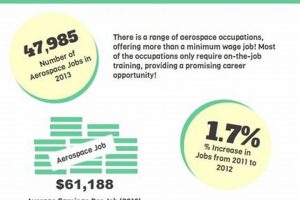
Opportunities in the design, manufacturing, and maintenance of aircraft and spacecraft components situated in south-central Kansas are a significant facet of the region’s economy. These positions encompass a broad spectrum of roles, from entry-level technician positions to highly specialized engineering and management roles, all located in the Air Capital of the world.
The presence of a strong aviation industry benefits the local economy through direct job creation, indirect support of related industries, and the attraction of skilled labor to the area. Historically, the region has been a central hub for aircraft production, leading to a well-established infrastructure and a deep talent pool. This concentration fosters innovation and provides a competitive advantage in the global aerospace market.
The subsequent discussion will delve into the specific types of available positions, the key employers driving this sector, the required qualifications for various roles, and the economic outlook for this vital industry within the local area.
The following guidance addresses key considerations for individuals seeking roles within the region’s aircraft manufacturing and related industries. Success requires a strategic approach.
Tip 1: Target Specific Companies: Research primary employers such as Textron Aviation (Cessna/Beechcraft), Spirit AeroSystems, and Bombardier. Understand their product lines, recent projects, and specific departmental needs. Tailor applications accordingly.
Tip 2: Emphasize Relevant Skills: Highlight experience in areas such as aircraft assembly, composite materials, avionics, quality control, engineering design (CAD/CAM), and FAA regulations. Quantify accomplishments whenever possible (e.g., “Reduced assembly time by 15%”).
Tip 3: Obtain Relevant Certifications: Acquire certifications such as A&P (Airframe and Powerplant) licenses, FAA repairman certificates, or specialized training in composite repair. These credentials demonstrate competence and increase employability.
Tip 4: Network Actively: Attend industry events, job fairs, and professional association meetings (e.g., Wichita Aero Club). Connect with individuals working in target companies and leverage informational interviews.
Tip 5: Utilize Online Resources: Monitor job boards specific to the aviation and aerospace sectors, such as Aviation Week, LinkedIn, and company career pages. Set up job alerts to receive notifications of new openings promptly.
Tip 6: Prepare for Technical Assessments: Expect technical interviews and skills-based assessments. Review fundamental concepts in aerodynamics, materials science, and manufacturing processes. Practice problem-solving exercises.
Tip 7: Demonstrate Commitment to Safety: Emphasize adherence to safety protocols and regulations. Highlight experience in implementing safety programs or conducting safety audits. A strong safety record is crucial in aviation.
Adhering to these recommendations can significantly improve an applicant’s prospects in a competitive hiring landscape. Preparation and a focused approach are paramount.
The subsequent sections will explore the long-term career paths available within these specialized industries.
1. Engineering design positions
Engineering design roles constitute a critical component of the aerospace sector in south-central Kansas. These positions are fundamental to the development, modification, and sustainment of aircraft and related systems, directly impacting the performance, safety, and efficiency of aerospace products manufactured and maintained within the region.
- Airframe Design and Analysis
This facet involves the conceptualization, design, and structural analysis of aircraft fuselages, wings, and control surfaces. Engineers in these roles utilize advanced software to model and simulate airframe behavior under various flight conditions, ensuring structural integrity and compliance with airworthiness regulations. A recent example includes the design of composite wing structures for enhanced fuel efficiency in next-generation aircraft.
- Systems Integration
Systems integration engineers are responsible for the seamless integration of various aircraft systems, including avionics, electrical, hydraulic, and propulsion systems. These professionals ensure that these systems function harmoniously to meet performance requirements and operational safety standards. This includes the integration of advanced flight control systems and sensor technologies.
- Propulsion Systems Design
This specialized area focuses on the design and analysis of aircraft propulsion systems, including jet engines, turboprops, and related components. Engineers in these roles work to optimize engine performance, reduce emissions, and improve fuel efficiency. This involves computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis and testing to validate design performance.
- Interior Design and Configuration
This area focuses on the design and layout of aircraft interiors, including passenger seating, cabin amenities, and emergency equipment. Considerations include passenger comfort, safety regulations, and weight optimization. Recent examples focus on modular cabin designs for increased flexibility and customization.
