Positions within institutions dedicated to advanced learning in aeronautics and astronautics constitute a specific employment sector. These roles encompass a diverse range of opportunities, including instruction, research, administration, and technical support, all focused on advancing knowledge and preparing individuals for careers in the aerospace field. An example would be a faculty member at a specialized school training future engineers for the space industry.
The value of these career paths resides in their contribution to technological progress and workforce development within a critical industry. Historically, these institutions have played a pivotal role in shaping the aerospace landscape, driving innovation, and providing the specialized training necessary to meet the evolving demands of the sector. They are vital conduits for expertise and advancements, impacting everything from commercial aviation to space exploration.
Subsequent sections will delve into specific examples of positions available within these institutions, the required qualifications for various roles, and the career trajectories that professionals might pursue within this specialized environment. Furthermore, this analysis will address the current market trends and the future outlook for professionals seeking employment in this sphere.
Guidance for Securing a Position in Advanced Aeronautical Education
Individuals pursuing opportunities within specialized educational settings centered on aerospace disciplines should adopt a strategic and informed approach. The following points outline key considerations for maximizing the potential for successful employment.
Tip 1: Cultivate Specialized Expertise: Demonstrable mastery in a specific aerospace engineering discipline or related field is paramount. Advanced degrees, research publications, and relevant industry experience are highly valued.
Tip 2: Emphasize Pedagogical Skills: The ability to effectively communicate complex technical concepts is essential. Experience in teaching, mentoring, or presenting technical information should be highlighted.
Tip 3: Network Strategically: Active participation in professional organizations and attendance at industry conferences provides valuable opportunities to connect with potential employers and learn about available openings.
Tip 4: Tailor Application Materials: Each application should be specifically tailored to the requirements of the position and the mission of the institution. Generic applications are unlikely to be successful.
Tip 5: Showcase Research Contributions: For research-oriented roles, a strong track record of publications, patents, or grant funding is critical. The impact and relevance of the research should be clearly articulated.
Tip 6: Highlight Curriculum Development Experience: Experience in designing and implementing innovative curricula that meet industry needs is highly desirable, particularly in fast-evolving areas like autonomous systems or advanced materials.
Tip 7: Demonstrate a Commitment to Continuous Learning: The aerospace field is constantly evolving. A willingness to stay abreast of the latest advancements and adapt teaching methods accordingly is essential.
By focusing on developing specialized skills, honing pedagogical abilities, and networking strategically, aspiring professionals can significantly enhance their prospects. A commitment to continuous learning and tailored application materials further strengthens candidacy.
The subsequent section will address the common challenges encountered during the application process and strategies for overcoming these obstacles, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of securing a fulfilling role in advanced aeronautical education.
1. Instruction
Instruction is a fundamental pillar of institutions dedicated to advanced aeronautical education. This aspect directly pertains to imparting knowledge and skills crucial for future aerospace professionals. Effective pedagogical practices within these settings directly correlate with the quality of graduates entering the industry. A faculty member lecturing on aerodynamics principles is an example, where the quality of their delivery and depth of their understanding directly influences the students’ comprehension and subsequent application of these principles in real-world scenarios.
Beyond lectures, “Instruction” encompasses laboratory sessions, design projects, and research mentorship. These elements provide practical, hands-on experience complementing theoretical knowledge. For example, leading a student design team through the process of building and testing a small-scale aircraft directly translates theoretical knowledge into tangible engineering skills. Similarly, mentoring students in research projects allows them to engage in cutting-edge advancements and prepares them for innovative research careers. The design, building, and testing phases of aerospace studies are necessary applications of learned concepts.
In summary, “Instruction” forms the bedrock of career opportunities within specialized aerospace education. The effectiveness of instructional practices significantly impacts the quality of the aerospace workforce and the progression of technological advancements. Understanding the multifaceted role of “Instruction”encompassing lectures, practical application, and mentorshipis essential for both educators and aspiring professionals in this field. An innovative and informative approach ensures educators are equipped to nurture and prepare the next generation.
2. Research
Research constitutes a vital function within aerospace educational institutions, directly impacting the advancement of knowledge and the development of innovative technologies. Its presence is a key indicator of an institution’s commitment to leadership in the field, shaping both the curriculum and the opportunities available within its structure.
- Fundamental Investigation
This facet encompasses the exploration of core scientific principles relevant to aerospace engineering. Examples include investigating novel materials for aircraft construction or developing advanced algorithms for flight control systems. Such research contributes to the foundational knowledge base upon which future aerospace technologies will be built. For those holding “aerospace academy jobs” focused on research, these investigations are often the core of their work and contribute significantly to their professional standing.
