Leading entities within Europe’s aerospace sector are characterized by substantial revenue, extensive workforce, and significant market share. These organizations engage in diverse activities, ranging from the design and manufacturing of aircraft and spacecraft to the development of advanced aerospace technologies and provision of related services. As an illustration, consider a corporation that produces both commercial airliners and defense systems, employing tens of thousands of individuals across multiple countries.
The impact of these major players extends beyond mere economic metrics. They serve as vital drivers of innovation, research and development, and employment creation within the European Union and associated nations. Their activities foster technological advancements, enhance national security capabilities, and contribute significantly to the overall competitiveness of the European economy on a global scale. Furthermore, their historical trajectory reveals a continuous adaptation to evolving market demands and technological breakthroughs.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific examples of prominent organizations and explore their contributions to fields such as commercial aviation, defense, space exploration, and emerging aerospace technologies, thus providing a more detailed understanding of their operations and impact.
Insights into Major European Aerospace Manufacturers
Navigating the landscape of Europe’s foremost aerospace manufacturers necessitates understanding key facets of their operations, strategic priorities, and contributions to the global industry.
Tip 1: Identify Core Competencies: Focus on the specific areas of expertise where each organization excels. For example, one company may be renowned for its expertise in commercial aircraft manufacturing, while another may specialize in defense systems or space technology.
Tip 2: Assess Revenue and Market Share: Analyze publicly available financial data to gauge the economic influence and market position of each entity. Larger revenue streams and significant market share often indicate greater stability and potential for future growth.
Tip 3: Evaluate Research and Development Investments: Examine the extent to which these manufacturers allocate resources to research and development. A strong commitment to innovation is a crucial indicator of their ability to remain competitive and adapt to evolving technological landscapes.
Tip 4: Consider Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations: Observe the nature and scope of partnerships and collaborations with other organizations, both within and outside Europe. These alliances often provide access to new technologies, markets, and resources.
Tip 5: Understand Governmental Influence: Recognize that governmental policies, regulations, and procurement contracts play a significant role in the success of these manufacturers. Analyze how governmental support impacts their operations and strategic decisions.
Tip 6: Monitor Technological Advancements: Stay abreast of the latest technological developments within the aerospace industry and assess how these entities are adopting and integrating these advancements into their products and services.
Tip 7: Analyze Workforce Composition and Skills: The skill and expertise of the workforce are critical factors in determining the manufacturing quality and innovation capabilities. Review the educational backgrounds and skill sets of employees in those companies.
These insights enable a more informed perspective on the operational dynamics, strategic considerations, and overall significance of Europe’s foremost aerospace organizations.
The concluding section will summarize these insights and offer a final perspective on the broader implications for the aerospace industry.
1. Revenue Generation
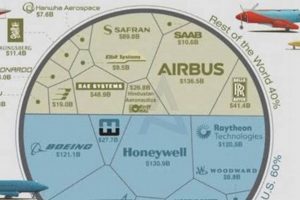
Revenue generation stands as a critical determinant of the size and influence of European aerospace entities. The capacity to generate substantial revenue streams directly enables these companies to invest in research and development, expand manufacturing capabilities, and secure larger market shares. Without consistent and significant revenue, organizations are limited in their ability to compete effectively on a global scale. For example, Airbus’s ability to invest heavily in new aircraft designs, like the A350, is directly attributable to its substantial revenue from aircraft sales and related services. This investment, in turn, allows them to compete effectively with Boeing and maintain its position as one of the largest aerospace companies.
The composition of revenue streams for these organizations is diverse, often encompassing commercial aircraft sales, defense contracts, space exploration initiatives, and related services such as maintenance and training. A robust and diversified revenue base provides resilience against economic downturns or shifts in market demand. Consider Safran, which generates revenue from aircraft engines, nacelles, and various aerospace equipment. Their diverse product portfolio allows them to mitigate risks associated with fluctuations in specific market segments. Successful revenue generation also strengthens their bargaining power in negotiations with suppliers and customers, resulting in more favorable terms and increased profitability.
