Positions within the aeronautics and space industries located in the Southern California city and county comprise the focus of this discussion. This encompasses roles in engineering, manufacturing, research and development, and related support functions that contribute to the design, production, and maintenance of aircraft, spacecraft, satellites, and associated technologies.
The concentration of these opportunities in this geographic area offers significant economic benefits to the region, attracting skilled labor, fostering innovation, and contributing to local tax revenue. Historically, the area’s strong military presence and established defense contractors have cultivated a robust ecosystem that supports continued growth in these high-technology fields.
The following sections will delve into the specific sectors driving this employment landscape, the types of qualifications and experience sought by employers, and the resources available to individuals pursuing careers in this dynamic and impactful domain.
Maximizing prospects within the aeronautics and space sectors in the specified location requires a strategic approach. The following guidance provides insights into optimizing career advancement.
Tip 1: Specialize Technical Expertise: Developing expertise in a high-demand technical area, such as aerospace engineering, avionics, or composite materials, enhances marketability. Employers prioritize candidates with demonstrable skills applicable to specific project requirements.
Tip 2: Cultivate Security Clearance Eligibility: Many positions, especially those with defense contractors, necessitate security clearance. Understanding the requirements and proactively addressing potential disqualifiers strengthens candidacy.
Tip 3: Network Strategically: Actively participate in industry events, connect with professionals on platforms such as LinkedIn, and attend informational sessions hosted by aerospace companies. Networking expands awareness of available opportunities and facilitates valuable connections.
Tip 4: Target Key Employers: Research prominent aerospace companies and identify specific roles aligned with skills and career goals. Tailoring applications to address the unique requirements of each employer increases the likelihood of success.
Tip 5: Highlight Relevant Experience: When applying, emphasize projects, accomplishments, and quantifiable results directly related to the target position. Demonstrating a track record of successful contributions strengthens the application.
Tip 6: Consider Advanced Education: Pursuing advanced degrees or certifications in specialized areas enhances competitiveness and demonstrates commitment to professional development. A Master’s degree or specialized certification may be advantageous for certain roles.
Tip 7: Leverage Local Resources: Utilize resources such as career centers at local universities, professional associations, and online job boards specializing in aerospace opportunities. These resources provide valuable information, training programs, and networking opportunities.
Effective preparation and a focused approach are essential for navigating the employment market. Adhering to these principles significantly improves prospects for securing a fulfilling and impactful career.
The next section will focus on the long-term outlook for careers in this sector and the emerging trends shaping the future workforce.
1. Engineering Specializations
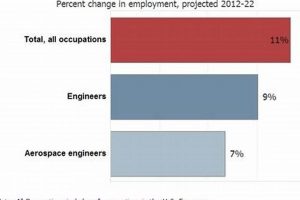
Engineering specializations are a fundamental determinant of the availability and nature of aeronautics and space positions in the Southern California region. The local industry ecosystem relies heavily on a workforce possessing advanced skills in distinct engineering disciplines. The demand for specific skills drives the overall job market, shaping the career paths and educational requirements for individuals seeking entry into this field. For example, the design and integration of unmanned aerial systems (UAS) requires engineers specializing in areas like control systems, robotics, and computer vision. This increased demand directly translates into job creation focused on UAS development and support.
The cause-and-effect relationship between specialized engineering knowledge and job opportunities is significant. The presence of major aerospace companies in the region directly fuels the demand for talent with expertise in fields such as structural analysis, propulsion systems, and materials science. Companies actively recruit engineers with specialized knowledge to address particular design and manufacturing challenges, innovate and produce new products, and remain competitive in the global market. The practical significance lies in the necessity for individuals to focus on developing relevant, in-demand skills, through formal education, targeted training, and gaining experience, to increase their prospects.
In summary, engineering specializations constitute a critical element in the Southern California aerospace job market. The industry’s reliance on advanced technical expertise creates a direct link between specialized skills and employment opportunities. Understanding the demand for specific engineering disciplines enables prospective candidates to strategically align their educational and professional development with the needs of the industry, thereby increasing their chances of securing rewarding and impactful careers. However, this also underscores the challenge of continuous learning and adaptation, as the industry evolves and new technologies emerge.
2. Defense Industry Presence
The significant presence of the defense industry in the Southern California region exerts a powerful influence on the availability and types of aeronautics and space positions. This concentration of defense contractors creates a unique employment landscape characterized by specific requirements and opportunities.
