The University of Florida (UF) offers a graduate-level program focused on the design, development, and testing of aircraft and spacecraft. This advanced degree equips students with specialized knowledge in areas such as aerodynamics, propulsion, structures, and control systems related to flight vehicles. Graduates often pursue careers in the aerospace industry, government research labs, or academic institutions. Successful completion of this program signifies a high level of expertise in the field.
Advanced education in this discipline provides a pathway to contribute to technological advancements in air and space travel. It allows professionals to take on leadership roles in engineering projects, conduct cutting-edge research, and contribute to national defense or space exploration initiatives. Historically, these types of programs have been vital in propelling innovation in aerospace technology, driving economic growth, and addressing complex challenges related to flight.
The following sections will delve deeper into the specific curriculum, research opportunities, faculty expertise, and career prospects associated with pursuing advanced study in this specialized field at the University of Florida. Furthermore, information regarding admission requirements, funding options, and student resources will be provided.
The pursuit of a master’s degree in aerospace engineering demands focused preparation and strategic planning. These tips offer guidance for individuals considering or currently enrolled in a rigorous program.
Tip 1: Solidify Foundational Knowledge: A strong understanding of undergraduate-level physics, mathematics, and engineering principles is crucial. Review core concepts in fluid dynamics, thermodynamics, and structural mechanics to ensure a robust foundation for advanced coursework.
Tip 2: Define Research Interests: Identify specific areas of aerospace engineering that align with long-term career goals. Focusing on a niche area, such as hypersonics, autonomous systems, or advanced materials, allows for deeper engagement with research and specialized coursework.
Tip 3: Engage with Faculty Research: Actively explore faculty research profiles and contact professors whose work aligns with personal interests. Participating in research projects provides valuable hands-on experience and enhances understanding of current challenges in the field.
Tip 4: Cultivate Strong Communication Skills: Effective communication is essential for collaborating with peers, presenting research findings, and disseminating technical information. Practice clear and concise writing, presentation skills, and active listening.
Tip 5: Network with Industry Professionals: Attend conferences, workshops, and career fairs to connect with engineers and researchers in the aerospace industry. Networking opportunities can lead to internships, mentorships, and future employment prospects.
Tip 6: Master Simulation Software: Proficiency in industry-standard simulation software is highly valued. Familiarize yourself with tools like ANSYS, MATLAB, and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) packages to enhance analytical and problem-solving capabilities.
Tip 7: Prioritize Time Management: The curriculum is demanding, requiring effective time management skills to balance coursework, research, and extracurricular activities. Develop a schedule and prioritize tasks to ensure consistent progress.
Adhering to these recommendations can contribute to a more successful and rewarding experience in aerospace engineering graduate studies. A proactive approach to learning and professional development is vital for achieving academic and career aspirations.
The following sections will provide more specific details about optimizing the educational path, resource allocation, and maximizing the potential benefits derived from pursuing this advanced degree.
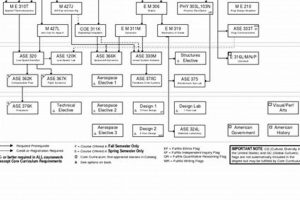
1. Curriculum Specialization
Curriculum specialization within the University of Florida’s aerospace engineering master’s program is a critical component, allowing students to develop in-depth knowledge and expertise in specific areas of the field. This focused approach enhances their competitiveness in a highly specialized job market.
- Aerodynamics and Fluid Mechanics
This specialization focuses on the behavior of air and other fluids around aircraft and spacecraft. Students delve into computational fluid dynamics, boundary layer theory, and experimental techniques. This knowledge is essential for designing efficient and stable flight vehicles, improving fuel economy, and reducing noise pollution.
- Structures and Materials
This area explores the structural integrity and material properties critical to aerospace vehicles. Students learn about composite materials, finite element analysis, and fracture mechanics. This specialization enables graduates to design lightweight and robust structures that can withstand extreme environments.
- Propulsion Systems
The study of propulsion systems encompasses the design and analysis of jet engines, rocket engines, and other advanced propulsion technologies. Students gain expertise in thermodynamics, combustion, and fluid dynamics as applied to engine performance. This knowledge is crucial for developing more efficient and powerful propulsion systems for both atmospheric and space flight.
