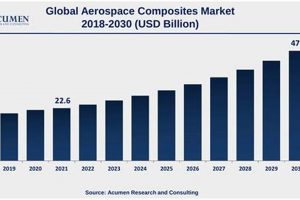
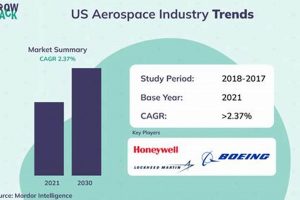
The sector encompassing establishments primarily engaged in the research, development, manufacture, and operation of vehicles capable of flight, and the systems related to their function, constitutes a significant portion of the advanced manufacturing landscape. This includes the production of aircraft, spacecraft, missiles, and related components, as well as the provision of associated services such as maintenance, repair, and overhaul. A tangible example is the manufacturing of commercial airliners, defense systems, and space exploration vehicles, all requiring highly specialized engineering and production processes.
The economic impact of this area is substantial, driving innovation, creating high-skilled jobs, and contributing significantly to the balance of trade. Historically, government investment in military programs and space exploration has played a pivotal role in its development, fostering technological advancements that have subsequently found applications in civilian sectors. This has resulted in advancements in materials science, aerodynamics, and propulsion systems, thereby impacting related fields.
The following discussion will delve into specific aspects of this sector, including the key players involved, the technological advancements shaping its future, the regulatory environment governing its operations, and the challenges and opportunities it faces in a globalized marketplace. This will provide a more in-depth understanding of its overall structure and dynamics.
Strategic Considerations for Stakeholders
This section presents critical considerations for entities operating within, or seeking to engage with, this sophisticated domain. Adherence to these points can enhance strategic positioning and operational effectiveness.
Tip 1: Invest in Research and Development: Continuous innovation is paramount. Allocate resources towards advanced materials, propulsion systems, and autonomous technologies to maintain a competitive edge. For example, investment in sustainable aviation fuel research is crucial for long-term viability.
Tip 2: Prioritize Supply Chain Resilience: Diversification of suppliers and robust risk management strategies are essential to mitigate disruptions. Monitor geopolitical factors and economic trends that could impact the availability of critical components.
Tip 3: Foster a Highly Skilled Workforce: Develop robust training programs and partnerships with educational institutions to cultivate a talent pool proficient in advanced manufacturing techniques, aerospace engineering, and data analytics.
Tip 4: Navigate Regulatory Compliance Effectively: Maintain a thorough understanding of evolving aviation regulations and safety standards. Proactive compliance minimizes risks and ensures operational legitimacy. For instance, staying abreast of FAA regulations is essential for aircraft manufacturers.
Tip 5: Embrace Digital Transformation: Implement digital technologies such as AI, machine learning, and the Internet of Things to optimize manufacturing processes, enhance predictive maintenance, and improve operational efficiency.
Tip 6: Strengthen Cybersecurity Measures: Implement robust cybersecurity protocols to protect sensitive data and prevent cyberattacks that could compromise operations or intellectual property. Regular security audits and employee training are vital.
Tip 7: Explore Strategic Partnerships: Collaborate with other organizations, including research institutions, government agencies, and industry peers, to share knowledge, leverage resources, and accelerate innovation. Joining industry consortia can provide valuable insights and opportunities.
Adopting these strategies will enhance an organization’s ability to navigate the complexities of this sector and capitalize on emerging opportunities. Proactive planning and diligent execution are crucial for sustained success.
The subsequent sections will elaborate on the current state and future trends shaping the overall trajectory of the industry.
1. Manufacturing Capabilities
Manufacturing capabilities are fundamental to the strength and competitiveness of the North American aerospace industries. These capabilities encompass the entire spectrum of activities involved in producing aircraft, spacecraft, and related components, from design and engineering to fabrication and assembly. The capacity to efficiently and reliably produce these complex systems underpins the sector’s global leadership.
