The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) offers a rigorous and comprehensive program focused on the design, development, and analysis of aircraft, spacecraft, and related systems. This field combines principles of mathematics, physics, and engineering to address challenges in flight within Earth’s atmosphere and beyond.
This area of study holds significance due to its contributions to national defense, space exploration, and commercial aviation. Graduates of programs like this are often at the forefront of technological advancement, contributing to innovations in areas such as sustainable aviation, satellite technology, and autonomous systems. Historically, programs like this have played a pivotal role in shaping the aerospace industry, from the development of jet engines to the exploration of the solar system.
The following sections will delve into specific aspects of the curriculum, research opportunities, and the faculty expertise that define the program. These elements are crucial in understanding the depth and breadth of the educational experience provided.
Success in this challenging academic pursuit requires a dedicated and strategic approach. The following are essential considerations for students pursuing studies in this domain.
Tip 1: Establish a Strong Foundation in Core Sciences: A thorough understanding of mathematics, physics, and computer science is paramount. These disciplines provide the bedrock for comprehending advanced aerospace concepts.
Tip 2: Engage Actively in Hands-on Projects: Theoretical knowledge is most effectively reinforced through practical application. Participation in design-build-fly competitions or research projects offers invaluable experience.
Tip 3: Cultivate Strong Communication Skills: The ability to articulate complex technical ideas clearly and concisely, both verbally and in writing, is critical for collaboration and project management.
Tip 4: Seek Mentorship from Faculty and Industry Professionals: Guidance from experienced individuals can provide invaluable insights into career paths, research opportunities, and industry trends.
Tip 5: Master Computational Tools and Software: Proficiency in industry-standard software for modeling, simulation, and data analysis is essential for modern aerospace engineers.
Tip 6: Prioritize Time Management and Organizational Skills: The demanding curriculum requires meticulous planning and execution. Effective time management is crucial for balancing coursework, research, and extracurricular activities.
Tip 7: Participate in Research Opportunities: Working on cutting-edge research projects, whether in aerodynamics, propulsion, or materials science, provides invaluable hands-on experience and exposure to real-world problems.
Adherence to these guidelines can significantly enhance the learning experience and prepare students for successful careers in the field. Cultivating these skills and strategies will prove invaluable throughout a career in this dynamic industry.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific aspects of career prospects and future trends within the industry, providing a comprehensive overview for prospective students.
1. Cutting-edge Research
Cutting-edge research is integral to the academic environment at MIT, shaping the institution’s aerospace engineering program and establishing its prominence in the field. The focus on pioneering discoveries and innovative applications is essential for educating future leaders and advancing technological frontiers.
- Hypersonics Research
Research into hypersonic flight explores the dynamics of vehicles traveling at five times the speed of sound or greater. MIT’s contributions involve designing advanced materials and propulsion systems to withstand extreme aerodynamic heating and pressure. These endeavors have implications for future high-speed transportation and national defense capabilities. The institution’s wind tunnels and simulation facilities support this research.
- Sustainable Aviation Initiatives
Sustainable aviation research at MIT addresses the environmental impact of air travel by developing alternative fuels, designing more efficient aircraft, and optimizing air traffic management. This encompasses work on electric and hybrid-electric propulsion systems, biofuels, and advanced composite materials to reduce aircraft weight and emissions. These efforts contribute to mitigating climate change and promoting a more environmentally responsible aerospace industry.
- Autonomous Systems Development
The development of autonomous systems for aerospace applications involves creating self-governing aircraft and spacecraft capable of performing complex tasks with minimal human intervention. MIT’s research in this area includes the development of advanced sensors, algorithms for decision-making, and robust control systems. Applications range from unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for surveillance and reconnaissance to autonomous satellites for Earth observation and space exploration.
- Advanced Materials and Structures
Research into advanced materials and structures focuses on creating lightweight, high-strength materials for aerospace vehicles. This involves exploring novel alloys, composites, and nanomaterials with enhanced properties. MIT’s work in this area contributes to the development of more fuel-efficient aircraft, spacecraft capable of withstanding extreme environments, and innovative designs for aerospace structures. These developments directly impact performance and safety.
