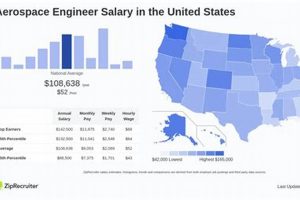
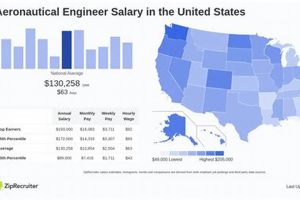
Compensation for professionals in the field of aircraft and spacecraft design, development, and testing, specifically within the New York City metropolitan area, is a significant factor for those considering or already employed in this sector. This metric reflects the demand for skilled engineers, the cost of living in the region, and the overall economic climate affecting the aerospace industry.
Understanding income expectations is crucial for career planning and financial stability. Analyzing this data provides insights into the value placed on expertise in this specialized engineering discipline within a major economic hub. Furthermore, historical trends in remuneration can reveal the industry’s growth and its response to technological advancements and market fluctuations.
The subsequent sections will examine the factors influencing earning potential for these engineers, compare typical earnings to national averages, and discuss strategies for maximizing compensation within the five boroughs and surrounding areas.
Maximizing Earning Potential for Aerospace Engineers in New York City
Strategies to enhance income as an aerospace engineer in the New York City area require a multifaceted approach, encompassing education, skill development, and strategic career planning.
Tip 1: Pursue Advanced Education: Obtaining a Master’s degree or a Ph.D. in a specialized area such as aerodynamics, propulsion, or structural mechanics can significantly increase earning potential. Advanced degrees often qualify candidates for higher-level positions with increased responsibilities and commensurate salaries.
Tip 2: Develop Specialized Skills: Proficiency in specialized software and technologies relevant to the aerospace industry, such as CAD/CAM software, computational fluid dynamics (CFD), or finite element analysis (FEA), makes engineers more valuable to employers. Certifications in these areas can further demonstrate expertise.
Tip 3: Gain Relevant Experience: Internship and co-op experiences during academic studies provide practical skills and industry connections. Prior experience working on specific aerospace projects is highly valued by employers.
Tip 4: Network Strategically: Attending industry conferences, joining professional organizations like the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA), and engaging with professionals in the field can open doors to new opportunities and provide insights into salary trends.
Tip 5: Seek Opportunities in High-Demand Areas: Certain sectors within aerospace, such as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), space exploration, or advanced materials, may experience higher demand and offer more competitive salaries. Focus professional development on these areas.
Tip 6: Negotiate Effectively: Thoroughly research prevailing salary ranges for similar positions in the New York City area using resources such as salary surveys and online databases. Be prepared to articulate one’s value proposition based on skills, experience, and education during salary negotiations.
Tip 7: Consider Location within the NYC Metro Area: Proximity to major aerospace employers and research institutions within the New York City metropolitan area can influence earning potential. Certain locations may offer higher salaries due to increased competition for skilled engineers.
Maximizing earning potential in this field requires continuous learning, strategic networking, and a proactive approach to career development. A combination of advanced education, specialized skills, and relevant experience, coupled with effective negotiation, contributes to improved compensation.
The concluding section will summarize the key findings and offer insights into the future outlook for this profession in the region.
1. Cost of Living
The cost of living within the New York City metropolitan area exerts a significant influence on compensation expectations for aerospace engineers. The high expenses associated with housing, transportation, and general goods necessitate commensurate remuneration to maintain a reasonable standard of living.
- Housing Costs
Rental and purchase prices for residential properties in New York City are substantially higher than national averages. Aerospace engineers must factor these elevated housing expenses into their salary considerations, potentially requiring higher compensation to afford adequate housing within a reasonable commute distance to their place of employment.
- Transportation Expenses
While public transportation is widely available, monthly commuting costs in New York City can be considerable. Furthermore, the expense of owning and maintaining a vehicle, including parking, insurance, and tolls, is also a factor influencing the overall cost of living. An appropriate earnings package must account for these transportation-related expenditures.
- Tax Burden
New York State and New York City impose state and local income taxes, respectively, which contribute to a higher overall tax burden compared to many other regions. Aerospace engineers should be cognizant of these tax implications when evaluating potential job offers and negotiating compensation.
- Goods and Services
The prices of everyday goods and services, including groceries, utilities, and entertainment, are generally higher in New York City than in other areas of the United States. These increased costs contribute to the overall financial pressure on residents and are indirectly reflected in the expected income levels for professionals, including aerospace engineers.
In summary, the elevated cost of living in New York City necessitates a higher compensation baseline for aerospace engineers to ensure financial stability and attract qualified professionals to the region. Employers must consider these factors to remain competitive in the labor market and retain talent within this specialized field.
2. Experience Level
Years of professional experience within aerospace engineering directly correlate with compensation levels in the New York City metropolitan area. Entry-level positions, typically requiring a bachelor’s degree and limited prior experience (0-3 years), command lower salaries compared to those with mid-career experience (5-10 years) or senior-level expertise (10+ years). This is due to the increased proficiency, specialized knowledge, and demonstrated problem-solving abilities that are acquired over time. For instance, a recent graduate might start with tasks involving basic design or testing under supervision, whereas a seasoned engineer would lead complex projects, manage teams, and make critical decisions that impact product development and safety.