In summary, revenue generation is an indispensable element for maintaining and expanding the footprint of Europe’s major aerospace companies. It fuels innovation, enables strategic investments, and underpins global competitiveness. Challenges lie in navigating economic cycles, geopolitical shifts, and technological disruptions, which necessitate adaptable strategies to sustain revenue streams and ensure long-term viability within the dynamic aerospace landscape.
2. Workforce Size
The workforce size of leading European aerospace entities is directly proportional to their scope of operations, manufacturing output, and technological innovation capabilities. A substantial workforce allows these organizations to undertake complex projects, manage extensive supply chains, and maintain competitiveness in the global market. The size of the workforce reflects the scale of the company’s undertakings, from aircraft assembly to research and development of new technologies. Airbus, for instance, maintains a large, highly skilled workforce to manage the intricacies of designing, manufacturing, and supporting its commercial and military aircraft.
Moreover, the composition of the workforce, including the proportion of engineers, technicians, and skilled laborers, is a critical factor. A highly skilled workforce enables companies to develop cutting-edge technologies, improve manufacturing processes, and ensure the quality and reliability of their products. Rolls-Royce, a major player in aero-engine manufacturing, employs a significant number of engineers and technicians to drive innovation in engine design and performance. Similarly, Thales relies on a large workforce of specialists to develop sophisticated avionics, defense systems, and cybersecurity solutions. These factors enable the success and sustainability of large-scale enterprises.
In summary, workforce size is not merely a numerical indicator; it is a reflection of operational capacity, technological expertise, and the ability to compete effectively within the global aerospace arena. Maintaining a skilled and adaptable workforce is a significant challenge, requiring ongoing investment in training and education. The relationship between workforce size and company performance is central to understanding the dynamics of European aerospace.
3. Technological Advancement
Technological advancement forms a cornerstone of success for the largest European aerospace companies. The relentless pursuit of innovation is not merely a strategic option but a necessity for survival and leadership in this highly competitive sector. These companies engage in continuous research and development to enhance aircraft performance, improve fuel efficiency, develop more sustainable technologies, and create advanced defense systems. For instance, Airbus’s ongoing development of hydrogen-powered aircraft and Safran’s advancements in more efficient jet engines directly exemplify the impact of technological progress.
The impact of technological advancement extends to enhanced operational efficiency and cost reduction. The implementation of advanced materials, such as composites, lowers aircraft weight, reducing fuel consumption and emissions. Automation in manufacturing processes improves productivity and reduces labor costs. Furthermore, these companies benefit from the ability to offer cutting-edge technologies to customers, thereby commanding premium pricing and securing long-term contracts. Examples include enhanced avionics systems for improved flight control and safety, and advanced cybersecurity solutions for protecting aircraft and data. Investments in technological advancement therefore yield practical and tangible benefits for the aerospace sector.
In summary, technological advancement is intrinsically linked to the success and sustainability of the largest European aerospace companies. Their ability to invest in, develop, and deploy new technologies differentiates them in the global market, driving efficiency, enhancing performance, and contributing to long-term growth. This persistent focus on innovation ensures they remain at the forefront of the aerospace industry, addressing future challenges and opportunities with advanced solutions.
Market share serves as a critical indicator of the competitive strength and overall success of leading European aerospace entities. It reflects a company’s ability to capture a significant portion of the total industry revenue within specific product or service categories, directly influencing profitability, growth prospects, and long-term sustainability.
- Commercial Aircraft Dominance
Within the commercial aviation sector, market share is often determined by the number of aircraft orders and deliveries. Airbus, for instance, competes directly with Boeing for global dominance, with market share fluctuating based on technological innovation, pricing strategies, and customer preferences. A larger share in this segment translates to greater revenue, enhanced brand recognition, and the potential for future growth.