- Precision Engineering and Fabrication
The North American aerospace sector is characterized by its high standards of precision engineering and fabrication. This involves the use of advanced materials, such as composites and specialized alloys, and sophisticated manufacturing processes like CNC machining and additive manufacturing. The production of critical components, such as turbine blades for jet engines, exemplifies this precision. Errors in these processes can lead to catastrophic failures, underscoring the importance of meticulous execution.
- Assembly and Integration Processes
Assembling complex aerospace vehicles requires intricate integration processes. The assembly lines of companies like Boeing and Airbus (in North America) involve the coordination of thousands of parts and systems. Efficient assembly processes are vital for minimizing production time and ensuring the structural integrity of the final product. Advanced automation and robotics are increasingly used to streamline these processes and reduce human error.
- Supply Chain Management
Robust supply chain management is crucial for maintaining manufacturing capabilities. Aerospace companies rely on a network of suppliers to provide components, raw materials, and specialized services. Effective supply chain management ensures the timely delivery of these inputs, preventing production delays. Disruptions in the supply chain, whether due to natural disasters or geopolitical events, can severely impact manufacturing output.
- Quality Control and Testing
Stringent quality control and testing procedures are integral to aerospace manufacturing. Every component and system undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets safety and performance standards. Non-destructive testing methods, such as X-ray inspection and ultrasonic testing, are used to detect defects without damaging the material. These measures are essential for preventing accidents and maintaining the reputation for safety associated with the aerospace industry.
These integrated facets of manufacturing capabilities form the bedrock of the North American aerospace industries. Without them, the design and innovation within the sector would remain unrealized. Ongoing investment in these areas is essential for maintaining a competitive advantage and ensuring the continued production of safe and reliable aerospace systems. The evolution of these capabilities reflects the broader advancements in manufacturing technology and the increasing demands of the aerospace market.
2. Technological Innovation
Technological innovation is a critical driver within the North American aerospace industries, directly shaping its competitiveness and future trajectory. Advancements in materials science, propulsion systems, avionics, and manufacturing techniques continuously redefine the possibilities for aircraft and spacecraft design. These innovations are not merely incremental improvements; they represent fundamental shifts that enable enhanced performance, efficiency, and safety. For instance, the development of lightweight composite materials has significantly reduced aircraft weight, leading to improved fuel efficiency and extended range. Similarly, advancements in engine technology, such as more efficient turbine designs, contribute to lower emissions and reduced operating costs.
The relationship between technological innovation and this sector is symbiotic. Government funding for research and development, coupled with private sector investment, fuels a cycle of discovery and implementation. NASA’s contributions to aerospace technology, for example, have directly benefited commercial aviation and space exploration. Furthermore, the pressure to maintain a competitive edge in the global market compels companies to prioritize innovation. Companies are investing heavily in areas like autonomous flight systems, hypersonic technologies, and sustainable aviation fuels. The practical applications of these innovations extend beyond aircraft design to encompass areas like air traffic management, satellite communications, and space-based research.
The continued success of North American aerospace industries hinges on its ability to foster and integrate technological innovation. However, challenges remain, including the high costs associated with research and development, regulatory hurdles, and the need for a skilled workforce capable of implementing new technologies. Overcoming these challenges requires a coordinated effort involving government, industry, and academia. By prioritizing technological innovation, this sector can maintain its global leadership and contribute to advancements in areas ranging from transportation to national security.
3. Regulatory Frameworks
The regulatory environment governing aerospace activities in North America is a complex network of rules, standards, and oversight mechanisms. These frameworks are designed to ensure safety, security, and environmental responsibility within the sector. Their influence permeates every aspect of operations, from aircraft design and manufacturing to airspace management and maintenance practices. Compliance is not merely a legal obligation; it is a fundamental prerequisite for maintaining public trust and safeguarding the overall health of the industry.
- Airworthiness Standards and Certification
Airworthiness standards, primarily enforced by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the United States and Transport Canada Civil Aviation (TCCA) in Canada, dictate the design, construction, and performance requirements for aircraft. Manufacturers must undergo rigorous certification processes to demonstrate compliance with these standards before an aircraft can be commercially operated. These certifications cover a wide range of aspects, including structural integrity, engine performance, and avionics systems. Non-compliance can result in significant penalties, including grounding of aircraft and revocation of operating licenses. The Boeing 737 MAX incidents serve as a stark reminder of the critical importance of adhering to airworthiness standards.