- Control and Guidance Systems
Focusing on the autonomous control and navigation of aircraft and spacecraft, this specialization covers topics such as flight dynamics, robotics, and sensor integration. Students develop algorithms and systems that enable vehicles to fly autonomously, improving safety and efficiency in various applications, including drones and satellites.
The availability of these specializations within the University of Florida’s aerospace engineering master’s program allows students to tailor their education to align with their career aspirations, providing a competitive advantage in the aerospace industry or further research endeavors.
2. Research Opportunities
Research opportunities constitute a fundamental component of advanced study at the University of Florida’s aerospace engineering master’s program. Active engagement in research is not merely supplementary; it functions as a crucial catalyst for developing practical skills, expanding specialized knowledge, and fostering innovation. Students participating in research projects gain exposure to real-world engineering challenges, working alongside faculty on externally funded projects that often address pressing industry or government needs. For instance, students may contribute to NASA-sponsored research aimed at developing novel propulsion systems for future space missions or participate in Air Force-funded initiatives focused on improving the aerodynamic performance of unmanned aerial vehicles. These experiences provide valuable insights that complement theoretical coursework and enhance graduates’ readiness for employment.
The availability and scope of research opportunities within the program have a direct impact on the quality of the educational experience and the career prospects of its graduates. Students who actively participate in research have a higher likelihood of publishing their findings in peer-reviewed journals or presenting at international conferences, thus establishing their expertise and building their professional networks. Furthermore, research involvement equips students with valuable problem-solving, data analysis, and experimental skills that are highly sought after by employers in the aerospace industry. For example, a student involved in research focused on composite materials might develop expertise in non-destructive testing techniques, finite element modeling, and materials characterization, making them a highly desirable candidate for companies involved in the design and manufacturing of aircraft components.
In summary, research opportunities are integral to the value proposition of the University of Florida’s aerospace engineering master’s program. These opportunities not only enhance the learning experience and skill development of students but also contribute to the advancement of aerospace technology. The program’s commitment to fostering a vibrant research environment is a key factor in attracting top students and producing graduates who are well-prepared to address the complex challenges facing the aerospace industry. The significance of research involvement underscores the program’s position as a prominent center for aerospace engineering education and innovation.
3. Faculty Expertise
The quality and scope of faculty expertise are central to the value and reputation of the aerospace engineering master’s program at the University of Florida. The knowledge, experience, and research activities of the faculty directly influence the curriculum, research opportunities, and overall educational experience available to students.
- Research Leadership and Innovation
Faculty members lead cutting-edge research in diverse areas of aerospace engineering, securing funding from government agencies and industry partners. This leadership fosters an environment of innovation, where students can engage in groundbreaking projects and contribute to the advancement of aerospace technology. For example, faculty expertise in hypersonics may lead to research projects aimed at developing next-generation hypersonic vehicles, offering students the opportunity to work on complex and challenging problems.
- Curriculum Development and Instruction
Faculty expertise directly informs the design and delivery of the master’s program curriculum. Their deep understanding of aerospace engineering principles and current industry practices ensures that students receive a relevant and up-to-date education. Experienced faculty may incorporate case studies and real-world examples into their courses, providing students with a practical perspective on the application of theoretical concepts.
- Mentorship and Career Guidance
Faculty members play a critical role in mentoring students and providing career guidance. Their extensive networks within the aerospace industry allow them to connect students with internship opportunities, research collaborations, and potential employers. Faculty can offer personalized advice on career paths, helping students align their academic and research interests with their long-term career goals. Their experience contributes substantially to career development.
- Industry Collaboration and Partnerships
Many faculty members maintain strong ties with the aerospace industry, collaborating on research projects and providing consulting services. These collaborations ensure that the curriculum remains aligned with industry needs and that students gain exposure to real-world engineering challenges. Industry partnerships can lead to capstone projects, providing students with the opportunity to work on practical problems for aerospace companies, significantly enhancing their skills and making them more competitive in the job market.
In conclusion, faculty expertise constitutes a vital pillar of the University of Florida’s aerospace engineering master’s program. Their contributions to research, curriculum development, mentorship, and industry collaboration significantly enhance the educational experience and career prospects of graduates. The program’s standing as a leading center for aerospace engineering education relies heavily on the dedication and expertise of its faculty.
