Compensation for professionals in the field of aircraft and spacecraft design, development, and testing, as it is offered within the French Republic, constitutes a significant factor for individuals considering careers or relocation. This remuneration is subject to various influences, including experience level, specialization, geographical location within the country, and the specific employer, be it a large corporation or a smaller enterprise.
Understanding the financial aspects of this career path is crucial for effective career planning and financial forecasting. It allows potential engineers to assess the viability of pursuing this vocation and helps current practitioners negotiate equitable terms of employment. Factors such as the competitive landscape of the French aerospace industry, government investment in research and development, and the overall economic climate of the nation exert considerable influence on the prevailing compensation levels.
The following sections will delve into the typical earnings at different career stages, the impact of specialization on income, a comparison of compensation packages offered by different types of employers, and an overview of the cost of living in various regions of France, providing a holistic view of the financial realities for those working in this sector.
Maximizing potential earnings within the French aerospace sector requires a strategic approach. The following tips are designed to inform individuals seeking to optimize their compensation trajectory.
Tip 1: Prioritize Specialized Skills: Engineers possessing expertise in high-demand areas such as propulsion systems, advanced materials, or avionics command higher salaries. Concentrating on these specialized fields can significantly enhance earning potential.
Tip 2: Seek Advanced Education: Possessing a Master’s degree or doctorate, particularly from a renowned French institution or an international equivalent, typically translates to a higher starting salary and accelerated career advancement within French aerospace companies.
Tip 3: Develop Strong Language Proficiency: Fluency in French is essential, while proficiency in English, often the language of international collaboration, is highly valued. Enhanced language skills can lead to opportunities within multinational corporations and increased responsibilities.
Tip 4: Target Large Corporations: Major aerospace corporations, such as Airbus or Safran, tend to offer more competitive compensation packages and comprehensive benefits compared to smaller firms or startups. Researching and targeting these established entities can prove advantageous.
Tip 5: Negotiate Effectively: Before accepting a job offer, thoroughly research the prevailing rates for comparable positions. Be prepared to articulate the value of your skills and experience and negotiate for a salary that reflects your worth.
Tip 6: Consider Location Strategically: Certain regions of France, particularly those with a high concentration of aerospace companies, may offer higher salaries to attract talent. Explore opportunities in these strategic locations to maximize earning potential.
Tip 7: Continuously Update Skills: The aerospace industry is constantly evolving. Staying abreast of the latest technological advancements and acquiring new skills through professional development courses demonstrates a commitment to growth and can lead to salary increases.
By implementing these strategies, individuals can significantly improve their prospects for earning a competitive income in the French aerospace industry. Proactive planning and continuous professional development are key to long-term financial success.
The subsequent sections will address specific strategies for career advancement and long-term compensation growth within the French aerospace engineering sector.
1. Experience Level
Experience level functions as a primary determinant of compensation within the French aerospace engineering sector. A direct correlation exists between the years of practical application and the remuneration offered. Entry-level positions, typically occupied by recent graduates, command salaries at the lower end of the spectrum. As engineers accumulate experience, demonstrated competence, and a track record of successful project contributions, their earning potential escalates. This reflects the increased value placed on seasoned professionals who can effectively manage complex projects, mentor junior engineers, and contribute to strategic decision-making.
For instance, an engineer with 1-3 years of experience may focus on specific tasks under supervision, while an engineer with 5-7 years of experience might lead small teams or manage critical subsystems. Correspondingly, their compensation would reflect these expanded responsibilities and contributions. Senior engineers, often with over 10 years of experience, typically assume leadership roles, directing large-scale projects and influencing organizational strategy. Their salaries are commensurately higher, reflecting their accumulated expertise and strategic importance to the company. Compensation packages also increasingly incorporate performance-based incentives as experience grows, aligning individual contributions with overall company objectives.
In summary, the advancement in experience level forms a foundational pillar upon which career progression and increased earnings are built within the French aerospace engineering landscape. Recognizing and understanding this dynamic is imperative for both aspiring and established professionals seeking to optimize their career trajectory and achieve competitive remuneration within this specialized field.
2. Specialized Skills
The compensation structure for aerospace engineers in France exhibits a strong correlation with the possession of specialized skills. Demand for specific expertise creates upward pressure on salaries, as companies compete to secure professionals capable of addressing intricate technical challenges. The acquisition of specialized skills, therefore, represents a direct pathway to enhanced earning potential within this field.
Engineers specializing in areas such as advanced materials, propulsion systems, avionics, or cybersecurity for aerospace applications often command higher salaries than those with more general skill sets. For example, professionals proficient in computational fluid dynamics (CFD) or finite element analysis (FEA) are highly sought after for their ability to simulate and optimize aircraft and spacecraft designs, contributing directly to improved performance and reduced development costs. Similarly, experts in autonomous systems and artificial intelligence are increasingly valuable due to the growing emphasis on unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and advanced control systems. The practical significance lies in the ability of these specialized engineers to solve complex problems that directly impact project timelines, budgets, and overall mission success. This expertise is then reflected in their compensation packages.