- Airspace Management and Air Traffic Control
The safe and efficient management of airspace is essential for preventing collisions and minimizing delays. Regulatory frameworks govern air traffic control procedures, communication protocols, and navigation systems. Agencies like the FAA and Nav Canada are responsible for overseeing air traffic operations and implementing measures to enhance safety and efficiency. The NextGen program in the United States aims to modernize the air traffic control system through the implementation of satellite-based navigation and data communication technologies. Effective airspace management is critical for accommodating the growing volume of air traffic and ensuring the smooth flow of operations.
- Export Controls and Security Regulations
Aerospace technologies and products are subject to strict export controls and security regulations due to their potential military applications. Regulations like the International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) in the United States and the Export and Import Permits Act in Canada restrict the export of sensitive technologies to certain countries and entities. These regulations aim to prevent the proliferation of advanced weaponry and protect national security interests. Compliance with export control regulations requires meticulous record-keeping and adherence to licensing requirements.
- Environmental Regulations and Sustainability Initiatives
Increasingly, environmental regulations are shaping the operations of the aerospace sector. Regulations aimed at reducing aircraft noise and emissions are driving the development of more fuel-efficient engines and alternative fuels. International organizations like the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) are setting global standards for environmental performance. Initiatives such as the Carbon Offsetting and Reduction Scheme for International Aviation (CORSIA) aim to mitigate the climate impact of air travel. Airlines are investing in sustainable aviation fuels (SAF) and exploring electric and hybrid propulsion systems to reduce their carbon footprint and comply with evolving environmental regulations.
These regulatory facets illustrate the pervasive influence of governmental oversight on the North American aerospace industries. Compliance with these frameworks is not simply a matter of ticking boxes; it requires a proactive commitment to safety, security, and environmental responsibility. The ongoing evolution of these regulations reflects the changing demands and challenges facing the sector, underscoring the need for continuous adaptation and innovation.
4. Economic Impact
The association between economic impact and North American aerospace industries constitutes a significant driver of regional and national prosperity. The sector’s activities generate substantial revenue streams through aircraft manufacturing, maintenance, research and development, and the operation of air transport services. This revenue, in turn, supports a wide range of ancillary industries, including materials science, electronics, and software development. The presence of major aerospace hubs, such as those in Washington State and California, demonstrably elevates regional economic activity through direct employment, supply chain expenditures, and induced consumption. As an example, the development and production of a new commercial aircraft can create tens of thousands of jobs and contribute billions of dollars to the GDP.
Furthermore, the contribution to trade balances cannot be overstated. The export of aircraft, engines, and related components represents a crucial element of North American exports, offsetting trade deficits in other sectors. The highly skilled workforce required within these industries supports higher wages and increased tax revenues for federal, state, and local governments. Investment in aerospace technology fosters innovation that spills over into other sectors, enhancing overall economic competitiveness. For example, technologies developed for space exploration have found applications in fields such as medical imaging and telecommunications, yielding broader societal benefits.
Ultimately, understanding the economic impact of North American aerospace industries is critical for policymakers and business leaders. Strategic investments in aerospace research, infrastructure, and workforce development are vital for sustaining the sector’s economic contribution. However, challenges remain, including fluctuating demand cycles, increasing global competition, and the need to address environmental concerns. Addressing these challenges requires a collaborative approach involving government, industry, and educational institutions, with the goal of ensuring the long-term viability and economic contributions of the industries concerned.
