The study of flight vehicle design, construction, and operation, coupled with the exploration of space, represents a dynamic and challenging field. At Texas Christian University, this discipline fosters innovation and prepares students for careers in a rapidly evolving industry. The program emphasizes both theoretical foundations and practical application, ensuring graduates are well-equipped to contribute to advancements in aviation and space exploration.
A robust academic grounding in this area provides numerous benefits. Students gain expertise in aerodynamics, propulsion, structural analysis, and control systems. This knowledge base is crucial for addressing complex engineering problems and developing cutting-edge technologies. Furthermore, the historical context of advancements in flight and space travel informs current research and future endeavors, pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific aspects of this field of study within the university environment, examining curriculum details, research opportunities, faculty expertise, and potential career pathways for graduates.
Guidance for Success in the Field
Success in the demanding realm of aerospace engineering requires a strategic approach to academic pursuits and professional development. The following guidelines are designed to enhance the preparedness and overall effectiveness of individuals pursuing this career path.
Tip 1: Emphasize Foundational Coursework: A solid understanding of mathematics, physics, and computer science is paramount. These disciplines provide the necessary tools for analyzing complex systems and developing innovative solutions.
Tip 2: Engage in Hands-On Projects: Seek opportunities to apply theoretical knowledge through practical projects, such as designing and building model aircraft or participating in engineering competitions. These experiences offer invaluable insights into the real-world challenges of the profession.
Tip 3: Cultivate Strong Communication Skills: Effective communication is essential for collaborating with multidisciplinary teams and presenting technical information to diverse audiences. Practice writing technical reports, delivering presentations, and participating in group discussions.
Tip 4: Seek Mentorship from Experienced Professionals: Guidance from faculty members, industry experts, or senior engineers can provide valuable insights into career paths, research opportunities, and industry trends. Actively seek out mentorship opportunities to gain valuable perspectives.
Tip 5: Develop Proficiency in Industry-Standard Software: Familiarity with software tools used for computer-aided design (CAD), computational fluid dynamics (CFD), and finite element analysis (FEA) is crucial for performing engineering analyses and simulations. Invest time in learning and mastering these essential tools.
Tip 6: Pursue Relevant Internships and Research Opportunities: Gaining practical experience through internships or research positions can significantly enhance career prospects. These experiences provide opportunities to apply classroom knowledge to real-world problems and develop valuable professional skills.
Tip 7: Maintain a Strong Ethical Foundation: Adherence to ethical principles is essential for ensuring the safety and integrity of engineering projects. Uphold the highest standards of professionalism in all endeavors.
By prioritizing foundational knowledge, hands-on experience, and professional development, individuals can significantly enhance their prospects for success in this challenging and rewarding field.
The subsequent section will provide a detailed overview of the curriculum, research facilities, and faculty expertise that support individuals pursuing a career in this field.
1. Aerodynamics
Aerodynamics, the study of air in motion and its interaction with solid objects, forms a cornerstone of the aerospace engineering curriculum at TCU. Understanding aerodynamic principles is fundamentally necessary for the design and analysis of aircraft and spacecraft, directly influencing flight performance, stability, and control. The airfoil shape, for instance, dictates lift and drag characteristics, impacting fuel efficiency and maneuverability. Without a thorough grounding in aerodynamics, achieving optimal designs is impossible.
The application of aerodynamic principles extends beyond theoretical calculations. Wind tunnel testing and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations, integral components of the TCU program, allow students to visualize and quantify airflow patterns around complex geometries. Real-world examples abound: The design of commercial aircraft wings, the optimization of racing car downforce, and the development of wind turbine blades all rely heavily on sophisticated aerodynamic analyses. The impact of aerodynamics on these technologies demonstrates its practical significance.
In summary, proficiency in aerodynamics is indispensable for aerospace engineers at TCU. It provides the foundation for innovative design, performance optimization, and safe operation of flight vehicles. Challenges in this field include the modeling of turbulent flows and the development of efficient aerodynamic shapes for supersonic flight. Continuous advancements in aerodynamic research directly contribute to progress across the aerospace industry, driving innovations in aircraft design and space exploration.
