The discipline encompassing the design, development, testing, and production of aircraft and spacecraft is a crucial sector within the nation’s technological landscape. This field integrates principles of aerodynamics, propulsion, materials science, and structural analysis to create innovative solutions for both atmospheric and space-based applications. Examples of its application range from the development of advanced commercial airliners to the creation of sophisticated satellite systems for communication and remote sensing.
The significance of this expertise lies in its contribution to national security, economic growth, and scientific advancement. Historically, the field has been fostered through government investment in research institutions and defense programs. Benefits extend to improved air transportation infrastructure, enhanced communication networks, and advancements in space exploration capabilities. Furthermore, the sector generates high-skilled employment opportunities and stimulates innovation across various related industries.
The following sections will delve into the educational opportunities available within this specialized area, the key players driving its progress, the ongoing research initiatives shaping its future, and the career prospects for aspiring professionals.
This section provides practical guidance for individuals seeking to establish a successful career trajectory within the specialized field of aerospace engineering in the Indian context.
Tip 1: Emphasize Foundational Knowledge. A strong grasp of fundamental principles in mathematics, physics, and engineering is paramount. This base allows for a deeper understanding of complex aerospace concepts and facilitates problem-solving in real-world scenarios. For example, a thorough understanding of fluid dynamics is crucial for designing efficient aircraft wings.
Tip 2: Pursue Specialization Strategically. The field encompasses various specializations, including aerodynamics, propulsion, structures, and avionics. Selecting a specific area of focus allows for targeted skill development and increases employability. Consider, for instance, specializing in composite materials for aircraft construction, a growing area in modern aerospace.
Tip 3: Gain Practical Experience Through Internships. Hands-on experience is invaluable. Actively seek internships at aerospace companies, research organizations, or government agencies. These experiences provide exposure to industry practices and allow for the application of theoretical knowledge. Participating in a project involving computational fluid dynamics simulation is a relevant example.
Tip 4: Develop Proficiency in Software Tools. The aerospace industry relies heavily on specialized software for design, analysis, and simulation. Gaining proficiency in tools such as CATIA, ANSYS, and MATLAB is essential. Familiarity with these platforms enables effective contribution to engineering projects and streamlines workflows.
Tip 5: Prioritize Strong Communication Skills. Effective communication is crucial for collaborating with engineers from diverse backgrounds and presenting technical information clearly. This includes both written and oral communication skills. Presenting research findings at a conference, for instance, requires strong communication abilities.
Tip 6: Stay Abreast of Industry Trends. The aerospace field is constantly evolving. It is imperative to remain updated on the latest technological advancements, industry standards, and regulatory changes. Subscribing to industry journals, attending conferences, and participating in online forums are effective methods for staying informed.
Tip 7: Network Actively with Professionals. Building a professional network can provide access to valuable mentorship, career opportunities, and industry insights. Attend industry events, join professional organizations, and connect with engineers on platforms like LinkedIn. Networking can facilitate career advancement and provide guidance on navigating the industry.
Adhering to these guidelines will significantly enhance the prospects of securing a rewarding and impactful career contributing to the advancement of aerospace engineering within the country.
The subsequent sections will explore specific career paths and the evolving landscape of opportunities available within the field.
1. Education and Training
Education and training form the bedrock of aerospace engineering in India, dictating the quality and capabilities of its workforce, and ultimately, the advancement of the sector. The availability and rigor of educational programs directly impact the nation’s ability to innovate, design, and manufacture advanced aerospace systems. The following facets highlight key aspects of this critical foundation.
- Undergraduate Programs
Bachelor’s degree programs in aerospace engineering, offered by institutions such as the IITs and IIITs, provide a broad-based foundation in fundamental engineering principles and specialized aerospace subjects. These programs equip students with the theoretical knowledge and practical skills necessary for entry-level positions in the industry. The curriculum typically covers areas like aerodynamics, propulsion, structures, and control systems, preparing graduates to contribute to various aspects of aerospace projects. The quality of instruction and the availability of modern laboratory facilities directly influence the competence of graduating engineers.
