Positions within the aeronautics and astronautics sectors located in the Texas capital present opportunities for engineers, technicians, and administrative personnel. These roles encompass design, manufacturing, testing, and maintenance of aircraft, spacecraft, and related systems. For example, a mechanical engineer might design components for a satellite, while a technician could assemble wiring harnesses for an aircraft.
The availability of these specialized employment options contributes to the city’s economic diversification and technological advancement. Historically, the region’s concentration of technology companies and research institutions has fostered the growth of this industry, attracting skilled labor and investment. The benefits include high-paying jobs, stimulating innovation, and strengthening the region’s position in a globally competitive market.
The following sections will provide further details regarding specific companies in this field, required qualifications for various positions, and resources for job seekers. Information about the projected growth of the industry within the region will also be addressed, offering a comprehensive overview for those interested in pursuing a career.
The pursuit of opportunities within the Austin aeronautics and astronautics sector requires strategic planning and a focused approach. The following tips provide guidance for prospective candidates.
Tip 1: Targeted Skill Development: Focus on acquiring skills highly valued by aerospace employers. Examples include proficiency in CAD software, knowledge of materials science, and experience with aerospace-specific manufacturing processes. Certifications and advanced coursework can enhance candidacy.
Tip 2: Networking within the Industry: Attend industry conferences, seminars, and workshops to establish connections with professionals. Engage with relevant professional organizations. Networking can provide insights into unadvertised positions and facilitate referrals.
Tip 3: Tailoring Application Materials: Customize resumes and cover letters to align with specific job requirements. Highlight relevant experience and skills. Emphasize accomplishments and quantifiable results from previous roles.
Tip 4: Researching Target Companies: Thoroughly investigate potential employers’ missions, values, and ongoing projects. Understand the company’s role within the aeronautics and astronautics landscape. This knowledge demonstrates genuine interest and informs interview responses.
Tip 5: Preparing for Technical Interviews: Anticipate technical questions related to aerospace engineering principles, problem-solving methodologies, and specific technologies. Practice articulating technical concepts clearly and concisely. Be prepared to discuss relevant projects and experiences in detail.
Tip 6: Utilizing Online Job Boards: Actively monitor industry-specific job boards and company websites for open positions. Set up job alerts to receive notifications of new opportunities. Regularly update online profiles to increase visibility to recruiters.
Tip 7: Seeking Mentorship: Connect with experienced professionals in the aeronautics and astronautics sector for guidance and advice. A mentor can provide valuable insights into career paths, industry trends, and professional development opportunities.
Implementing these strategies can significantly improve the likelihood of securing a position in the dynamic field of aeronautics and astronautics within the Austin region.
The subsequent sections will delve deeper into specific companies and available roles, further enhancing the preparedness of interested candidates.
1. Engineering Design
Engineering design serves as a cornerstone of opportunities in the Austin aerospace sector. Its influence permeates various facets of these specialized positions, directly affecting project outcomes and overall operational success. These roles necessitate the application of scientific principles to innovate, develop, and refine aerospace systems. A real-world example involves engineers designing more efficient turbine blades for aircraft engines, increasing fuel economy and reducing emissions. This showcases how design directly translates to tangible improvements in operational efficiency and environmental sustainability within the industry.
The integration of advanced software tools, such as CAD and FEA, is essential for the precision required in engineering design. Engineers leverage these tools to simulate performance, optimize designs, and ensure structural integrity. Consider the design of a satellite’s solar panel deployment mechanism, a project demanding meticulous attention to detail and rigorous simulation to guarantee successful operation in orbit. Moreover, the design phase heavily influences subsequent stages, including manufacturing and testing, therefore impacting project timelines and budgets.
In summation, proficiency in engineering design principles is not merely advantageous but rather a fundamental prerequisite for many positions in the Austin aerospace landscape. The ability to conceptualize, analyze, and execute designs that meet stringent performance and safety standards is critical. Continued advancements in materials science and computational methods present ongoing challenges, demanding that engineers continually upgrade their skills and knowledge base to maintain competitiveness in this evolving field.
2. Systems Integration
Systems integration forms a critical nexus within the Austin aerospace sector, directly influencing the functionality and efficacy of complex aerospace systems. Its significance stems from the need to consolidate disparate components and subsystems into a cohesive, operational whole. Successful systems integration is paramount for achieving optimal performance and reliability in aerospace applications.