2. Spacecraft Design
Spacecraft design, a critical subdiscipline within aerospace engineering at TCU, focuses on the principles and practices involved in creating vehicles intended for operation beyond Earth’s atmosphere. Its significance is rooted in the ever-increasing demand for advanced space-based technologies, including communication satellites, Earth observation platforms, and deep-space exploration probes. The curriculum’s emphasis on spacecraft design is a direct response to the evolving needs of the aerospace industry. A firm grasp of these concepts is essential for any student aspiring to contribute to the future of space exploration. Examples like the design of the James Webb Space Telescope or the Mars rovers showcase the practical application of spacecraft design principles, demonstrating how theoretical knowledge translates into tangible technological advancements.
The practical implications of spacecraft design extend beyond simple vehicle construction. Students explore critical areas such as orbital mechanics, attitude control, thermal management, and power systems. Consider the intricate interplay between orbital mechanics and the design of a communication satellite’s propulsion system. Precise orbit maintenance is crucial for uninterrupted service, requiring sophisticated algorithms and efficient thrusters. Similarly, attitude control systems guarantee the accurate pointing of scientific instruments, directly impacting the quality of gathered data. The development of robust thermal management solutions enables spacecraft to withstand extreme temperature variations in the vacuum of space, a critical aspect of long-duration missions. These factors illustrate the multifaceted nature of spacecraft design and its pivotal role in ensuring mission success.
In summary, the study of spacecraft design forms an integral part of the TCU aerospace engineering program. It cultivates a comprehensive understanding of the challenges inherent in creating space-faring vehicles and equips students with the skills necessary to address these challenges. The challenges in this field include the ever-present drive for increased performance within strict weight and power constraints. Continued innovation in this field drives progress in various sectors, from telecommunications to scientific research.
3. Propulsion Systems
Propulsion systems are integral to aerospace engineering, particularly at TCU, where the curriculum aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of flight and space travel. These systems are the engines that enable aircraft and spacecraft to overcome gravity and atmospheric drag, achieving controlled movement through air and space.
- Rocket Engines
Rocket engines are paramount for space travel, producing thrust through the expulsion of high-velocity exhaust. TCU aerospace engineering students study the thermodynamics, combustion, and nozzle design of various rocket engine types, including solid-propellant, liquid-propellant, and hybrid systems. These concepts are critical for designing efficient and reliable propulsion for satellites, spacecraft, and launch vehicles.
- Jet Engines
Jet engines are essential for atmospheric flight, powering commercial airliners and military aircraft. TCU students delve into the intricacies of turbine engines, ramjets, and scramjets, examining compressor and turbine design, combustion processes, and overall engine performance. This expertise enables graduates to contribute to the development of more efficient and environmentally friendly aviation technologies.
- Propeller Systems
Propeller systems, while less common in modern aerospace, remain relevant for smaller aircraft and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). The TCU curriculum includes the study of propeller aerodynamics, blade design, and engine matching, providing students with a well-rounded understanding of various propulsion methods. This knowledge is vital for designing efficient and reliable power systems for these vehicles.
- Electric Propulsion
Electric propulsion systems are increasingly significant for space applications, offering high efficiency and precise control for long-duration missions. TCU aerospace engineering students explore ion thrusters, Hall-effect thrusters, and other advanced electric propulsion technologies. This knowledge prepares graduates for contributing to the development of next-generation spacecraft with extended operational capabilities.
These facets of propulsion systems, each studied within the framework of TCU’s aerospace engineering program, provide students with a thorough understanding of the principles and applications of various propulsion technologies. The knowledge gained prepares them for careers in the aerospace industry, where they can contribute to designing, analyzing, and improving the engines that power flight and space exploration.
4. Structural Analysis
Structural analysis forms a critical component of the aerospace engineering curriculum at TCU, underpinning the safety and reliability of all aerospace vehicles and structures. It provides the framework for predicting how these structures respond to various forces and environmental conditions.