In conclusion, the development of specialized skills significantly influences earning potential within the aerospace engineering sector in France. Focusing on high-demand areas not only enhances career prospects but also provides a tangible advantage in salary negotiations. Continuous professional development and the acquisition of cutting-edge expertise are crucial for maximizing long-term financial rewards within this technically demanding and constantly evolving industry.
3. Company Size
The size of an aerospace engineering company in France exerts a significant influence on the compensation packages offered to its engineers. This relationship is multi-faceted, extending beyond mere revenue figures and encompassing aspects of organizational structure, project scope, and resource availability.
- Financial Resources and Stability
Larger aerospace corporations generally possess greater financial resources and stability compared to smaller firms or startups. This allows them to offer more competitive salaries, comprehensive benefits packages (including health insurance, retirement plans, and stock options), and performance-based bonuses. The financial security of these established entities translates into a more predictable and potentially lucrative career trajectory for their engineering staff.
- Project Scale and Complexity
The scale and complexity of projects undertaken by larger companies often necessitate a higher level of specialized expertise and managerial oversight. Consequently, engineers involved in these projects may command higher salaries, reflecting the increased responsibilities and technical challenges they face. Smaller companies, while potentially offering more entrepreneurial opportunities, may be limited to less complex projects, which can impact the overall compensation structure.
- Career Advancement Opportunities
Larger aerospace organizations typically offer more structured career advancement pathways and opportunities for professional development. This can include access to internal training programs, mentorship initiatives, and international assignments. The prospect of upward mobility and the accumulation of valuable skills and experience can contribute to higher long-term earning potential within these larger entities.
- Competitive Landscape and Talent Acquisition
Major aerospace corporations in France operate in a highly competitive global market, requiring them to attract and retain top engineering talent. To remain competitive, these companies must offer attractive compensation packages that meet or exceed industry standards. Smaller companies may face challenges in competing with the salaries and benefits offered by larger corporations, potentially impacting their ability to recruit and retain skilled engineers.
The influence of company size on aerospace engineering compensation in France is a critical consideration for both job seekers and employers. Understanding the distinct advantages and disadvantages associated with different organizational scales is essential for making informed career decisions and developing effective talent management strategies. While larger corporations often offer greater financial security and career advancement opportunities, smaller companies may provide more entrepreneurial environments and faster-paced project cycles. Ultimately, the ideal company size depends on individual career goals and priorities.
4. Location Impact
Geographic location exerts a demonstrable influence on the compensation levels for aerospace engineering professionals within France. Regional economic disparities, industrial concentrations, and cost-of-living variations contribute to significant salary differences across the country.
- Regional Industrial Hubs
The presence of major aerospace industrial hubs, such as Toulouse (home to Airbus headquarters) and the Paris region, correlates with higher average salaries. These areas concentrate a significant proportion of aerospace companies and research institutions, fostering a competitive labor market that drives up compensation. The proximity to major employers and specialized infrastructure creates a demand for skilled engineers, resulting in premium salaries.
- Cost of Living Adjustment
Salaries are often adjusted to reflect the prevailing cost of living in different regions. Metropolitan areas, such as Paris, typically exhibit higher living expenses compared to smaller cities or rural areas. Consequently, aerospace engineers working in Paris may receive higher base salaries to offset these costs. However, this does not necessarily translate to a higher disposable income, as a significant portion of earnings is allocated to housing, transportation, and everyday expenses.
- Local Economic Conditions
The overall economic health of a region can impact the demand for aerospace engineers and influence salary levels. Regions with robust economic growth and strong government investment in the aerospace sector tend to offer more competitive compensation packages. Conversely, areas experiencing economic stagnation or decline may see a reduction in hiring activity and downward pressure on salaries.
- Proximity to Research Institutions
Areas in close proximity to leading aerospace research institutions and universities often attract a highly skilled workforce and foster innovation. This concentration of talent can lead to higher salaries for engineers involved in research and development activities. The collaboration between industry and academia drives technological advancements, creating a demand for engineers with specialized knowledge and expertise.
These interconnected factors highlight the significance of geographic location in determining aerospace engineering salaries in France. Prospective engineers must consider these regional variations when evaluating job offers and planning their careers. While the presence of major industrial hubs and higher cost-of-living adjustments may translate to higher nominal salaries, the overall economic conditions and career advancement opportunities within a specific region are equally important considerations for long-term financial success.