5. Skilled Workforce
The vitality of North American aerospace industries is inextricably linked to the availability and quality of its skilled workforce. This workforce, encompassing engineers, technicians, scientists, and specialized manufacturers, constitutes the fundamental capacity for innovation, production, and maintenance within the sector. The presence of a highly skilled cohort directly influences the sector’s ability to compete globally, adapt to technological advancements, and maintain rigorous safety standards. A shortage of qualified personnel creates constraints on growth, potentially leading to delays in production, compromised quality, and a diminished capacity for innovation. For example, the development of advanced aircraft engines requires engineers with expertise in thermodynamics, materials science, and computational fluid dynamics; a deficit in any of these areas limits the sector’s progress. The continuous demand for increasingly sophisticated products and services underscores the critical role of a well-trained and adaptable workforce.
Numerous initiatives are underway to address the ongoing need for a skilled workforce. These include partnerships between educational institutions and aerospace companies to develop specialized training programs, apprenticeships, and internship opportunities. Government support for STEM education plays a crucial role in cultivating interest and expertise in aerospace-related fields. Moreover, continuous professional development and retraining programs are essential for ensuring that existing employees remain proficient in emerging technologies and manufacturing processes. The implementation of advanced automation and robotics in manufacturing necessitates a workforce capable of operating and maintaining these systems, requiring specialized skills in areas such as mechatronics and computer programming. Investment in workforce development yields tangible benefits, including increased productivity, reduced error rates, and enhanced innovation capabilities. Specific cases, such as Boeing’s partnerships with community colleges to train aircraft mechanics, demonstrate the effectiveness of collaborative workforce development programs.
In summary, the skilled workforce represents a non-negotiable component of North American aerospace industries. Challenges related to workforce shortages and skills gaps must be proactively addressed to ensure the sector’s sustained competitiveness and contribution to economic growth. Initiatives that foster education, training, and continuous professional development are essential for maintaining a highly qualified workforce capable of meeting the evolving demands of the aerospace sector. Strategic alignment between industry needs, educational curricula, and government policies is paramount for cultivating and retaining the talent necessary to propel the sector forward.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses prevalent inquiries regarding the North American aerospace industries, providing concise and authoritative responses to promote clarity and understanding.
Question 1: What constitutes the primary economic driver within North American aerospace industries?
Manufacturing and associated exports form the principal economic engine. The production of aircraft, spacecraft, and related components generates significant revenue and supports a substantial supply chain.
Question 2: How do regulatory frameworks impact operational aspects?
Stringent regulations, overseen by agencies like the FAA and Transport Canada, dictate safety standards, airworthiness certifications, and airspace management practices. Compliance is mandatory for all operators within the sector.
Question 3: What role does technological innovation play?
Innovation is crucial. Advancements in materials science, propulsion systems, and avionics continually redefine the capabilities and efficiency of aircraft and spacecraft.
Question 4: Why is a skilled workforce so critical?
A proficient workforce encompassing engineers, technicians, and specialized manufacturers is essential for innovation, production quality, and adherence to safety protocols.
Question 5: What are the main challenges confronting North American aerospace industries?
Key challenges include increasing global competition, fluctuating demand cycles, stringent regulatory requirements, and the need to address environmental concerns.
Question 6: How can organizations enhance strategic positioning?
Investing in research and development, prioritizing supply chain resilience, fostering a highly skilled workforce, and embracing digital transformation are pivotal strategies.
These responses underscore the core tenets governing this sector: technological advancement, rigorous safety standards, and economic viability. Understanding these facets is crucial for stakeholders and observers alike.
The following section will delve into further considerations relevant to the long-term sustainability and evolution of North American aerospace industries.
Conclusion
This exploration has elucidated the multi-faceted nature of North American aerospace industries, underscoring its integral role in technological advancement, economic prosperity, and national security. Core competencies in manufacturing, innovation, and a skilled workforce, coupled with stringent regulatory oversight, define its operational framework. The competitive landscape, characterized by evolving technologies and global pressures, necessitates strategic adaptability and continuous improvement.
Sustained investment in research and development, coupled with a commitment to workforce development and regulatory compliance, remains paramount. The future success of North American aerospace industries hinges on its ability to navigate these complexities and capitalize on emerging opportunities. The continued strength of this sector is essential for maintaining a global leadership position and driving technological innovation that benefits both the industry and society at large. A proactive and collaborative approach is necessary to ensure continued progress.