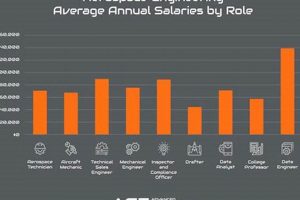
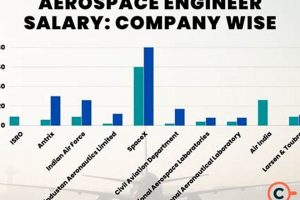
The advantages derived from the field dedicated to designing, developing, testing, and producing aircraft and spacecraft are multifaceted. These advantages encompass advancements in materials science, propulsion systems, and aerodynamic efficiency. For instance, innovations in composite materials, initially developed for aircraft, have found applications in diverse sectors such as automotive and sports equipment manufacturing.
This sector’s contributions extend far beyond air and space travel, positively impacting areas such as medicine, telecommunications, and environmental monitoring. The drive for lighter, stronger, and more fuel-efficient designs has fostered technological progress across multiple industries. Historically, investments in this field have spurred significant economic growth and national security enhancements.
The subsequent sections will explore how developments in aeronautics have revolutionized air travel, how space exploration has broadened scientific understanding, and how these engineering innovations contribute to economic growth and technological advancement across various sectors.
Guidance on Leveraging Aerospace Engineering Advancements
The following points offer guidance on appreciating and capitalizing on the advantages stemming from advancements in aerospace engineering, emphasizing practical applications and societal gains.
Tip 1: Foster Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Encourage cooperation between aerospace engineers and professionals in other fields, such as medicine or environmental science, to identify new applications for aerospace technologies.
Tip 2: Invest in Research and Development: Prioritize funding for basic and applied research in areas such as advanced materials, propulsion systems, and autonomous flight control, recognizing that these investments yield long-term dividends.
Tip 3: Promote STEM Education: Support educational programs that cultivate interest and expertise in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, ensuring a pipeline of skilled professionals to drive future innovation.
Tip 4: Facilitate Technology Transfer: Establish mechanisms to transfer aerospace technologies to other sectors, enabling industries beyond aerospace to benefit from advancements in materials, sensors, and computational modeling.
Tip 5: Advocate for Regulatory Reform: Support regulatory frameworks that encourage innovation and entrepreneurship in the aerospace sector, while ensuring safety and environmental responsibility.
Tip 6: Support Space Exploration Initiatives: Recognize that space exploration serves as a catalyst for technological advancement, inspiring innovation in areas such as robotics, materials science, and life support systems.
Tip 7: Develop Sustainable Aerospace Technologies: Invest in the development of environmentally friendly aircraft and spacecraft, reducing the environmental impact of air and space travel through innovations in fuel efficiency and alternative propulsion systems.
Adhering to these guidelines can unlock the full potential of aerospace engineering, generating significant economic, social, and environmental progress.
The subsequent discussion will examine the challenges and opportunities facing the aerospace engineering sector, and how these challenges can be overcome through strategic planning and investment.
1. Material Science Innovation
Material science innovation forms a foundational pillar underpinning numerous advancements in aerospace engineering. The development and application of novel materials are central to enhancing performance, safety, and efficiency within the aerospace sector, directly contributing to its overall value.
- Lightweight Composites
The creation of high-strength, low-weight composite materials, such as carbon fiber reinforced polymers, enables the construction of lighter aircraft and spacecraft. This reduction in weight directly translates to improved fuel efficiency, increased payload capacity, and enhanced maneuverability. Examples include the Boeing 787 Dreamliner, which utilizes a significant proportion of composite materials, leading to substantial fuel savings.
- High-Temperature Alloys
Aerospace applications demand materials capable of withstanding extreme temperatures and pressures, particularly in propulsion systems. High-temperature alloys, such as nickel-based superalloys, are crucial for turbine blades and engine components. Their ability to maintain structural integrity at elevated temperatures enhances engine performance and longevity, facilitating more efficient and reliable flight.
- Advanced Coatings
Protective coatings are essential for safeguarding aerospace components from corrosion, erosion, and thermal degradation. Advanced coatings, including ceramic coatings and thermal barrier coatings, extend the lifespan of critical components and reduce maintenance requirements. These coatings enhance the durability of aircraft and spacecraft, ensuring safe operation in harsh environments.
