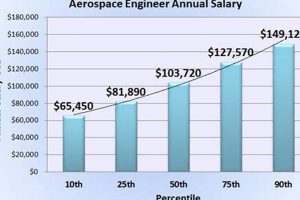
Compensation for professionals specializing in the design, development, and implementation of self-governing systems within the aeronautics and astronautics sectors is multifaceted. This remuneration reflects the complex skill set required to integrate robotics, artificial intelligence, and control systems into aircraft, spacecraft, and related technologies. As an example, individuals in this role might oversee the creation of autonomous navigation systems for drones or develop automated control algorithms for spacecraft maneuvers, directly impacting project success and operational efficiency.
The earning potential in this field is driven by several factors, including the increasing demand for autonomous capabilities in both commercial and defense applications. A competitive package is essential to attract and retain qualified engineers who can navigate the intricate challenges of creating safe, reliable, and efficient autonomous systems. Historically, investment in research and development within the aerospace industry has significantly influenced the value placed on specialized expertise, shaping the compensation landscape and ensuring continuous innovation.
Understanding the nuances of this earning potential requires consideration of experience level, geographic location, educational background, and the specific employer. Subsequent sections will delve into these individual components, providing a detailed analysis of the various elements that contribute to the overall compensation structure for engineers working at the intersection of aerospace and autonomous technologies.
Guidance for Maximizing Earning Potential
The following recommendations are designed to assist professionals in optimizing their compensation prospects within the field. These strategies emphasize skill development, strategic career planning, and a proactive approach to professional advancement.
Tip 1: Cultivate Specialized Expertise: Acquire in-depth knowledge and skills in niche areas such as sensor fusion, path planning, or fault-tolerant control systems. For example, proficiency in developing robust algorithms for autonomous landing systems can significantly enhance marketability.
Tip 2: Pursue Advanced Education: Consider obtaining a master’s degree or doctorate in a relevant field, such as aerospace engineering, robotics, or computer science. Advanced degrees often correlate with higher starting salaries and increased opportunities for leadership roles.
Tip 3: Gain Industry Certifications: Obtain certifications related to specific autonomous systems or software development methodologies. Certifications demonstrate a commitment to professional development and validate specialized skills.
Tip 4: Develop Strong Programming Skills: Master programming languages commonly used in aerospace and autonomous systems, such as C++, Python, and MATLAB. Proficiency in these languages is crucial for developing and implementing complex algorithms.
Tip 5: Seek Internships and Research Opportunities: Gain practical experience through internships or research positions at aerospace companies, research institutions, or government agencies. Practical experience provides valuable insights and networking opportunities.
Tip 6: Network Actively: Attend industry conferences, workshops, and networking events to connect with potential employers and learn about emerging trends. Building a strong professional network can lead to valuable career opportunities.
Tip 7: Enhance Communication Skills: Develop strong written and verbal communication skills to effectively convey technical information to colleagues, clients, and stakeholders. Clear and concise communication is essential for collaboration and project success.
Tip 8: Understand Compensation Benchmarks: Research current salary ranges for similar roles in various geographic locations and industries. This knowledge empowers individuals to negotiate effectively and advocate for fair compensation.
By actively pursuing these strategies, individuals can significantly enhance their earning potential and establish a rewarding career trajectory in this dynamic and rapidly evolving field. A proactive approach to skill development, career planning, and networking is essential for maximizing long-term financial success.
The next section will examine the potential future trends and challenges that may impact compensation within the aerospace autonomous systems engineering sector.
1. Experience
The relationship between experience and compensation for aerospace autonomous systems engineers is fundamentally linear, though with diminishing returns at higher experience levels. Entry-level positions, typically requiring a bachelor’s degree and perhaps an internship, offer starting salaries that reflect the foundational knowledge acquired through academic training. As engineers accumulate practical experience, their salaries increase proportionally to their proven ability to contribute to project success. For example, an engineer with five years of experience designing and implementing autonomous navigation algorithms for unmanned aerial vehicles will command a higher salary than a recent graduate due to their demonstrated capacity to solve real-world problems and manage complex projects independently.
The importance of experience stems from its direct correlation with an engineer’s proficiency in applying theoretical knowledge to practical challenges. Experienced engineers are often better equipped to anticipate potential issues, troubleshoot technical problems, and make informed decisions under pressure. Their accumulated expertise translates into increased efficiency, reduced project timelines, and improved system performance, all of which contribute to a company’s bottom line. Moreover, experienced engineers often serve as mentors to junior colleagues, further enhancing their value to the organization. For instance, a senior engineer with a decade of experience in developing fault-tolerant control systems might lead a team of younger engineers in designing a new autonomous flight control system, leveraging their experience to guide the project and ensure its success.