These diverse engineering design roles collectively drive innovation and maintain competitiveness within the aerospace landscape of south-central Kansas. The demand for skilled engineers in these areas remains robust, directly influencing the economic vitality of the region and solidifying its position as a key center for aircraft design and manufacturing.
2. Manufacturing technician openings
Manufacturing technician roles are a cornerstone of the aerospace industry in south-central Kansas, representing a significant proportion of the available positions. These openings are directly linked to the region’s historical strength in aircraft production and ongoing manufacturing activities. The presence of major aerospace companies, such as Textron Aviation and Spirit AeroSystems, necessitates a substantial workforce of skilled technicians for assembling, testing, and maintaining aircraft components and systems. The demand for these technicians is a direct consequence of the volume of aircraft production and maintenance carried out in the area.
The importance of manufacturing technicians lies in their direct involvement in the physical creation and upkeep of aircraft. They are responsible for interpreting blueprints, using precision tools, and adhering to strict quality control standards. A real-life example can be found in the assembly lines at Spirit AeroSystems, where technicians meticulously assemble fuselage sections for commercial airliners. The precision and attention to detail required in these roles are critical for ensuring the safety and airworthiness of the final product. Furthermore, as new materials and manufacturing techniques are introduced, technicians must continually adapt their skills through ongoing training programs.
In conclusion, manufacturing technician openings are an integral and vital part of the aerospace job landscape in south-central Kansas. Their presence reflects the region’s continued prominence in aircraft manufacturing. Understanding the role and its connection to the broader industry provides valuable insight for both job seekers and those analyzing the economic health of the region. However, challenges remain in attracting and retaining skilled technicians, requiring ongoing investment in training and competitive compensation packages to sustain this critical sector of the economy.
3. Quality control inspectors
The role of quality control inspectors is fundamentally intertwined with the aerospace sector in south-central Kansas. These inspectors are essential components in ensuring aircraft safety and regulatory compliance. The region’s significant concentration of aerospace manufacturing activity directly results in a substantial demand for skilled quality control personnel. The presence of firms like Textron and Spirit AeroSystems necessitates rigorous inspection processes at every stage of production, from raw materials to finished aircraft. The efficacy of these inspections directly impacts the airworthiness of products leaving these facilities.
Quality control inspectors meticulously examine components, assemblies, and finished products against engineering drawings, specifications, and regulatory standards (e.g., FAA regulations). They employ various inspection techniques, including visual inspection, dimensional measurement, non-destructive testing (NDT), and functional testing. As a practical example, inspectors at Spirit AeroSystems use ultrasonic testing to detect subsurface flaws in composite materials used in aircraft fuselages. Any deviation from established standards triggers a corrective action process, which can range from rework to rejection of the affected parts. The ability to identify and rectify defects early in the manufacturing process is crucial for minimizing downstream costs and ensuring product reliability.
In summary, the presence of numerous quality control inspector positions within the aerospace industry in south-central Kansas underscores the region’s commitment to aircraft safety and manufacturing excellence. These roles act as a critical safeguard, preventing defective products from reaching the market and ensuring the continued integrity of the aircraft produced and maintained in the area. Challenges for the future involve adapting inspection techniques to evolving manufacturing processes, such as additive manufacturing, and maintaining a highly skilled workforce capable of performing complex inspections.
4. Supply chain management
Effective supply chain management is a critical element underpinning the success and efficiency of the aerospace industry in south-central Kansas. Given the intricate nature of aircraft manufacturing, involving thousands of components and specialized materials, a well-optimized supply chain is essential for timely production and cost control.
- Material Sourcing and Procurement
This facet encompasses the identification, selection, and acquisition of raw materials, components, and sub-assemblies required for aircraft manufacturing. Supply chain professionals in this area are responsible for negotiating contracts, managing supplier relationships, and ensuring that materials meet stringent quality standards. For instance, the sourcing of specialized aluminum alloys for aircraft fuselages requires meticulous supplier qualification and adherence to material certifications. The efficient procurement process directly affects production timelines and material costs.