- Shape Memory Alloys
Shape memory alloys (SMAs) are materials that can return to a predetermined shape after being deformed. In aerospace, SMAs are used in actuators, morphing wings, and vibration damping systems. These applications improve aircraft performance, reduce noise, and enhance passenger comfort. For example, SMA-based actuators can enable more precise control of aircraft control surfaces, leading to improved flight characteristics.
The ongoing pursuit of materials with superior properties directly propels progress within aerospace engineering, leading to more efficient, safer, and more capable aircraft and spacecraft. Continued investment in materials science research is crucial for unlocking further advancements in this domain and realizing the full potential of aerospace technology.
2. Enhanced National Security
The relationship between advancements in aerospace engineering and the strengthening of national security is direct and consequential. Aerospace technologies provide essential capabilities for defense, surveillance, and strategic response. These technologies serve as critical instruments in safeguarding national borders, protecting critical infrastructure, and maintaining global stability. Without sustained progress in aerospace, a nation’s ability to deter threats and respond effectively to crises is demonstrably diminished.
A primary example lies in the development of advanced surveillance satellites. These platforms provide persistent monitoring of strategic locations, enabling early detection of potential threats and informed decision-making. Similarly, military aircraft, ranging from advanced fighter jets to unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), offer a range of capabilities from air superiority to reconnaissance. The performance of these assets directly relies on ongoing progress in aerodynamics, propulsion systems, and sensor technologiesall domains within aerospace engineering. The development of missile defense systems provides another example. These complex systems, designed to intercept and neutralize incoming ballistic missiles, rely heavily on sophisticated radar technology, advanced control systems, and high-performance interceptor missiles. Each component is a direct result of aerospace engineering innovation.
In summation, aerospace engineering directly underpins a nation’s capacity to ensure its security. Continuous investment in this field is therefore not merely a matter of technological advancement but a fundamental imperative for maintaining national defense capabilities and responding effectively to evolving global security challenges. The development of advanced technologies and the maintenance of a skilled workforce within the aerospace sector are essential to preserving national security interests.
3. Improved Air Transportation
Progress in air transportation is directly correlated with advancements in aerospace engineering. Every facet of modern air travel, from aircraft design to air traffic management, benefits from innovations in this field. Improved air transportation encompasses safer, faster, more efficient, and more comfortable air travel experiences, all of which are outcomes of continuous refinement in aerospace technology. This improvement relies on developments in areas such as aerodynamics, materials science, propulsion systems, and avionics.
The adoption of fuel-efficient aircraft designs, such as blended wing bodies and advanced turbofan engines, leads to reduced fuel consumption and lower operating costs for airlines, thus directly contributing to the affordability of air travel. Enhanced air traffic management systems, enabled by sophisticated sensors and data analytics, optimize flight paths and minimize delays, reducing both travel time and environmental impact. Enhanced safety measures in aircraft design, avionics, and air traffic control, contribute to air travel’s status as one of the safest modes of transportation. The development of quieter and more comfortable aircraft cabins, incorporating noise-reduction technologies and ergonomic seating, enhances the overall passenger experience. Real-world examples, such as the development of more fuel-efficient jet engines and the implementation of advanced air traffic control systems, demonstrate the direct impact of aerospace engineering on the air travel sector.
In summary, enhanced air transportation is a tangible outcome of continuous progress in aerospace engineering, driven by ongoing research and development efforts. While challenges remain, such as reducing aviation’s environmental footprint and addressing capacity constraints, these are being actively tackled through further innovations in aerospace technology. Sustained investment in aerospace engineering remains crucial for ensuring that air transportation continues to evolve, meeting the growing demands of global connectivity while minimizing its environmental impact and maximizing passenger safety and comfort.