- Postgraduate and Doctoral Studies
Master’s and doctoral programs provide opportunities for advanced specialization and research. These programs foster innovation by enabling students to delve deeper into specific areas of interest, such as computational fluid dynamics, composite materials, or space systems engineering. Doctoral research contributes to the development of novel technologies and solutions, driving the advancement of the field. The presence of strong research programs, often linked to government funding or industry collaborations, is crucial for nurturing a culture of innovation and producing highly skilled researchers.
- Vocational Training and Skill Development
Beyond formal degree programs, vocational training institutes and skill development programs play a vital role in providing the specialized skills needed for manufacturing, maintenance, and other technical roles. These programs equip technicians and skilled workers with the practical abilities to operate, maintain, and repair aerospace equipment. The quality and relevance of these programs are essential for ensuring the efficient operation of the industry and maintaining high standards of safety and reliability. These programs contribute significantly to supporting the overall aerospace ecosystem.
- Industry-Academia Collaboration
The strength of the aerospace sector is significantly enhanced by effective collaboration between educational institutions and industry. Joint research projects, industry-sponsored scholarships, and internship programs provide students with real-world experience and expose them to the challenges and opportunities within the aerospace industry. Such partnerships ensure that the curriculum remains relevant to industry needs and that graduates are well-prepared to contribute to the workforce. Active industry participation in curriculum development is a key indicator of a thriving aerospace education ecosystem.
The aforementioned facets illustrate how robust education and training create a highly-skilled workforce, essential for driving innovation and progress within the nations aerospace sector. The effectiveness of these programs directly impacts India’s ability to compete globally in the aerospace market and achieve its strategic goals in space exploration and defense. Investment in high-quality education and training remains a cornerstone for the continued growth and success of aerospace engineering within the country.
2. Research and Development
Research and development (R&D) constitutes a critical engine driving progress within the aerospace engineering sector of India. Investment in R&D directly correlates with advancements in indigenous technology, reduced reliance on foreign imports, and enhanced competitiveness in the global market. For instance, the development of the cryogenic engine for India’s GSLV program exemplifies the impact of sustained R&D efforts. This indigenous capability significantly boosted the nation’s satellite launch autonomy. Without consistent R&D, sustained growth and self-reliance within the domain are unattainable.
The practical significance of this connection is evident in various applications. The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) undertakes extensive R&D to develop cutting-edge aerospace technologies for defense purposes, spanning from unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) to advanced missile systems. Similarly, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) conducts R&D focused on satellite technology, launch vehicle development, and space exploration missions. These efforts not only enhance national security and technological capabilities but also stimulate economic growth by creating high-skilled jobs and fostering innovation across related industries. The development and implementation of advanced navigation systems, such as the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), showcase the tangible benefits of focused R&D in this field.
However, challenges persist. Limited funding, bureaucratic hurdles, and a shortage of skilled personnel can impede R&D progress. Addressing these challenges through increased investment, streamlined processes, and enhanced collaboration between academia, industry, and government is essential for maximizing the impact of R&D on aerospace engineering within India. Continued emphasis on basic research, coupled with translational efforts to convert research findings into practical applications, will determine the nation’s future success in this strategically important sector.
3. Manufacturing Capabilities
The scope of aerospace engineering within India is fundamentally dependent upon its inherent manufacturing capabilities. The ability to produce airframes, engines, avionics, and other critical components directly dictates the nation’s self-reliance and its capacity to engage in both domestic and international aerospace markets. A robust manufacturing sector allows for the translation of engineering designs into tangible products, driving innovation and economic growth. The development of the Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas, for example, necessitated the establishment and enhancement of indigenous manufacturing processes across numerous domains, highlighting the critical interplay between engineering design and production prowess.
The presence of advanced manufacturing facilities, skilled labor, and supportive infrastructure is essential for the success of aerospace ventures. The integration of technologies like additive manufacturing, robotics, and advanced materials processing further strengthens the manufacturing base, enabling the production of complex geometries and high-performance components. Consider the production of satellite components within ISRO facilities, requiring stringent quality control measures and advanced manufacturing techniques to ensure mission success. Enhanced manufacturing capabilities also facilitate the development of a domestic supply chain, reducing dependence on foreign vendors and fostering indigenous expertise. This promotes a sustainable ecosystem for aerospace activities.