- Logistics and Transportation
The movement of materials and components from suppliers to manufacturing facilities constitutes a critical aspect of supply chain management. This involves optimizing transportation routes, coordinating deliveries, and managing inventory levels to minimize storage costs and prevent production delays. As an example, the transport of large aircraft components, such as wings or fuselage sections, requires specialized handling and transportation infrastructure. Logistical inefficiencies can significantly disrupt production schedules and increase overall costs.
- Inventory Management
Effective inventory management is essential for balancing the need to have materials readily available for production with the desire to minimize storage costs and prevent obsolescence. This involves forecasting demand, implementing inventory control systems, and managing warehouse operations. For example, the management of specialized fasteners and electronic components requires precise tracking and storage to prevent damage or degradation. Poor inventory management can lead to material shortages or excessive inventory carrying costs.
- Supplier Relationship Management
Building and maintaining strong relationships with suppliers is critical for ensuring the reliability and responsiveness of the supply chain. This involves regular communication, performance monitoring, and collaborative problem-solving. For example, aerospace companies in the region work closely with their suppliers to implement continuous improvement initiatives and address quality issues. Effective supplier relationship management is essential for mitigating supply chain risks and ensuring the timely delivery of high-quality components.
These facets of supply chain management are inextricably linked to the viability of aerospace manufacturing. The positions within this field are crucial for maintaining the competitive edge of the industry in south-central Kansas. Disruptions in any of these areas can have cascading effects, underscoring the importance of skilled professionals managing these complex systems.
5. Avionics installation/repair
The maintenance, upgrade, and integration of electronic systems within aircraft constitute a substantial segment of the aerospace sector. South-central Kansas, with its deep roots in aircraft manufacturing and maintenance, provides numerous opportunities in this specialized field. The demand for skilled avionics technicians and engineers is directly tied to the regions legacy as a center for aircraft production and its continued prominence in aircraft maintenance and modification.
- Installation of New Avionics Systems
This facet involves the physical installation and integration of new avionics equipment, such as navigation systems, communication systems, and flight control systems, into both new and existing aircraft. Technicians and engineers must possess a thorough understanding of aircraft electrical systems, wiring diagrams, and installation procedures. As an example, retrofitting a legacy aircraft with a modern glass cockpit requires careful planning, wiring, and testing to ensure compatibility and functionality. The successful installation of new avionics enhances aircraft capabilities and extends operational lifespan.
- Repair and Maintenance of Existing Avionics
The ongoing maintenance and repair of existing avionics systems are critical for ensuring aircraft safety and reliability. This includes troubleshooting malfunctions, replacing faulty components, and performing routine inspections and calibrations. A common task is diagnosing and repairing issues with aircraft radar systems or autopilot systems. Effective repair and maintenance minimize downtime and ensure that aircraft operate safely and efficiently.
- Avionics Upgrades and Modifications
This area encompasses the upgrade or modification of existing avionics systems to improve performance, enhance functionality, or comply with regulatory requirements. This might involve replacing older equipment with newer, more advanced models or modifying existing systems to meet specific operational needs. For instance, upgrading an aircraft’s navigation system to comply with new air traffic control mandates requires specialized knowledge and skills. These upgrades keep aircraft current with evolving technological standards.
- Certification and Compliance
Avionics installation and repair activities must adhere to stringent regulatory requirements set forth by aviation authorities such as the FAA. This involves documenting all work performed, ensuring that equipment meets specified performance standards, and obtaining the necessary certifications and approvals. Technicians and engineers must be familiar with relevant regulations and procedures to ensure compliance. Proper certification is essential for maintaining the airworthiness of aircraft and ensuring legal compliance.
The activities described above directly relate to the availability of specialized aircraft-related occupations in the region. A skilled workforce specializing in avionics provides a tangible benefit, reinforcing the appeal of south-central Kansas to businesses and individuals engaged in the aerospace industry.
6. Program management roles
Program management roles within the aerospace sector in south-central Kansas are instrumental in orchestrating complex projects, ensuring that they are completed on time, within budget, and to the required specifications. These positions are inextricably linked to the region’s aerospace industry, driving efficiency and innovation across various facets of aircraft design, manufacturing, and maintenance.
