This benchmark serves as a key performance indicator for the segment of the stock market focused on companies involved in aerospace and defense. It comprises entities listed on a major exchange that are classified within these sectors. Its value is calculated based on the market capitalization of its constituent companies, providing a weighted average that reflects the overall performance of the tracked firms. For instance, if several major defense contractors experience significant stock price increases, the index will likely rise accordingly.
It is utilized by investors and analysts to gauge the financial health and investment potential of businesses within the aerospace and defense domains. Tracking its movement can indicate broader trends such as increased government spending on defense, advancements in aerospace technology, or shifts in global security landscapes. Understanding its historical behavior offers valuable context for making informed investment decisions and evaluating the relative strength of companies operating in these specific industries.
The following analysis delves into factors influencing its fluctuations, dissects the key players within the tracked sectors, and explores the implications of macroeconomic events on the index’s performance. Furthermore, we will examine its role as a barometer for innovation and growth within the aerospace and defense communities.
The fluctuations of equities within the aerospace and defense sector, as reflected by a key market indicator, demand careful consideration and a strategic approach to investment. Adhering to these guidelines can aid in informed decision-making.
Tip 1: Conduct Thorough Company Analysis: Assess the financial health of individual companies, examining factors such as revenue growth, profitability, debt levels, and order backlogs. A company with a strong track record of delivering on contracts and maintaining healthy financials is generally a more stable investment.
Tip 2: Monitor Geopolitical Developments: Global events, international relations, and government defense spending policies can significantly impact sector performance. Increased tensions or defense budget increases typically benefit companies involved in military technology and arms manufacturing.
Tip 3: Understand Technological Advancements: Evaluate the potential of new technologies and innovations within the aerospace and defense industries. Companies at the forefront of advancements, such as autonomous systems or advanced materials, may present opportunities for long-term growth.
Tip 4: Consider Diversification Within the Sector: Aerospace and defense encompasses a broad range of activities. Diversifying investments across different sub-sectors, such as commercial aviation, space exploration, or cybersecurity, can mitigate risk.
Tip 5: Track Government Contracts and Regulations: Government contracts form the backbone of many companies’ revenues. Closely follow contract awards, renewals, and regulatory changes that could impact profitability and market position.
Tip 6: Assess Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: The aerospace and defense sectors are often reliant on complex global supply chains. Understanding potential disruptions or vulnerabilities in the supply chain is crucial for risk management.
Tip 7: Factor in Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Considerations: Increasing attention is being paid to ESG factors in investment decisions. Evaluate companies’ environmental impact, labor practices, and governance structures to ensure alignment with investment values.
By diligently applying these guidelines, investors can navigate the intricacies of the aerospace and defense sectors, optimizing potential returns while managing associated risks.
The subsequent sections will further explore the market dynamics and emerging trends shaping the future of aerospace and defense investments.
1. Sector Performance
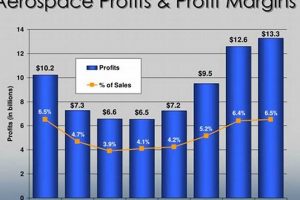
The performance of the aerospace and defense sector is intrinsically linked to the value and movement of the relevant equities benchmark. This link operates on a cause-and-effect basis: positive performance within the sector, reflected in the financial results and stock valuations of its constituent companies, generally leads to an increase in the index value. Conversely, a downturn in sector performance, stemming from factors like reduced government spending or decreased orders, typically results in a decline. Sector performance is a fundamental component as it aggregates the market capitalization-weighted returns of the companies included in that category, serving as a primary indicator for investors.
For example, consider a scenario where a major defense contractor announces a significant contract win. This news typically boosts the company’s stock price, contributing to a rise in sector performance. If several large companies within the sector experience similar positive events, the index is highly likely to increase. Conversely, if a major aerospace manufacturer reports lower-than-expected earnings due to supply chain disruptions, its stock price will likely decrease, dragging down the sector performance. Understanding this interplay is of practical significance for investors seeking to gauge the overall health and investment potential of the aerospace and defense industries.
In summary, the index acts as a consolidated reflection of the aerospace and defense sector’s financial health. Monitoring sector performance is critical for interpreting the index’s movements and making informed investment decisions. Challenges arise from the inherent volatility within the sector, influenced by geopolitical instability and fluctuating government policies, emphasizing the need for diligent analysis and risk management.
2. Market Capitalization
Market capitalization plays a pivotal role in the construction and interpretation of the S&P 500 Aerospace & Defense Industry Index. It serves as the primary weighting mechanism, influencing the index’s sensitivity to the performance of individual companies within the sector. A thorough understanding of its mechanics is critical for stakeholders.