Ultimately, the strength of manufacturing capabilities is a key determinant of the competitiveness and sustainability of India’s aerospace engineering sector. Addressing challenges such as technology gaps, workforce skill development, and infrastructure limitations is crucial for realizing the full potential of aerospace engineering endeavors. The synergy between advanced engineering design and robust manufacturing processes is paramount for establishing India as a prominent player in the global aerospace arena.
4. Government Initiatives
Government initiatives are central to the advancement of aerospace engineering within India. These policies, funding programs, and regulatory frameworks establish the foundation upon which the sector develops and expands. A primary example is the “Make in India” program, which actively promotes domestic manufacturing, including aerospace components and systems. This initiative encourages foreign companies to establish production facilities within India, fostering technology transfer and generating employment opportunities. Its impact is visible in the increased indigenous production of aircraft parts and the growing involvement of Indian companies in global aerospace supply chains. Such policies are crucial for building a self-reliant aerospace ecosystem.
Furthermore, government funding for research and development, channeled through organizations like the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), directly supports innovation in aerospace technologies. These investments facilitate the development of advanced materials, propulsion systems, and satellite technologies. The successful development of indigenous cryogenic engines and the Mars Orbiter Mission are direct outcomes of sustained government support for R&D in this sector. These programs not only enhance technological capabilities but also build a skilled workforce capable of driving future advancements. Additionally, governmental regulations and policies shape the operational environment for aerospace companies. Clear and consistent regulations promote investment and ensure fair competition within the industry.
In summary, government initiatives are an indispensable component of aerospace engineering in India. They provide the financial resources, policy frameworks, and regulatory guidance necessary for the sector to thrive. Challenges remain, including bureaucratic delays and the need for greater coordination between different government agencies. However, continued government commitment to fostering aerospace development is essential for achieving strategic goals in defense, space exploration, and economic growth. The synergy between government support and private sector innovation will determine India’s future success in the global aerospace arena.
5. Private Sector Involvement
Private sector involvement increasingly shapes the trajectory of aerospace engineering in India, transitioning the industry from a primarily government-driven domain to one with significant private participation. This shift generates both opportunities and challenges, impacting technological innovation, manufacturing capabilities, and the overall competitiveness of the sector. The entry of private companies brings financial investment, advanced management practices, and a greater focus on commercial viability, leading to more efficient and streamlined operations. For instance, private firms are now actively involved in manufacturing aircraft components, developing satellite technologies, and providing aerospace engineering services, augmenting the capabilities of traditional public sector entities. This increased participation directly contributes to the expansion and diversification of the aerospace industry within the nation.
The consequences of private sector engagement are multifaceted. It fosters competition, leading to the adoption of innovative technologies and efficient production processes. Companies such as Larsen & Toubro and Godrej Aerospace are prime examples, contributing significantly to the production of critical aerospace components and systems through partnerships with both domestic and international players. This collaborative approach facilitates technology transfer and enhances the skill base within the country. Furthermore, private investment promotes the development of specialized aerospace services, including maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) operations, which are crucial for sustaining the operational readiness of aircraft fleets. The growth of private MRO providers enhances service quality and reduces dependence on foreign providers, strengthening the nation’s aerospace infrastructure.
In conclusion, private sector involvement is indispensable for the continued growth and modernization of aerospace engineering in India. While challenges such as regulatory hurdles and access to technology persist, the increasing participation of private companies is driving innovation, enhancing manufacturing capabilities, and creating new opportunities for skilled professionals. Continued policy support from the government, aimed at fostering a favorable business environment and encouraging public-private partnerships, will be essential for unlocking the full potential of the private sector and establishing India as a significant player in the global aerospace market. The integration of private sector expertise with the established capabilities of public institutions is a strategic imperative for ensuring sustained progress and competitiveness in this critical sector.