These research areas, among others, demonstrate MIT’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of aerospace knowledge and technology. The practical impact of these initiatives is far-reaching, affecting industries, governments, and the overall advancement of aerospace capabilities worldwide. The institution’s dedication to research ensures its continued leadership in the field.
2. Rigorous Curriculum
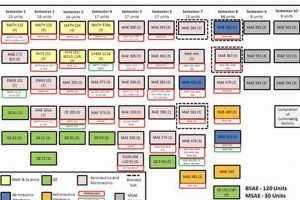
A rigorous curriculum is fundamental to aerospace engineering education at MIT. It ensures graduates possess the deep technical knowledge and problem-solving abilities necessary to excel in the demanding aerospace industry. The curriculum’s intensity and comprehensive nature are hallmarks of the program.
- Foundational Coursework in Mathematics and Physics
The program begins with a strong emphasis on mathematics (calculus, differential equations, linear algebra) and physics (classical mechanics, electromagnetism, thermodynamics). This groundwork is essential, as these principles underpin all subsequent aerospace engineering topics. For instance, understanding fluid dynamics (rooted in calculus and physics) is crucial for designing efficient airfoils. A weak foundation in these areas hinders progress in specialized aerospace courses.
- Core Aerospace Engineering Disciplines
Students delve into core disciplines such as aerodynamics, propulsion, structures, and control systems. Aerodynamics courses cover the behavior of airfoils and aircraft, while propulsion examines jet engines and rocket propulsion. Structures focuses on the design and analysis of aircraft and spacecraft components. Control systems involve developing systems that ensure stability and maneuverability. Successful completion of these core subjects is paramount for progressing to more advanced topics.
- Design and Project-Based Learning
The curriculum incorporates extensive design and project-based learning opportunities. Students work on teams to design, build, and test aerospace systems, such as aircraft, rockets, or satellites. These projects provide invaluable hands-on experience, bridging the gap between theory and practice. For instance, a team might design a small unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) from concept to flight testing, facing real-world engineering challenges along the way.
- Advanced Electives and Specializations
The program offers a wide range of advanced electives, allowing students to specialize in areas of interest, such as space systems engineering, autonomous systems, or computational fluid dynamics. These electives enable students to tailor their education to specific career goals or research interests. For example, a student interested in space exploration might take electives in orbital mechanics and spacecraft design.
The rigorous curriculum is a defining feature of the aerospace engineering program at MIT. By emphasizing foundational knowledge, core disciplines, hands-on experience, and advanced specialization, it prepares graduates to tackle the most challenging problems in the aerospace field. The demanding nature of the program reflects the high standards and expectations of the industry it serves.
3. World-renowned Faculty
The distinction of the aerospace engineering program at MIT is fundamentally linked to the presence of its world-renowned faculty. Their expertise, research contributions, and dedication to education form the cornerstone of the program’s excellence and influence on the aerospace industry.
- Expertise in Diverse Aerospace Disciplines
The faculty comprises experts spanning the breadth of aerospace engineering, from aerodynamics and propulsion to space systems and autonomous vehicles. This diverse expertise ensures students are exposed to the latest advancements and fundamental principles across the field. For example, a professor specializing in computational fluid dynamics may contribute significantly to aircraft design optimization. Their involvement provides real-world context and specialized training.
- Pioneering Research Contributions
Many faculty members are actively engaged in cutting-edge research, pushing the boundaries of aerospace technology. Their contributions often result in patents, publications in leading journals, and the development of innovative technologies. A professor leading research on sustainable aviation fuels, for instance, might influence future environmental regulations and industry practices. This research informs the curriculum and provides students with opportunities to participate in groundbreaking projects.
- Dedication to Student Mentorship
The faculty are committed to mentoring students, providing guidance and support for their academic and professional development. This mentorship often extends beyond the classroom, with faculty advising student projects, research endeavors, and career paths. A professor advising a student team in a design-build-fly competition, for example, instills practical engineering skills and teamwork. This mentorship is invaluable for shaping future leaders in the aerospace sector.