- New Product Introduction
Program managers oversee the entire process of bringing new aircraft or aerospace components to market. This involves coordinating engineering, manufacturing, marketing, and sales efforts to ensure a successful product launch. For instance, when Textron Aviation introduces a new aircraft model, a program manager is responsible for guiding the project from initial design through certification and entry into service. The successful execution of new product introductions is critical for maintaining competitiveness and driving revenue growth within the local aerospace economy.
- Major Modification and Upgrade Programs
These roles involve managing large-scale modifications or upgrades to existing aircraft. This might include retrofitting aircraft with new avionics, enhancing cabin interiors, or implementing structural modifications. Program managers coordinate engineering design, procurement, and installation activities to ensure that the modifications are completed to customer specifications and regulatory requirements. An example would be a program to upgrade the avionics systems of a fleet of regional jets, requiring careful coordination of engineering changes, parts procurement, and installation work to minimize aircraft downtime.
- Supply Chain Optimization Programs
Program managers are often tasked with leading initiatives to optimize the aerospace supply chain, reducing costs, improving efficiency, and enhancing responsiveness. This involves working with suppliers, logistics providers, and internal stakeholders to streamline processes and implement best practices. An illustration would be a program to consolidate the number of suppliers for a particular component, negotiating better pricing, and improving delivery performance. Effective supply chain management is essential for maintaining a competitive cost structure and ensuring the timely availability of materials for aircraft production.
- Research and Development (R&D) Project Management
Program managers play a crucial role in overseeing research and development projects aimed at developing new aerospace technologies and capabilities. This involves coordinating the efforts of scientists, engineers, and technicians to conduct research, develop prototypes, and test new concepts. For example, a program manager might lead a project to develop a new type of composite material for aircraft structures, requiring coordination of research activities, material testing, and manufacturing process development. Successful R&D projects can lead to breakthroughs that give the region’s aerospace industry a competitive advantage.
In summary, program management roles within the aerospace sector in south-central Kansas are diverse and critical to the industry’s success. These roles require strong leadership, communication, and problem-solving skills, and they provide opportunities to make a significant impact on the design, manufacture, and maintenance of aircraft and aerospace systems. Effective program management is essential for maintaining the region’s position as a leading center for aerospace activity, enabling it to compete effectively in the global marketplace.
7. Regulatory compliance specialists
Regulatory compliance specialists are vital to the aerospace industry, particularly in a hub like south-central Kansas, where aircraft design, manufacturing, and maintenance activities are concentrated. These specialists ensure that companies adhere to the complex web of regulations governing the aerospace sector, impacting nearly every aspect of operations.
- FAA Compliance Management
Compliance with Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) regulations is paramount. Specialists in this area interpret and implement FAA directives related to aircraft design, production, and maintenance. For example, they ensure that aircraft modifications are conducted in accordance with Supplemental Type Certificates (STCs), documenting the process and ensuring adherence to safety standards. Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines, production shutdowns, or even revocation of operating licenses, making FAA compliance a core function.
- Environmental Regulations Adherence
Aerospace operations are increasingly subject to environmental regulations concerning emissions, waste disposal, and noise pollution. Regulatory compliance specialists monitor and manage these aspects, ensuring companies meet requirements set by agencies like the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). A real-world scenario involves managing the disposal of hazardous materials used in aircraft manufacturing, such as solvents and paints, in accordance with EPA guidelines. Failure to comply can result in significant financial penalties and reputational damage.
- Export Control Compliance
The export of aircraft, components, and related technology is subject to strict export control regulations, such as the International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) and the Export Administration Regulations (EAR). Compliance specialists ensure that companies adhere to these regulations when exporting products or technology. This includes obtaining necessary licenses, screening transactions, and implementing security measures to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information. Violations can lead to severe penalties, including criminal charges and debarment from exporting.
- Safety Management Systems (SMS) Implementation
Regulatory bodies increasingly require aerospace companies to implement formal Safety Management Systems (SMS) to proactively identify and mitigate safety risks. Compliance specialists play a key role in developing, implementing, and maintaining these systems. This involves conducting risk assessments, establishing safety policies and procedures, and monitoring safety performance. SMS implementation is a continuous process aimed at improving safety culture and reducing the likelihood of accidents and incidents. For instance, a compliance specialist might lead a team in identifying potential hazards associated with a particular aircraft maintenance procedure and implementing controls to mitigate those hazards.