In summary, experience is a critical determinant of compensation for aerospace autonomous systems engineers. While formal education provides the necessary theoretical framework, practical experience hones the skills and judgment required to excel in this demanding field. Employers recognize the value of experience and are willing to pay a premium for engineers who can demonstrate a proven track record of success. However, it’s important to note that the rate of salary growth tends to slow down as experience increases, suggesting that continued professional development and skill enhancement are essential for maximizing long-term earning potential. The next section will analyze the impact of geographic location on compensation within this specialty.
2. Location
Geographic location exerts a considerable influence on compensation within the aerospace autonomous systems engineering profession. Regional economic factors, industry concentration, and cost of living are key determinants of salary levels.
- Regional Aerospace Industry Presence
Areas with a significant concentration of aerospace companies, research institutions, and government agencies tend to offer higher salaries. This increased demand for skilled engineers drives up compensation. For example, regions like Southern California (Los Angeles, San Diego), Seattle, and the Boston metropolitan area, with established aerospace clusters, generally provide more competitive salaries compared to areas with limited industry presence. Boeings presence in Seattle, for instance, creates a robust market for aerospace engineers, impacting salary expectations.
- Cost of Living Adjustments
Salary levels often reflect the cost of living in a particular area. High-cost regions, such as the San Francisco Bay Area, typically offer higher salaries to offset expenses related to housing, transportation, and other essential goods and services. An identical role in a lower cost-of-living area, such as Huntsville, Alabama, may have a lower nominal salary, but the purchasing power could be comparable due to reduced living expenses.
- State and Local Tax Policies
Tax policies at the state and local levels can indirectly affect an engineer’s net compensation. States with lower income taxes or no state income tax might be more attractive to some professionals, even if the gross salary is slightly lower than in a higher-tax state. These considerations influence the perceived value of a compensation package.
- Proximity to Educational Institutions
Areas with prominent universities offering specialized aerospace engineering programs often attract both talent and companies, leading to a competitive job market and potentially higher salaries. The presence of institutions like MIT, Stanford, or Caltech contributes to a talent pool that employers are willing to pay a premium to access. These regions also benefit from research collaborations and technology transfer, further fueling innovation and demand for skilled engineers.
In summary, geographic location is a significant factor in determining compensation for aerospace autonomous systems engineers. The concentration of aerospace industries, cost of living adjustments, state and local tax policies, and proximity to top educational institutions all contribute to regional variations in salary levels. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for both employers seeking to attract talent and engineers seeking to maximize their earning potential.
3. Education
Formal education is a primary driver influencing compensation for aerospace autonomous systems engineers. The attainment of higher academic qualifications, such as a Master’s degree or a Ph.D., often correlates directly with increased earning potential. This relationship stems from the advanced knowledge and specialized skills acquired during graduate-level studies, which equip engineers to tackle more complex challenges and contribute to innovation within the field. For instance, an engineer holding a doctorate in robotics may possess expertise in advanced control algorithms and sensor fusion techniques, enabling them to develop cutting-edge autonomous systems for aerospace applications. This expertise translates to a higher value proposition for employers, justifying a premium salary.
The specific field of study is also a significant factor. Degrees in aerospace engineering, robotics, computer science, and electrical engineering are highly relevant. However, specialization within these fields, such as a focus on autonomous systems, artificial intelligence, or control theory, can further enhance an engineer’s marketability and earning potential. For example, an engineer with a Master’s degree in aerospace engineering specializing in autonomous flight control systems is likely to command a higher salary than a general aerospace engineer with a Bachelor’s degree. The reason being their specialized skill set directly aligns with the demands of the industry. Moreover, continued learning and professional development, such as attending workshops, obtaining certifications, or participating in industry conferences, further contribute to an engineer’s expertise and earning power.
In conclusion, education plays a critical role in shaping the compensation landscape for aerospace autonomous systems engineers. Higher degrees, specialized fields of study, and continuous learning are all strong indicators of increased earning potential. Employers value the advanced knowledge and specialized skills acquired through formal education, and they are willing to pay a premium for engineers who can demonstrate a strong foundation in the theoretical principles and practical applications of autonomous systems. However, it is crucial to note that education is only one component of the overall compensation package; experience, location, and skills also play significant roles.