- Applied Development
This focuses on translating theoretical knowledge into practical applications. Projects in this area might involve designing and testing new aircraft components, optimizing propulsion systems, or developing simulation tools for flight training. This directly enhances the capabilities of the aerospace industry and provides opportunities for institutions to partner with companies on cutting-edge projects. It also allows for individuals in research-focused “aerospace academy jobs” to work on projects that have tangible results in the wider world.
- Technological Advancement
This facet focuses on pushing the boundaries of aerospace technology, exploring novel concepts and approaches. Research into hypersonic flight, space exploration technologies, or the development of autonomous aerial vehicles exemplifies this area. These endeavors often attract significant funding and recognition, positioning institutions and their faculty as leaders in their respective fields. Academic positions with “aerospace academy jobs” may find that this facet provides exciting development and discovery.
- Educational Integration
This refers to the incorporation of research findings into the curriculum, ensuring that students receive up-to-date information and are exposed to the latest advancements. Furthermore, integrating students into research projects provides valuable hands-on experience and prepares them for careers in research and development. Mentoring students within research settings represents a crucial component of many “aerospace academy jobs”, ensuring the next generation are innovators.
These interwoven facets illustrate the central role “research” plays within specialized aerospace institutions. Through these activities, these establishments significantly influence the trajectory of the entire sector, offering a range of opportunities to individuals pursuing careers in education and innovation.
3. Curriculum
The curriculum constitutes a critical component directly influencing the landscape of opportunities within aerospace education. Its design, implementation, and continuous refinement are fundamental responsibilities associated with numerous “aerospace academy jobs.” The cause-and-effect relationship is evident: a well-designed curriculum attracts high-caliber students, fosters research excellence, and ultimately enhances the reputation of the institution. This, in turn, creates a demand for qualified faculty and staff to deliver and support the program. For instance, the introduction of a new specialization in advanced propulsion systems necessitates the recruitment of professors with expertise in that area, lecturers to teach specialized courses, and laboratory technicians to maintain associated equipment. The curriculum functions as a driving force, shaping the required skill sets and experience profiles of individuals holding “aerospace academy jobs”.
The importance of the curriculum as a central tenet of employment can be further exemplified by considering accreditation standards. Aerospace programs seeking accreditation from bodies such as ABET (Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology) must demonstrate a rigorous and relevant curriculum that meets specific learning outcomes. This necessitates a continuous evaluation and updating process, often led by faculty committees and academic administrators. These individuals, occupying various “aerospace academy jobs,” are tasked with ensuring that the curriculum remains aligned with industry needs, technological advancements, and evolving accreditation criteria. Their involvement directly influences the institution’s ability to maintain its accreditation, which subsequently impacts its attractiveness to prospective students and employers.
In conclusion, understanding the central role of the curriculum is essential for both job seekers and employers in the field of aerospace education. The curriculum dictates the specific knowledge and skills required for various positions, drives the demand for specialized expertise, and directly influences the reputation and accreditation of the institution. The design, delivery, and ongoing evaluation are integral functions linked to “aerospace academy jobs.” Challenges remain in maintaining relevance and adapting to rapid technological advancements; however, those who excel in navigating these challenges contribute significantly to the success and advancement of aerospace education.
4. Mentorship
Within the ecosystem of “aerospace academy jobs,” mentorship serves as a critical bridge connecting academic theory with practical application and professional development. Its significance extends beyond simple guidance, fostering the growth of future leaders and innovators in the aerospace sector.
- Student Guidance and Project Supervision
Faculty members in “aerospace academy jobs” often oversee student research projects and design teams. This involves providing technical expertise, guiding students through the research process, and fostering critical thinking skills. Effective mentorship in this context translates to students who are not only technically proficient but also capable of independent problem-solving and innovation, qualities highly valued by prospective employers in the aerospace industry. An example includes a professor advising a student team designing a small satellite, guiding them through the complexities of system integration and testing.
- Career Development and Networking
Mentorship extends beyond academic instruction to encompass career guidance and networking opportunities. Faculty members leverage their industry connections to help students secure internships, co-op positions, and entry-level jobs. This assistance is particularly crucial in a competitive field like aerospace engineering. A mentor might introduce a promising student to a contact at a major aerospace company, facilitating an invaluable internship experience that launches the student’s career. Mentorship can be the key for a career path.
- Ethical and Professional Standards
Mentorship plays a critical role in instilling ethical and professional standards within the next generation of aerospace professionals. Faculty members in “aerospace academy jobs” serve as role models, demonstrating integrity, responsibility, and a commitment to safety. They guide students in navigating complex ethical dilemmas, preparing them to make sound decisions in their future careers. An ethical dilemma where mentorship and academic experience is needed.
- Fostering a Culture of Innovation
Effective mentorship encourages students to think creatively and challenge conventional wisdom. Faculty in aerospace academy jobs who are skilled mentors nurture innovative thinking by providing a safe and supportive environment for students to explore new ideas and develop their own solutions. This can include encouraging students to pursue unconventional research topics or to participate in design competitions that push the boundaries of aerospace technology. Fostering a culture of innovation is key to progress.
