Entities operating within the aviation and space sectors, and whose ownership is distributed among the general public through shares listed on stock exchanges, represent a distinct subset of businesses. Boeing, Airbus, and Lockheed Martin are well-known examples of this classification, where anyone can purchase a portion of their equity.
The availability of stock market investment allows these organizations to raise capital more easily, funding research and development, expansion, and acquisitions. The transparency associated with being listed on a public exchange subjects them to increased scrutiny, potentially enhancing accountability and efficiency. Historically, publicly listed status has propelled growth and innovation within the field.
This overview will delve into various aspects of these enterprises. These aspects include financial performance, industry trends, the impact of regulatory environments, and considerations for investors navigating this complex landscape.
This section provides critical insights for stakeholders considering involvement with firms in the aerospace sector whose shares are openly traded.
Tip 1: Conduct Thorough Due Diligence: Before investing, meticulously examine financial statements, including balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements, over several years. Analyze key ratios such as price-to-earnings (P/E), debt-to-equity, and return on equity (ROE) to gauge financial health and performance.
Tip 2: Understand Industry Dynamics: The aviation and space industries are subject to cyclical patterns, technological advancements, and geopolitical influences. Stay informed about emerging trends, such as electric propulsion, autonomous flight, and space tourism, and their potential impact on the company’s prospects.
Tip 3: Assess Regulatory Environment: Heavily regulated sectors, such as aviation and space exploration, are significantly affected by government policies and international agreements. Monitor regulatory changes and their potential consequences for companies’ operations and profitability.
Tip 4: Evaluate Competitive Landscape: The aerospace industry features a mix of established players and emerging entrants. Assess the competitive advantages of the entity under consideration, including its technological capabilities, market share, and customer relationships.
Tip 5: Consider Geopolitical Risks: International tensions, trade disputes, and security concerns can significantly influence aviation and space ventures. Evaluate the potential impact of geopolitical events on the company’s operations, supply chains, and market access.
Tip 6: Scrutinize Management Team: A capable and experienced management team is crucial for navigating the complexities of the aerospace sector. Examine the backgrounds, track records, and strategic vision of the company’s leadership.
Tip 7: Diversify Investment Portfolio: As with any investment, it is essential to diversify across multiple companies and asset classes to mitigate risk. Avoid concentrating investment holdings in a single company or industry.
Applying these guidelines can enhance the decision-making process when considering investments in organizations with publicly available stock in the aerospace arena.
The subsequent sections delve into additional considerations for analyzing this investment class.
1. Financial Performance
The financial performance of publicly traded aerospace companies serves as a crucial indicator of their operational efficiency, strategic effectiveness, and overall investment potential. Publicly traded status mandates transparency, requiring these entities to disclose detailed financial statements, including revenue, expenses, profits, assets, and liabilities. Consequently, financial performance metrics directly influence investor confidence and stock valuation. For instance, a company reporting consistent revenue growth and strong profit margins is likely to attract greater investment, increasing its market capitalization. Conversely, declining financial performance can lead to decreased stock prices and potential shareholder activism.
Aerospace firms’ financial health is inextricably linked to their ability to secure government contracts, develop innovative technologies, and navigate complex supply chains. Companies such as Boeing and Airbus invest significantly in research and development; their financial performance reflects the success of these investments. Failure to secure key contracts or delays in product development can negatively impact revenue projections and profitability. Moreover, macroeconomic factors, such as fluctuations in fuel prices and interest rates, directly affect the cost structure and profitability. Therefore, in-depth analysis of key financial ratios, cash flow analysis, and balance sheet strength is necessary to ascertain the long-term viability of such organizations.
In summary, the financial performance of publicly traded aerospace firms is a critical factor in their success and valuation. It is a composite measure of strategic decisions, operational effectiveness, and market conditions. Transparency in financial reporting allows for informed investment decisions, while consistent performance drives investor confidence and long-term growth. Challenges stemming from economic volatility or technological disruption necessitate ongoing monitoring and strategic adaptation to maintain financial stability and stakeholder value.
2. Market Capitalization
Market capitalization, a key metric representing the total value of a publicly traded company’s outstanding shares, is a significant indicator of size, investor confidence, and influence within the aerospace sector. For firms in aviation and space whose shares are available for public purchase, market capitalization directly reflects the aggregated perception of their current value and future potential.
- Calculation and Representation
Market capitalization is derived by multiplying the current share price by the total number of outstanding shares. This figure represents the hypothetical cost to acquire all of a company’s publicly traded stock at the current market price. A high market capitalization signifies a large, well-established entity, while a lower capitalization may indicate a smaller, more volatile enterprise.