- Government Contracts and Funding
Government contracts represent a primary source of revenue for many aerospace firms. These contracts often dictate the scope and scale of projects, directly impacting the number of engineering, manufacturing, and support roles required. For example, a contract to develop a new missile defense system can create hundreds of new positions across various disciplines.
- Security Clearance Requirements
A substantial proportion of positions within defense-related aerospace firms mandate security clearance. This necessitates background checks and investigations, potentially restricting the pool of eligible candidates. Many employers require candidates to be U.S. citizens and able to meet stringent security criteria.
- Specialized Skill Sets
Defense contracts often demand specialized skills and expertise in areas such as military aircraft design, electronic warfare, and secure communication systems. This creates a demand for engineers, technicians, and scientists with specific training and experience relevant to military applications.
- Innovation and Technology Development
The defense industry fosters innovation and technology development, driving advancements in areas such as propulsion systems, materials science, and sensor technology. This leads to the creation of positions focused on research, development, and testing of cutting-edge technologies.
The interplay between the defense industry and aerospace creates a complex and dynamic job market. Understanding the specific demands and requirements associated with defense-related positions is essential for individuals seeking careers in the field. The region’s continued reliance on defense contracts ensures the long-term significance of this sector in shaping the employment landscape.
3. Research and development
Research and development (R&D) form a critical nexus within the aeronautics and space sector in the Southern California region. This area’s concentration of expertise, coupled with substantial investment in technological advancements, generates a demand for specialized roles and directly shapes the trajectory of career opportunities. R&D initiatives drive innovation, fostering job creation across various disciplines.
- Advanced Materials Development
The pursuit of lighter, stronger, and more heat-resistant materials is a central focus of aerospace R&D. Scientists and engineers explore new alloys, composites, and coatings to enhance aircraft performance and fuel efficiency. This translates to positions for materials scientists, chemical engineers, and mechanical engineers specializing in materials characterization and testing. For instance, the development of ceramic matrix composites for turbine engine components requires expertise in materials processing, high-temperature testing, and computational modeling.
- Propulsion Systems Innovation
Efforts to improve propulsion systems encompass research into more efficient combustion processes, advanced engine designs, and alternative fuels. These initiatives drive demand for aerospace engineers specializing in thermodynamics, fluid dynamics, and combustion. For example, research into scramjet engines for hypersonic flight necessitates engineers with expertise in high-speed aerodynamics, computational fluid dynamics, and high-temperature materials.
- Autonomous Systems and Robotics
The integration of autonomous systems and robotics into aircraft and spacecraft operations represents a growing area of R&D. This includes research into artificial intelligence, machine learning, and sensor technologies. This leads to positions for software engineers, robotics specialists, and electrical engineers specializing in control systems and sensor integration. The development of autonomous navigation systems for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) requires expertise in computer vision, sensor fusion, and path planning algorithms.
- Space Exploration Technologies
R&D efforts focused on space exploration technologies encompass areas such as advanced spacecraft design, life support systems, and planetary science instrumentation. These initiatives drive demand for aerospace engineers, physicists, and planetary scientists. For instance, the development of advanced life support systems for long-duration space missions requires expertise in environmental control, water recycling, and food production in closed-loop environments.
The collective impact of R&D in these areas significantly influences the composition and growth of aeronautics and space positions. The continuous pursuit of technological advancements necessitates a workforce equipped with specialized skills and knowledge. Investment in R&D ensures the continued competitiveness of the sector and creates opportunities for individuals pursuing careers in innovative and impactful roles.
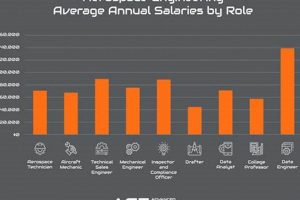
4. Skilled Labor Demand
The demand for skilled labor is a critical factor shaping the landscape. The specialized and technically demanding nature of the work requires a workforce with specific expertise and training, directly influencing the availability and types of employment opportunities.
- Engineering Expertise and the Talent Pipeline
The aeronautics and space sector requires a robust supply of engineers specializing in fields such as aerospace, mechanical, electrical, and software engineering. The talent pipeline, encompassing educational institutions and training programs, must effectively produce graduates and professionals equipped with the necessary skills. A shortage of qualified engineers can constrain growth and innovation, impacting the ability to fill positions and execute projects.
- Specialized Manufacturing and Technician Roles
Manufacturing positions, including machinists, technicians, and assemblers, necessitate proficiency in advanced manufacturing techniques, precision tooling, and quality control. These roles are essential for producing high-quality components and systems that meet stringent aerospace standards. The availability of skilled technicians is crucial for maintaining efficient production processes and ensuring product reliability. The rise of automation and advanced manufacturing technologies further necessitates continuous training and upskilling of the workforce.
