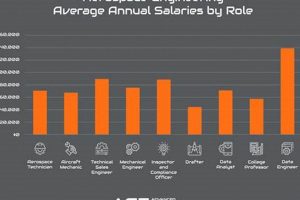
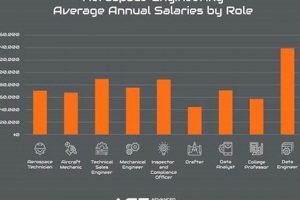
Positions in this field involve the design, development, testing, and production of aircraft, spacecraft, satellites, and missiles. These roles demand a strong foundation in mathematics, physics, and engineering principles. An example includes designing a new wing for a commercial airplane or developing propulsion systems for space exploration.
Opportunities in this sector are vital for advancements in air travel, national defense, and space exploration. Historically, these positions have driven innovation, leading to safer and more efficient air travel, improved communication satellites, and the expansion of our understanding of the universe. The ongoing need for skilled professionals ensures continued technological progress and economic growth.
The subsequent sections will delve into the specific responsibilities, necessary qualifications, prevalent industries, and the projected outlook for individuals pursuing a career in this dynamic engineering discipline.
Guidance for Securing Aerospace Engineering Roles
The following guidance provides valuable insights for individuals pursuing opportunities in aerospace engineering. Adhering to these points can significantly enhance one’s prospects in this competitive field.
Tip 1: Emphasize Technical Proficiency. Demonstrating expertise in relevant software such as CAD, MATLAB, and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is crucial. Specific project examples showcasing the application of these tools should be included in the application.
Tip 2: Cultivate Relevant Internship Experience. Prior experience within the aerospace industry, whether through internships or research positions, is highly valued. Focus on experiences directly related to the specific role being pursued.
Tip 3: Highlight Problem-Solving Skills. Employers seek individuals capable of addressing complex engineering challenges. Illustrate problem-solving abilities through concrete examples where innovative solutions were implemented.
Tip 4: Showcase Strong Communication Abilities. Effective communication is paramount for collaborating within engineering teams. Demonstrating clear and concise technical writing and presentation skills can greatly improve candidacy.
Tip 5: Obtain Advanced Certifications. Pursuing certifications relevant to specific areas within aerospace engineering, such as FAA certifications for aircraft maintenance, demonstrates commitment and specialized knowledge.
Tip 6: Tailor Resume to Specific Job Description. Modify the resume to explicitly address the requirements and responsibilities outlined in the specific job posting. Use keywords from the description throughout the resume and cover letter.
Tip 7: Network within the Aerospace Industry. Attend industry conferences and career fairs to connect with professionals and learn about potential openings. Building relationships can often lead to unadvertised opportunities.
Successfully implementing these strategies necessitates a proactive approach and a commitment to continuous learning and professional development. The benefits include increased competitiveness in the employment market and a greater likelihood of securing a desirable position.
The subsequent section will offer insight into the common pitfalls to avoid during the job search process, and how to avoid them.
1. Design Expertise
Design expertise forms a fundamental component of roles in the aerospace engineering field. The efficacy of any aircraft, spacecraft, or related system directly correlates with the quality and innovation embedded in its design. Therefore, professionals in these positions are expected to possess a deep understanding of aerodynamic principles, material science, structural analysis, and control systems, enabling them to conceive and refine designs that meet stringent performance, safety, and regulatory requirements. For example, designing the wing of a new commercial aircraft necessitates expertise in optimizing lift and minimizing drag while ensuring structural integrity under varying flight conditions. Inadequate design expertise can result in compromised performance, increased operational costs, and, in extreme cases, catastrophic failures.
The practical application of design expertise extends beyond initial conceptualization to encompass detailed modeling, simulation, and testing. Advanced tools like CAD software and finite element analysis (FEA) are employed to virtually prototype designs, assess their performance characteristics, and identify potential weaknesses. A real-world instance of this is the development of heat shields for spacecraft re-entering the Earth’s atmosphere. The design must withstand extreme temperatures and aerodynamic forces, requiring sophisticated modeling and rigorous testing to ensure successful operation. Furthermore, modifications and improvements to existing designs are a frequent aspect of the role, demanding adaptability and a continuous pursuit of optimization.
In summary, design expertise is an indispensable attribute for individuals pursuing careers in aerospace engineering. Its effective application directly influences the safety, efficiency, and performance of aerospace systems. The ongoing pursuit of innovation and the continuous refinement of design methodologies are essential to addressing the ever-evolving challenges within this field, and improving our industry.