- Investor Sentiment and Valuation
Market capitalization is influenced by investor sentiment regarding the company’s prospects. Positive news, technological advancements, or securing lucrative contracts can drive up the share price, increasing market capitalization. Conversely, negative reports, regulatory setbacks, or economic downturns can decrease share value and capitalization. Changes in market capitalization reflect the collective assessment of future performance.
- Benchmarking and Comparison
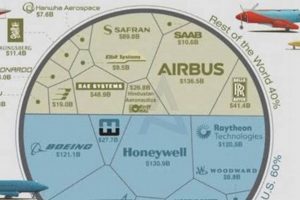
Market capitalization provides a benchmark for comparing the relative size and importance of different aerospace firms. For example, comparing the market capitalization of Boeing and Airbus offers insights into their respective positions within the global commercial aviation market. These comparisons can assist investors in evaluating investment opportunities and assessing the competitive landscape.
- Access to Capital and Growth Potential
Companies with higher market capitalizations generally have easier access to capital through equity offerings or debt financing. A larger market capitalization demonstrates financial strength and investor confidence, enabling the entity to secure favorable terms for borrowing or raising capital. This, in turn, facilitates investment in research and development, expansion initiatives, and acquisitions, contributing to long-term growth potential.
In summary, market capitalization provides a comprehensive snapshot of how the investment community perceives the overall worth of organizations in the aerospace sector whose shares are traded publicly. Changes in this metric are vital for evaluating organizational performance, potential for growth, and comparative position within the aviation and space domain.
3. Industry Trends
Industry trends exert a significant influence on the valuation and strategic direction of aerospace firms with publicly traded stock. These trends encompass technological advancements, shifts in consumer demand, regulatory changes, and macroeconomic factors. Aerospace organizations are compelled to adapt to these trends to maintain competitiveness and investor confidence, thereby impacting their stock performance. For example, the growing emphasis on sustainable aviation necessitates investment in electric or hybrid-electric propulsion systems. Companies that proactively embrace these technologies may attract greater investment and achieve higher valuations.
Conversely, companies that fail to adapt to changing industry trends may experience decreased investor interest and declining stock prices. The COVID-19 pandemic, for instance, substantially reduced air travel demand, negatively affecting the revenue and stock performance of aircraft manufacturers like Boeing and Airbus. However, companies that diversified into space exploration or defense sectors experienced more stable performance. Furthermore, regulatory shifts, such as stricter emissions standards, can necessitate costly upgrades or modifications to existing aircraft fleets, impacting short-term profitability but potentially leading to long-term competitive advantages for companies with compliant products.
In conclusion, understanding prevailing industry trends is critical for evaluating the potential risks and opportunities associated with publicly traded aviation and space corporations. Successfully navigating these trends is integral to sustaining financial performance and attracting investor support. Those with publicly available stock must demonstrate the capacity to anticipate and adapt to industry changes to remain competitive and deliver value to shareholders.
4. Regulatory Oversight
Regulatory oversight exerts a profound influence on aerospace entities with publicly traded stock. These organizations operate within a complex framework of international and domestic regulations governing safety, environmental impact, and security. Compliance with these standards is not merely a legal requirement; it directly affects operational costs, market access, and investor confidence. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the United States and the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) represent primary regulatory bodies that establish and enforce these standards.
Stringent regulations can lead to increased research and development expenditures as companies strive to meet evolving environmental mandates, such as reduced emissions or noise pollution. Non-compliance, on the other hand, can result in substantial fines, operational restrictions, or even the grounding of aircraft, leading to significant financial losses and reputational damage. The Boeing 737 MAX crisis serves as a clear example of how failures in regulatory compliance can impact an aerospace company’s market value and financial stability. The grounding of the aircraft due to safety concerns prompted intense scrutiny from regulatory agencies worldwide and led to billions of dollars in losses. Furthermore, the Defense Contract Audit Agency (DCAA) provides regulatory financial oversight, demanding an additional layer of compliance and monitoring over business processes.
In conclusion, regulatory oversight is an inextricable component of publicly traded aerospace companies. These regulations, while often viewed as constraints, also drive innovation and enhance safety, ultimately contributing to long-term sustainability. Understanding the regulatory landscape is crucial for investors assessing the risks and opportunities within the aerospace sector. Successfully navigating these oversight mechanisms is essential for these companies to maintain their financial viability and public trust.
5. Technological Innovation
Technological innovation serves as a primary driver for the growth, competitiveness, and valuation of aerospace companies whose shares are publicly traded. These firms operate in a sector characterized by rapid technological advancements, necessitating continuous investment in research and development to maintain market leadership and meet evolving customer demands. The ability to innovate effectively directly impacts financial performance, stock valuation, and long-term sustainability.