- Industry and Government Collaboration
Many faculty maintain strong ties with industry and government agencies, facilitating collaboration on research projects and providing students with access to internships and career opportunities. A professor consulting with NASA on a mission to Mars, for example, brings real-world challenges and insights into the classroom. These collaborations ensure the curriculum remains relevant and responsive to the evolving needs of the aerospace industry.
In summary, the world-renowned faculty are not merely instructors but active contributors to the aerospace field, whose expertise, research, mentorship, and industry connections are critical in shaping the educational experience and preparing students for success in aerospace engineering at MIT.
4. Interdisciplinary collaboration
Interdisciplinary collaboration constitutes a fundamental component of the aerospace engineering experience at MIT. The complex nature of aerospace challenges, ranging from advanced materials development to autonomous systems design, necessitates the integration of knowledge and methodologies from diverse fields. This collaborative approach is not merely supplementary; it is integral to fostering innovation and problem-solving within the program. Real-world examples abound, such as joint projects involving the Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics, the Department of Mechanical Engineering, and the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science to create more efficient and reliable flight control systems. The impact of this collaboration extends to graduates who are equipped to navigate complex projects requiring diverse expertise.
Furthermore, the emphasis on interdisciplinary collaboration extends beyond traditional engineering domains. Collaborations with the Sloan School of Management, for example, allow students to gain insight into the economic and logistical aspects of the aerospace industry, enhancing their ability to contribute to strategic decision-making. Research teams frequently include members from diverse academic backgrounds, reflecting the reality that comprehensive aerospace solutions often require considering ethical, economic, and societal factors. The practical application of this understanding is demonstrated in projects focusing on sustainable aviation, which necessitate a combination of engineering expertise and policy considerations.
In conclusion, interdisciplinary collaboration serves as a crucial catalyst for innovation in aerospace engineering at MIT. The emphasis on integrating knowledge from various fields prepares students to tackle the multifaceted challenges of the aerospace industry. While logistical and communication challenges can arise when managing such diverse teams, the benefits of a more holistic and comprehensive approach to problem-solving outweigh these difficulties. The ability to bridge disciplinary gaps and work effectively in collaborative environments is a defining characteristic of graduates from the program.
5. Innovation Leadership
Innovation leadership is a defining characteristic of the aerospace engineering program at MIT. The institution cultivates an environment where students and faculty are encouraged to challenge existing paradigms and drive transformative advancements in the field. This emphasis on pioneering new solutions ensures that graduates are not merely competent engineers but also visionary leaders capable of shaping the future of aerospace.
- Cultivating a Culture of Experimentation
MIT fosters a culture where experimentation is valued, and failure is viewed as a learning opportunity. Students are encouraged to pursue unconventional ideas and explore novel approaches to aerospace challenges. This mindset is crucial for breakthroughs and fosters an atmosphere where innovative solutions can emerge. For instance, student-led initiatives like the MIT Rocket Team allow students to design, build, and launch rockets, providing hands-on experience in overcoming complex engineering problems and pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
- Emphasis on Fundamental Research
Innovation leadership is directly tied to a strong foundation in fundamental research. Faculty and students at MIT engage in cutting-edge research across a broad spectrum of aerospace disciplines, from advanced materials to autonomous systems. This research provides the knowledge base for developing new technologies and solving complex engineering problems. For instance, research into new propulsion systems can lead to breakthroughs in fuel efficiency and reduced emissions, transforming the aviation industry.
- Translation of Research into Real-World Applications
The aerospace engineering program at MIT prioritizes the translation of research findings into tangible, real-world applications. Students are encouraged to participate in projects that have the potential to impact industry and society. This emphasis on practical application fosters a sense of responsibility and encourages students to think critically about the societal implications of their work. An example is the development of new satellite technologies that can be used to monitor climate change or provide communication services to remote areas.
- Fostering Entrepreneurial Mindset
The program instills an entrepreneurial mindset in its students, encouraging them to identify unmet needs and develop innovative solutions that can be commercialized. This entrepreneurial spirit is supported by resources and programs that help students launch their own companies and bring their ideas to market. For example, students may develop new sensor technologies for aircraft maintenance and then found a startup to commercialize their technology, creating new jobs and contributing to economic growth.
