Positions in the field related to design, development, testing, and maintenance of aircraft and spacecraft within the San Francisco Bay Area represent a specific segment of the broader aerospace industry. These roles encompass a diverse range of functions, from structural analysis to propulsion systems engineering, all located within the geographical confines of the Bay Area. For example, a design engineer working on a next-generation satellite in Mountain View would fall under this category.
The concentration of such opportunities in this region is driven by factors like proximity to technological innovation hubs, including Silicon Valley, and the presence of major aerospace companies and research institutions. This localized market offers professionals career advancement and participation in cutting-edge projects. Historically, the area’s strong economy and pool of skilled workers have made it a desirable location for companies engaged in aerospace activities.
The following sections will delve into the specific types of roles available, the necessary qualifications for these positions, and an overview of prominent employers in this sector. Further discussion will explore the current market trends and future prospects for professionals seeking a career within this specialized area.
Strategies for Securing Opportunities
Navigating the employment landscape within this specialized field requires a targeted and well-informed approach. The following strategies can enhance a candidate’s prospects.
Tip 1: Network Strategically: Attending industry conferences, joining professional organizations such as AIAA, and actively engaging on professional networking platforms allows for direct interaction with potential employers and provides access to unadvertised vacancies. For instance, connecting with engineers at a space technology symposium could lead to valuable introductions.
Tip 2: Tailor Resumes and Cover Letters: Generic applications are often overlooked. Emphasize relevant skills and experience that align with specific job requirements. For example, if a position requires proficiency in computational fluid dynamics (CFD), highlight projects where CFD analysis was utilized and the resulting outcomes.
Tip 3: Acquire Relevant Certifications: Pursuing certifications such as those related to project management (PMP) or specific software packages (e.g., CATIA, ANSYS) demonstrates a commitment to professional development and enhances marketability. A certification in systems engineering, for instance, can be advantageous for roles involving complex integration projects.
Tip 4: Target Specific Companies: Research companies known for their presence in the area and align skills and career aspirations with their specific projects. Understanding a company’s current initiatives, such as developing electric propulsion systems or advancing satellite technology, allows for a more targeted application.
Tip 5: Build a Strong Online Presence: Maintaining a professional online profile showcasing projects, publications, and skills demonstrates expertise and credibility. Regularly updating a portfolio with relevant work samples allows potential employers to assess qualifications effectively.
Tip 6: Prepare for Technical Interviews: Technical interviews often involve problem-solving scenarios and questions on fundamental aerospace engineering principles. Practicing common interview questions and reviewing core concepts ensures a confident and informed response.
Implementing these strategies can increase visibility and enhance the probability of success in securing a position. A proactive and informed approach is essential for navigating this competitive market.
The subsequent sections will provide further insights into market trends and future opportunities within the specific geographic area.
1. Job availability
The number of open positions in the field is a direct indicator of the health and activity within that sector in the specified region. A high volume of available roles suggests robust growth, investment, and technological advancement, attracting qualified candidates and fostering further expansion. Conversely, a scarcity of openings signals potential stagnation, budget cuts, or a shift in priorities within the aerospace companies located there. For example, a surge in contract awards to local firms like SpaceX or Planet Labs for satellite deployment would likely result in a corresponding increase in demand for engineers with expertise in areas such as propulsion, avionics, and structural analysis.
The geographical concentration of aerospace firms within this region creates a dynamic interplay between company needs and talent supply. Increased project activity and technological breakthroughs generate a demand for specialized skill sets, impacting the distribution of available roles across different engineering disciplines. The presence of NASA Ames Research Center, for example, contributes to consistent demand for research scientists and engineers focused on aeronautics, space exploration, and related technologies. These federal investments can drive the creation of new positions, spurring overall growth in the local aerospace industry.
Understanding the fluctuations in job availability provides critical insight into the economic prospects and career opportunities for professionals seeking to enter or advance within this sector. Monitoring industry reports, attending job fairs, and networking with professionals allow for a more accurate assessment of the current market and future trends. Ultimately, a proactive approach to understanding job availability ensures informed decision-making and enhances the potential for career success in the described field.