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA)
FEA is a numerical technique used to simulate the behavior of complex structures under load. Students at TCU utilize FEA software to model and analyze aircraft wings, fuselage sections, and spacecraft components. Real-world applications include predicting stress concentrations around rivet holes in aircraft skins and optimizing the design of lightweight satellite structures. The effective application of FEA ensures structural integrity and minimizes the risk of failure.
- Material Properties
A thorough understanding of material properties, such as tensile strength, yield strength, and fatigue resistance, is essential for structural analysis. TCU aerospace engineering students study the behavior of various aerospace materials, including aluminum alloys, composites, and titanium. The correct selection and application of these materials are vital for creating structures that can withstand the harsh conditions of flight and space. For example, choosing the appropriate composite material for an aircraft wing requires careful consideration of its strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to environmental degradation.
- Load Analysis
Load analysis involves determining the forces acting on an aerospace structure during flight or operation. TCU students learn to calculate aerodynamic loads on aircraft surfaces, thermal loads on spacecraft, and dynamic loads caused by turbulence or engine vibrations. Accurately predicting these loads is crucial for ensuring the structure can withstand the expected stresses. For instance, analyzing the loads on a landing gear strut during touchdown requires considering factors such as aircraft weight, landing speed, and runway conditions.
- Structural Testing
Structural testing validates the results of analytical studies and provides empirical data for design improvements. TCU aerospace engineering students participate in structural testing experiments, subjecting components to simulated flight loads and environmental conditions. These tests provide valuable insights into the actual behavior of structures and help identify potential weaknesses. A practical example includes conducting a static load test on a wing section to verify its load-carrying capacity and identify failure modes.
The study of structural analysis equips TCU aerospace engineering graduates with the skills necessary to design safe, reliable, and efficient aerospace vehicles. The integration of analytical techniques, material science, and experimental testing provides a comprehensive understanding of structural behavior, ensuring that graduates are well-prepared to address the challenges of the aerospace industry. Knowledge of structural analysis plays a vital role in designing aerospace systems.
5. Flight Dynamics
Flight dynamics, a fundamental discipline within aerospace engineering, addresses the motion and control of aircraft and spacecraft. Its integration into the TCU aerospace engineering curriculum is essential for students to understand and predict the behavior of flight vehicles under various conditions. This understanding forms the basis for designing stable and controllable aircraft and spacecraft.
- Aircraft Stability
Aircraft stability refers to the tendency of an aircraft to return to its original equilibrium state after being disturbed. TCU aerospace engineering students study longitudinal, lateral, and directional stability, analyzing factors such as aerodynamic forces, moments, and control surface deflections. Examples include designing an aircraft with inherent stability to minimize pilot workload or developing active control systems to enhance stability in turbulent conditions. Understanding aircraft stability is critical for ensuring safe and predictable flight characteristics.
- Aircraft Control
Aircraft control involves the use of control surfaces, such as ailerons, elevators, and rudders, to maneuver an aircraft. TCU aerospace engineering students learn about control system design, including feedback control loops, actuator dynamics, and control law implementation. Real-world applications include designing autopilot systems that maintain altitude and heading, or developing fly-by-wire systems that enhance aircraft maneuverability and safety. Effective aircraft control is essential for achieving precise flight paths and responding to changing conditions.
- Spacecraft Attitude Dynamics
Spacecraft attitude dynamics concerns the orientation and motion of spacecraft in space. TCU aerospace engineering students study the principles of rotational dynamics, including inertia tensors, torques, and angular momentum. Examples include designing attitude control systems for satellites that maintain precise pointing accuracy, or developing methods for stabilizing spacecraft during orbital maneuvers. Understanding spacecraft attitude dynamics is critical for successful space missions.
- Orbital Mechanics
Orbital mechanics is the study of spacecraft trajectories and orbital maneuvers. TCU aerospace engineering students learn about Kepler’s laws, orbital elements, and orbit transfer techniques. Real-world applications include designing efficient trajectories for interplanetary missions, or developing strategies for satellite constellation deployment and maintenance. A firm grasp of orbital mechanics is essential for planning and executing successful space missions.