- Weighting Mechanism
The index is capitalization-weighted, meaning that companies with larger market capitalizations exert a greater influence on its overall performance. This is due to the fact that the index calculation involves multiplying the price of each stock by the number of shares outstanding. Companies with higher market caps have a larger share of the index and any stock price change in a company that has high market cap will move the needle. For example, a significant price increase in Boeing, a large-cap company, will have a more substantial positive impact on the index than a similar percentage increase in a smaller aerospace component supplier.
- Index Sensitivity
The weighting based on market capitalization introduces varying degrees of sensitivity to different companies’ performance. Companies with large market caps will move the index and can drown out smaller companies’ performance. In periods where certain large-cap entities experience unusual volatility or significant shifts in their valuations, the index can experience amplified fluctuations even if the broader sector exhibits stability. The market cap of a firm can even influence other firms by the perception of the investment community in seeing one firm grow and believing others will follow.
- Liquidity and Investability
Market capitalization generally correlates with a company’s trading volume and liquidity. Stocks with higher market caps tend to be more liquid, which facilitates easier trading and lower transaction costs for investors. This is because it is easy to buy and sell high cap firms with no major effects on its price. This also influences the investability of the index as a whole, making it more attractive to institutional investors and those managing large portfolios.
- Performance Attribution
Analyzing performance requires understanding the relative contribution of each constituent company. A company’s contribution is directly proportional to its weight. Therefore, pinpointing the drivers of index movements involves scrutinizing the performance of the larger, more heavily weighted entities. Attributing gains or losses to specific firms, based on their market capitalization, becomes a key analytical step.
The market capitalization-weighted methodology ensures the index provides a representative snapshot of the aerospace and defense industry’s financial health. However, it is important to remember the inherent bias towards larger entities. Therefore, a holistic understanding of the sector also necessitates monitoring smaller companies and their potential for disruptive growth. The next analysis will examine the indexs connection to macroeconomic and geopolitical forces.
3. Economic Indicators
Economic indicators provide crucial insight into the overall economic environment and exert a significant influence on the performance of the aerospace and defense sector. Monitoring these indicators enables stakeholders to anticipate potential shifts in demand and investment trends related to entities tracked.
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Growth
GDP growth reflects the overall health of an economy. Strong GDP growth often correlates with increased government revenues, potentially leading to higher defense spending. Conversely, economic slowdowns may result in budget cuts affecting defense contracts and sector profitability. For example, during periods of robust economic expansion, governments may invest more heavily in advanced military technologies or infrastructure, boosting the revenues of aerospace and defense companies. A recession, however, may lead to decreased investment.
- Interest Rates
Interest rates impact both government borrowing costs and the cost of capital for aerospace and defense companies. Lower interest rates may encourage investment and expansion, whereas higher rates could stifle growth by increasing borrowing expenses. For instance, low rates may enable defense contractors to secure financing for research and development projects, while high rates could make acquisitions more expensive.
- Inflation Rates
Inflation affects the cost of raw materials, labor, and other inputs for aerospace and defense companies. Rising inflation can erode profit margins if companies are unable to pass on these costs to customers. Long-term government contracts, common in this sector, may be particularly vulnerable to inflationary pressures. For example, if the price of steel or aluminum increases significantly due to inflation, the cost of manufacturing aircraft or military vehicles will rise, potentially impacting profitability.
- Unemployment Rates
Unemployment rates can reflect the demand for labor within the aerospace and defense sectors. Low unemployment typically indicates a strong economy and high demand for skilled workers, potentially driving up labor costs and increasing competition for talent. High unemployment may signal a slowdown in economic activity and potential layoffs within the sector, affecting investor sentiment. For example, an increasing shortage of engineers and skilled technicians can drive up wages and increase operational costs.
The relationship between macroeconomic indicators and this equities barometer highlights the interconnectedness of the aerospace and defense sector with the broader economy. By carefully monitoring these indicators, investors and industry professionals can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the forces shaping the performance of companies included in the index and make more informed investment decisions.
4. Geopolitical Events
Geopolitical events exert a significant influence on the performance of the equities market barometer for aerospace and defense firms. Global tensions, conflicts, and shifts in international relations directly impact demand for military equipment, defense technologies, and related services. These events often trigger substantial fluctuations in the valuations of the companies comprising this index.
- Armed Conflicts and Regional Instability
Active conflicts and heightened regional instability frequently lead to increased defense spending by governments seeking to bolster their security capabilities. This, in turn, translates to higher revenues and order backlogs for aerospace and defense companies, positively affecting their stock prices and the overall index. For example, escalating tensions in a specific region may prompt nations to invest in advanced weapons systems, surveillance technologies, or military aircraft, benefiting companies specializing in these areas. However, it is also true that stability in regions can allow countries to dedicate resources to build up their armies instead of needing it.