4. Space Exploration Advancements
Space exploration advancements represent a significant domain within the broader spectrum of aerospace engineering benefits. They are not merely ancillary outcomes but rather a driving force behind innovation across numerous engineering disciplines. Progress in space exploration necessitates the development of cutting-edge technologies in propulsion, materials science, robotics, and life support systems, subsequently yielding practical applications with far-reaching implications on Earth. For instance, the development of lightweight, high-strength materials for spacecraft has directly translated into improved designs for aircraft, automobiles, and even medical implants. Similarly, advanced propulsion systems developed for space missions have spurred innovation in energy generation and conservation. Space exploration acts as a demanding proving ground, pushing the boundaries of what is technologically feasible and delivering tangible value beyond the immediate context of space activities.
The practical applications stemming from space exploration advancements are diverse and impactful. Telecommunications rely heavily on satellite technology, providing global connectivity for communication, navigation, and broadcasting. Remote sensing technologies developed for Earth observation from space provide invaluable data for environmental monitoring, resource management, and disaster response. Medical technologies, such as MRI and CAT scan, benefit from image processing and sensor technologies initially developed for space-based astronomy. Furthermore, the rigorous standards and reliability requirements associated with space missions have fostered a culture of excellence and precision in engineering practices, influencing manufacturing and quality control processes across various industries. The Apollo program, for instance, spurred widespread innovation in computer technology, materials science, and management techniques that continue to shape technological development today.
In conclusion, space exploration advancements constitute a vital component of the overall benefits derived from aerospace engineering. They serve as a catalyst for technological innovation, driving progress in diverse fields and delivering practical solutions to global challenges. While the immediate objective of space exploration may be to expand human knowledge and presence beyond Earth, the long-term impact extends far beyond scientific discovery, yielding significant economic, social, and technological advantages for society as a whole. Continued investment in space exploration and aerospace engineering is thus essential for sustaining this virtuous cycle of innovation and maximizing the societal value of these endeavors.
5. Economic Growth Stimulation
Aerospace engineering serves as a catalyst for economic expansion through multiple interconnected pathways. The industry generates high-value employment opportunities, fosters technological innovation, and attracts significant investment, both public and private. The development and production of aircraft, spacecraft, and related technologies require a highly skilled workforce, leading to the creation of well-compensated jobs for engineers, technicians, and manufacturing specialists. This influx of high-income earners bolsters local economies, driving consumer spending and supporting a range of ancillary businesses. The sector’s focus on cutting-edge research and development fuels innovation across diverse technological domains, contributing to advancements in materials science, propulsion systems, and computer technology. These innovations often have applications extending far beyond aerospace, stimulating growth in other sectors such as automotive, telecommunications, and healthcare. Government investment in aerospace projects, motivated by national security concerns or space exploration goals, provides a substantial economic stimulus. Contracts awarded to aerospace companies support manufacturing activity, generate employment, and foster technological progress. The commercialization of aerospace technologies also creates new business opportunities and export markets, further enhancing economic prosperity.
The presence of a thriving aerospace industry often attracts foreign direct investment, as international companies seek to capitalize on the region’s technological expertise and skilled workforce. This influx of capital further stimulates economic activity, supporting infrastructure development and enhancing competitiveness. Clusters of aerospace companies and research institutions tend to emerge, creating synergistic ecosystems that foster innovation and economic growth. These clusters attract talent, facilitate knowledge sharing, and promote collaboration among companies, universities, and government agencies. The economic impact of aerospace engineering is evident in regions such as California, Washington, and Texas, where the industry has played a pivotal role in driving economic growth and technological leadership. These regions have benefited from significant investments in aerospace, leading to the creation of high-paying jobs, the development of advanced technologies, and the attraction of foreign investment.
In summary, the economic growth stimulation associated with aerospace engineering is a multifaceted phenomenon driven by employment generation, technological innovation, and investment attraction. The industry’s focus on research and development creates a virtuous cycle of innovation and economic expansion, benefiting both the aerospace sector itself and the broader economy. While challenges remain, such as managing technological disruptions and addressing skills gaps, continued investment in aerospace engineering remains crucial for fostering economic growth and maintaining technological competitiveness in the 21st century. The economic benefits of aerospace engineering are not limited to specific regions or industries but rather have a broad impact on national economies and global competitiveness.