These facets of flight dynamics are carefully integrated into the TCU aerospace engineering program, providing students with a comprehensive understanding of the principles and applications of flight vehicle motion and control. The knowledge gained equips graduates to address diverse challenges in the aerospace industry, from designing stable and controllable aircraft to planning and executing complex space missions. Knowledge in the area of flight dynamics enables engineering students to contribute to the next generation of aerospace innovations.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding the aerospace engineering program at Texas Christian University. It aims to provide clear and concise information about various aspects of the program, including admission requirements, curriculum specifics, research opportunities, and career prospects.
Question 1: What are the specific admission requirements for the TCU Aerospace Engineering program?
Admission to the TCU Aerospace Engineering program requires a strong academic record, including a demonstrated proficiency in mathematics and science. Prospective students should submit standardized test scores (SAT or ACT), high school transcripts, and letters of recommendation. Specific minimum GPA requirements and test score thresholds are subject to change and should be verified with the TCU Office of Admission.
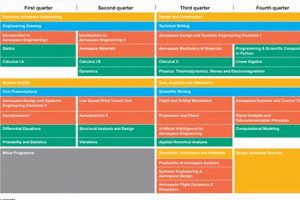
Question 2: What is the curriculum structure of the Aerospace Engineering program at TCU?
The curriculum is designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of aerospace engineering principles. It encompasses core courses in mathematics, physics, and computer science, followed by specialized courses in aerodynamics, propulsion, structural analysis, flight dynamics, and spacecraft design. The curriculum also includes laboratory experiences, design projects, and opportunities for undergraduate research.
Question 3: What research opportunities are available for undergraduate students in TCU Aerospace Engineering?
Undergraduate research opportunities are actively encouraged within the TCU Aerospace Engineering program. Students can participate in faculty-led research projects focusing on areas such as advanced materials, computational fluid dynamics, and autonomous systems. These opportunities provide valuable hands-on experience and allow students to contribute to cutting-edge research.
Question 4: What types of laboratory facilities are available to TCU Aerospace Engineering students?
TCU provides access to well-equipped laboratory facilities, including wind tunnels, structural testing equipment, and computer-aided design (CAD) and simulation software. These resources enable students to conduct experiments, analyze data, and develop practical engineering skills.
Question 5: What career paths are typically pursued by graduates of the TCU Aerospace Engineering program?
Graduates of the TCU Aerospace Engineering program pursue a variety of career paths in the aerospace industry and related fields. Common career options include roles in aircraft design, spacecraft engineering, propulsion systems development, and aerospace research. Graduates may also find employment in government agencies, consulting firms, and other engineering sectors.
Question 6: Does TCU Aerospace Engineering offer opportunities for internships or cooperative education programs?
The TCU Aerospace Engineering program strongly encourages students to participate in internships and cooperative education programs. These opportunities provide valuable practical experience and allow students to apply their knowledge in real-world settings. The Career Services office at TCU provides resources and support for students seeking internship and co-op positions.
In summary, the TCU Aerospace Engineering program offers a rigorous academic curriculum, hands-on research opportunities, and access to state-of-the-art facilities. These elements collectively prepare graduates for successful careers in the dynamic and demanding field of aerospace engineering.
The subsequent section will provide information on how to connect with the TCU Aerospace Engineering department and learn more about the program.
Conclusion
This exploration of TCU Aerospace Engineering has highlighted the key elements of the program. From its comprehensive curriculum encompassing aerodynamics, propulsion, structural analysis, and flight dynamics, to its emphasis on practical application through research and laboratory experiences, the program aims to cultivate well-rounded engineers. The study of these fundamental disciplines prepares graduates to address complex challenges in the aerospace industry.
The ongoing demand for innovation in flight and space exploration underscores the significance of robust aerospace engineering programs. The TCU program aims to equip students with the knowledge and skills necessary to contribute to the advancement of aerospace technology. Further information can be found through the university’s engineering department website or by contacting program advisors directly.





![Learn Aerospace Engineering with Khan Academy - [Year] Guide Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions Learn Aerospace Engineering with Khan Academy - [Year] Guide | Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/th-236-300x200.jpg)