- Component Compatibility
Ensuring compatibility between diverse hardware and software components represents a fundamental aspect of systems integration. This requires meticulous planning and testing to prevent conflicts and ensure seamless interoperability. For instance, integrating a new sensor suite into an existing flight control system necessitates rigorous verification to guarantee accurate data transmission and processing. Improper component compatibility can lead to system failures and compromised safety.
- Data Management
Efficient data management is vital in systems integration, particularly given the vast amounts of data generated by aerospace systems. This includes data acquisition, storage, processing, and distribution. An example includes integrating weather data, flight telemetry, and radar information into a pilot’s display to enhance situational awareness. Effective data management ensures timely and accurate information delivery for critical decision-making.
- Interface Standardization
Adherence to interface standards is crucial for facilitating seamless integration of different systems. Standardized interfaces enable different manufacturers and developers to create components that can be easily integrated without requiring extensive modifications. An illustration of this includes using standardized communication protocols to enable seamless data exchange between different avionics systems. Standardized interfaces foster interoperability and reduce integration complexity.
- Testing and Validation
Rigorous testing and validation are indispensable components of systems integration, ensuring that the integrated system performs as intended under various operating conditions. This involves conducting comprehensive simulations, laboratory tests, and flight tests to identify and resolve potential issues. For example, comprehensive testing of an integrated navigation system can verify its accuracy and reliability in diverse environments. Thorough testing and validation are crucial for mitigating risks and ensuring mission success.
In summary, systems integration plays an indispensable role in the Austin aerospace industry. Successful integration efforts, characterized by component compatibility, efficient data management, interface standardization, and rigorous testing, are vital for ensuring the performance, reliability, and safety of aerospace systems. The demand for skilled systems integration professionals will likely increase as aerospace technology continues to evolve.
3. Manufacturing Processes
Manufacturing processes constitute a fundamental pillar within the Austin aerospace sector, directly influencing the availability, nature, and quality of associated employment opportunities. The intricacies of these processes demand specialized skills and knowledge, creating a diverse range of job roles essential to the industry’s operations.
- Precision Machining
Precision machining involves the use of advanced equipment to create aerospace components with exacting tolerances. This facet includes roles such as CNC machinists, who program and operate milling machines and lathes, ensuring parts meet stringent specifications. For example, manufacturing turbine blades for jet engines requires micron-level precision to guarantee optimal performance and fuel efficiency. The demand for skilled machinists in Austin’s aerospace industry is consistently high due to the critical nature of their work.
- Composites Fabrication
Composites fabrication focuses on the creation of lightweight, high-strength structures using materials such as carbon fiber and epoxy resins. This process includes hand layup, automated fiber placement, and resin transfer molding. Aerospace jobs in this area include composite technicians, who meticulously layer materials according to design specifications. The manufacture of aircraft fuselages and wing components relies heavily on composite materials to reduce weight and enhance structural integrity, driving the demand for skilled composite fabricators.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, employs layer-by-layer construction to create complex geometries and customized parts. This innovative process is increasingly utilized in the aerospace sector for rapid prototyping and the production of specialized components. Roles within this facet include 3D printing engineers and technicians, who operate and maintain 3D printing equipment, optimize printing parameters, and ensure the quality of printed parts. The ability to rapidly prototype and customize components through additive manufacturing opens up opportunities for innovation and efficiency gains, contributing to the growth of related jobs.
- Quality Control and Inspection
Quality control and inspection are indispensable elements of manufacturing processes, ensuring that aerospace components meet stringent quality standards and regulatory requirements. This facet involves the use of advanced inspection techniques, such as non-destructive testing (NDT) and coordinate measuring machines (CMM), to identify defects and verify dimensional accuracy. Aerospace jobs in this field include quality control inspectors and NDT technicians, who meticulously examine components to ensure compliance with specifications. The maintenance of high-quality standards is paramount in the aerospace industry, driving the need for skilled quality control personnel.