4. Industry Connections
Robust industry connections are a vital component of the University of Florida’s aerospace engineering master’s program. These connections provide students with invaluable opportunities to apply their academic knowledge in real-world settings, gain practical experience, and build professional networks. The strength of these relationships directly impacts the career readiness and long-term success of program graduates.
- Internship Programs
The aerospace engineering master’s program actively facilitates internship opportunities with leading aerospace companies, government research laboratories, and defense contractors. These internships allow students to gain hands-on experience in design, analysis, testing, and manufacturing processes. For example, students may intern at companies like Boeing or Lockheed Martin, contributing to projects related to aircraft design, satellite systems, or advanced materials. This practical exposure significantly enhances their skill sets and prepares them for full-time employment. The program’s reputation helps place students in competitive roles.
- Industry-Sponsored Research
Many research projects within the aerospace engineering department are sponsored by industry partners. This collaboration allows students to work on real-world problems and contribute to the development of innovative technologies. Industry-sponsored research provides students with access to cutting-edge equipment, data, and expertise, further bridging the gap between academia and industry. These projects can directly lead to job offers or career advancements upon graduation.
- Guest Lectures and Seminars
The program regularly hosts guest lectures and seminars presented by industry experts. These events provide students with insights into current trends, challenges, and opportunities within the aerospace sector. Industry professionals share their experiences, offer career advice, and provide networking opportunities. This direct interaction allows students to learn from seasoned engineers and build connections that can benefit their careers.
- Capstone Projects
Capstone projects, often conducted in collaboration with industry partners, provide students with the opportunity to apply their knowledge and skills to solve complex engineering problems. These projects simulate real-world engineering scenarios, requiring students to work in teams, manage budgets, and deliver tangible results. Successful completion of a capstone project demonstrates a student’s ability to effectively apply their knowledge and contribute to the success of an engineering project, significantly enhancing their job prospects.
In summary, industry connections are an integral aspect of the University of Florida’s aerospace engineering master’s program, contributing significantly to its success and the career outcomes of its graduates. The program’s proactive approach to fostering these relationships ensures that students are well-prepared to meet the challenges and opportunities within the dynamic aerospace industry.
5. Career Pathways
A graduate degree in aerospace engineering from the University of Florida (UF) serves as a conduit to diverse career pathways within the aerospace sector and related industries. The program equips graduates with advanced knowledge and skills applicable to a wide range of roles, influencing both initial job placement and long-term career trajectory. Successful completion of the UF aerospace engineering master’s program frequently leads to positions involving design, research, development, and management in various organizations. Examples include roles as aerospace engineers at companies like Boeing or SpaceX, research scientists at NASA centers, or project managers at defense contractors such as Lockheed Martin. The depth of technical expertise gained through the program is a primary determinant of access to these specialized opportunities.
The specific curriculum and research focus within the UF aerospace engineering master’s program significantly shape career outcomes. Students specializing in areas such as propulsion, aerodynamics, or structural mechanics often find employment in corresponding sectors. Practical experiences gained through internships, research projects, and industry collaborations further refine career paths and enhance job prospects. Graduates who actively engage in these opportunities demonstrate their ability to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world problems, a skill highly valued by employers. For instance, participation in a research project involving computational fluid dynamics may lead to a career in aerodynamic design, while experience with composite materials testing can open doors in the aerospace manufacturing industry. These experiences are essential building blocks for a successful professional career.
In conclusion, the UF aerospace engineering master’s program directly impacts career pathways by providing specialized knowledge, research experience, and industry connections. The program functions as a critical step for individuals seeking to advance their careers in the aerospace sector. While successful completion of the program increases employment opportunities, graduates must continue to develop their skills and knowledge to adapt to the evolving needs of the industry. The relationship between the program and career success is complex, requiring continued learning and professional development to achieve long-term career goals.
6. Program Reputation
The reputation of the University of Florida’s aerospace engineering master’s program is a crucial determinant of its perceived value and the career prospects of its graduates. This reputation stems from multiple factors and impacts various aspects of the program’s standing within academia and industry.
- Research Output and Recognition
The volume and impact of research conducted by faculty and students significantly contribute to the program’s reputation. High-quality publications in respected journals, presentations at international conferences, and successful grant acquisitions elevate the program’s profile. For example, consistently publishing impactful research on novel propulsion technologies or advanced materials strengthens the program’s standing as a center for innovation in those areas. This, in turn, attracts talented students and faculty.