- Defense Sector Procurement
Market share in the defense sector depends significantly on government procurement contracts and international arms sales. Companies like BAE Systems and Thales rely on securing lucrative defense contracts to maintain their market position. Winning these contracts not only generates revenue but also strengthens relationships with governments and enhances technological capabilities, further reinforcing their competitiveness.
- Space Exploration Ventures
In the burgeoning space exploration sector, market share is influenced by participation in space missions, satellite launches, and the development of space-related technologies. Companies like ArianeGroup compete for contracts with space agencies and private space companies, aiming to increase their market share by providing reliable launch services and advanced space technologies. A larger share in this sector signifies technological leadership and the potential for future expansion.
- Aftermarket Services and Support
Beyond initial sales, market share is also determined by aftermarket services, including maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) services, as well as the provision of spare parts. Companies like Safran and Rolls-Royce generate substantial revenue from these services, contributing significantly to their overall market share. Maintaining a strong presence in the aftermarket ensures long-term customer relationships and a stable revenue stream.
In summary, market share is a multifaceted metric reflecting the competitive landscape and operational effectiveness of the largest European aerospace organizations. Success in capturing and maintaining a significant market share necessitates continuous innovation, strategic partnerships, and the ability to adapt to evolving market dynamics. These factors, when combined, determine the long-term viability and influence of these companies within the global aerospace industry.
5. Defense Contracts
Defense contracts represent a pivotal revenue stream and strategic imperative for leading European aerospace entities. These agreements, awarded by national governments and international defense organizations, dictate research and development, production quotas, and technological advancements. The procurement of military aircraft, weapons systems, and associated services is thus a significant driver of activity for these companies.
- Sustained Revenue and Financial Stability
Securing substantial defense contracts provides a predictable and reliable income stream, which is crucial for maintaining financial stability. Companies such as BAE Systems and Thales benefit from multi-year contracts for military aircraft and defense technologies, which allows them to invest in long-term projects and manage operational costs effectively. Revenue from these contracts often exceeds that from commercial ventures, particularly during economic downturns.
- Technological Advancement and Innovation
Defense contracts frequently necessitate the development of cutting-edge technologies with stringent performance criteria. This demand drives innovation in areas such as advanced materials, avionics, and cybersecurity. For example, the Eurofighter Typhoon project, involving several European aerospace companies, has spurred advancements in composite materials and flight control systems. These technological advances have direct implications for both military and civilian applications.
- Geopolitical Influence and Strategic Partnerships
Defense contracts often involve complex political considerations and international collaborations. European aerospace companies, in securing these contracts, play a vital role in shaping national defense strategies and fostering strategic partnerships with other nations. Such collaborations can lead to further contracts and expanded market access. An example is the multinational cooperation involved in the development and production of the A400M Atlas military transport aircraft.
- Employment and Economic Impact
Defense contracts support a substantial number of jobs across various sectors, including engineering, manufacturing, and logistics. The production and maintenance of military equipment require a skilled workforce, contributing to economic growth in regions where these companies operate. Furthermore, the economic impact extends to the supply chain, benefiting numerous smaller businesses that provide components and services to the aerospace industry.
In summary, defense contracts form a vital component of the overall business strategy and financial health of leading European aerospace organizations. The symbiotic relationship between these companies and national defense priorities ensures sustained revenue, technological innovation, geopolitical influence, and substantial economic impact. Understanding the dynamics of defense procurement is essential for evaluating the competitive landscape and long-term viability of these organizations.
6. Space Exploration
Space exploration serves as a critical catalyst for technological advancement and a significant source of revenue for prominent European aerospace entities. Companies engaged in space-related activities, such as satellite manufacturing, launch services, and the development of space infrastructure, derive substantial benefits from both governmental funding and commercial contracts. These activities drive innovation in areas such as advanced materials, propulsion systems, and remote sensing technologies. For example, ArianeGroup, a joint venture between Airbus and Safran, secures substantial revenue through its operation of the Ariane launch system, facilitating access to space for various payloads. Such projects contribute directly to the company’s financial stability and technological prowess.