The interplay of these manufacturing processes directly influences the skill sets demanded in related Austin aerospace employment. Continued advancements in manufacturing technologies and materials science will likely shape future job roles and skill requirements within the sector. As the industry evolves, professionals with expertise in advanced manufacturing processes will remain highly sought after, contributing to the region’s competitive advantage in the global aerospace market.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance forms a non-negotiable element within Austin aerospace jobs, dictating the operational parameters and safety standards adhered to by all industry participants. Non-adherence carries significant legal and financial ramifications, impacting both individual professionals and employing organizations. This requirement stems from the highly regulated nature of the aerospace industry, where adherence to directives from agencies such as the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is paramount. For instance, an engineer designing aircraft components must ensure these parts conform to FAA airworthiness standards, incorporating validated materials and manufacturing processes. Failure to comply could result in grounding of aircraft and liability lawsuits.
The practical significance of understanding regulatory compliance is multifaceted. Aerospace engineers and technicians must remain current on evolving regulations, integrating updated standards into design, manufacturing, and maintenance procedures. A quality control inspector, for example, uses FAA-approved inspection methods to verify component integrity. Furthermore, projects necessitate comprehensive documentation, demonstrating adherence to applicable standards. The rigorous tracking and reporting of activities guarantee traceability and accountability throughout the product lifecycle. This meticulous approach reduces risks and strengthens public trust in the safety and reliability of air travel.
In summary, regulatory compliance is not merely an ancillary task within Austin aerospace positions but constitutes an intrinsic aspect of professional responsibility. The challenges of adhering to complex regulations necessitate continuous learning and adaptation. Embracing a compliance-focused mindset minimizes risks, fosters innovation, and reinforces the commitment to safety that characterizes the aerospace field. The industry’s ongoing evolution demands skilled professionals with a deep understanding of these requirements.
5. Research and Development
Research and development (R&D) represents a critical engine driving innovation and advancement within the Austin aerospace sector, shaping the landscape of available positions and their associated skill requirements. Investment in R&D is directly proportional to the creation of new opportunities and the enhancement of existing roles within the industry. This focus on innovation is essential for maintaining competitiveness and securing future growth.
- New Materials Development
The development of novel materials, such as advanced composites and alloys, directly impacts positions related to materials science, engineering, and manufacturing. These materials necessitate specialized testing, characterization, and processing techniques. For example, the development of self-healing polymers for aircraft structures requires engineers and technicians skilled in polymer chemistry, materials testing, and advanced manufacturing processes. Such advancements can lead to improved aircraft performance, reduced maintenance costs, and enhanced safety.
- Advanced Propulsion Systems
Research into advanced propulsion systems, including electric propulsion, hypersonic engines, and alternative fuels, generates opportunities for aerospace engineers, physicists, and chemists. These positions involve designing, modeling, and testing propulsion systems to achieve greater efficiency and performance. For instance, the development of scramjet engines for hypersonic flight requires expertise in thermodynamics, fluid dynamics, and combustion. Successful development of these systems has the potential to revolutionize air and space travel.
- Autonomous Systems and Robotics
The integration of autonomous systems and robotics into aerospace applications creates opportunities for software engineers, robotics specialists, and systems engineers. These roles involve developing algorithms, sensors, and control systems for autonomous aircraft, drones, and space vehicles. Consider the development of autonomous inspection drones for aircraft maintenance, requiring expertise in computer vision, machine learning, and robotics. The incorporation of autonomous systems can improve efficiency, reduce human error, and enable new mission capabilities.
- Space Exploration Technologies
R&D focused on space exploration technologies, such as advanced life support systems, propulsion technologies, and robotic explorers, generates positions for engineers, scientists, and technicians. These roles involve designing, building, and testing technologies for human and robotic space missions. An example includes developing advanced radiation shielding materials for spacecraft, requiring expertise in materials science, nuclear physics, and engineering. Innovations in space exploration technologies expand human reach and knowledge of the universe.
In conclusion, the dynamic relationship between research and development and Austin aerospace positions is characterized by continuous innovation and the demand for specialized skills. Investment in these areas remains crucial for driving technological advancement and creating high-value job opportunities within the region. The emphasis on novel materials, propulsion systems, autonomous systems, and space exploration technologies will continue to shape the future of the Austin aerospace sector.
6. Project Management
Effective project management is a critical function underpinning the success of endeavors within Austin aerospace jobs. Project managers in this sector are responsible for orchestrating complex initiatives from conception to completion, ensuring projects adhere to budgetary constraints, timelines, and stringent quality standards. The high-stakes nature of aerospace projects necessitates meticulous planning, resource allocation, and risk mitigation strategies. For instance, the development of a new satellite system involves coordinating teams of engineers, scientists, and technicians, each contributing specialized expertise. Without robust project management, these projects can easily exceed budgets, fall behind schedule, or fail to meet performance requirements, resulting in significant financial and reputational consequences.
