Compensation for professionals in the field dedicated to designing, developing, testing, and maintaining aircraft, spacecraft, and related systems is a key consideration for both aspiring and established engineers. The remuneration package typically includes a base salary, benefits, and potential bonuses, reflecting the complexity and critical nature of the work performed. Location, experience, education, and specific skill sets all factor into the determination of individual earning potential.
Understanding income expectations is important for career planning and financial stability. The financial rewards associated with this profession have historically served as an incentive for attracting and retaining highly skilled individuals in a field vital to national security, scientific advancement, and commercial aviation. Competitive compensation packages help to maintain a strong workforce capable of pushing the boundaries of aerospace technology.
The following sections will explore in detail the various factors impacting earnings, including geographic location, education level, specialization, and experience. Industry comparisons and future trends in this competitive market will also be examined, providing a comprehensive overview of the financial landscape for professionals in this domain.
Maximizing earnings in the field requires a strategic approach to career development and negotiation. The following tips offer insights into how professionals can enhance their earning potential and secure competitive compensation packages.
Tip 1: Specialize in High-Demand Areas: Focusing on emerging technologies such as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), advanced materials, or sustainable aviation can increase marketability and command a premium salary. Demonstrate expertise through relevant projects and certifications.
Tip 2: Pursue Advanced Education: Obtaining a master’s degree or doctorate can significantly impact earning potential. Advanced degrees often open doors to higher-level positions and specialized roles with increased compensation.
Tip 3: Gain Relevant Experience: Internships and entry-level positions provide valuable experience and exposure to industry practices. Proactively seek opportunities to contribute to significant projects and develop sought-after skills.
Tip 4: Develop Strong Negotiation Skills: Research industry benchmarks and understand the value of acquired skills and experience before entering salary negotiations. Confidently articulate accomplishments and contributions.
Tip 5: Consider Location Strategically: Geographic location plays a significant role in determining pay scales. Major aerospace hubs or areas with high demand for engineers often offer more competitive salaries.
Tip 6: Obtain Professional Certifications: Certifications such as the Professional Engineer (PE) license demonstrate competence and commitment to the profession, potentially leading to higher earning potential and career advancement.
Tip 7: Stay Updated with Industry Trends: Continuous learning and professional development are crucial for maintaining a competitive edge. Attend conferences, workshops, and training programs to stay abreast of the latest advancements and technologies.
By implementing these strategies, professionals can proactively manage their careers and maximize their earning potential within this dynamic and competitive field.
The subsequent sections will delve into the long-term career prospects and potential for further advancement in this field.
1. Experience
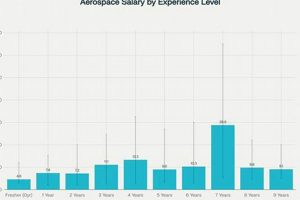
Years of experience directly correlate with increased compensation within the aerospace engineering profession. Entry-level positions typically offer lower salaries, reflecting the limited practical application of theoretical knowledge. As engineers accumulate experience through project involvement, problem-solving, and exposure to diverse aspects of design, manufacturing, and testing, their value to an organization increases, thereby driving up compensation.
For example, an engineer with 5-7 years of experience might assume project leadership roles, involving budget management, team coordination, and client interaction. This expanded responsibility, coupled with a proven track record of successful project completion, warrants a significant salary increase compared to an entry-level counterpart. Similarly, engineers with 10+ years of experience often transition into senior management positions, contributing to strategic decision-making and technical oversight, which justifies a considerably higher remuneration.
In summary, experience acts as a primary determinant of earnings. The direct relationship underscores the importance of continuous professional development, active participation in challenging projects, and a proactive approach to expanding one’s skill set. While education and specialization are critical, the practical application of knowledge through experience is the key driver of sustained career progression and financial rewards in this field.
2. Education
Educational attainment significantly influences compensation prospects within the field. The level of academic achievement, from bachelor’s degrees to doctorates, plays a pivotal role in shaping earning potential and career trajectory.
- Bachelor’s Degree
A bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering serves as the entry point for most positions. While providing a foundational understanding of core concepts, initial salary offerings may be comparatively lower than those with advanced degrees. Opportunities for rapid salary growth typically depend on acquiring specialized skills and practical experience.
- Master’s Degree
Pursuing a master’s degree allows for specialized study in areas such as propulsion, aerodynamics, or structural mechanics. The focused knowledge gained often translates into higher starting salaries and access to more advanced roles within organizations. Master’s-level engineers are frequently sought after for research and development positions.
- Doctorate (Ph.D.)
A doctoral degree signifies advanced research capabilities and expertise. Individuals with Ph.D.s are typically hired for leadership roles in research institutions, universities, or within research and development departments of aerospace companies. The earning potential for doctoral graduates is generally higher due to their specialized skills and contributions to innovation.