- Cybersecurity and Data Science Professionals
With increasing reliance on digital systems and interconnected networks, the demand for cybersecurity professionals and data scientists in the sector has grown significantly. Protecting sensitive data, securing communication networks, and analyzing large datasets are essential for maintaining operational integrity and preventing cyberattacks. These roles require specialized knowledge of cybersecurity protocols, data analytics techniques, and threat intelligence.
- Project Management and Leadership Skills
The successful execution of complex aerospace projects requires strong project management and leadership skills. Project managers are responsible for planning, coordinating, and overseeing all aspects of a project, ensuring that it is completed on time and within budget. Leadership skills are essential for motivating teams, fostering collaboration, and driving innovation. The availability of experienced project managers and leaders is crucial for managing complex projects and achieving organizational goals.
In summation, the robust demand for skilled labor is a defining characteristic of the sector in Southern California. Addressing the talent gap through targeted education, training, and workforce development initiatives is crucial for sustaining growth and competitiveness. The availability of qualified personnel across various disciplines is essential for driving innovation, executing projects, and maintaining the region’s position as a hub for aerospace activity.
5. Security Clearance Requirements
Security clearance requirements represent a significant consideration for individuals pursuing careers within the aeronautics and space sector located in the Southern California region. The presence of numerous defense contractors and government research facilities necessitates a substantial number of positions requiring access to classified information.
- Levels of Clearance and Scope
Security clearances are tiered, with common levels including Confidential, Secret, and Top Secret. The level required depends on the sensitivity of the information accessed. Background investigations are commensurate with the clearance level, scrutinizing an individual’s personal history, financial records, and foreign contacts. For example, a software engineer working on a classified military aircraft program may require a Secret clearance, while a physicist involved in designing advanced weaponry might necessitate a Top Secret clearance.
- Investigation and Adjudication Processes
The clearance process involves a comprehensive investigation conducted by agencies such as the Defense Counterintelligence and Security Agency (DCSA). This includes interviews with the applicant and their references, verification of employment history, and review of criminal records. The information gathered is then adjudicated to determine whether the applicant presents an unacceptable risk to national security. Delays in the adjudication process can impact hiring timelines and project schedules.
- Factors Affecting Eligibility
Numerous factors can affect an individual’s eligibility for security clearance, including criminal history, financial issues (such as bankruptcy or tax delinquency), drug use, and close association with foreign nationals. These issues do not automatically disqualify an applicant, but they trigger closer scrutiny and require thorough explanation. For example, past drug use may be mitigated by demonstrating a period of abstinence and rehabilitation.
- Impact on Career Opportunities
The requirement for security clearance significantly narrows the pool of eligible candidates for many aerospace positions in the region. Individuals without existing clearance may face longer hiring timelines due to the time required to complete the investigation process. Possessing an active security clearance can provide a competitive advantage, increasing an applicant’s attractiveness to potential employers.
The prevalence of security clearance requirements in the Southern California aerospace sector underscores the importance of understanding the application process and maintaining a clean background. Individuals seeking careers in this field should be prepared to undergo thorough background investigations and address any potential issues proactively. The ability to obtain and maintain security clearance is often a prerequisite for accessing a wide range of rewarding career opportunities in this dynamic and technologically advanced industry.
6. Economic Contribution
The presence of aerospace jobs within the San Diego, CA, region demonstrably bolsters the local economy. The aerospace sector’s activities generate significant direct and indirect economic benefits. Direct economic contributions stem from the salaries and wages paid to employees in these positions, resulting in increased consumer spending and tax revenues for local governments. Indirect contributions arise from the sector’s demand for goods and services from other local businesses, creating a multiplier effect. For instance, the procurement of raw materials, specialized equipment, and professional services by aerospace companies supports jobs in manufacturing, logistics, and consulting sectors. The concentration of aerospace expertise also attracts further investment and innovation, strengthening the region’s economic base.
The sector’s role in fostering technological advancement is also a crucial aspect of its economic impact. Aerospace companies often engage in research and development activities, leading to the creation of new technologies that can be applied in other industries. These innovations contribute to increased productivity, improved products, and new business opportunities across the broader economy. For example, advancements in materials science and manufacturing techniques developed for aerospace applications have been adapted for use in medical devices and automotive industries. Moreover, the presence of a skilled aerospace workforce enhances the region’s attractiveness to other high-technology companies, leading to further economic diversification and growth.