6. International Collaboration
International collaboration represents a cornerstone for advancing aerospace engineering within India. These partnerships enable the sharing of knowledge, technology, and resources, fostering innovation and enhancing the nation’s capabilities in this strategically important sector. Such collaborations are not merely beneficial but often essential for accessing cutting-edge technologies and expertise not readily available domestically.
- Technology Transfer and Acquisition
International partnerships facilitate the transfer of advanced technologies to India, bridging technological gaps and accelerating the development of indigenous capabilities. For example, collaborations with foreign aerospace companies can provide access to advanced manufacturing processes, materials science expertise, and design methodologies. This transfer allows Indian companies and research institutions to acquire and adapt technologies, reducing dependence on foreign imports and fostering self-reliance in critical areas such as engine development and avionics. Technology transfer agreements often involve training programs for Indian engineers and scientists, building a skilled workforce capable of utilizing and further developing these technologies.
- Joint Research and Development Programs
Collaborative research initiatives with international organizations enable the pooling of resources and expertise to address complex aerospace challenges. These programs foster innovation by bringing together scientists and engineers from different backgrounds, promoting cross-fertilization of ideas and accelerating the pace of discovery. Joint projects may focus on areas such as advanced materials, propulsion systems, or space exploration technologies. For instance, collaborative projects with space agencies like NASA or ESA can provide access to cutting-edge research facilities and expertise, enhancing India’s capabilities in space science and technology. Such partnerships also provide opportunities for Indian researchers to participate in international scientific missions, expanding their knowledge and expertise.
- Joint Ventures and Manufacturing Partnerships
Establishing joint ventures and manufacturing partnerships with foreign aerospace companies allows Indian firms to participate in global supply chains and gain access to international markets. These partnerships facilitate the co-development and co-production of aircraft components, systems, and even entire aircraft. This not only enhances India’s manufacturing capabilities but also promotes exports and generates employment opportunities. Joint ventures often involve technology sharing, training programs, and the establishment of advanced manufacturing facilities within India, contributing to the growth of a domestic aerospace ecosystem. The involvement of Indian companies in the production of components for international aircraft programs demonstrates the tangible benefits of these partnerships.
- Participation in International Space Missions
Participation in international space missions provides invaluable opportunities for Indian scientists and engineers to gain experience in designing, developing, and operating complex space systems. Collaborative missions allow Indian researchers to contribute to cutting-edge scientific discoveries and develop expertise in areas such as satellite technology, launch vehicle development, and space exploration. For example, Indian instruments have been flown on international missions to Mars and the Moon, allowing Indian scientists to contribute to the understanding of these celestial bodies. Such participation enhances India’s prestige in the global space community and fosters international cooperation in space exploration.
The described facets highlight the multifaceted benefits of international collaboration for aerospace engineering within India. Such partnerships drive technological advancement, enhance manufacturing capabilities, and foster a skilled workforce. Sustained engagement in international collaborations is essential for India to achieve its strategic goals in aerospace and establish itself as a prominent player in the global aerospace arena. By actively participating in collaborative projects and fostering strong relationships with international partners, India can leverage global expertise and resources to accelerate the development of its aerospace sector and contribute to the advancement of aerospace technology worldwide.
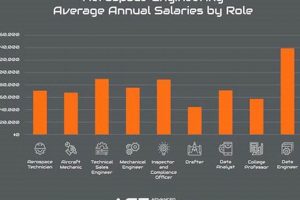
7. Career Opportunities
Aerospace engineering in India presents a spectrum of career opportunities directly linked to the growth and sophistication of the nation’s aerospace sector. The increasing demand for skilled professionals arises from both government initiatives, like the “Make in India” program and the expansion of private aerospace companies. Consequently, career trajectories encompass roles in design, development, testing, and maintenance of aircraft, spacecraft, satellites, and related systems. For instance, engineers contribute to designing more fuel-efficient aircraft, developing advanced propulsion systems, or creating cutting-edge satellite technologies, driving innovation and progress in the aerospace field. The presence of organizations such as ISRO, DRDO, HAL, and a growing number of private aerospace firms exemplifies the practical demand for qualified aerospace engineers.