- Continuing Education and Certifications
Beyond formal degrees, ongoing education and professional certifications contribute to career advancement and salary increases. Participation in workshops, conferences, and certification programs demonstrates a commitment to staying current with industry trends and developing specialized skills valued by employers.
In summary, the level of education attained directly impacts initial compensation levels and long-term earning potential. Advanced degrees often provide access to higher-paying positions and specialized roles, while continuous learning ensures professionals remain competitive and valuable assets within the industry. The investment in education translates to a higher potential return on investment over the course of a career. This reinforces the importance of strategic educational planning for maximizing earning potential in this field.
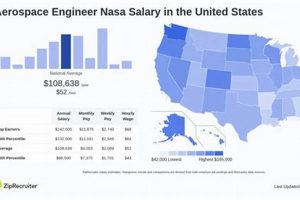
3. Location
Geographic location exerts a significant influence on compensation levels for professionals in the aerospace engineering sector. Regional economic factors, concentration of aerospace industries, and cost of living variations contribute to disparities in earning potential across different areas.
- Cost of Living Adjustments
Salaries are often adjusted to reflect the cost of living in a particular region. Metropolitan areas with higher living expenses, such as California’s Silicon Valley or the Washington, D.C. area, typically offer higher salaries to compensate for increased housing costs, transportation, and other expenses. However, the increased cost of living may offset some of the perceived benefit of a higher salary.
- Industry Hubs and Demand
Regions with a high concentration of aerospace companies, research institutions, or government agencies involved in aerospace activities tend to offer more competitive salaries. Areas like Seattle (Boeing), Southern California (various aerospace contractors), and Florida’s Space Coast (space exploration) attract a skilled workforce and necessitate competitive compensation packages to retain talent. High demand drives up salary levels.
- State and Local Tax Implications
State and local tax structures can impact the actual disposable income for aerospace engineers. States with lower income tax rates or no state income tax may effectively increase the value of a given salary compared to states with higher tax burdens. This factor influences the attractiveness of certain locations for employment.
- Proximity to Educational Institutions
Areas near prominent universities with strong aerospace engineering programs often benefit from a steady influx of talent, which can influence salary levels. The presence of these institutions also stimulates research and development activities, creating additional employment opportunities and competitive pressure on compensation.
In conclusion, location is a crucial factor in determining compensation. The interplay between cost of living, industry concentration, tax implications, and proximity to educational institutions shapes regional salary standards. Professionals should carefully consider these aspects when evaluating employment opportunities to maximize financial well-being and career growth.
4. Specialization
Within the field, the choice of specialization exerts a significant influence on compensation. Deep expertise in a niche area often translates to increased demand and higher earning potential due to the specialized knowledge and skills possessed by the engineer.
- Propulsion Systems
Engineers specializing in propulsion systems, including jet engines, rocket engines, and advanced propulsion technologies, are highly sought after due to the critical role these systems play in aircraft and spacecraft performance. Their expertise in designing, developing, and testing these complex systems commands a premium salary, particularly in organizations focused on space exploration or advanced military applications.
- Avionics and Control Systems
The design, development, and integration of avionics and control systems require specialized knowledge of electronics, software engineering, and control theory. Engineers in this field are responsible for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of aircraft and spacecraft. Their expertise in areas like flight control, navigation, and communication systems makes them valuable assets, resulting in competitive salary offers.
- Structural Mechanics and Materials
Specialization in structural mechanics and materials science is crucial for ensuring the integrity and safety of aircraft and spacecraft structures. Engineers in this field analyze stress, strain, and fatigue behavior of materials under extreme conditions. Expertise in composite materials, finite element analysis, and structural testing is highly valued, leading to increased compensation levels.
- Aerodynamics and Fluid Dynamics
Aerodynamics and fluid dynamics engineers focus on understanding and predicting the flow of air and other fluids around aircraft and spacecraft. Their expertise is essential for optimizing aerodynamic performance, reducing drag, and improving fuel efficiency. This specialization requires advanced knowledge of computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and wind tunnel testing, skills which are highly valued by aerospace companies.
The demand for specialized expertise drives compensation levels upward. Engineers with advanced knowledge and proven skills in these areas are often in short supply, allowing them to command higher salaries. Furthermore, as technology advances and new challenges emerge, the need for highly specialized engineers will continue to grow, further enhancing the link between specialization and increased earning potential in the field.
5. Industry
The sector of employment, or industry, exerts a considerable influence on compensation within the aerospace engineering profession. The type of organization ranging from government agencies to private corporations and research institutions directly impacts salary scales, benefits packages, and opportunities for professional development. This influence stems from differences in funding models, project types, risk profiles, and overall strategic objectives across various segments of the aerospace industry.