The multifaceted nature of mentorship highlights its essential role in shaping the future aerospace workforce and creating a positive work environment. Through guidance, networking, and ethical development, mentorship contributes significantly to the success of individuals holding “aerospace academy jobs,” ultimately fostering the progress and integrity of the aerospace industry.
5. Administration
Within specialized institutions focused on aeronautical and astronautical education, the “Administration” function forms the operational backbone that supports teaching, research, and student development. Its efficacy directly influences the overall performance and reputation of the institution, thereby affecting the nature and availability of “aerospace academy jobs”.
- Resource Management
This facet encompasses the strategic allocation of financial, physical, and human capital to support the institution’s mission. Responsibilities include budget development and oversight, facilities maintenance, and procurement of equipment and supplies. For “aerospace academy jobs,” effective resource management translates to well-equipped laboratories, state-of-the-art computational resources, and competitive salaries for faculty and staff. A real-world example is the administration securing funding for a new wind tunnel, benefiting both research capabilities and the educational experience for students.
- Regulatory Compliance
This involves adhering to federal, state, and local regulations, as well as accreditation standards. Compliance activities range from ensuring safety protocols in research laboratories to maintaining accurate student records. For “aerospace academy jobs,” this ensures that the institution maintains its accreditation, a crucial factor in attracting funding, students, and qualified personnel. Consider an administrative team managing FAA regulations regarding drone operations on campus, mitigating legal risks and fostering a safe research environment.
- Strategic Planning
This facet focuses on setting the institution’s long-term goals and developing strategies to achieve them. It includes assessing market trends, identifying new opportunities, and fostering partnerships with industry and government agencies. A strategic plan that prioritizes the development of a new aerospace engineering program, for example, would create new “aerospace academy jobs” for faculty with expertise in that area, as well as administrative staff to support the program’s operations.
- Student Services
This function includes student admissions, registration, advising, and career counseling. Well-managed student services are crucial for attracting and retaining talented students, ultimately enhancing the institution’s reputation. Consider the scenario in which the administration enhances career services, facilitating industry connections and job placement for graduating students, which strengthens the institution’s appeal to prospective students and their families.
These elements are inextricably linked, influencing everything from facility quality to curriculum development. Institutions that invest in robust administrative structures are better positioned to attract top talent and provide a superior educational experience, ultimately solidifying the value and demand for “aerospace academy jobs”. A functional Administration can ensure smooth operation.
6. Innovation
The capacity for generating novel ideas and translating them into tangible advancements constitutes a fundamental element of institutions dedicated to aerospace education. The presence of a robust innovation ecosystem directly impacts the attractiveness and effectiveness of these institutions, subsequently influencing the nature and scope of “aerospace academy jobs.” A cause-and-effect relationship exists wherein a commitment to innovation attracts funding, high-caliber faculty and students, and industry partnerships. Consider a university developing a breakthrough propulsion system, which in turn attracts research grants, top-tier professors with expertise in propulsion, and collaborations with aerospace companies seeking to implement the technology. Positions in “aerospace academy jobs” are then created or enhanced as a result. Innovation is a key element of “aerospace academy jobs.”
Further analysis reveals practical applications stemming from this connection. For example, the curriculum design and development processes within aerospace programs must continually adapt to emerging technologies and industry needs. Faculty members in “aerospace academy jobs” are tasked with incorporating new research findings, simulation tools, and design methodologies into their courses. This requires a commitment to staying abreast of the latest advancements and developing innovative pedagogical approaches. Another instance includes the creation of specialized research centers focused on areas such as autonomous aerial vehicles or advanced materials. These centers attract talented researchers and provide opportunities for students to engage in cutting-edge projects, further fostering a culture of innovation and development for new technologies in aviation. Aerospace academy personnel have a huge responsibility on this.
In summary, innovation serves as a catalyst for progress and a defining characteristic of leading institutions in aerospace education. The pursuit of innovation is not merely an academic exercise; it is a strategic imperative that drives institutional growth, enhances the quality of education, and shapes the landscape of “aerospace academy jobs”. Challenges exist in fostering and sustaining a culture of innovation, requiring investments in infrastructure, interdisciplinary collaboration, and a supportive environment for risk-taking. The emphasis on innovation within “aerospace academy jobs” is therefore a clear indication of the sector’s dynamic nature and its commitment to shaping the future of aerospace technology. Without them, the progress in this arena would be stale and outdated.