- Graduate Placement and Success
The career trajectories and achievements of program alumni play a vital role in shaping its reputation. Consistent placement of graduates in desirable positions at leading aerospace companies, government research laboratories, and academic institutions reinforces the program’s effectiveness. Success stories of alumni who have made significant contributions to the field, such as developing groundbreaking technologies or leading major engineering projects, further enhance its prestige.
- Faculty Credentials and Expertise
The qualifications, experience, and recognition of the faculty members teaching in the program are key drivers of its reputation. Faculty with distinguished academic backgrounds, extensive industry experience, and a track record of research excellence contribute to the program’s credibility. Awards, fellowships, and editorial positions on prestigious journals are indicators of faculty expertise that enhance the program’s standing within the academic community.
- Accreditation and Rankings
Accreditation by recognized engineering bodies and rankings in reputable publications influence the perceived quality of the program. Accreditation ensures that the program meets established standards for curriculum, faculty qualifications, and resources. Rankings provide a relative measure of the program’s performance compared to other institutions, which can impact its attractiveness to prospective students and employers. Consistent high rankings and accreditations significantly bolster the program’s overall reputation.
These facets are interconnected and collectively contribute to the overall reputation of the University of Florida’s aerospace engineering master’s program. A strong reputation attracts top students, enhances graduate career prospects, and facilitates research collaborations. The program’s sustained success relies on maintaining a commitment to excellence in research, teaching, and graduate outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding the University of Florida’s aerospace engineering master’s program. It aims to provide clear and concise information to prospective applicants and current students.
Question 1: What are the minimum admission requirements for the UF Aerospace Engineering Master’s program?
Applicants typically require a bachelor’s degree in engineering or a closely related field from an accredited institution. A minimum GPA is often specified, alongside satisfactory scores on standardized tests such as the GRE. Specific requirements are subject to change and should be verified with the department’s admissions office.
Question 2: What specializations are offered within the UF Aerospace Engineering Master’s program?
Common specializations include aerodynamics, propulsion, structures, and control systems. However, available specializations may vary based on faculty research interests and course offerings. Prospective students should consult the program’s website for the most current list of specializations.
Question 3: Are there financial aid opportunities available for students pursuing a UF Aerospace Engineering Master’s degree?
Financial aid options may include fellowships, assistantships (teaching and research), and loans. The availability and eligibility criteria for these options vary. Applicants are encouraged to explore internal and external funding sources early in the application process.
Question 4: What career paths are commonly pursued by graduates of the UF Aerospace Engineering Master’s program?
Graduates often find employment in the aerospace industry, government research labs, and academic institutions. Common roles include aerospace engineers, research scientists, and project managers. Specific career paths are often influenced by specialization and research experience.
Question 5: What is the typical duration of the UF Aerospace Engineering Master’s program?
The program typically requires two years of full-time study to complete. However, the actual duration can vary depending on individual course load, research involvement, and prior academic credits.
Question 6: Does the UF Aerospace Engineering Master’s program offer online learning options?
The availability of online courses or fully online program options varies. Prospective students should consult the program’s website or contact the department directly to inquire about current online learning opportunities.
This FAQ section provides a brief overview of common questions regarding the UF Aerospace Engineering Master’s program. For more comprehensive information, prospective students are advised to consult the program’s official website or contact the department directly.
The subsequent sections will provide information about the benefits of this program.
Concluding Remarks
This exploration of the University of Florida’s aerospace engineering master’s degree has illuminated its various facets, encompassing curriculum specialization, research opportunities, faculty expertise, industry connections, career pathways, and program reputation. The synthesis of these elements underscores the comprehensive nature of the educational experience, highlighting the program’s dedication to producing skilled and knowledgeable professionals. The analysis also emphasized the program’s role in advancing aerospace technology and fostering innovation.
Prospective students are encouraged to thoroughly investigate the program’s offerings and determine their suitability for individual academic and professional aspirations. The field of aerospace engineering continues to evolve, demanding professionals equipped with advanced knowledge and practical skills. The pursuit of such qualifications represents a significant investment in the future and a contribution to the advancement of aerospace technology.