For instance, engineers employed by government entities such as NASA or the Department of Defense often encounter structured pay scales dictated by civil service regulations. While these positions may offer stability and comprehensive benefits, the potential for rapid salary growth might be limited compared to opportunities in the private sector. Conversely, private corporations, particularly those engaged in competitive commercial aviation or defense contracting, frequently offer higher base salaries and performance-based bonuses to attract and retain top talent. Aerospace start-ups, although potentially offering equity-based compensation, may present higher risk and variable short-term financial rewards. The type of projects undertaken also affects earning potential; engineers working on cutting-edge research and development projects might command higher salaries due to the specialized knowledge required.
Understanding the industry-specific compensation trends is crucial for career planning. Individuals should thoroughly research salary benchmarks for different roles within various aerospace organizations. Evaluating the long-term growth potential, benefits packages, and the stability of the employer alongside the base salary is essential for making informed career decisions. Ultimately, the interplay between industry segment and career goals significantly shapes the financial landscape for those in this profession.
6. Certifications
Professional certifications serve as a quantifiable validation of an aerospace engineer’s competence, specialized knowledge, and commitment to industry standards, often leading to increased earning potential. Certifications such as the Professional Engineer (PE) license, or specialized certifications related to areas like project management or specific software tools, demonstrate a dedication to maintaining expertise and adhering to best practices. Employers frequently view these credentials as indicators of an engineer’s ability to perform at a higher level, take on greater responsibilities, and contribute to project success. The acquisition of relevant certifications can directly translate to higher salary offers or serve as a catalyst for promotions and salary increases within an organization. For example, an engineer with a PE license may be eligible to oversee engineering projects and sign off on designs, roles that typically command higher compensation due to the increased responsibility and liability involved.
The specific impact of certifications on compensation depends on several factors, including the type of certification, the experience level of the engineer, and the industry sector. Certifications aligned with high-demand skills or emerging technologies tend to have a more pronounced effect on salary. Moreover, the value of certifications can be amplified when combined with practical experience and a proven track record of successful project completion. For instance, an engineer specializing in structural analysis who possesses a certification in finite element analysis (FEA) software may be more competitive in the job market and command a higher salary compared to an engineer without such certification. Companies may be willing to pay more for engineers who can immediately contribute to projects without extensive training.
In summary, professional certifications can significantly enhance an aerospace engineer’s earning potential by validating competence, demonstrating commitment, and aligning skills with industry demands. However, the pursuit of certifications should be strategic, focusing on those that are relevant to career goals and aligned with the needs of the aerospace industry. While certifications are valuable, they are most effective when coupled with practical experience and a dedication to continuous professional development, ensuring that engineers remain competitive and valuable assets in a dynamic technological landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Aerospace Engineer Compensation
The following addresses common inquiries concerning the financial aspects of a career in aerospace engineering.
Question 1: What is the typical starting salary for an aerospace engineer with a bachelor’s degree?
Entry-level compensation is influenced by location, specialization, and employer. However, a general estimate for a graduate with a bachelor’s degree typically falls within a range reflecting market demand and economic conditions.
Question 2: How does obtaining a master’s degree impact earning potential?
A master’s degree often leads to higher starting salaries and access to more advanced roles. The specialized knowledge gained can position candidates for research and development positions with increased compensation.
Question 3: What are the most lucrative specializations within aerospace engineering?
Specializations in high-demand areas such as propulsion systems, avionics, and advanced materials tend to command higher salaries due to the critical nature of these skills and the limited number of qualified professionals.
Question 4: How does geographic location affect compensation levels?
Compensation is influenced by the cost of living, the concentration of aerospace industries, and regional economic factors. Areas with higher living expenses and greater demand for aerospace engineers typically offer more competitive salaries.
Question 5: Does obtaining a Professional Engineer (PE) license impact salary?
A PE license signifies competence and commitment, often leading to increased earning potential. It demonstrates the ability to take on greater responsibilities and oversee engineering projects, roles which typically command higher compensation.
Question 6: What are the long-term salary growth prospects for aerospace engineers?
Salary growth depends on continuous professional development, experience accumulation, and the ability to adapt to technological advancements. Those who actively pursue new skills and take on challenging roles are more likely to experience significant salary increases over time.
Key takeaways include the significance of education, specialization, location, and professional certifications in determining financial compensation within this career field.
The next section will offer a conclusion, summarizing the most important insights regarding this field’s earning potential.
Aerospace Engineers Salary
The examination of the keyword has revealed a multifaceted landscape influencing earning potential. Factors such as education, specialization, experience, location, and certifications all play a critical role in determining compensation. A strategic approach to career development, encompassing continuous learning and the acquisition of in-demand skills, is essential for maximizing financial prospects within this field. Variations in compensation reflect the diverse roles, responsibilities, and expertise levels required across different segments of the aerospace industry.
Understanding these factors is crucial for both aspiring and established professionals. Informed decision-making regarding educational investments, career paths, and geographic considerations can significantly impact long-term financial well-being. As the aerospace industry continues to evolve, staying abreast of emerging technologies and market trends will remain paramount for maintaining a competitive edge and securing optimal remuneration.