after, given the increasing reliance on complex software systems and the growing threat of cyberattacks on aerospace infrastructure.
Question 3: What are the primary geographical hubs for aerospace companies and associated jobs within California?
Southern California, particularly Los Angeles and Orange counties, represents the largest concentration of aerospace activity. The San Francisco Bay Area also hosts a significant number of aerospace companies, with a focus on space technology and satellite communications. Other regions, such as the Mojave Desert, serve as test and development sites for aerospace vehicles.
Question 4: What are some of the key skills that enhance a candidate’s prospects for securing a position within the California aerospace sector?
Beyond core engineering knowledge, strong analytical and problem-solving skills are essential. Proficiency in relevant software tools (e.g., CAD, CAE) is also critical. Effective communication and teamwork skills are highly valued, given the collaborative nature of most aerospace projects. Furthermore, a demonstrated ability to learn and adapt to new technologies is increasingly important in this rapidly evolving field.
Question 5: Are there specific government regulations that impact hiring practices within the California aerospace industry?
Yes, aerospace companies operating in California are subject to various federal regulations, including those related to export control, security clearances, and environmental compliance. Hiring practices must align with these regulations, and some positions may require U.S. citizenship or the ability to obtain a security clearance.
Question 6: What are some of the emerging trends shaping the future of aerospace employment in California?
Several trends are poised to reshape the industry, including the rise of commercial space activities, the increasing adoption of additive manufacturing, the development of autonomous aircraft, and the growing emphasis on sustainable aviation technologies. These trends will create new opportunities for skilled professionals with expertise in these areas.
This FAQ section provides a foundation for understanding key aspects related to aerospace jobs in California. Individuals are encouraged to consult additional resources and seek personalized guidance to make informed career decisions.
The subsequent section will provide a listing of resources beneficial to career development within the field.
Aerospace Jobs in California
This exploration has detailed the multifaceted nature of aerospace jobs in california, highlighting key elements such as required education, specialized skills, geographic concentrations, and regulatory considerations. The examination of engineering design, manufacturing processes, research and development, testing and validation, regulatory compliance, and location clusters provides a comprehensive overview of the sector’s dynamics and demands.
The continued prominence of aerospace jobs in california is contingent on sustained investment in research, development, and education, coupled with a proactive approach to addressing evolving technological and regulatory landscapes. The future success of California’s aerospace sector necessitates a commitment to cultivating a highly skilled workforce capable of driving innovation and maintaining global competitiveness. Further research into emerging technologies and evolving workforce needs is essential for ensuring the long-term vitality of this critical industry.