The availability of positions within the aeronautics and astronautics sector in the Lone Star State constitutes a significant element of the regional and national economy. These roles encompass a wide spectrum of activities, including engineering, manufacturing, research, and management, all contributing to the design, development, and production of aircraft, spacecraft, and related technologies. For instance, a mechanical engineer might be involved in designing the structural components of a new commercial airliner, while a software developer could work on the flight control systems for a satellite.
The significance of these professional opportunities lies in their contribution to technological advancement, economic growth, and national security. Historically, Texas has served as a crucial hub for aerospace activities, benefiting from a skilled workforce, a favorable business climate, and strategic investments in research and development. This legacy has fostered a dynamic ecosystem that attracts both established aerospace companies and innovative startups, further solidifying the state’s position as a leader in the field. The presence of these jobs supports not only individual careers but also the broader infrastructure and educational institutions dedicated to advancing aerospace knowledge and capabilities.
The following will examine the factors influencing the growth and evolution of the aeronautical and astronautical industry within Texas, highlighting specific areas of opportunity, the skills and qualifications required for success, and the future outlook for individuals seeking to contribute to this dynamic sector.
Successfully securing a position within the aeronautics and astronautics sector in Texas requires strategic preparation and a comprehensive understanding of industry demands.
Tip 1: Target Specific Companies: Research prominent aerospace entities with operations in Texas, such as Lockheed Martin, Boeing, or SpaceX. Tailor applications to align with their specific needs and projects.
Tip 2: Enhance Technical Skills: Focus on acquiring specialized skills relevant to the aerospace field, including proficiency in CAD software, programming languages (e.g., Python, MATLAB), and knowledge of aerospace engineering principles.
Tip 3: Pursue Relevant Certifications: Obtaining industry-recognized certifications, such as those offered by organizations like the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA), can enhance credibility and demonstrate expertise.
Tip 4: Network Strategically: Attend industry conferences, career fairs, and networking events in Texas to connect with aerospace professionals and learn about potential opportunities. Utilize platforms like LinkedIn to build professional relationships.
Tip 5: Highlight Relevant Experience: Emphasize projects, internships, or research experience related to aerospace in resumes and cover letters. Quantify accomplishments whenever possible to demonstrate impact.
Tip 6: Tailor Resumes and Cover Letters: Customize each application to match the specific requirements and keywords listed in the job description. Showcase relevant skills and experience that directly address the employer’s needs.
Tip 7: Prepare for Technical Interviews: Anticipate technical questions related to aerospace engineering principles, problem-solving skills, and specific technologies. Practice articulating solutions clearly and concisely.
These guidelines offer a foundational framework for individuals seeking to enter or advance within the competitive Texas aeronautics and astronautics employment market. Diligent preparation and targeted efforts are crucial for achieving success.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific career paths within the Texas aerospace industry and provide insights into long-term career development strategies.
1. Engineering
Engineering constitutes a critical component of the aeronautics and astronautics industry within Texas, forming the foundation for innovation, design, and manufacturing processes. These positions are essential for maintaining the state’s competitive edge in the global aerospace market.
- Aerospace Design Engineer
Aerospace design engineers are responsible for conceiving and developing the structural and functional elements of aircraft and spacecraft. This involves utilizing sophisticated software tools to model and simulate performance characteristics, ensuring designs meet stringent safety and performance criteria. A practical example would be an engineer working on the design of a new wing structure for a commercial airliner, optimizing it for fuel efficiency and structural integrity.
- Propulsion Engineer
Propulsion engineers specialize in the design, development, and testing of propulsion systems for aircraft and spacecraft. Their work focuses on improving engine efficiency, reducing emissions, and enhancing overall performance. For example, a propulsion engineer in Texas might be involved in developing more efficient rocket engines for future space missions, contributing to advancements in space exploration.
- Avionics Engineer
Avionics engineers work on the electronic systems used in aircraft and spacecraft, including navigation, communication, and flight control systems. These professionals ensure the integration and functionality of complex electronic components, maintaining safety and reliability. A real-world scenario could involve an avionics engineer developing an advanced autopilot system for a new generation of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).
- Materials Engineer
Materials engineers research, develop, and test new materials for use in aerospace applications. Their work involves selecting materials that can withstand extreme temperatures, pressures, and stresses, ensuring the durability and longevity of aerospace components. An example could be a materials engineer developing a new composite material for use in the construction of spacecraft heat shields, protecting them during atmospheric re-entry.