- International Arms Control Agreements and Disarmament Treaties
Conversely, international agreements aimed at arms control and disarmament can have a negative impact on the sector’s performance. Reduced demand for certain types of weaponry, resulting from treaty obligations, can lead to decreased revenues and profits for affected companies. An arms limitations treaty on nuclear weapons, for instance, could decrease the potential sales of a weapons system for firms working on those.
- Changes in Government Defense Policies
Shifts in government defense policies, such as increased investment in cybersecurity or space-based technologies, can reshape the landscape of the aerospace and defense sector. Companies that are well-positioned to capitalize on these policy changes often experience significant growth, driving up their stock prices. The move from traditional warfare to drone technology influences which firms rise.
- Trade Wars and Sanctions
Trade wars and economic sanctions can disrupt global supply chains and impact the ability of aerospace and defense companies to source components or sell their products internationally. Such disruptions can lead to increased costs, reduced profitability, and decreased investor confidence. For example, sanctions on a particular country could prevent a company from selling its aircraft or defense systems to that nation, negatively affecting its revenues.
In summary, geopolitical events create a complex and dynamic environment for the aerospace and defense sector. While conflicts and instability often provide short-term boosts to the industry, long-term stability and arms control efforts can lead to adjustments and diversification. Understanding the interplay between global events and government policies is essential for assessing the investment prospects and navigating the inherent risks associated with these sectors, as these factors significantly influence the performance of companies that comprise this key market gauge.
5. Defense Spending
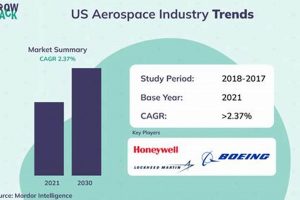
Government allocations to defense budgets represent a critical economic and geopolitical factor directly influencing the financial performance of companies within the aerospace and defense sectors. The level and direction of defense spending are key drivers of revenue, profitability, and overall market sentiment within the industry, with direct implications for companies included in the tracked benchmark.
- Direct Revenue Impact
Increased defense spending translates directly into larger contracts and orders for aerospace and defense companies. Government contracts form the backbone of revenue for many of these firms, and a rise in defense budgets leads to higher sales, increased production, and enhanced financial performance. For example, a significant increase in the U.S. defense budget could lead to substantial orders for new fighter jets, missile defense systems, or military vehicles, benefiting companies like Lockheed Martin, Boeing, and General Dynamics. These increases and new contracts directly contribute to the company’s bottom line which is displayed on the stock exchanges.
- Research and Development Funding
Defense budgets often include significant allocations for research and development (R&D) of new technologies. This funding enables aerospace and defense companies to innovate and develop cutting-edge solutions, maintaining their competitive edge and securing future contracts. Increased R&D funding can spur advancements in areas such as artificial intelligence, autonomous systems, and advanced materials, creating new opportunities for growth and profitability. For instance, a boost in R&D spending could accelerate the development of next-generation drone technology or hypersonic weapons, benefiting companies at the forefront of these innovations.
- Geopolitical Influence
Defense spending decisions are heavily influenced by geopolitical events and international relations. Increased global tensions, regional conflicts, or perceived threats often lead to higher defense budgets as governments seek to strengthen their military capabilities. This heightened demand for military equipment and services creates a favorable environment for aerospace and defense companies. For example, escalating tensions in Eastern Europe or the Middle East could prompt increased defense spending by NATO allies and regional powers, boosting the revenues of companies that supply military hardware and support services. When government defense departments signal to the world of instability, it sends messages to investors that they may consider companies within the S&P 500.
- Investor Sentiment and Market Valuation
Defense spending trends significantly influence investor sentiment towards the aerospace and defense sector. Rising defense budgets and strong order backlogs tend to create positive market sentiment, leading to increased investor confidence and higher stock valuations. Conversely, declining defense spending or budget cuts can dampen investor enthusiasm and negatively impact share prices. For example, a major defense policy announcement, such as a significant increase in the defense budget, could trigger a rally in aerospace and defense stocks as investors anticipate increased revenues and profits. Decreases may also indicate government spending to sectors outside of the defense industry.
The relationship between government defense spending and this major sector index is direct and consequential. Changes in defense budgets, driven by economic conditions and geopolitical events, directly affect the financial performance of companies and, thus, the index’s value. Understanding these dynamics is essential for investors seeking to navigate the sector’s complexities and make informed decisions. The next part of this analysis dives into technological innovation within the sector.