- Advanced Materials and Manufacturing
The development and adoption of advanced materials, such as carbon fiber composites and titanium alloys, enhance aircraft performance, reduce fuel consumption, and extend service life. Similarly, advanced manufacturing techniques, including additive manufacturing (3D printing), enable the production of complex components with greater precision and efficiency. Aerospace organizations that successfully integrate these innovations, like GE Aviation with its 3D-printed fuel nozzles, gain a competitive edge, attracting investors and driving up their stock value. The transition to lighter, more durable aircraft materials increases operational efficiency and lowers maintenance costs, directly impacting profitability.
- Autonomous Systems and Robotics
Investment in autonomous systems and robotics is transforming aircraft manufacturing, maintenance, and operations. Autonomous drones are utilized for infrastructure inspection, reducing the risks and costs associated with manual inspection methods. The development of autonomous flight systems for commercial aircraft promises to improve safety, reduce pilot workload, and optimize fuel efficiency. Boeing’s work in autonomous flight technology, though currently facing challenges, aims to reshape air travel in the long term. Companies spearheading these innovations are likely to capture significant market share and attract investor interest.
- Digitalization and Data Analytics
Digitalization and data analytics are revolutionizing aircraft design, maintenance, and operations. The use of digital twins allows engineers to simulate aircraft performance under various conditions, optimizing design and reducing development time. Predictive maintenance algorithms analyze sensor data from aircraft to identify potential failures before they occur, minimizing downtime and reducing maintenance costs. Rolls-Royce’s utilization of data analytics to monitor engine performance and provide predictive maintenance services exemplifies this trend. These digital capabilities improve operational efficiency and safety, positively influencing investor perceptions.
- Sustainable Technologies
Growing environmental concerns drive investment in sustainable technologies, including electric propulsion, alternative fuels, and aerodynamic improvements. Airbus and Boeing are actively developing electric and hybrid-electric aircraft to reduce carbon emissions and meet increasingly stringent environmental regulations. Investment in sustainable technologies not only enhances a company’s environmental credentials but also positions it for long-term success as environmental regulations become more stringent. Companies that prioritize sustainable technologies are more likely to attract environmentally conscious investors and secure government support.
These facets of technological innovation, ranging from materials science to sustainable practices, are critical determinants of success for aerospace companies whose shares are publicly traded. Successful integration of these innovations enhances competitiveness, attracts investment, and ensures long-term sustainability in a rapidly evolving industry. Companies demonstrating a commitment to technological leadership are poised to deliver superior returns to their shareholders.
6. Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape within the aerospace sector profoundly shapes the strategies, valuations, and long-term viability of aviation and space firms with publicly traded stock. The dynamics of this landscape are defined by factors influencing market share, technological advancement, regulatory compliance, and the ability to secure lucrative contracts.
- Market Share and Key Players
Dominance in specific market segments influences the financial performance of publicly listed aerospace entities. Companies such as Boeing and Airbus control significant portions of the commercial aircraft market, directly impacting revenue streams and overall profitability. Competition for government defense contracts from firms like Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman further exemplifies the interplay between market share and financial success. Investors closely monitor these competitive dynamics to assess the long-term growth potential of each enterprise.
- Technological Innovation and Differentiation
The capacity for technological innovation serves as a critical differentiator within the competitive landscape. Companies that successfully develop and deploy cutting-edge technologies, such as SpaceX with its reusable rocket technology, gain a competitive advantage. These advancements not only attract investors but also disrupt established market norms, compelling other firms to innovate or risk losing market share. Publicly traded firms that lag in technological advancement may face declining valuations and diminished prospects.
- Barriers to Entry and Consolidation
High barriers to entry, due to substantial capital requirements and regulatory hurdles, limit the number of viable competitors in the aerospace sector. This often leads to consolidation, as larger firms acquire smaller, specialized entities to expand their capabilities or market reach. Mergers and acquisitions, such as United Technologies’ acquisition of Rockwell Collins, reshape the competitive landscape, creating new market dynamics that influence investor sentiment toward the involved organizations.
- Global Supply Chains and Geopolitical Factors
Aerospace firms rely on complex global supply chains, making them susceptible to geopolitical risks and trade disputes. Disruptions in these supply chains, such as those caused by international conflicts or trade restrictions, can negatively impact production schedules and financial performance. Companies with diversified supply chains and strong risk management strategies are better positioned to navigate these challenges, enhancing their competitive resilience and investor appeal.
Collectively, these facets of the competitive landscape directly impact the financial health and market positioning of aviation and space enterprises with publicly traded stock. The ability to navigate these competitive pressures, innovate effectively, and manage global supply chains distinguishes market leaders from laggards, ultimately influencing investor confidence and long-term shareholder value.