4. Company Size
Company size significantly influences the compensation offered to aerospace autonomous systems engineers. Larger corporations generally possess more substantial financial resources, enabling them to offer more competitive salaries and benefits packages compared to smaller companies or startups. This disparity arises from several factors, including the scale of projects undertaken, the complexity of technological challenges addressed, and the overall organizational structure. For example, a major aerospace defense contractor involved in developing autonomous spacecraft is likely to offer a higher salary than a small drone startup focused on agricultural applications due to the increased complexity and strategic importance of the projects.
The size of a company often dictates the level of specialization required within engineering roles. Larger organizations may have dedicated teams focused on specific aspects of autonomous systems, such as sensor integration, path planning, or control algorithm development. This specialization can lead to increased efficiency and expertise but may also limit an engineer’s exposure to the broader system. Smaller companies, on the other hand, may require engineers to wear multiple hats, demanding a broader skill set but potentially offering less opportunity for deep specialization. Furthermore, larger companies typically have more established career development programs, providing opportunities for advancement and salary growth, while smaller companies may offer a more direct path to leadership roles and equity ownership. A practical example of this is the difference in compensation and career trajectory between an engineer at Boeing versus an engineer at a new autonomous aircraft company; the former provides structured growth with established salary bands, while the latter potentially offers substantial equity but possibly lower initial pay.
In summary, company size is a critical consideration when evaluating compensation packages for aerospace autonomous systems engineers. Larger companies tend to offer higher salaries, more comprehensive benefits, and structured career development paths, while smaller companies may provide opportunities for broader responsibilities, direct leadership roles, and equity ownership. Understanding the trade-offs between these factors is essential for engineers seeking to optimize their career paths and maximize their earning potential. The challenges of choosing between the stability and resources of a large company versus the potential for rapid growth and innovation in a smaller one must be carefully weighed against individual career goals and financial priorities.
5. Skills
Technical proficiencies stand as a primary determinant of compensation for aerospace autonomous systems engineers. The specific skills an engineer possesses directly influence their ability to contribute to project success and organizational value, which, in turn, affects their earning potential.
- Programming Languages and Software Proficiency
Expertise in programming languages such as C++, Python, and MATLAB is crucial for developing and implementing complex algorithms. Proficiency in simulation software (e.g., Simulink) and embedded systems programming further enhances an engineer’s ability to design, test, and deploy autonomous systems. For instance, an engineer skilled in developing autonomous navigation algorithms in C++ for a drone will be more valuable than one without these capabilities, leading to a higher compensation.
- Control Systems Design and Implementation
A deep understanding of control theory, including classical and modern control techniques, is essential for designing stable and robust autonomous systems. Experience with sensor fusion, estimation algorithms (e.g., Kalman filters), and path planning techniques is also highly valued. For example, engineers capable of designing fault-tolerant control systems for autonomous aircraft or spacecraft command a premium due to the critical nature of these systems.
- Robotics and Artificial Intelligence
Knowledge of robotics principles, including kinematics, dynamics, and motion planning, is vital for developing autonomous robots used in aerospace applications. Familiarity with artificial intelligence techniques, such as machine learning and computer vision, enables engineers to create intelligent systems that can perceive and react to their environment. Individuals who can implement AI to improve autonomous navigation or system efficiency may earn significantly more.
- Hardware Integration and Testing
The ability to integrate software algorithms with hardware components, such as sensors, actuators, and microprocessors, is a critical skill. Experience with hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) simulation and flight testing is also highly valued, as it allows engineers to validate the performance and reliability of autonomous systems in realistic scenarios. An engineer proficient in testing and validating autonomous system hardware to meet rigorous industry standards will likely be highly sought after and command a competitive salary.
The accumulation and demonstration of these skills directly correlate with increased compensation for aerospace autonomous systems engineers. Employers prioritize candidates who possess a strong technical foundation, practical experience, and the ability to solve complex problems, resulting in enhanced earning potential.
6. Demand
The demand for aerospace autonomous systems engineers exerts a significant influence on their compensation. An increase in demand generally leads to higher salaries as companies compete to attract and retain qualified professionals.