7. Advancement
The concept of professional “Advancement” is inextricably linked to the landscape of “aerospace academy jobs,” shaping career trajectories, institutional prestige, and the overall direction of the aerospace field. A direct correlation exists between an individual’s dedication to professional development and the opportunities available within this sector. For example, continuous engagement with cutting-edge research and a demonstrable commitment to pedagogical innovation directly influences the potential for promotion from a lecturer position to a tenured professorship or administrative leadership role. The impetus for academic and professional growth serves as a fundamental driver within specialized learning environments that are focused on aerospace expertise.
Consider the practical applications of this understanding. Institutions that prioritize faculty “Advancement” through mentorship programs, research funding, and conference support are more likely to attract and retain top talent. This, in turn, contributes to a higher quality of education and research output, enhancing the institution’s reputation and competitiveness. Furthermore, actively seeking positions that offer clear pathways for professional “Advancement” enables individuals to not only increase their earning potential but also to make a greater contribution to the field through leadership roles, curriculum development, and mentorship of future aerospace professionals. Successful leaders, educators, and employees of this industry are often seen advancing to make innovations and achievements in this field.
In conclusion, “Advancement” represents a critical component of “aerospace academy jobs,” influencing both individual career paths and institutional success. Recognizing the importance of continuous learning, research engagement, and pedagogical development is essential for navigating this specialized environment. Challenges remain in ensuring equitable access to opportunities for “Advancement” and in fostering a culture that values both individual and collective growth. Nevertheless, a commitment to “Advancement” remains a defining characteristic of successful professionals and institutions in aerospace education, driving progress and shaping the future of the field. This continuous improvement ensures that aviation development continues and expands.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Aerospace Academy Jobs
The following addresses common inquiries concerning employment opportunities within specialized aerospace institutions. The information presented aims to provide clarity and informed guidance to prospective applicants.
Question 1: What are the typical qualifications required for faculty positions within aerospace academies?
Typically, faculty positions demand a doctoral degree in aerospace engineering or a closely related field. A strong record of research publications, teaching experience, and relevant industry experience are highly valued. Some positions may also require professional certifications or licenses.
Question 2: Are there opportunities for individuals with backgrounds in fields other than aerospace engineering?
While aerospace engineering is the most common background, related fields such as mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, physics, and mathematics may be considered for certain positions, particularly those involving specialized research areas or interdisciplinary programs. Possessing unique skills or knowledge may be necessary.
Question 3: How competitive are “aerospace academy jobs” compared to industry positions?
The level of competition varies depending on the specific position and institution. Faculty positions at prestigious universities or research institutions are generally highly competitive, while positions at smaller or less well-known academies may be less so. Industry demands skills and qualifications in order to be hired.
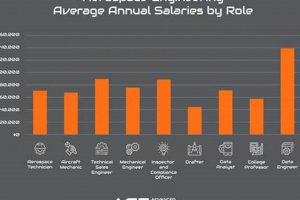
Question 4: What is the typical salary range for various “aerospace academy jobs”?
Salary ranges vary significantly based on factors such as position, experience, institution, and geographic location. Faculty salaries are generally competitive with industry positions, particularly for senior-level positions. Administrative and support staff salaries may be lower than those in industry.
Question 5: Are there opportunities for individuals seeking part-time or adjunct positions?
Yes, many aerospace academies offer part-time or adjunct positions for instructors, researchers, and technical staff. These positions can be a good option for individuals seeking flexible work arrangements or those transitioning into academia.
Question 6: What is the career progression path for individuals working in “aerospace academy jobs”?
Career progression paths vary depending on the specific position and institution. Faculty members typically advance through the ranks of assistant professor, associate professor, and full professor. Administrative and support staff may advance to positions with greater responsibility and higher salaries.
In summary, aerospace academy positions represent a diverse range of opportunities for individuals with a passion for aerospace and a commitment to education and research. Understanding the specific requirements, qualifications, and career paths associated with these roles is essential for prospective applicants.
The subsequent section will provide insights into strategies for preparing for a successful career in this dynamic and challenging field.
Concluding Analysis of Opportunities in Advanced Aeronautical and Astronautical Education
This exploration has elucidated the multifaceted nature of “aerospace academy jobs,” underscoring their importance in driving technological advancement and shaping the future workforce. The analysis encompassed the diverse roles available, ranging from instruction and research to administration and mentorship, each contributing to the overall mission of these specialized institutions. Further consideration was given to the required qualifications, the career trajectories, and the prevailing market trends that define this sector. In sum, the investigation of “aerospace academy jobs” offers individuals critical insight into the potential for impactful and fulfilling careers within advanced aeronautical and astronautical education.
The enduring significance of these positions lies in their contribution to the continued progress of the aerospace field. As technology evolves and the demand for skilled professionals increases, the role of these academies in providing specialized training and fostering innovation will remain paramount. Prospective candidates are encouraged to pursue opportunities within this sector, recognizing the profound impact their expertise can have on the future of aerospace. The importance of these opportunities is clear and will continue to affect the aerospace landscape.