2. Problem-Solving Skills
Problem-solving skills constitute a cornerstone competency for professionals in aerospace engineering. The complex nature of designing, developing, and maintaining aerospace systems necessitates the ability to identify, analyze, and resolve multifaceted challenges effectively. A robust problem-solving approach ensures system reliability, performance optimization, and adherence to stringent safety standards.
- System-Level Troubleshooting
System-level troubleshooting involves diagnosing and rectifying issues within integrated aerospace systems. An example is identifying the cause of intermittent sensor failures in a satellite. This requires a systematic approach to isolate the faulty component, which may involve analyzing telemetry data, reviewing system schematics, and conducting diagnostic tests. The implications extend to maintaining satellite functionality and preventing service disruptions.
- Design Optimization and Trade-offs
Design optimization and trade-offs are intrinsic to the engineering process, requiring professionals to balance competing design parameters. For example, increasing the fuel efficiency of an aircraft might necessitate compromises in payload capacity. This requires engineers to evaluate various design options, analyze performance metrics, and determine the optimal configuration that meets mission requirements while adhering to regulatory constraints. The ultimate impact is improving the overall performance and cost-effectiveness of the aircraft.
- Failure Analysis and Prevention
Failure analysis and prevention involve investigating the root causes of component failures or system malfunctions and implementing measures to prevent recurrence. A case in point is analyzing the failure of a turbine blade in a jet engine. This entails metallurgical analysis, stress testing, and computational modeling to understand the failure mechanism. Corrective actions might involve redesigning the blade, modifying operating parameters, or implementing enhanced inspection protocols. The result is enhanced engine reliability and reduced risk of in-flight failures.
- Algorithm Development for Autonomous Systems
Algorithm development for autonomous systems necessitates creating sophisticated algorithms that enable unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or spacecraft to perform complex tasks autonomously. An example is developing an algorithm for a UAV to autonomously navigate a predefined route while avoiding obstacles. This involves integrating sensor data, implementing path-planning algorithms, and incorporating real-time decision-making capabilities. The implications span diverse applications, including surveillance, reconnaissance, and delivery services.
The aforementioned facets of problem-solving underscore their integral role in aerospace engineering. From troubleshooting complex systems to optimizing designs and developing autonomous capabilities, the ability to effectively solve problems is critical for advancing the field and ensuring the safety and reliability of aerospace technologies. These skills are vital for the success of individuals working in this technical area.
3. Software Proficiency
Software proficiency is a non-negotiable requirement for success in positions within the aerospace engineering sector. The complexities of modern aerospace systems necessitate the utilization of specialized software tools for design, analysis, simulation, and testing. A strong command of these tools directly impacts an engineer’s ability to contribute effectively to the entire lifecycle of aerospace projects.
- CAD (Computer-Aided Design) Software
CAD software is fundamental for creating detailed 2D and 3D models of aerospace components and systems. For instance, aerospace engineers use CAD to design the fuselage of an aircraft, precisely defining its shape, dimensions, and structural elements. These models serve as the basis for manufacturing processes and further analyses. Lack of proficiency in CAD limits an engineer’s capacity to visualize and translate design concepts into tangible forms, impeding the design process.
- CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering) Software
CAE software is used to simulate and analyze the behavior of aerospace structures and systems under various operating conditions. Finite element analysis (FEA) software, a subset of CAE, is employed to assess the structural integrity of an aircraft wing subjected to aerodynamic loads. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) software is utilized to simulate airflow around an aircraft to optimize its aerodynamic performance. Without CAE skills, it’s difficult to predict the behavior of designs before creating physical models.
- MATLAB and Simulink
MATLAB and Simulink are essential for modeling and simulating dynamic systems, developing control algorithms, and analyzing data in the aerospace domain. For example, these tools are used to model the flight dynamics of a spacecraft during atmospheric entry, enabling the design of control systems that ensure stable and controlled descent. Inability to use these tools hinders the development of advanced control and navigation systems.
- Programming Languages (e.g., Python, C++)
Proficiency in programming languages like Python and C++ is increasingly important for tasks such as data analysis, automation, and developing custom software tools. Engineers might use Python to analyze large datasets of flight test data or C++ to develop embedded software for avionics systems. A lack of programming skills limits an engineer’s ability to process data and build the tools needed to handle specific needs that aren’t handled by off-the-shelf software.
These examples demonstrate that software proficiency is not merely a desirable skill but a core competency for aerospace engineers. Mastery of these tools empowers engineers to design innovative solutions, analyze complex systems, and contribute to the advancement of aerospace technology, thus improving outcomes and results.