The practical significance of adept project management manifests in various facets of aerospace operations. Consider the manufacturing of aircraft components, a process demanding precise coordination between design, engineering, and production teams. A project manager oversees this process, ensuring the timely delivery of materials, efficient allocation of labor, and adherence to strict quality control protocols. Moreover, effective communication is paramount in project management. Regular status updates, risk assessments, and stakeholder engagement are essential for maintaining project momentum and addressing potential challenges proactively. Software tools, such as project scheduling and collaboration platforms, often facilitate communication and streamline project workflows.
In summary, project management is an indispensable component of Austin aerospace jobs, contributing directly to the successful execution of complex engineering and manufacturing projects. The ability to plan, organize, and control project resources effectively is a highly valued skill in this sector. While the challenges inherent in managing aerospace projects are significant, the rewards of successful project completion are substantial, contributing to technological advancement and economic growth within the Austin region and beyond.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Austin Aerospace Positions
The following questions address common inquiries concerning employment opportunities within the aeronautics and astronautics sectors of the Austin metropolitan area.
Question 1: What types of skills are most in demand for these specialized positions?
Expertise in areas such as aerospace engineering, mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, software engineering, and materials science are frequently sought. Knowledge of CAD/CAM software, finite element analysis, and systems integration is also highly valued. Familiarity with industry-specific regulations and quality control standards is essential.
Question 2: Which companies are prominent employers in the region?
While specific details may fluctuate, several established companies and emerging startups maintain a presence in the Austin aerospace sector. These entities are involved in various facets of the industry, including aircraft component manufacturing, space technology development, and defense contracting. Specific company names are subject to change based on market dynamics.
Question 3: What educational background is typically required to enter this field?
A bachelor’s degree in a relevant engineering or scientific discipline is generally considered a minimum requirement. Advanced degrees, such as a Master’s or Ph.D., may be necessary for research-oriented positions or roles requiring specialized expertise. Certifications and professional licenses can also enhance career prospects.
Question 4: Are internship opportunities available for students interested in aerospace careers?
Internship programs represent a valuable pathway into the industry, providing students with practical experience and networking opportunities. Students should actively seek internships with aerospace companies in the Austin area, focusing on roles that align with their academic interests and career goals. These programs typically occur during summer breaks or academic semesters.
Question 5: How competitive is the job market for positions within this field?
The level of competition varies depending on the specific role and skill requirements. Highly specialized positions often attract a large number of qualified applicants, making it crucial for candidates to possess relevant experience and a strong academic record. Building a professional network and showcasing demonstrable skills can enhance a candidate’s competitiveness.
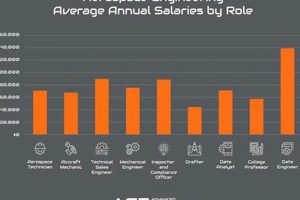
Question 6: What is the typical salary range for aerospace positions in the Austin area?
Salary ranges are contingent upon factors such as education, experience, job title, and employer. Entry-level positions typically offer lower salaries, while senior-level roles commanding specialized expertise will usually command higher compensation packages. Industry surveys and salary benchmarking tools can provide insights into prevailing compensation trends.
In summary, pursuing a career in the Austin aerospace sector requires a strong educational foundation, relevant skills, and a strategic approach to job searching. Proactive networking, continuous professional development, and a commitment to industry best practices are essential for success.
The subsequent section will explore resources available to individuals seeking to advance their careers in the Austin aerospace field.
Conclusion
This analysis has illuminated key facets of employment within the Austin aerospace sector, emphasizing necessary skills, prominent employers, educational prerequisites, and competitive dynamics. Understanding manufacturing processes, regulatory compliance, research & development, and project management provides critical insight for navigating this specialized field.
The sustained growth of Austin aerospace jobs relies on continued investment in technological advancement and a commitment to attracting and retaining skilled professionals. The future promises further opportunities for those equipped with the necessary expertise and dedication to this demanding, yet rewarding, industry.




![Is Aerospace Engineer Job Availability Rising? [2024 Trends] Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions Is Aerospace Engineer Job Availability Rising? [2024 Trends] | Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-520-300x200.jpg)

