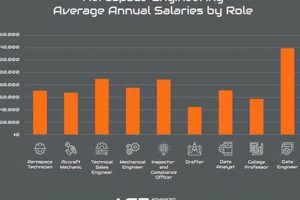
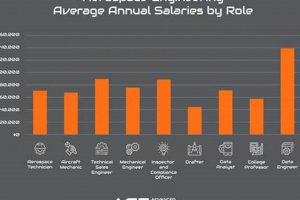
Positions within Heizer Aerospace encompass a range of roles related to the design, manufacturing, and maintenance of aircraft and spacecraft components. These opportunities can span engineering, production, quality control, and administrative functions, all contributing to the company’s operational success. For example, a mechanical engineer might design landing gear, while a quality inspector ensures adherence to stringent safety standards.
The significance of these employment opportunities lies in their contribution to the advancement of aerospace technology and the facilitation of air and space travel. They often offer individuals challenging and rewarding careers, with the potential for professional growth and development. Historically, the aerospace industry has been a driver of innovation, and fulfilling roles within companies like Heizer Aerospace contribute to that legacy.
The following sections will delve into specific areas related to career prospects, required qualifications, and the overall landscape of the aerospace sector, providing a more detailed understanding of the options available to those seeking employment in this dynamic field.
Guidance for Aspiring Candidates
The pursuit of placement at Heizer Aerospace necessitates strategic preparation and a focused understanding of industry requirements. This section presents key considerations for individuals seeking opportunities within the organization.
Tip 1: Target Skill Development: A strong foundation in relevant engineering disciplines, such as aerospace, mechanical, or electrical, is paramount. Focused coursework and hands-on projects demonstrably showcasing expertise in these areas are invaluable.
Tip 2: Emphasize Regulatory Compliance Knowledge: Familiarity with industry standards, including FAA regulations and AS9100 quality management systems, is highly beneficial. Certification or prior experience with these standards provides a significant advantage.
Tip 3: Highlight Practical Experience: Internships or co-op programs within the aerospace or related industries provide valuable practical experience. These experiences should be clearly articulated on resumes and during interviews, demonstrating the application of theoretical knowledge.
Tip 4: Demonstrate Problem-Solving Abilities: The aerospace industry frequently encounters complex challenges. Candidates should highlight instances where they successfully resolved technical problems, using examples that illustrate analytical and innovative thinking.
Tip 5: Network Actively: Attendance at industry events and engagement with professional organizations, such as AIAA, can facilitate valuable connections with industry professionals and potential hiring managers. These connections can provide insights into available positions and company culture.
Tip 6: Craft a Targeted Resume: Resumes should be tailored to specific roles within Heizer Aerospace. Highlighting relevant skills, experiences, and accomplishments that align with the job description is crucial for capturing the attention of recruiters.
Tip 7: Prepare for Technical Interviews: Technical interviews often involve in-depth discussions of engineering principles and problem-solving scenarios. Thorough preparation, including reviewing fundamental concepts and practicing technical questions, is essential for success.
These recommendations serve as a framework for individuals aiming to secure employment. Consistent effort in skill development, knowledge acquisition, and professional networking enhances the likelihood of success.
The concluding sections will synthesize these insights and offer a broader perspective on navigating the professional path within the aerospace domain.
1. Engineering Design
Engineering Design serves as a foundational pillar for many roles within Heizer Aerospace. It directly influences the functionality, safety, and efficiency of the company’s products and services. A failure in the design phase can cascade into significant problems during manufacturing and operation, potentially leading to costly recalls or, more seriously, safety risks. Consequently, positions requiring engineering design expertise are critical within the organizational structure.
Consider, for example, the design of a new composite wing structure. Engineers would be responsible for selecting appropriate materials, calculating stress tolerances, and creating detailed blueprints for manufacturing. These activities directly influence manufacturing, as processes must be tailored to meet the specifications outlined during the design phase. Quality assurance is then tasked with verifying that the final product meets the original design parameters, thereby upholding safety and performance standards. Positions such as stress analysts, CAD designers, and materials engineers exemplify the crucial connection between design and available opportunities.