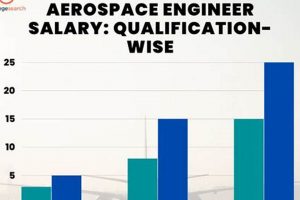
The availability and quality of career prospects are profoundly shaped by educational qualifications and specialized skill sets. Entry-level positions often require a bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering, while advanced roles may necessitate a master’s or doctoral degree with a focus on a specific area, such as aerodynamics, structures, or propulsion. Skill development in areas like computational fluid dynamics, finite element analysis, and CAD/CAM software directly enhances employability. Career progression may involve roles such as design engineer, systems engineer, project manager, or research scientist, each requiring a unique blend of technical expertise and leadership abilities. The practical applications of this understanding are manifest in the career paths of numerous engineers employed by ISRO who have contributed to satellite launches and space exploration missions, or those at HAL who are involved in the production of military and civilian aircraft.
In summary, career opportunities are an integral component of the aerospace engineering landscape in India, driving technological advancements and contributing to economic growth. The availability of these opportunities is contingent upon continued investment in education, research, and manufacturing, as well as supportive government policies. Challenges such as skills gaps and bureaucratic hurdles must be addressed to ensure a sustainable pipeline of qualified professionals and maximize the potential of this vital sector. Ultimately, the growth trajectory of aerospace engineering in India depends on fostering a robust ecosystem that attracts, develops, and retains talented engineers, ensuring that the sector continues to innovate and thrive.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding the field of aerospace engineering within the Indian context, offering clarity on its various aspects.
Question 1: What are the primary areas of focus within aerospace engineering programs in India?
Aerospace engineering curricula in India typically encompass core areas such as aerodynamics, propulsion, structures, control systems, and avionics. These areas provide a comprehensive understanding of aircraft and spacecraft design, development, and operation.
Question 2: Which institutions in India offer reputable aerospace engineering programs?
Several institutions in India are recognized for their aerospace engineering programs, including the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs), the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), and the Indian Institutes of Space Science and Technology (IIST). These institutions offer undergraduate, postgraduate, and doctoral programs in the field.
Question 3: What are the typical career paths for aerospace engineers in India?
Career paths for aerospace engineers in India may include roles in design, development, testing, and maintenance within organizations such as the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), and various private aerospace companies.
Question 4: How significant is the “Make in India” initiative for aerospace engineering in India?
The “Make in India” initiative is significantly impacting the sector by promoting domestic manufacturing of aerospace components and systems. This initiative aims to reduce reliance on foreign imports and foster a self-reliant aerospace industry within the nation.
Question 5: What role does international collaboration play in advancing aerospace engineering in India?
International collaboration is crucial for accessing advanced technologies and expertise not readily available domestically. Joint research programs, technology transfer agreements, and partnerships with foreign aerospace companies contribute to the advancement of the sector.
Question 6: What are the key skills and qualifications sought by employers in the aerospace engineering sector in India?
Employers typically seek candidates with a strong foundation in engineering principles, specialized knowledge in aerospace disciplines, proficiency in relevant software tools (e.g., CATIA, ANSYS), and effective communication skills. Advanced degrees and practical experience through internships enhance employability.
This section has addressed key inquiries concerning the field. Additional resources are available for deeper investigation into specific areas of interest.
The subsequent section will present concluding remarks, summarizing the key themes discussed and offering a final perspective on the future of aerospace engineering in India.
Conclusion
This exposition has surveyed several critical facets of aerospace engineering in India, from educational foundations and research endeavors to manufacturing capabilities, government initiatives, private sector involvement, international collaborations, and career opportunities. It demonstrates that the domain is multifaceted and strategically vital, encompassing defense, space exploration, and economic development.
The sustained growth and global competitiveness of aerospace engineering in India hinges upon continued investment in education, robust research and development initiatives, and the fostering of strong public-private partnerships. The realization of its full potential demands the proactive mitigation of existing challenges and a steadfast commitment to indigenous innovation and technological advancement.