The demand for regulatory compliance specialists within the aerospace industry in south-central Kansas reflects the sector’s commitment to safety, quality, and ethical conduct. These roles are critical for mitigating risks, ensuring legal compliance, and maintaining the industry’s reputation for excellence. Understanding the connection between regulatory mandates and operational practices is paramount for sustained success in this field.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding employment prospects within the aerospace sector in south-central Kansas.
Question 1: What types of aerospace companies are located in Wichita, Kansas?
Wichita hosts a range of aerospace firms, including those involved in aircraft manufacturing (e.g., Textron Aviation, Cessna, Beechcraft), aerostructures (e.g., Spirit AeroSystems), and specialized services such as aircraft maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) operations. Smaller companies specializing in avionics, tooling, and engineering services are also present.
Question 2: What qualifications are typically required for aerospace positions in Wichita?
Required qualifications vary significantly based on the specific role. Engineering positions often necessitate a bachelor’s or master’s degree in aerospace, mechanical, electrical, or a related field. Manufacturing technician roles may require an associate’s degree or vocational training, along with relevant certifications such as A&P licenses. Quality control positions typically demand experience in inspection techniques and familiarity with aerospace standards. Program management roles often require a bachelor’s degree in business or engineering, along with project management certifications.
Question 3: What is the job market outlook for aerospace professionals in Wichita?
The job market outlook for aerospace professionals in Wichita is generally positive, driven by ongoing aircraft production, maintenance activities, and technological advancements. However, fluctuations in the global economy and aircraft demand can impact hiring trends. Maintaining awareness of industry trends and acquiring relevant skills enhances employment prospects.
Question 4: Are there opportunities for recent graduates in the Wichita aerospace industry?
Opportunities exist for recent graduates, particularly in engineering, manufacturing, and technical support roles. Many companies offer internships and entry-level programs to attract and develop talent. Actively participating in internships and networking with industry professionals during academic pursuits enhances competitiveness.
Question 5: What is the salary range for aerospace positions in Wichita?
Salary ranges vary considerably depending on the position, experience level, and company. Entry-level positions may offer salaries in the range of $40,000 to $60,000 per year, while experienced engineers and managers can earn significantly more. Researching specific salary data for target roles is recommended to gain a realistic understanding of compensation expectations.
Question 6: How can individuals effectively search for aerospace positions in Wichita?
Effective search strategies include monitoring online job boards specific to the aerospace industry, visiting company career websites, attending industry job fairs, and networking with aerospace professionals. Tailoring resumes and cover letters to highlight relevant skills and experience is crucial for maximizing application success. Furthermore, proactively engaging with recruiters specializing in the aerospace sector can provide access to unadvertised opportunities.
This FAQ section provides a concise overview of essential considerations for individuals pursuing careers in the region’s aircraft manufacturing industry. Diligence and awareness are paramount.
The subsequent discussion will address strategies for long-term career advancement and professional development within the Wichita aerospace sector.
Aerospace Wichita KS Jobs
This examination has detailed the multifaceted nature of the aerospace industry within the south-central Kansas region, focusing on the spectrum of available positions. It underscored the significance of manufacturing technician roles, engineering design, quality control, regulatory compliance, program management, and the nuanced requirements for each. The exploration extended to critical advice on effectively navigating the job market, including strategic targeting of specific companies, acquisition of relevant certifications, and diligent networking practices. Further, it clarified some of the most frequent inquiries from potential candidates, offering essential insights into qualifications, market outlook, and realistic salary expectations.
The persistent demand within the aerospace sector of Wichita, KS, warrants continued attention. Individuals seeking involvement in this sector must commit to acquiring and maintaining specialized skills. Continued dedication to education and adaptability to ever-changing technological progress are the cornerstones of success. The area’s continuing importance on a global scale is directly tied to the expertise of its workforce. Therefore, investing in human capital is crucial for maintaining competitiveness and safeguarding the future of the aerospace industry in this vital geographic region.