The effect of experience on earnings stems from several factors. Experienced engineers possess a deeper understanding of industry standards, regulatory requirements, and best practices. They are also more adept at anticipating challenges, mitigating risks, and optimizing designs for performance and efficiency. Furthermore, senior engineers often have established networks within the industry, enabling them to secure better deals, negotiate favorable contracts, and attract top talent. Real-life examples include project managers with ten years of experience earning significantly more than junior engineers due to their proven ability to deliver projects on time and within budget. Similarly, specialists in areas like propulsion or avionics, with extensive experience, are often highly sought after and command premium salaries.
In conclusion, experience level serves as a significant determinant of compensation for aerospace engineers within New York City. While education and specialized skills are also important, the demonstrated ability to apply knowledge and solve real-world problems through years of practical application is a key driver of increased earning potential. A clear understanding of this relationship is crucial for engineers at all career stages to strategically plan their professional development and negotiate appropriate compensation based on their experience and expertise. Navigating salary expectations based on experience level can be challenging and requires thoughtful planning and a deep understanding of the value experience brings to the organization, it is still the main keypoint to the overall success.
3. Company Size
The size of an aerospace engineering firm operating within the New York City metropolitan area is demonstrably linked to compensation structures. Larger organizations, characterized by greater revenue streams and more extensive project portfolios, often exhibit the capacity to offer more competitive salaries compared to smaller or mid-sized companies.
- Resource Availability and Financial Stability
Larger aerospace companies typically possess greater financial resources, enabling them to invest more heavily in employee compensation and benefits packages. This financial stability translates into a higher baseline salary for aerospace engineers, reflecting the reduced risk associated with employment at established firms. Examples include major aerospace contractors with government contracts offering more lucrative packages than smaller, specialized firms focused on niche markets.
- Project Scope and Complexity
Larger companies often handle more complex and high-profile projects, requiring specialized expertise and advanced skill sets. These projects frequently demand a greater degree of responsibility and technical proficiency from engineers, justifying higher salaries to attract and retain qualified personnel. The opportunity to work on cutting-edge technologies and challenging assignments at larger firms can also contribute to increased earning potential.
- Hierarchical Structure and Career Advancement
Larger aerospace companies generally have more defined hierarchical structures and career advancement pathways. The potential for upward mobility within the organization, coupled with opportunities for professional development and training, can indirectly influence salary expectations. The prospect of progressing to higher-level positions with increased responsibilities serves as an incentive for engineers to remain with larger firms and contribute to long-term organizational goals.
- Benefits and Compensation Packages
Larger companies often provide more comprehensive benefits packages, including health insurance, retirement plans, stock options, and other perks. These benefits contribute to the overall value of employment and can offset differences in base salary between larger and smaller firms. The availability of robust benefits packages can be a significant factor in attracting and retaining talented aerospace engineers, particularly in a competitive labor market like New York City.
In summation, company size serves as a key determinant of aerospace engineer salaries in New York City. Larger organizations, due to their greater resources, project complexity, and structured career paths, are generally positioned to offer more competitive compensation packages, creating a discernible correlation between company scale and earning potential.
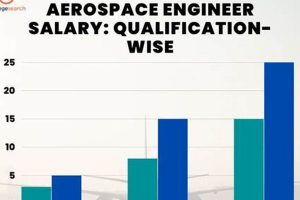
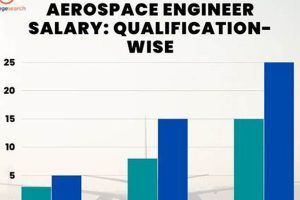
4. Education Attainment
Education attainment is a substantial determinant of compensation for aerospace engineers in the New York City area. A bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering is typically the minimum requirement for entry-level positions. However, the attainment of advanced degrees, such as a Master of Science (M.S.) or Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.), often correlates with increased earning potential. This is due to the specialized knowledge and advanced skills acquired through graduate-level coursework and research, which are highly valued by employers.
The effect of educational qualifications on earnings manifests in several ways. Aerospace engineers with advanced degrees are often qualified for more specialized roles, such as research and development, design engineering, or project management. These positions typically command higher salaries due to the increased responsibility and technical expertise required. For example, an engineer with a Ph.D. specializing in computational fluid dynamics may be hired to lead a team developing advanced aerodynamic models, a role that would likely be compensated at a higher rate than a position focused on routine testing or analysis. Furthermore, advanced degrees often enhance career advancement opportunities, leading to increased salaries over time. Many leadership roles within aerospace companies require or strongly prefer candidates with graduate-level education.
In conclusion, higher education attainment significantly influences the income of aerospace engineers in New York City. While a bachelor’s degree provides a foundation for entry into the field, pursuing advanced degrees often leads to increased earning potential through access to more specialized roles, greater responsibilities, and enhanced career advancement opportunities. Understanding the relationship between education and earning capacity is critical for aspiring and practicing aerospace engineers to make informed decisions about their career development and investment in further education.