Beyond financial gains, participation in space exploration enhances a company’s reputation and attracts skilled personnel. The prestige associated with involvement in ambitious space missions, such as the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Rosetta mission, positions these entities as leaders in technological innovation. Furthermore, the technologies developed for space applications often find practical use in terrestrial industries. For instance, satellite-based communication and navigation systems, initially designed for space exploration, have become integral components of modern communication networks and transportation systems. Airbus Defence and Space, for example, leverages its expertise in satellite technology to provide critical Earth observation and communication services.
In conclusion, the connection between space exploration and leading European aerospace organizations is symbiotic. Space exploration drives innovation, provides revenue, and enhances the reputation of these entities, while their expertise and resources are essential for enabling space missions and developing space-related technologies. The future of space exploration hinges on the continued collaboration between governmental agencies, private companies, and research institutions, ensuring that Europe remains at the forefront of space innovation and exploration.
Frequently Asked Questions About Leading European Aerospace Organizations
This section addresses commonly asked questions regarding the major corporations operating within the European aerospace sector, providing factual and concise responses.
Question 1: What criteria define a company as one of the “largest European aerospace companies?”
Several factors are considered. These include annual revenue, employee headcount, market share in key segments (e.g., commercial aircraft, defense, space), research and development investment, and the overall economic impact within the European Union.
Question 2: How do European aerospace firms compare to their American counterparts in terms of market dominance?
The European and American aerospace sectors exhibit distinct strengths. American firms often lead in defense and government contracts, while European companies demonstrate considerable strength in commercial aviation and collaborative space programs. Overall market dominance varies depending on the specific segment under consideration.
Question 3: What are the primary challenges facing these large European aerospace entities?
Key challenges include navigating complex regulatory environments, managing global supply chains, adapting to technological disruptions (e.g., electric propulsion, autonomous flight), addressing environmental sustainability concerns, and competing with emerging aerospace industries in Asia and elsewhere.
Question 4: How do these companies contribute to the European economy and employment?
These organizations serve as significant drivers of economic growth and employment. They contribute substantially to research and development, generate high-skilled jobs, and support a vast network of suppliers and related industries throughout Europe.
Question 5: What role do government subsidies and partnerships play in the success of these companies?
Government subsidies and strategic partnerships are instrumental in the development and competitiveness of European aerospace. Government funding supports research initiatives, infrastructure development, and the creation of a skilled workforce. Collaborative projects foster innovation and enable these companies to compete effectively in the global market.
Question 6: What emerging technologies and trends are these companies focusing on to ensure future growth?
These entities are heavily investing in emerging technologies such as sustainable aviation fuels, electric and hybrid propulsion systems, advanced materials, artificial intelligence for flight operations, and cybersecurity solutions to protect aircraft and data networks.
The answers provided offer a concise overview of the prominent aspects and challenges faced by leading European aerospace companies.
The following section will summarize the overall findings and provide a final perspective on the future of the European aerospace sector.
Concluding Remarks
This exploration of the largest European aerospace companies reveals the sector’s pivotal role in driving economic growth, technological innovation, and defense capabilities across the continent. The revenue generation, workforce size, technological advancements, market share, defense contracts, and space exploration endeavors undertaken by these entities collectively define the landscape of European aerospace. Success hinges on sustained investment in research and development, strategic partnerships, and the ability to adapt to evolving global challenges.
The future of European aerospace depends on its commitment to sustainability, digital transformation, and the cultivation of a highly skilled workforce. Stakeholders should remain vigilant in monitoring technological breakthroughs, regulatory shifts, and geopolitical dynamics to ensure the continued competitiveness and prosperity of this strategically important sector. Ongoing evaluation and adaptation will be essential to navigate the complexities and capitalize on future opportunities within the global aerospace arena.



![Top Michigan Aerospace Companies: [Your Company] & More Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions Top Michigan Aerospace Companies: [Your Company] & More | Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-289-300x200.jpg)