2. Required qualifications
The prerequisite skills and knowledge serve as a critical filter for individuals seeking positions in the aerospace engineering sector within the specified geographic area. These qualifications are not merely academic credentials but a comprehensive demonstration of competency aligned with the demands of complex engineering tasks. A mismatch between an applicant’s skill set and the specified needs of employers will directly hinder their prospects in this competitive environment. For instance, a structural engineer position at a satellite manufacturer in Palo Alto will require demonstrated proficiency in finite element analysis software (e.g., ANSYS, ABAQUS) and a thorough understanding of composite materials, as opposed to general engineering knowledge. The absence of these specific qualifications renders an application significantly less competitive.
The concentration of technologically advanced companies in the Bay Area necessitates that candidates possess cutting-edge expertise and adaptability. Many firms are engaged in the development of innovative technologies such as electric propulsion systems, autonomous aircraft, and advanced materials. Therefore, experience with these emerging fields significantly enhances an applicant’s appeal. Furthermore, the ability to collaborate effectively within multidisciplinary teams and a proven track record of problem-solving are highly valued attributes. A candidate might be deemed qualified based on academic credentials alone, but practical experience in a relevant aerospace project, such as a CubeSat development program or a research internship at NASA Ames, is often the deciding factor.
In conclusion, the possession of required qualifications represents a fundamental determinant of success in securing a position in this field. The Bay Area’s demanding aerospace industry necessitates a blend of theoretical knowledge, practical experience, and adaptability to emerging technologies. Failing to meet these qualification standards presents a significant barrier to entry and advancement. Therefore, aspiring aerospace engineers seeking employment must prioritize the development of targeted skills and actively seek opportunities to gain relevant practical experience.
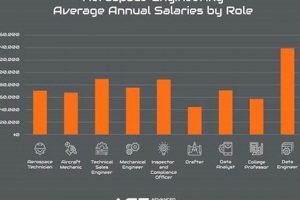
3. Salary expectations
Compensation for aerospace engineering roles within the San Francisco Bay Area is a multifaceted consideration, significantly influenced by factors unique to both the industry and the geographical location. Understanding the dynamics of these expectations is crucial for both prospective employees and employers operating within this market.
- Cost of Living Adjustment
The Bay Area’s exceptionally high cost of living, particularly concerning housing, directly impacts salary expectations. Compensation packages must reflect these inflated expenses to attract and retain qualified professionals. For instance, a mid-level aerospace engineer might command a significantly higher salary in the Bay Area compared to a similar position in a less expensive region. This disparity is necessary to maintain a comparable standard of living.
- Competition for Talent
The concentration of technology companies in the Bay Area creates intense competition for skilled engineering talent. Aerospace firms must offer competitive salaries to attract candidates who may otherwise be drawn to software engineering or other high-paying tech sectors. The presence of companies like Google, Apple, and Tesla influences the overall compensation benchmark for engineering professionals, including those in aerospace.
- Company Size and Funding
Salary expectations often vary depending on the size and financial stability of the aerospace company. Established, publicly traded corporations may offer more structured compensation packages with benefits and stock options. Startups and smaller companies may provide higher base salaries to attract talent, but with potentially greater risk and fewer benefits. Understanding a company’s financial situation is vital in assessing the reasonableness of salary expectations.
- Specialized Skill Sets
Demand for specialized skills, such as expertise in advanced composite materials, autonomous systems, or space propulsion technologies, directly influences salary negotiations. Engineers possessing these in-demand skill sets command higher salaries due to their perceived value to the organization. A candidate with extensive experience in developing electric propulsion systems for satellites, for example, will likely have higher salary expectations than a general aerospace engineer.
In conclusion, salary expectations for these roles within the Bay Area are a complex equation. Cost of living, competition, company characteristics, and specialized skills all converge to shape compensation benchmarks. A clear understanding of these influences is essential for both job seekers and employers navigating this dynamic market, and those that are knowledgeable in the aerospace engineering jobs bay area field.