6. Cross-Disciplinary Applications
The influence of aerospace engineering extends considerably beyond its core focus on aircraft and spacecraft, permeating numerous other sectors through cross-disciplinary applications. This dissemination of aerospace technologies and methodologies constitutes a significant element of the overall advantages derived from advancements in the field. The stringent requirements for performance, reliability, and efficiency in aerospace systems necessitate innovation that often finds adaptation in seemingly unrelated areas. This phenomenon generates a ripple effect, amplifying the return on investment in aerospace research and development.
A prime example of this cross-pollination is the application of computational fluid dynamics (CFD), initially developed for aerodynamic analysis of aircraft, in the design of more efficient wind turbines and automotive vehicles. Similarly, advanced materials developed for spacecraft thermal protection, such as ceramics and composites, have been adapted for use in high-performance brake systems and industrial machinery, enhancing their durability and performance. Furthermore, the development of sophisticated sensor technologies for space exploration has led to breakthroughs in medical imaging and environmental monitoring. The principles of systems engineering, honed in the design of complex aerospace projects, are now widely applied in project management across diverse industries, improving efficiency and reducing risk.
In summary, the cross-disciplinary applications arising from aerospace engineering innovations represent a crucial component of its overall societal benefits. The transfer of technology and knowledge from aerospace to other sectors drives economic growth, enhances productivity, and improves quality of life. Recognizing and fostering these cross-disciplinary connections is essential for maximizing the return on investment in aerospace research and development, and for leveraging the technological advancements of the field to address challenges in other domains. The continued exploration and exploitation of these connections remains crucial for further solidifying the broader benefits of aerospace engineering.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common inquiries concerning the range and implications of advancements originating in the field of aerospace engineering.
Question 1: What tangible advantages does aerospace engineering offer to sectors beyond aviation and space exploration?
Aerospace engineering innovations often find application in diverse sectors. Materials science, computational modeling, and advanced manufacturing techniques developed for aerospace contribute to advancements in automotive engineering, medical technology, and energy production.
Question 2: How does aerospace engineering contribute to national security?
Aerospace engineering underpins the development of advanced defense systems, surveillance technologies, and communication networks. These capabilities are essential for safeguarding national borders, protecting critical infrastructure, and maintaining strategic advantage.
Question 3: What are the primary environmental considerations related to aerospace engineering, and how are these being addressed?
Aerospace engineering contributes to environmental concerns through emissions from aircraft and spacecraft. Current research focuses on developing more fuel-efficient engines, alternative fuels, and sustainable aviation practices to minimize environmental impact.
Question 4: How does aerospace engineering contribute to economic growth?
Aerospace engineering stimulates economic growth through job creation, technological innovation, and investment attraction. The industry generates high-value employment, fosters advancements in related fields, and attracts foreign direct investment.
Question 5: What role does aerospace engineering play in advancing scientific knowledge?
Aerospace engineering is fundamental to space exploration, enabling the development of spacecraft, instruments, and mission architectures that expand human understanding of the universe. This includes research on planetary science, astrophysics, and astrobiology.
Question 6: What is the projected future impact of aerospace engineering on society?
Aerospace engineering is expected to drive further advancements in transportation, communication, and resource management. Future innovations may include hypersonic air travel, space-based solar power, and advanced robotics for exploration and manufacturing.
These responses provide a concise overview of the diverse and far-reaching benefits stemming from aerospace engineering. The field’s contributions extend beyond its immediate domains, positively impacting various aspects of modern life.
The subsequent section will delve into the potential challenges and risks associated with future advancements in aerospace engineering.
Aerospace Engineering Benefits
This exploration has elucidated the multifaceted contributions of aerospace engineering, highlighting its impact on technological innovation, economic growth, and national security. Advancements in this field propel progress in diverse sectors, ranging from transportation and communication to medicine and environmental monitoring. The benefits are tangible and far-reaching, underscoring the strategic importance of continued investment in aerospace research and development.
Recognizing the enduring significance of aerospace engineering, a commitment to fostering its advancement is essential. Such a commitment ensures continued innovation, economic competitiveness, and the realization of future opportunities for technological progress and societal betterment. The long-term benefits derived from aerospace engineering necessitate a sustained focus on education, research, and strategic planning within this critical sector.