These engineering disciplines collectively contribute to the advancement of the aeronautics and astronautics sector in Texas, driving innovation and ensuring the continued success of the industry. The expertise of these professionals is essential for maintaining the state’s leadership in aerospace technology and exploration.
2. Manufacturing
The manufacturing sector represents a cornerstone of the aerospace industry within Texas, encompassing the processes and facilities dedicated to producing aircraft, spacecraft, and related components. Its significance lies in its direct contribution to job creation, technological advancement, and economic prosperity within the state.
- Assembly and Integration
Assembly and integration roles are critical to the aerospace manufacturing process, involving the precise joining of various components to create functional systems. Examples include technicians assembling circuit boards for satellite communication systems or workers integrating propulsion systems into aircraft. The accuracy and efficiency of these processes directly impact the reliability and performance of the final aerospace products.
- Machining and Fabrication
Machining and fabrication positions focus on the shaping and forming of raw materials into finished parts and structures. This may involve operating computer numerical control (CNC) machines to create precision components or welding and fabricating large structural elements for aircraft fuselages. The expertise of machinists and fabricators is essential for producing high-quality aerospace parts that meet stringent specifications.
- Quality Control and Assurance
Quality control and assurance personnel ensure that aerospace products meet rigorous standards and regulations. This involves inspecting components, conducting tests, and verifying that manufacturing processes adhere to established procedures. The role of quality control is paramount in preventing defects and ensuring the safety and reliability of aerospace products, thus protecting human lives and property.
- Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management professionals oversee the flow of materials and components from suppliers to manufacturing facilities. This includes coordinating logistics, managing inventory, and ensuring timely delivery of essential resources. Effective supply chain management is critical for maintaining smooth production operations and minimizing disruptions in the manufacturing process.
Collectively, these manufacturing facets contribute to the vibrant ecosystem of the Texas aerospace sector, offering diverse career opportunities and driving economic growth. The skills and expertise of manufacturing professionals are essential for maintaining the state’s competitive advantage in the global aerospace industry.
3. Research roles
Research roles are integral to the advancement of the aerospace sector in Texas. These positions drive innovation, develop cutting-edge technologies, and contribute to the state’s prominence in aeronautics and astronautics. The following outlines key facets of research roles within the context of Texas aerospace opportunities.
- Advanced Materials Development
This research area focuses on creating and testing new materials with enhanced properties suitable for aerospace applications. Examples include developing lightweight composites, heat-resistant alloys, and self-healing materials. These innovations contribute to safer, more efficient aircraft and spacecraft, solidifying Texas’s position as a leader in materials science within the aerospace field.
- Autonomous Systems and Robotics
Research in this area emphasizes the development of autonomous systems and robotics for aerospace operations. This includes designing self-navigating drones, robotic arms for in-space assembly, and automated control systems for aircraft. Texas, with its growing technological infrastructure, serves as a hub for research aimed at improving efficiency, safety, and mission capabilities through automation in aerospace.
- Space Exploration Technologies
This area focuses on research related to space travel, including propulsion systems, life support systems, and radiation shielding. Texas’s historical connection to space exploration, particularly through NASA’s Johnson Space Center, makes it a prime location for research aimed at enabling longer-duration space missions, developing new propulsion technologies, and protecting astronauts from the harsh environment of space.
- Aerodynamics and Flight Control
Research in aerodynamics and flight control concentrates on improving aircraft design and flight dynamics. This involves computational fluid dynamics simulations, wind tunnel testing, and the development of advanced flight control algorithms. These efforts aim to enhance aircraft performance, fuel efficiency, and stability, driving innovation in the design and operation of aircraft within the Texas aerospace industry.
The research conducted in these key areas not only fosters technological advancements but also generates high-skilled employment opportunities, contributing to the economic vitality and global competitiveness of the aerospace sector in Texas. Such research-driven roles are critical for sustaining the state’s leadership position in the national and international aerospace landscape.
4. Management positions
The effective oversight of projects, teams, and resources within the aerospace industry in Texas hinges significantly on qualified individuals in management positions. These roles are essential for guiding technical operations, ensuring regulatory compliance, and driving strategic growth within various aerospace organizations operating in the state.