In summary, Engineering Design is not merely a preliminary stage but a continuous process that shapes the entirety of a project lifecycle within Heizer Aerospace. The demand for skilled design engineers reflects the industry’s emphasis on innovation, safety, and precision. Understanding the symbiotic relationship between Engineering Design and subsequent operational phases is vital for prospective candidates seeking relevant opportunities.
2. Manufacturing Processes
Manufacturing processes are integral to the realization of aerospace designs, forming a crucial link between engineering concepts and tangible products. The efficiency, precision, and quality of these processes directly impact the performance, reliability, and safety of aerospace components. The availability and nature of employment at Heizer Aerospace are therefore heavily influenced by the specific manufacturing technologies and techniques employed.
- Precision Machining and Fabrication
This facet encompasses the use of advanced machinery and skilled technicians to create components with tight tolerances. Examples include CNC milling, turning, and grinding operations, crucial for producing engine parts, structural elements, and landing gear components. Positions in this area require expertise in materials science, machining techniques, and quality control, ensuring adherence to stringent aerospace standards.
- Composites Manufacturing
The utilization of composite materials, such as carbon fiber reinforced polymers, is increasingly prevalent in aerospace for their high strength-to-weight ratio. Manufacturing processes include layup, curing, and bonding techniques. Expertise in composite materials, tooling design, and non-destructive testing is essential for roles related to composites manufacturing. These processes play a critical role in aircraft weight reduction and performance enhancement.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing techniques are revolutionizing aerospace production by enabling the creation of complex geometries and customized parts. Powder bed fusion and directed energy deposition are examples of additive processes used in aerospace. Positions involving additive manufacturing necessitate a strong understanding of materials, process parameters, and post-processing techniques. This area enables rapid prototyping and the creation of highly optimized components.
- Assembly and Integration
The final stage involves the assembly of individual components into larger subassemblies or complete aircraft systems. This process requires meticulous attention to detail, adherence to assembly procedures, and comprehensive testing to ensure proper functionality and integration. Opportunities in assembly and integration demand proficiency in mechanical assembly, electrical wiring, and systems integration, contributing to the safe and reliable operation of aerospace vehicles.
The diverse range of manufacturing processes employed by Heizer Aerospace translates into a variety of employment opportunities for individuals with relevant skills and expertise. From precision machining to advanced composites manufacturing, each process requires specialized knowledge and contributes to the overall success of the company. The continued evolution of manufacturing technologies in aerospace ensures a dynamic and challenging environment for professionals in this field.
3. Quality Assurance
Quality Assurance is a critical function within Heizer Aerospace, directly impacting flight safety, product reliability, and regulatory compliance. Roles within Quality Assurance are thus integral to the company’s operational success and reflect the stringent demands of the aerospace industry. The performance of individuals in these positions determines the effectiveness of the quality management system and the overall reputation of the organization.
- Inspection and Testing
Inspection and testing involve the systematic examination of materials, components, and finished products to verify conformance with engineering specifications and regulatory standards. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT), dimensional inspection, and functional testing are frequently employed. Inspectors, test technicians, and quality engineers are essential for these processes. A real-world example includes the inspection of turbine blades for micro-cracks using radiographic techniques. The consequences of inadequate inspection can range from premature component failure to catastrophic accidents, underscoring the critical nature of these roles.
- Process Control and Auditing
Process control focuses on monitoring and optimizing manufacturing processes to minimize variation and defects. Statistical Process Control (SPC) techniques and process capability studies are often implemented. Internal audits are conducted to assess compliance with quality management systems, such as AS9100. Quality auditors and process engineers are key players in this area. The implementation of rigorous process control can prevent defects from occurring in the first place, significantly reducing scrap rates and improving product yield. An example is the monitoring of temperature and humidity during composite layup to ensure proper curing and prevent delamination.
- Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA)
The CAPA system is designed to identify, investigate, and resolve quality issues. Corrective actions are taken to address existing problems, while preventive actions aim to prevent future occurrences. Root cause analysis, risk assessments, and implementation of mitigation strategies are essential components. Quality specialists, engineers, and managers are involved in the CAPA process. An example involves investigating a recurring defect in a landing gear component and implementing changes to the manufacturing process to eliminate the root cause.
- Documentation and Records Management
Maintaining accurate and complete documentation is crucial for demonstrating compliance with regulatory requirements and providing traceability throughout the product lifecycle. This includes inspection reports, test data, calibration records, and material certifications. Document control specialists and quality assurance administrators play a key role in managing these records. Comprehensive documentation is essential for audits, investigations, and product liability claims. A practical instance is the meticulous recording of all material properties and processing parameters for each batch of composite material used in aircraft construction.
These facets of Quality Assurance demonstrate the breadth and depth of roles available within Heizer Aerospace. Each function requires specialized skills and expertise, but all contribute to the overarching goal of ensuring product quality and safety. Consequently, opportunities in Quality Assurance provide a pathway for individuals to contribute directly to the reliability and integrity of aerospace products and services.
4. Project Management
Project Management within Heizer Aerospace is not merely an administrative function but a core discipline that dictates the successful execution of complex engineering and manufacturing endeavors. Its significance permeates various roles, impacting timelines, budgets, and the ultimate quality of deliverables. Therefore, understanding Project Management’s multifaceted influence is critical for anyone considering opportunities at Heizer Aerospace.
- Scope Definition and Planning
This facet involves meticulously outlining project objectives, deliverables, tasks, and resource requirements. In aerospace, this often includes defining the specifications for new aircraft components, system upgrades, or research and development initiatives. For example, the development of a new lightweight composite material requires a detailed scope definition encompassing research, testing, and manufacturing processes. Roles involved include project managers, project engineers, and systems engineers, who collaborate to ensure clarity and feasibility from project inception. Ineffective scope definition can lead to cost overruns, schedule delays, and compromised product quality.
- Resource Allocation and Scheduling
Effective resource allocation entails assigning personnel, equipment, and funding to specific tasks within a project. Accurate scheduling involves creating realistic timelines, identifying critical paths, and managing dependencies. Consider the manufacturing of a satellite payload, which requires specialized equipment, skilled technicians, and precisely timed delivery of components. Project managers, schedulers, and resource managers collaborate to optimize resource utilization and maintain project momentum. Inefficient resource allocation or unrealistic scheduling can result in bottlenecks, delays, and increased project costs.
- Risk Management and Mitigation
Aerospace projects inherently involve risks related to technical complexity, regulatory compliance, and potential system failures. Risk management involves identifying potential risks, assessing their impact, and developing mitigation strategies. For instance, the development of a new engine technology carries risks related to performance, reliability, and safety. Risk managers, engineers, and quality assurance specialists work together to identify and mitigate these risks. Inadequate risk management can lead to unforeseen problems, project delays, and potential safety hazards.
- Monitoring and Control
Monitoring and control involve tracking project progress, measuring performance against planned metrics, and implementing corrective actions as needed. This includes monitoring budget adherence, schedule compliance, and quality metrics. The construction of a new aircraft assembly line, for example, requires constant monitoring of progress, cost, and quality. Project managers, controllers, and quality engineers collaborate to ensure that the project stays on track and meets its objectives. Ineffective monitoring and control can lead to undetected problems, cost overruns, and compromised project outcomes.
In summary, Project Management provides the structured framework within which engineering and manufacturing expertise converge at Heizer Aerospace. Roles requiring project management skills are crucial for ensuring efficient operations, meeting deadlines, and maintaining the high standards of quality and safety demanded by the industry. Recognizing the importance of these interconnected facets highlights the professional opportunities available within this critical area.
5. Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory Compliance represents a cornerstone of operations within Heizer Aerospace, directly influencing the scope and requirements of numerous positions. The aerospace industry is subject to stringent regulations mandated by governmental bodies like the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and international agencies. Adherence to these regulations is not merely a matter of legal obligation but a fundamental prerequisite for ensuring the safety and airworthiness of aircraft and related components. The impact on employment opportunities within Heizer Aerospace is profound. For instance, positions related to quality assurance, engineering design, and manufacturing processes often require in-depth knowledge and application of regulatory standards such as FAA Part 21 (Certification Procedures for Products and Parts) and AS9100 (Aerospace Quality Management System). Any deviation from these standards can have severe consequences, including fines, production delays, or, more critically, safety compromises.
Practical applications of regulatory compliance knowledge are evident across various roles. Engineers must design components that meet stringent performance and safety requirements outlined in regulations. Manufacturing personnel must adhere to approved processes and quality control procedures to ensure that products are built to the required standards. Quality assurance specialists are responsible for auditing processes, inspecting products, and maintaining documentation to demonstrate compliance. For example, when designing a new aircraft engine, engineers must consider FAA regulations concerning engine safety, performance, and emissions. Manufacturing processes must be validated to ensure consistent product quality, and quality control inspections must verify that each engine meets the required standards. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in the engine not being certified for use, rendering the entire project commercially unviable.
In conclusion, Regulatory Compliance is an indispensable element embedded within the structure of Heizer Aerospace. Comprehending the significance of regulations and their direct impact on various roles offers candidates a considerable advantage when seeking related employment opportunities. Addressing the challenges of navigating complex regulatory frameworks and maintaining consistent compliance is a critical component of the company’s mission to ensure the safety, reliability, and regulatory adherence of all aerospace products and services.
Frequently Asked Questions About Positions at Heizer Aerospace
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding career prospects and requirements for employment with Heizer Aerospace. These questions are intended to provide clarity and insight for prospective applicants.
Question 1: What types of engineering disciplines are most relevant for employment opportunities?
A strong foundation in aerospace, mechanical, electrical, or materials engineering is generally preferred. Specific roles may require specialized expertise in areas such as structural analysis, propulsion systems, or avionics.
Question 2: Is prior experience in the aerospace industry a mandatory requirement?
While prior experience is advantageous, it is not always mandatory. Entry-level positions may be available for recent graduates with relevant academic backgrounds and strong technical skills. Internships or co-op experiences are highly valued.
Question 3: What is the significance of regulatory compliance knowledge for potential candidates?
Familiarity with industry standards such as FAA regulations and AS9100 quality management systems is highly beneficial. Certain positions, particularly in quality assurance and engineering, require a thorough understanding of regulatory requirements.
Question 4: How does Heizer Aerospace approach professional development and training for its employees?
Heizer Aerospace is committed to providing ongoing professional development opportunities to its employees. This may include training programs, mentorship opportunities, and tuition reimbursement for advanced education.
Question 5: What are the key qualities sought in prospective candidates beyond technical expertise?
In addition to technical proficiency, Heizer Aerospace values candidates who demonstrate strong problem-solving skills, teamwork abilities, a commitment to continuous improvement, and adherence to ethical principles.
Question 6: Where can individuals find information regarding current openings at Heizer Aerospace?
Information regarding current employment opportunities can typically be found on the company’s official website, through online job boards, and at industry-specific career fairs.
This compilation of questions and answers provides a foundational understanding of expectations and opportunities within the company.
The concluding sections will provide a broader perspective on navigating the professional path within the aerospace domain.
Conclusion
This article has explored various facets of employment opportunities within Heizer Aerospace, underscoring the diverse roles, required qualifications, and the significance of regulatory compliance. Emphasis was placed on key functional areas such as Engineering Design, Manufacturing Processes, Quality Assurance, Project Management, and Regulatory Compliance, highlighting the interconnectedness of these disciplines in achieving the company’s objectives.
The information presented should provide aspiring candidates with a foundational understanding of the landscape of “heizer aerospace jobs”. Further research and targeted preparation are recommended for those seeking to contribute to this dynamic sector. The pursuit of a fulfilling career in aerospace demands continuous learning and a commitment to excellence, driving innovation and ensuring the safety of air and space travel for generations to come.