In summary, the economic contribution of aerospace jobs in San Diego, CA, extends beyond direct employment figures. The sector’s activities stimulate economic growth through increased spending, support for local businesses, and the creation of technological innovations. Understanding this multifaceted economic impact is crucial for policymakers and business leaders seeking to foster sustainable economic development and maintain the region’s competitive edge in the global economy. Challenges related to workforce development and infrastructure investment must be addressed to ensure the continued prosperity of this vital sector and its contribution to the broader economic landscape.
7. Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are intrinsically linked to the evolution and nature of aeronautics and space positions in San Diego, CA. The region’s robust aerospace sector is driven by continuous innovation, making technological progress a critical component that shapes the demand for specific skills and expertise. As new technologies emerge, the composition and nature of roles within the sector shift, impacting both the required qualifications and the types of projects undertaken. For instance, the increased focus on autonomous systems requires engineers with expertise in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotics. This technological shift necessitates a workforce capable of developing, implementing, and maintaining these advanced systems.
The practical significance of understanding this connection lies in the ability to anticipate future skill requirements and align educational and training programs accordingly. Educational institutions and training providers must adapt their curricula to equip graduates with the skills needed to thrive in an environment of rapid technological change. Similarly, individuals seeking careers must proactively invest in acquiring relevant skills through targeted training, certifications, or advanced degrees. Consider the example of additive manufacturing (3D printing) in aerospace. As this technology becomes more widespread, there is increasing demand for engineers and technicians with expertise in design for additive manufacturing, materials science, and process optimization. This demands focused development initiatives.
In summary, technological advancements are not merely a trend but a fundamental driver of change. The ability to adapt to and leverage new technologies is essential for both individuals and organizations seeking to succeed in the aerospace sector. Continuous investment in research and development, coupled with a commitment to workforce development, is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge and ensuring the continued growth and prosperity of the region. There are challenges to manage to address these technologies. These challenges need to be addressed.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding employment prospects within the aeronautics and space sectors concentrated in San Diego, California. The information presented aims to provide clarity and guidance to individuals considering a career in this dynamic field.
Question 1: What are the primary industries driving the demand for these positions in San Diego?
The demand is primarily fueled by the presence of major defense contractors, aerospace manufacturers, and research institutions. These entities engage in a range of activities, from aircraft design and manufacturing to satellite development and space exploration technologies.
Question 2: What level of education is typically required for entry-level engineering positions?
A bachelor’s degree in a relevant engineering discipline, such as aerospace, mechanical, or electrical engineering, is generally the minimum requirement for entry-level engineering roles. Advanced degrees, such as a Master’s or Ph.D., may be preferred for research-oriented positions.
Question 3: Are security clearances frequently required, and what factors can affect eligibility?
Yes, a significant portion of positions, particularly those with defense contractors, mandate security clearance. Factors affecting eligibility include criminal history, financial issues, drug use, and foreign contacts. The specific requirements vary depending on the level of clearance required.
Question 4: What are some of the most in-demand skills and specializations in the sector?
In-demand skills include expertise in areas such as avionics, propulsion systems, composite materials, cybersecurity, and data analytics. Specializations in areas like artificial intelligence, robotics, and unmanned aerial systems are also highly sought after.
Question 5: Where can individuals find resources to assist in their job search?
Resources include career centers at local universities, online job boards specializing in aerospace opportunities, professional associations, and networking events. Direct engagement with company recruiters is also a valuable strategy.
Question 6: What is the general outlook for this employment market in San Diego?
The long-term outlook is generally positive, driven by continued investment in defense spending, space exploration initiatives, and technological advancements. However, the market is also subject to fluctuations based on economic conditions and government policies.
In summary, pursuing career opportunities in the aerospace sector requires careful planning, targeted skill development, and a proactive approach to networking and job searching. Understanding the specific requirements and dynamics of the market is essential for success.
The subsequent sections will explore emerging trends and future directions within the aeronautics and space employment landscape.
Conclusion
This examination of aerospace jobs in san diego ca has highlighted the multifaceted nature of this sector within a specific geographic locale. Engineering specializations, the robust defense industry presence, ongoing research and development initiatives, and the demand for a skilled workforce each contribute to the configuration of available opportunities. Furthermore, adherence to security clearance protocols and the sector’s significant economic contribution underscore its importance to the region.
Continued vigilance regarding technological advancements and proactive engagement with industry resources will be crucial for both job seekers and established professionals. Sustained growth in this sector necessitates a commitment to education, training, and adaptation to the evolving demands of aerospace engineering and related fields. Future success hinges on a strategic and informed approach.