- Program Management
Program managers oversee specific aerospace projects, ensuring they are completed on time, within budget, and to the required specifications. This role requires a strong understanding of project management methodologies, risk assessment, and stakeholder communication. For example, a program manager at a Texas-based aerospace company might be responsible for overseeing the development of a new satellite system, coordinating engineering, manufacturing, and testing efforts to meet launch deadlines.
- Engineering Management
Engineering managers lead teams of engineers and technicians in the design, development, and testing of aerospace systems. This role involves providing technical guidance, managing resources, and ensuring compliance with industry standards. A practical illustration would be an engineering manager overseeing the design and integration of a new avionics system for commercial aircraft, ensuring its compatibility with existing aircraft systems and adherence to safety regulations.
- Operations Management
Operations managers are responsible for overseeing the day-to-day operations of aerospace manufacturing facilities and ensuring efficient production processes. This role requires a deep understanding of manufacturing principles, supply chain management, and quality control procedures. In Texas, an operations manager might be responsible for optimizing the production line for manufacturing aircraft components, minimizing waste, and improving overall productivity.
- Business Development Management
Business development managers focus on identifying new business opportunities, building relationships with clients, and securing contracts for aerospace products and services. This role requires a strong understanding of the aerospace market, sales strategies, and negotiation skills. A business development manager in Texas might be responsible for pursuing contracts with government agencies or commercial clients for the development and production of aerospace technologies, contributing to the company’s revenue growth and market share.
These management roles collectively ensure the efficient operation and continued growth of the aerospace sector in Texas. Their expertise is vital for fostering innovation, managing complex projects, and maintaining the state’s competitive advantage in the global aerospace industry.
5. Space exploration
Space exploration represents a significant driver for a substantial number of professional opportunities within the Texas aeronautics and astronautics sector. The state’s long-standing involvement in space-related activities, particularly through NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, has fostered a robust ecosystem of companies and institutions dedicated to the research, design, development, and operation of space technologies. The practical effect is a consistent demand for skilled professionals across various disciplines, ranging from engineering and science to management and technical support. For example, the development of new spacecraft requires aerospace engineers, materials scientists, and software developers, while mission operations necessitate flight controllers, data analysts, and communications specialists. These demands directly translate into a broad spectrum of employment possibilities within Texas.
The importance of space exploration as a component of Texas aeronautics and astronautics roles extends beyond direct employment. It also fuels innovation and technological advancement, creating opportunities for spin-off technologies and new businesses. For instance, technologies developed for space missions, such as advanced sensors and communication systems, can find applications in other industries, including medicine, telecommunications, and environmental monitoring. This diffusion of technology creates further economic activity and expands the range of available career paths. The practical significance of understanding this connection lies in the ability to strategically target education, training, and career development efforts to meet the evolving needs of the space sector.
In summary, space exploration serves as a critical stimulus for the creation and evolution of many Texas aeronautics and astronautics job opportunities. Its influence spans direct employment in space-related activities, the generation of spin-off technologies, and the overall strengthening of the state’s economic and technological infrastructure. While challenges remain, such as maintaining funding for space programs and attracting and retaining a skilled workforce, the long-term outlook for space exploration in Texas remains positive, promising continued growth and opportunity within the state’s aerospace sector.
6. Aviation sector
The aviation sector functions as a critical component within the broader landscape of the aeronautics and astronautics industries in Texas, substantially influencing the scope and nature of employment opportunities. This sector encompasses a wide array of activities related to air transportation, aircraft manufacturing, maintenance, and support services. The demand for professionals in this field drives a significant portion of aerospace-related employment within the state. Examples include aircraft mechanics maintaining commercial airline fleets at major Texas airports, engineers designing and testing new aircraft components for manufacturers located within the state, and air traffic controllers managing airspace to ensure safe and efficient air travel. The operational demands of commercial airlines, private aviation companies, and government agencies contribute directly to the creation of aeronautics and astronautics related positions in Texas.
The importance of the aviation sector to the larger scope of Texas aerospace employment stems from its close integration with other aerospace activities. For example, companies specializing in aircraft maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) often require expertise in areas such as materials science, avionics, and structural engineering, mirroring skill sets needed in the broader aerospace industry. This interconnectedness results in a synergistic effect, whereby growth in the aviation sector fosters growth in related areas of aerospace. Further, the presence of major aerospace manufacturers and suppliers within Texas creates a demand for skilled workers in aviation-related roles, supporting a robust ecosystem of technical expertise and innovation. The economic impact of the aviation sector, therefore, extends beyond direct employment in airlines and airports to include a wide range of support industries and service providers.