4. Industry Experience
Within the realm of aerospace engineering, direct exposure to real-world projects, environments, and challenges distinguishes theoretical knowledge from practical application. “Industry Experience” serves as a critical differentiator for candidates, and contributes substantially to an engineer’s effectiveness and adaptability.
- Application of Theoretical Knowledge
Academic training provides the foundational principles of engineering, but “Industry Experience” allows for the application of this knowledge to tangible problems. An engineer may learn about aerodynamics in a classroom, but practical experience in a wind tunnel refines understanding through the observation and analysis of real-world airflow phenomena. The implications extend to improved design decisions and a more intuitive grasp of engineering trade-offs. This also ensures more effective and less costly outcomes.
- Exposure to Industry Standards and Practices
Aerospace engineering operates under a strict regulatory framework and adheres to industry-specific standards. Direct involvement in projects provides familiarity with these protocols, including design standards, safety regulations, and quality assurance procedures. For example, working on aircraft certification projects provides hands-on experience with FAA regulations, ensuring compliance and mitigating risks. This adherence is critical to ensuring the project’s success.
- Development of Practical Skills and Techniques
“Industry Experience” fosters the development of practical skills that are often absent in academic settings. This includes hands-on experience with manufacturing processes, testing methodologies, and troubleshooting techniques. An engineer might gain experience with composite material fabrication, non-destructive testing, or systems integration, enhancing their problem-solving abilities and adaptability to real-world challenges, and improving the industry as a whole.
- Networking and Collaboration Opportunities
Working within the aerospace industry provides opportunities to build professional networks and collaborate with experienced engineers, scientists, and technicians. These interactions facilitate knowledge transfer, mentorship, and access to industry insights. Participation in collaborative projects, such as developing a new propulsion system, exposes engineers to diverse perspectives and skill sets, promoting innovation and fostering long-term career development. This also allows for future opportunities to occur.
In summation, “Industry Experience” transcends the boundaries of academic learning, serving as a catalyst for skill enhancement, knowledge consolidation, and professional growth. Its contribution to practical application, regulatory compliance, hands-on skills, and networking opportunities solidifies its indispensable role in shaping well-rounded and effective aerospace engineers.
5. Communication Abilities
Effective conveyance of information represents a critical competency for professionals in aerospace engineering. The success of complex projects hinges on the ability of engineers to articulate ideas, share technical data, and collaborate effectively with diverse teams. Deficiencies in this area can impede progress, introduce errors, and compromise project outcomes.
- Technical Documentation and Reporting
The preparation of comprehensive and accurate technical documentation forms a cornerstone of aerospace engineering. This encompasses design specifications, test reports, and maintenance manuals. For instance, engineers are tasked with creating detailed documentation outlining the design and performance characteristics of a new aircraft wing. Clear and concise writing is essential to ensure that colleagues, regulatory agencies, and end-users understand the information. The implications of inadequate documentation can range from misinterpretations to safety hazards, ultimately affecting the performance of the aircraft and the safety of its operators.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Aerospace projects involve collaboration across multiple disciplines, including aerodynamics, propulsion, materials science, and avionics. Effective communication is vital to ensure that each team member understands the goals, constraints, and dependencies of their respective areas. For example, when designing a satellite, engineers from different specialties must effectively communicate their requirements and constraints to optimize the overall system design. Failure to do so can result in misaligned objectives, conflicting designs, and system-level inefficiencies. As a result, the performance is affected.
- Presentations and Demonstrations
The ability to present technical information clearly and persuasively is crucial for conveying project progress, justifying design decisions, and securing funding. Engineers may be required to present their work to stakeholders, including management, customers, and regulatory bodies. For instance, an engineer might present the results of a wind tunnel test to demonstrate the aerodynamic performance of a new aircraft design. Effective presentation skills can influence stakeholders’ perceptions and decisions, shaping the course of the project and organization as a whole.
- Cross-Functional Communication
Engineers often serve as intermediaries between technical teams and non-technical stakeholders, such as marketing, sales, and management. Clear and concise communication is essential to bridge the gap between technical jargon and business objectives. For example, an engineer might need to explain the technical challenges of developing a new engine to a marketing team, enabling them to accurately communicate the product’s features and benefits to potential customers. Failure to communicate effectively can lead to misunderstandings, misaligned expectations, and ultimately, a compromised product launch. Ineffective cross-functional communication will lead to a product launch disaster.