4. Key employers
The concentration of aerospace engineering positions within the San Francisco Bay Area is directly attributable to the presence and activities of specific key employers. These companies, ranging from established aerospace giants to burgeoning startups, serve as the primary generators of engineering opportunities within the region. Their operational scope, investment in research and development, and project acquisitions significantly influence the volume and types of available positions. For instance, the expansion of SpaceX’s facilities in Hawthorne and its increased launch cadence directly correlates with a surge in demand for propulsion engineers, structural analysts, and avionics specialists in the broader Bay Area job market.
The influence of these companies extends beyond simply providing jobs; they also shape the skill sets that are highly valued within the region. Companies like Lockheed Martin Space, with their expertise in satellite systems and defense technologies, create a demand for engineers proficient in areas such as systems engineering, cybersecurity, and radio frequency (RF) design. Furthermore, emerging players like Planet Labs, focused on earth observation technologies, drive demand for expertise in areas like image processing, remote sensing, and data analytics. Understanding the specific technological focuses and project portfolios of these key employers allows job seekers to tailor their skills and experience to align with the region’s most sought-after qualifications, thereby enhancing their prospects in securing a competitive position. The presence of NASA Ames Research Center also creates a demand for more research-oriented jobs.
In summary, the activities and priorities of key employers within the San Francisco Bay Area are fundamental to understanding the nature and availability of aerospace engineering jobs. These companies not only generate positions but also define the skills and qualifications that are most valued in the local market. Recognizing this connection allows job seekers to target their professional development efforts, increasing their competitiveness and ultimately contributing to the continued growth and innovation of the Bay Area’s aerospace sector.
5. Location benefits
The geographical positioning of aerospace engineering positions within the San Francisco Bay Area provides significant advantages that impact both the opportunities available and the overall attractiveness of the region to professionals in the field. These location-specific benefits extend beyond mere proximity and encompass a network of interconnected factors influencing career trajectories and industry growth.
- Proximity to Innovation Hubs
The Bay Area’s close connection to Silicon Valley and its concentration of technology companies fosters a synergistic environment for aerospace engineering. Collaboration and cross-pollination of ideas between aerospace and other tech sectors (e.g., software, AI, materials science) drive innovation and create novel opportunities. For example, the integration of AI algorithms into autonomous aircraft systems or the application of advanced materials developed for consumer electronics in spacecraft design. This proximity accelerates technological advancements within the field and attracts companies and talent seeking to leverage these synergies.
- Access to Venture Capital and Investment
The Bay Area’s status as a global financial center provides unparalleled access to venture capital and investment opportunities for aerospace startups and established companies. This influx of capital fuels research and development, leading to the creation of new jobs and the expansion of existing operations. The ability to secure funding is critical for aerospace ventures, given the high capital requirements for developing new technologies and entering the market. This financial ecosystem incentivizes innovation and entrepreneurial activity within the aerospace sector, making the region a prime location for career advancement.
- Highly Skilled Workforce
The presence of prestigious universities (e.g., Stanford, UC Berkeley) and a concentration of skilled engineers and scientists contribute to a highly competitive and knowledgeable workforce. This talent pool attracts aerospace companies seeking to recruit top-tier professionals and fosters a culture of innovation and expertise. The availability of specialized training programs and continuing education opportunities further enhances the skillset of the workforce, ensuring that the region remains at the forefront of aerospace technology. Competition for positions is intense, driving individuals to acquire advanced skills and remain current with industry advancements.
- Established Aerospace Infrastructure
Despite its association with tech, the Bay Area has a rich history in aviation and space exploration, creating an established network of suppliers, manufacturers, and research facilities. This infrastructure provides essential support for aerospace companies, enabling them to access specialized resources and expertise. The presence of facilities like NASA Ames Research Center further enhances the region’s capabilities in areas such as aeronautics, space exploration, and planetary science. The presence of the Moffett Federal Airfield and other smaller airports further contribute to making the bay area a central hub.
In conclusion, the location benefits afforded by the San Francisco Bay Area significantly influence the aerospace engineering landscape. Proximity to innovation, access to capital, a skilled workforce, and established infrastructure collectively contribute to a thriving environment for career opportunities and industry advancement. These factors reinforce the Bay Area’s position as a leading hub for aerospace engineering and attract professionals seeking to engage in cutting-edge research and development, as well as those in aerospace engineering jobs bay area.