- Growth of the Autonomous Systems Industry
The expansion of the autonomous systems sector across various applications, including unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), autonomous spacecraft, and advanced robotics, directly drives the demand for engineers with expertise in these areas. As companies invest heavily in developing and deploying autonomous technologies, the need for skilled engineers increases, thereby elevating the compensation levels to secure top talent. For example, the proliferation of drone technology in various industries, such as agriculture, logistics, and surveillance, has significantly increased the demand for engineers specializing in autonomous drone systems.
- Defense and National Security Applications
The defense sector’s reliance on autonomous systems for surveillance, reconnaissance, and autonomous weapon systems contributes substantially to the demand for these engineers. Government agencies and defense contractors are continuously seeking engineers capable of developing and implementing advanced autonomous capabilities, leading to increased salary opportunities. The development of autonomous navigation systems for military aircraft, for instance, necessitates skilled engineers, pushing up the demand and associated compensation.
- Research and Development Investments
Significant investments in research and development (R&D) related to autonomous systems drive the demand for engineers. Companies and research institutions engaged in cutting-edge R&D require highly skilled engineers to innovate and develop new autonomous technologies, contributing to higher salaries. For example, the ongoing research into autonomous vehicles and spacecraft propulsion systems creates a constant need for specialized engineers.
- Skills Gap and Talent Shortage
A persistent skills gap and talent shortage in the field of autonomous systems engineering intensifies the demand for qualified professionals. As the industry struggles to find enough engineers with the necessary expertise, companies are compelled to offer more competitive salaries and benefits to attract and retain the limited talent pool. The specific skills in high demand, such as machine learning, robotics, and control systems, command a premium in the compensation packages offered.
The interplay between these factors demonstrates the direct relationship between demand and the compensation of aerospace autonomous systems engineers. As the autonomous systems industry continues to evolve and expand, the demand for skilled engineers will likely remain high, ensuring competitive salaries and attractive career opportunities within the field. The increasing reliance on autonomous systems in both commercial and defense applications guarantees a continued need for professionals with specialized knowledge and expertise, solidifying the link between demand and compensation.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions and answers address common inquiries and clarify misconceptions regarding the earning potential for professionals in this specialized engineering field.
Question 1: What is the average starting compensation for an aerospace autonomous systems engineer with a bachelor’s degree?
The initial earning potential for such a position typically ranges from $75,000 to $95,000 annually, contingent upon factors such as geographic location, the specific employer, and any prior internship experience.
Question 2: How does obtaining a master’s degree influence an aerospace autonomous systems engineer salary?
Possessing a master’s degree generally leads to a salary increase ranging from 10% to 20% compared to an engineer with only a bachelor’s degree. The advanced knowledge and specialized skills acquired during graduate studies contribute to a higher earning potential.
Question 3: Which geographic locations offer the highest earning potential for aerospace autonomous systems engineers?
Regions with a high concentration of aerospace companies and research institutions, such as Southern California, the Seattle metropolitan area, and the Boston metropolitan area, typically offer the most competitive compensation packages.
Question 4: What technical skills are most valuable and contribute to higher compensation in this field?
Expertise in programming languages (C++, Python, MATLAB), control systems design, robotics, artificial intelligence, and hardware integration are highly valued and command premium salaries.
Question 5: How does experience level influence compensation for aerospace autonomous systems engineers?
Compensation increases with experience, reflecting enhanced proficiency and the ability to manage complex projects. Engineers with 5-10 years of experience typically earn significantly more than entry-level engineers.
Question 6: How does company size affect compensation in this engineering role?
Larger corporations typically offer more competitive salaries and comprehensive benefits packages compared to smaller companies or startups due to their greater financial resources and project scale.
In summary, compensation for aerospace autonomous systems engineers is influenced by a combination of factors including education, location, skills, experience, and company size. Continuous professional development and specialization in high-demand areas are crucial for maximizing earning potential.
The subsequent section will delve into future trends and projections related to compensation in this dynamic and rapidly evolving field.
Aerospace Autonomous Systems Engineer Salary
This exploration has illuminated the multifaceted determinants of compensation for aerospace autonomous systems engineers. Education, experience, location, skills, and company size are critical factors influencing earning potential within this specialized field. A comprehensive understanding of these elements is essential for both employers seeking to attract top talent and engineers aiming to maximize their career prospects.
The dynamic nature of the aerospace and autonomous systems industries suggests continued growth and innovation, ensuring a sustained demand for skilled engineers. Vigilance regarding emerging technologies, coupled with a commitment to continuous professional development, will be paramount for maintaining a competitive advantage and securing optimal compensation in this ever-evolving landscape.