In essence, effective communication skills are indispensable for aerospace engineers, enabling them to disseminate information, collaborate effectively, and influence decision-making. The ability to communicate clearly and concisely is not merely a soft skill but a core competency that significantly impacts project outcomes and professional success in this demanding field. Without these skills, the project is surely to fail.
6. Continuous Learning
The dynamic nature of aerospace engineering necessitates “Continuous Learning” as an integral component of related positions. The rapid pace of technological advancements in materials science, propulsion systems, avionics, and software development demands ongoing professional development. A failure to engage in “Continuous Learning” renders skills obsolete, limiting an engineer’s capacity to contribute effectively and adapt to evolving industry demands. For instance, an aerospace engineer who hasn’t updated their knowledge of composite materials may be ill-equipped to design components for modern aircraft, where weight reduction and enhanced performance are paramount. Consequently, career progression and the ability to innovate are hampered by a lack of current knowledge.
The benefits of “Continuous Learning” manifest in numerous practical applications. Engineers who actively pursue professional development are better positioned to implement new technologies, optimize existing designs, and solve complex engineering problems. For example, an engineer who completes a course on advanced computational fluid dynamics (CFD) can apply this knowledge to improve the aerodynamic efficiency of an aircraft wing, leading to reduced fuel consumption and enhanced performance. Furthermore, “Continuous Learning” ensures compliance with evolving regulatory standards and safety protocols, mitigating risks and enhancing the reliability of aerospace systems. Staying abreast of the latest FAA regulations regarding unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) is critical for engineers designing and operating these systems, ensuring legal compliance and safe operation.
In summary, “Continuous Learning” is not merely an optional pursuit but a fundamental requirement for aerospace engineers seeking to remain competitive and contribute meaningfully to the industry. Embracing ongoing education and professional development enables engineers to adapt to technological advancements, optimize designs, ensure compliance, and ultimately drive innovation in the aerospace sector. Challenges exist in allocating time and resources for “Continuous Learning,” but the long-term benefits far outweigh the short-term constraints. A commitment to “Continuous Learning” is an investment in both individual career success and the advancement of the aerospace industry as a whole.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Aerospace Engineering Positions
The following section addresses common inquiries and misconceptions pertaining to roles in the aerospace engineering field. Information presented is intended to provide clarity and guidance for prospective and current professionals.
Question 1: What are the primary responsibilities associated with positions in this field?
Primary responsibilities encompass the design, development, testing, and production of aircraft, spacecraft, satellites, and missiles. Roles may also involve research, project management, and systems integration.
Question 2: What educational qualifications are typically required?
A bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering or a closely related field is generally the minimum requirement. Advanced degrees, such as a Master’s or Ph.D., may be necessary for specialized roles or research positions.
Question 3: What technical skills are most valuable for prospective candidates?
Proficiency in CAD software, computational fluid dynamics (CFD), finite element analysis (FEA), MATLAB, and programming languages (e.g., Python, C++) are highly valued. Knowledge of aerospace materials, aerodynamics, and control systems is also essential.
Question 4: What industries commonly employ professionals in this field?
Common employers include aerospace manufacturers (e.g., Boeing, Airbus), government agencies (e.g., NASA, Department of Defense), research institutions, and private space exploration companies (e.g., SpaceX, Blue Origin).
Question 5: How can I increase my chances of securing a position in aerospace engineering?
Relevant internship experience, strong academic performance, demonstrable problem-solving skills, and active participation in engineering projects are crucial. Networking with industry professionals and obtaining relevant certifications can also enhance candidacy.
Question 6: What is the projected job outlook for aerospace engineers?
The job outlook is projected to grow, driven by increasing demand for air travel, advancements in space exploration, and ongoing national defense initiatives. Specific growth rates may vary depending on economic conditions and technological developments.
This FAQ section aims to provide a foundational understanding of key aspects pertaining to careers in aerospace engineering. For more detailed information, consult professional organizations and industry publications.
The subsequent segment will explore strategies for crafting a compelling resume and cover letter to secure opportunities in this competitive field.
Aerospace Engineer Jobs
This exploration has illuminated the multifaceted nature of aerospace engineer jobs, emphasizing the critical skills, qualifications, and industry knowledge necessary for success. The demanding yet rewarding character of these positions, spanning design, analysis, and innovation, has been consistently underscored.
As technological horizons continue to expand, the need for skilled professionals in these roles will remain paramount. Individuals aspiring to contribute to advancements in air travel, space exploration, and national security are encouraged to pursue rigorous training, cultivate expertise, and embrace the challenges inherent in this vital field, ensuring continued progress in aerospace technology.