In conclusion, innovation leadership is not just a buzzword; it is a core value that permeates the aerospace engineering program at MIT. By fostering a culture of experimentation, emphasizing fundamental research, translating research into real-world applications, and instilling an entrepreneurial mindset, the program empowers its graduates to become transformative leaders in the aerospace industry and beyond.
Frequently Asked Questions about Aerospace Engineering at MIT
The following addresses common inquiries regarding the curriculum, admission requirements, and career prospects associated with the aerospace engineering program at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Question 1: What are the specific admission requirements for the aerospace engineering program at MIT?
Admission to the aerospace engineering program at MIT is highly competitive. Applicants must demonstrate exceptional academic performance in mathematics, physics, and related STEM fields. Standardized test scores, particularly the SAT or ACT, are heavily weighted. Furthermore, successful applicants typically possess a strong background in engineering-related extracurricular activities, such as participation in robotics clubs or science competitions. A compelling personal essay articulating a clear passion for aerospace engineering is also crucial.
Question 2: What types of research opportunities are available to undergraduate students in aerospace engineering at MIT?
Undergraduate students have access to a wide array of research opportunities. These may include participation in faculty-led research projects focused on areas such as hypersonics, sustainable aviation, or autonomous systems. Students can also engage in independent research projects under the guidance of a faculty mentor. Furthermore, opportunities exist to contribute to research conducted at MIT’s affiliated research centers, such as the Lincoln Laboratory.
Question 3: What is the typical curriculum for an aerospace engineering undergraduate student at MIT?
The undergraduate curriculum is designed to provide a comprehensive foundation in aerospace engineering principles. The first two years typically consist of core coursework in mathematics, physics, computer science, and introductory engineering subjects. The subsequent years focus on specialized aerospace topics, including aerodynamics, propulsion, structures, and control systems. Students also have the opportunity to select elective courses in areas of interest and participate in design-build-test projects.
Question 4: What are the career prospects for graduates of the aerospace engineering program at MIT?
Graduates of the program enjoy a high rate of employment in diverse sectors of the aerospace industry. Potential career paths include roles in aircraft and spacecraft design, propulsion system development, aerospace research and development, and government agencies such as NASA. Opportunities also exist in related fields such as robotics, autonomous systems, and renewable energy.
Question 5: How does the aerospace engineering program at MIT differ from similar programs at other universities?
The program is distinguished by its rigorous curriculum, world-renowned faculty, and emphasis on hands-on research and design experiences. MIT’s close ties to industry and government agencies provide students with unparalleled access to cutting-edge research and career opportunities. Furthermore, the institute’s interdisciplinary approach fosters collaboration across different engineering disciplines, preparing students to tackle complex challenges.
Question 6: What resources are available to support students pursuing aerospace engineering at MIT?
MIT provides numerous resources to support students’ academic and professional development. These include access to state-of-the-art laboratory facilities, comprehensive library resources, and tutoring services. Students can also participate in student organizations focused on aerospace engineering and take advantage of career counseling and networking opportunities.
In summary, the aerospace engineering program at MIT offers a demanding but rewarding educational experience that prepares graduates for leadership roles in the aerospace industry and beyond.
The following section will provide some concluding thoughts.
Conclusion
This exploration of aerospace engineering at MIT has highlighted its core tenets: rigorous academics, pioneering research, and a faculty dedicated to shaping future leaders. The program’s commitment to interdisciplinary collaboration and cultivating innovative problem-solving skills positions its graduates at the forefront of the aerospace sector.
The challenges facing the aerospace industry demand highly skilled and forward-thinking engineers. Continued investment in programs such as this one is essential for ensuring sustained technological advancement and global competitiveness. The future of aerospace hinges on the dedication and expertise of those who pursue such rigorous study.


![Free MIT Aerospace Engineering Courses [Online & Self-Paced] Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions Free MIT Aerospace Engineering Courses [Online & Self-Paced] | Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-184-300x200.jpg)