5. Education Level
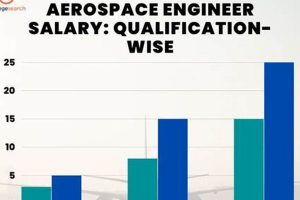
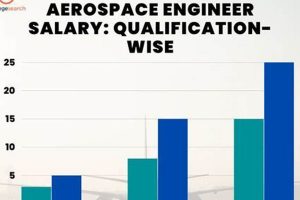
The level of education attained by an aerospace engineer directly impacts the compensation they can expect to receive in France. A bachelor’s degree serves as a foundational requirement for entry into the profession, providing individuals with the core engineering principles necessary for basic roles. However, advanced degrees, such as a Master’s or a Doctorate, often correlate with significantly higher earning potential. This is due, in part, to the specialized knowledge and research skills acquired during postgraduate studies, which enable engineers to contribute to more complex and demanding projects. For instance, an engineer with a doctorate in fluid dynamics might be involved in the design of more efficient aircraft wings, while an engineer with a master’s in control systems could work on developing advanced autopilot technologies. These specialized roles command higher salaries due to the expertise required.
Furthermore, specific institutions often carry a reputation for excellence within the aerospace industry. Graduates from prestigious engineering schools, both within France and internationally, may benefit from the perceived value of their education, leading to increased opportunities and higher starting salaries. A degree from cole Polytechnique, CentraleSuplec, or ISAE-SUPAERO, for example, can open doors to leading aerospace companies in France and potentially command a premium in compensation. These institutions often have strong ties to industry, providing graduates with valuable networking opportunities and exposure to real-world engineering challenges. Moreover, the curriculum often focuses on cutting-edge technologies and research, making graduates highly sought after by employers looking for innovative solutions.
In conclusion, the pursuit of advanced education is a strategic investment for aspiring aerospace engineers in France. While a bachelor’s degree provides a necessary entry point, a master’s or doctoral degree, particularly from a reputable institution, significantly enhances earning potential and career prospects. The specialized knowledge and research skills acquired during postgraduate studies equip engineers to tackle complex projects, contribute to technological advancements, and command higher salaries within the competitive French aerospace industry. This educational advantage, coupled with practical experience, forms a strong foundation for a successful and financially rewarding career.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the financial aspects of pursuing a career as an aerospace engineer in France, providing data-driven insights and dispelling potential misconceptions.
Question 1: What is the typical starting remuneration for a recent aerospace engineering graduate in France?
Entry-level salaries for aerospace engineers in France generally range from 32,000 to 38,000 per annum, contingent upon the university attended, specialization, and employer.
Question 2: How does experience level impact aerospace engineering income within France?
Compensation demonstrably increases with experience. Engineers with 5-10 years of experience typically earn between 45,000 and 65,000 annually, while those with over 10 years of experience can command salaries exceeding 75,000 or more, particularly in senior management or specialized technical roles.
Question 3: Do specific engineering specializations lead to higher compensation within the aerospace industry?
Yes. Expertise in high-demand areas such as avionics, propulsion systems, or advanced materials often translates to higher salaries compared to more general engineering roles. The disparity reflects the specialized knowledge and skills required for these critical domains.
Question 4: How does the size of the employing company affect compensation for aerospace engineers in France?
Larger aerospace corporations generally offer more competitive salaries and comprehensive benefits packages compared to smaller firms or startups. This reflects their greater financial resources and capacity to attract top talent.
Question 5: What is the impact of geographic location within France on aerospace engineering salary?
Salaries are often higher in regions with major aerospace industrial hubs, such as Toulouse and the Paris area, to compensate for higher cost-of-living and attract talent to those regions.
Question 6: Does possessing an advanced degree lead to higher income prospects in this industry?
Yes. A Master’s degree or a Doctorate significantly enhances earning potential. Employers often place a premium on the specialized knowledge and research skills acquired through postgraduate studies.
Understanding the multifaceted influences on aerospace engineering compensation in France empowers individuals to make informed career decisions and negotiate equitable employment terms.
The subsequent section will provide resources for further research and professional development within the French aerospace sector.
Conclusion
This exploration has illuminated the multifaceted factors influencing aerospace engineering salary in France. Experience, specialization, company scale, location, and education level all demonstrably contribute to the financial landscape of this profession. Understanding these dynamics enables informed career decisions for both aspiring and established aerospace engineers within the French Republic.
The aerospace sector represents a significant element of the French economy and technological advancement. Continued investment in research and development, coupled with a strategic focus on specialized skills, remains vital for ensuring competitive compensation and sustained growth within this industry. Further investigation into emerging technologies and evolving market demands will be essential for maintaining a robust and financially rewarding career path in aerospace engineering in France.


![Your Aerospace Engineering Salary in San Diego [Guide] Safem Fabrication - Precision Engineering & Custom Manufacturing Solutions Your Aerospace Engineering Salary in San Diego [Guide] | Safem Fabrication - Precision Engineering & Custom Manufacturing Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/th-4364-300x200.jpg)