The connection between the aviation sector and Texas aerospace careers provides both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, the ongoing expansion of air travel and the modernization of aircraft fleets create a steady demand for skilled professionals. On the other hand, the aviation sector is subject to economic fluctuations and regulatory changes, which can impact employment levels. To capitalize on the opportunities and mitigate the risks, individuals seeking careers in Texas aerospace should pursue specialized education and training, stay abreast of industry trends, and develop adaptable skill sets that can be applied across different areas of the aerospace sector. Understanding this dynamic is essential for effectively navigating the Texas aeronautics and astronautics employment landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions About Texas Aerospace Jobs
The following addresses common inquiries regarding professional opportunities within the aeronautics and astronautics sector in Texas.
Question 1: What educational background is typically required for entry-level positions?
A bachelor’s degree in a relevant field such as aerospace engineering, mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, or computer science is generally required for entry-level engineering positions. Some roles may also accept degrees in physics, mathematics, or other related scientific disciplines. Specific requirements may vary based on the employer and the nature of the position.
Question 2: What are the key skills and qualifications sought by employers?
Employers typically seek candidates with strong technical skills, problem-solving abilities, and communication skills. Proficiency in relevant software tools and programming languages is often essential. Certifications related to specific aerospace disciplines may also be advantageous. Demonstrated experience through internships, research projects, or relevant coursework is highly valued.
Question 3: Where are the primary aerospace job centers located in Texas?
Major metropolitan areas, including Houston, Dallas-Fort Worth, and San Antonio, serve as primary centers for aerospace employment in Texas. Houston, in particular, benefits from the presence of NASA’s Johnson Space Center and a concentration of aerospace companies. The Dallas-Fort Worth area hosts a number of large aerospace manufacturers and suppliers. San Antonio is home to military aviation facilities and related industries.
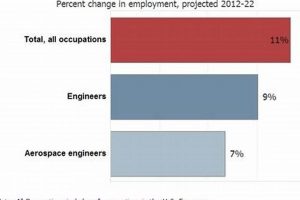
Question 4: What is the typical salary range for aerospace engineers in Texas?
Salary ranges for aerospace engineers in Texas vary based on experience, education, and the specific role. Entry-level positions may offer salaries in the range of \$65,000 to \$85,000 annually. Experienced engineers with advanced degrees can command salaries exceeding \$120,000 or more. These figures are estimates and can be influenced by market conditions and company size.
Question 5: How can I increase my chances of securing a position?
To enhance the likelihood of securing employment, one should focus on acquiring relevant skills and experience, networking with industry professionals, and tailoring resumes and cover letters to specific job requirements. Participating in internships, attending industry conferences, and pursuing advanced education or certifications can also improve competitiveness.
Question 6: What is the outlook for the aerospace industry in Texas?
The aerospace industry in Texas is generally considered to have a positive outlook, driven by factors such as increasing demand for air travel, government investment in space exploration, and the growth of the commercial space sector. The state’s favorable business climate and skilled workforce further contribute to the industry’s growth potential. However, economic conditions and technological advancements can influence the industry’s trajectory.
The answers to these frequently asked questions provide a foundational understanding of the Texas aerospace job market. Further research and engagement with industry resources are recommended for individuals seeking specific career paths.
The subsequent article section will discuss emerging trends and future prospects within the Texas aerospace industry.
Conclusion
This exploration of aeronautics and astronautics sector roles in Texas has highlighted the breadth of opportunities available, spanning engineering, manufacturing, research, and management. Key factors influencing success include targeted skills development, strategic networking, and a comprehensive understanding of industry demands. These professions play a critical role in technological advancement, economic development, and national security.
The future of the aeronautical and astronautical industry in Texas appears promising, yet requires continued investment in education, infrastructure, and innovation to maintain its competitive edge. Those considering a career in the Texas aeronautics and astronautics domain should pursue specialized education, cultivate adaptability, and proactively engage with industry resources to capitalize on the evolving landscape. The Texas aeronautics and astronautics market presents substantial opportunities for those prepared to meet its challenges.