6. Technological Innovation
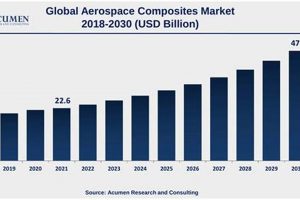
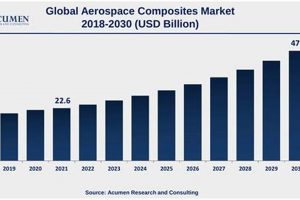
Technological innovation serves as a critical determinant in the long-term performance and composition of the benchmark for aerospace and defense companies. Investment in, and successful deployment of, new technologies drives revenue growth, market share gains, and ultimately, increased stock valuations for the companies involved. The index, reflecting the aggregate performance of these firms, becomes a barometer of the sector’s innovative capacity and its ability to adapt to evolving global security needs. For instance, companies pioneering advancements in areas such as hypersonic weapons, autonomous systems, or advanced cybersecurity solutions are often rewarded with higher valuations, positively impacting the index. The ability to stay ahead of the curve through technological innovation is not merely an operational advantage but a fundamental driver of financial success within these industries.
The impact of technological innovation extends beyond individual company performance, shaping the competitive landscape and creating opportunities for disruptive growth. Companies failing to invest adequately in R&D or adapt to emerging technologies risk losing market share to more innovative competitors. This dynamic is evident in the shift towards unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or commercial spaceflight, where companies that were early adopters have secured leading positions while others struggle to catch up. The success of companies pioneering satellite internet technologies such as Starlink for military use, has increased their revenue, which has increased their market cap, and thus has moved the needle for the index. This demonstrates how technological superiority can translate into significant financial advantages, driving the sector’s overall progress.
Understanding the relationship between technological innovation and this key index is essential for investors seeking to identify long-term opportunities in the aerospace and defense sector. By focusing on companies that prioritize research and development, foster a culture of innovation, and demonstrate a track record of successful technology commercialization, investors can position themselves to benefit from the sector’s future growth. The continued push for more efficient, affordable, and advanced technology will continue to drive change in the aerospace and defense sector. However, the challenges remain in balancing innovation with the often slow-moving and bureaucratic procurement processes of government contracts, emphasizing the importance of careful due diligence and strategic investment decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions About the S&P 500 Aerospace & Defense Industry Index
The following questions address common inquiries regarding the composition, function, and interpretation of this important financial benchmark.
Question 1: What constitutes inclusion in the benchmark?
Eligibility is contingent upon meeting specific criteria related to market capitalization, liquidity, and industry classification within aerospace and defense. Companies must be listed on a major stock exchange and derive a significant portion of their revenue from activities directly related to these sectors.
Question 2: How is the benchmark’s value calculated?
The value is calculated using a market capitalization-weighted methodology. This means that companies with larger market capitalizations have a greater influence on the index’s overall performance. Changes in the stock prices of larger companies will have a more pronounced impact than changes in the stock prices of smaller companies.
Question 3: What external factors most significantly influence its movement?
Geopolitical events, government defense spending policies, technological advancements, and macroeconomic conditions exert the most significant influence. Increases in geopolitical tensions or defense budgets typically lead to positive performance, while economic downturns may have a negative impact.
Question 4: How can investors utilize this index for investment strategies?
Investors can utilize it as a benchmark to evaluate the performance of individual aerospace and defense stocks or as the basis for investment vehicles such as exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that track the index’s performance. It offers a way to gain exposure to the sector as a whole and a measure of its overall financial health.
Question 5: What are the potential risks associated with investing in companies included in this benchmark?
Potential risks include dependence on government contracts, susceptibility to geopolitical instability, regulatory changes, and technological obsolescence. Diversification and careful analysis of individual company financials are crucial for mitigating these risks.
Question 6: How frequently is the composition of the index reviewed and rebalanced?
The composition is typically reviewed and rebalanced periodically, often quarterly, to ensure it accurately reflects the current state of the aerospace and defense sectors. This process involves adding or removing companies based on changes in their market capitalization, liquidity, and industry classification.
In summary, the S&P 500 Aerospace & Defense Industry Index offers a valuable tool for understanding and engaging with these sectors. A thorough grasp of its mechanics and influencing factors is essential for informed investment decisions.
The following provides resources for deeper analysis.
S&P 500 Aerospace & Defense Industry Index
The preceding analysis has explored the significance of the S&P 500 Aerospace & Defense Industry Index as a vital indicator of financial performance within these critical sectors. The examination encompasses its construction, the influence of market capitalization, the impact of macroeconomic factors, and the role of geopolitical events and defense spending policies. Technological innovation, a key driver of long-term growth and competitiveness, has been scrutinized for its effect on constituent companies.
Ultimately, comprehending the complexities of the S&P 500 Aerospace & Defense Industry Index is crucial for stakeholders navigating the investment landscape. Vigilant monitoring of market dynamics and geopolitical trends remains paramount. As global security and technological advancements continue to evolve, its function as a benchmark to measure the financial health of companies in the aerospace and defense sectors will continue to evolve and is subject to future study. Further investigation is warranted to understand these evolutions.