5. Industry Demand
Industry demand serves as a primary driver influencing compensation levels for aerospace engineers within the New York City metropolitan area. Fluctuations in the aerospace sector, driven by technological advancements, economic conditions, and government policies, directly impact the need for skilled professionals and, consequently, their earning potential.
- Government Spending and Contracts
Government investment in aerospace research, defense programs, and space exploration significantly affects demand for aerospace engineers. Increased government spending often leads to a surge in contract opportunities for aerospace companies, driving up the need for qualified engineers and increasing their salaries. For instance, a large-scale government project focused on developing next-generation aircraft could create numerous job openings and elevate compensation levels within the sector. Declines in government funding, conversely, can lead to layoffs and decreased salary prospects.
- Commercial Aviation Growth
The health and expansion of the commercial aviation industry directly impact the demand for aerospace engineers. An increase in air travel, driven by economic growth and globalization, necessitates the development of new aircraft, improved air traffic control systems, and enhanced maintenance procedures. This increased activity requires a larger workforce of skilled engineers, resulting in higher salaries. Conversely, economic downturns and reduced air travel can lead to a decrease in demand and potential salary stagnation or reductions.
- Technological Innovation and Emerging Markets
Breakthroughs in aerospace technology, such as the development of electric aircraft, autonomous flight systems, and advanced materials, create new opportunities and specialized roles for aerospace engineers. The emergence of new markets, like urban air mobility (UAM) and space tourism, also fuels demand for engineers with expertise in these areas. These innovations often command higher salaries due to the specialized knowledge and skills required. A surge in drone technology, for example, has led to increased demand and compensation for engineers specializing in UAV design and control.
- Geographic Concentration of Aerospace Companies
The concentration of aerospace companies and research institutions within a specific geographic area, such as the New York City metropolitan area, can impact the local demand for aerospace engineers. A high concentration of firms can lead to increased competition for qualified professionals, driving up salaries. Conversely, a limited number of employers may result in lower salary offers due to reduced competition. The presence of major aerospace hubs and research facilities around NYC influences the compensation structure of the region.
In conclusion, industry demand functions as a critical variable in determining “aerospace engineering salary nyc.” Factors such as government spending, commercial aviation growth, technological innovation, and geographic concentration collectively influence the demand for aerospace engineers, ultimately shaping compensation trends within the New York City metropolitan area. A comprehensive understanding of these dynamics is essential for both employers and employees to navigate the evolving landscape of the aerospace engineering profession and to strategically plan their career and business decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding remuneration for aerospace engineers working in the New York City metropolitan area. Information presented herein aims to provide a clear and objective overview of salary-related aspects within this professional domain.
Question 1: What is the average income for an aerospace engineer in New York City?
The average income fluctuates based on experience, education, and employer size. However, current estimates place the median salary within a range that reflects the high cost of living and demand for skilled professionals in the region. Consult industry-specific salary surveys for precise figures.
Question 2: How does experience level affect earning potential?
Experience significantly impacts income. Entry-level positions command lower salaries compared to mid-career and senior-level roles. Demonstrated expertise and proven track records in project management, design, and analysis are directly correlated with increased compensation.
Question 3: Does company size influence salaries?
Larger aerospace firms with greater financial resources and more complex projects typically offer higher salaries and more comprehensive benefits packages than smaller companies. However, smaller firms may offer unique opportunities for career advancement and specialized experience.
Question 4: What role does education play in determining income?
While a bachelor’s degree is generally the minimum requirement, advanced degrees such as a Master’s or Ph.D. often lead to higher earning potential. Specialized knowledge and research skills acquired through graduate studies are valued by employers.
Question 5: Are there specific skills that can increase earning potential?
Proficiency in specialized software, such as CAD/CAM tools and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) packages, as well as expertise in areas like avionics, propulsion, and materials science, can significantly enhance an engineer’s market value and earning capacity.
Question 6: How does the cost of living in New York City factor into salary considerations?
The high cost of living in New York City necessitates higher salaries to maintain a reasonable standard of living. Compensation packages must account for expenses related to housing, transportation, taxes, and general goods and services.
This overview underscores the multifaceted factors influencing aerospace engineering compensation in New York City. Careful consideration of these elements is crucial for both employers and employees in navigating the complexities of the labor market.
The subsequent section will provide resources for further research and career planning within this field.
Aerospace Engineering Salary NYC
This exploration has analyzed key determinants influencing compensation within the aerospace engineering sector of New York City. Factors such as experience, education, company size, cost of living, and industry demand collectively shape earning potential. A thorough understanding of these dynamics is essential for professionals seeking to maximize their remuneration and for employers aiming to attract and retain qualified talent.
The data presented underscores the competitive nature of the New York City job market for aerospace engineers. Continued vigilance regarding industry trends and strategic investment in professional development remain paramount for sustained career success. Further research and proactive engagement within the aerospace community are strongly encouraged to navigate the evolving compensation landscape.