7. Investor Sentiment
Investor sentiment, representing the overall attitude or feeling of investors toward a particular security or market, significantly impacts the valuation and performance of publicly traded aerospace companies. This sentiment, often driven by factors beyond pure financial metrics, can lead to fluctuations in stock prices irrespective of a company’s underlying fundamentals. For example, positive news regarding a successful test flight of a new aircraft model can trigger a surge in investor optimism, driving up the stock price of the associated company. Conversely, reports of safety incidents or regulatory setbacks can quickly erode investor confidence, leading to a sell-off and a decline in market capitalization. Understanding this interplay between sentiment and valuation is crucial for stakeholders in the aerospace sector.
Several real-world examples underscore the significance of investor sentiment. During periods of heightened geopolitical tensions or increased defense spending, defense-oriented aerospace companies often experience a boost in investor confidence, reflecting expectations of increased government contracts. Similarly, advancements in space exploration or the development of innovative technologies, such as reusable rockets, can generate excitement and attract investment. However, negative events, such as project delays, cost overruns, or ethical concerns, can swiftly reverse this positive sentiment. The long-term grounding of the Boeing 737 MAX due to safety concerns offers a compelling case study, where eroded investor confidence led to significant financial losses and reputational damage, highlighting the importance of maintaining investor trust through transparency and accountability.
In conclusion, investor sentiment serves as a critical, albeit often volatile, component in the valuation of publicly traded aerospace firms. While financial performance and technological innovation remain essential drivers, the collective perception of investors can amplify or diminish the impact of these factors. Successfully managing investor relations, maintaining transparency, and delivering on promises are essential strategies for aerospace companies seeking to cultivate positive investor sentiment and ensure long-term stability and growth. Recognizing the psychological underpinnings of market behavior is therefore as crucial as analyzing balance sheets and production forecasts.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses commonly encountered inquiries concerning aerospace companies whose shares are openly traded on public exchanges.
Question 1: What distinguishes aerospace companies publicly traded from private firms in the same sector?
Publicly traded entities are subject to stringent regulatory requirements for financial transparency and reporting, including quarterly and annual filings with securities regulators. This contrasts with private firms, which generally operate with less public disclosure and different capital-raising mechanisms.
Question 2: How does the regulatory environment impact the financial performance of aerospace companies with publicly available stock?
Regulatory compliance significantly affects financial performance through costs associated with adherence to safety standards, environmental regulations, and international trade agreements. Stringent oversight can lead to higher operational expenses but also fosters long-term sustainability and investor confidence.
Question 3: What key financial metrics should investors consider when evaluating publicly traded aviation and space businesses?
Essential financial metrics for assessment include revenue growth, profit margins, debt-to-equity ratio, return on equity, and cash flow. Analysis of these metrics provides insights into financial stability and operational efficiency.
Question 4: How do technological advancements influence the market capitalization of aerospace companies with shares trading on public markets?
Technological innovation, such as advancements in electric propulsion or autonomous flight, can significantly enhance a company’s competitive advantage and perceived future value, often leading to increased market capitalization and greater investor interest.
Question 5: What role does investor sentiment play in determining the stock prices of publicly traded firms in the aerospace industry?
Investor sentiment, driven by news events, geopolitical factors, and general market conditions, can significantly influence stock prices independent of underlying financial performance. Understanding investor psychology is crucial for navigating market volatility.
Question 6: How do geopolitical risks and global supply chain disruptions impact these organizations?
Geopolitical instability and disruptions to global supply chains can significantly affect the operational efficiency and financial stability of firms within the aerospace domain. Diversification of supply sources and strategic risk management are essential for mitigating these risks.
This FAQ section provides essential insights into the key considerations for evaluating publicly traded entities in the aviation and space industries.
The following section will provide a brief outlook.
Aerospace Companies Publicly Traded
This examination of aerospace companies publicly traded underscores the multifaceted nature of evaluating these entities. Critical factors, ranging from financial performance and technological innovation to regulatory oversight and investor sentiment, collectively determine their success and valuation. Comprehending these elements allows stakeholders to make informed decisions within this complex sector.
As the aviation and space sectors continue to evolve, driven by technological advancements and geopolitical influences, a vigilant and informed approach remains paramount. Further research and continuous monitoring of market dynamics are essential for navigating the opportunities and challenges that lie ahead in this ever-changing landscape.



![LA Aerospace Companies: Guide & Top Firms [2024] Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions LA Aerospace Companies: Guide & Top Firms [2024] | Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-342-300x200.jpg)