6. Industry growth
The expansion and evolution of the aerospace sector exert a direct and quantifiable influence on the availability and nature of engineering positions within the San Francisco Bay Area. Industry growth, characterized by technological advancements, increased investment, and evolving market demands, shapes the landscape of career opportunities for aerospace engineers in the region.
- Increased R&D Spending
A rise in research and development expenditure within the aerospace industry directly correlates with the creation of engineering positions focused on designing, testing, and implementing new technologies. For example, increased investment in electric propulsion systems or advanced materials would lead to a demand for engineers with expertise in these specific areas. Companies in the Bay Area receiving government grants or private funding for innovative projects will invariably seek qualified engineers to execute these initiatives, impacting the overall job market.
- Emergence of New Space Companies
The proliferation of “New Space” companies, focused on commercial space activities such as satellite deployment, space tourism, and resource extraction, directly contributes to the growth of aerospace engineering jobs. Companies in the Bay Area involved in these endeavors require a diverse range of engineering expertise, including propulsion, avionics, structural analysis, and systems engineering. The expansion of these companies, driven by private investment and commercial opportunities, translates into increased demand for qualified aerospace engineers.
- Government Contracts and Funding
The allocation of government contracts and funding for aerospace projects plays a significant role in shaping the job market in the Bay Area. Contracts awarded to local companies for defense systems, space exploration initiatives, or aeronautical research directly generate engineering positions. For example, a contract to develop a new generation of satellites for the Department of Defense would lead to a demand for engineers specializing in satellite design, communications, and data processing.
- Technological Advancements
Breakthroughs in aerospace technology create new opportunities and demands for engineers with specialized skills. For instance, advancements in autonomous flight systems necessitate engineers proficient in areas such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and sensor technology. Companies in the Bay Area at the forefront of these advancements actively seek engineers with the knowledge and experience to develop and implement these cutting-edge technologies, leading to growth in specialized roles.
In conclusion, industry growth, fueled by a confluence of factors including increased R&D spending, the rise of New Space companies, government contracts, and technological advancements, is a primary driver of aerospace engineering jobs in the Bay Area. The dynamism of the aerospace sector ensures a continuous demand for skilled engineers capable of contributing to the innovation and expansion of the industry.
7. Competition level
The degree of rivalry among job seekers for aerospace engineering positions within the San Francisco Bay Area constitutes a significant factor influencing individual career prospects and overall market dynamics. A high degree of competition, driven by factors such as a limited number of positions relative to the pool of qualified applicants, elevates the standard for required qualifications and necessitates strategic approaches for securing employment. The presence of numerous prestigious universities in the region, coupled with the area’s attractiveness to experienced professionals nationwide, contributes to this intensely competitive environment. For instance, a single opening for a propulsion engineer at a prominent Bay Area aerospace firm may attract hundreds of applications, requiring candidates to possess exceptional academic credentials, relevant industry experience, and demonstrable skills in specialized areas such as computational fluid dynamics or rocket engine design. This heightened competition level compels job seekers to differentiate themselves through targeted skill development, strategic networking, and meticulously crafted application materials.
The competition’s intensity also affects employers, potentially driving up salary expectations and necessitating more sophisticated recruitment strategies to attract and retain top talent. Companies might implement enhanced benefits packages, professional development opportunities, or innovative work environments to stand out in the competitive landscape. Furthermore, the pressure to secure skilled engineers quickly can lead to a greater emphasis on internships, co-op programs, and university partnerships as a means of identifying and cultivating promising candidates early in their careers. The competition also fuels the demand for specialized skill sets, prompting training programs and educational institutions to adapt their curricula to meet the evolving needs of the aerospace industry. Therefore, the competition among aerospace engineering jobs bay area is often stiff and demanding.
In summary, the high competition level for aerospace engineering positions within the San Francisco Bay Area creates both challenges and opportunities for job seekers and employers alike. For candidates, it necessitates a proactive and strategic approach to career development and job searching. For employers, it demands innovative recruitment strategies and a commitment to attracting and retaining top talent in a highly competitive market. A comprehensive understanding of this competition level is crucial for navigating the complexities of the local aerospace job market and maximizing the potential for success.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries concerning employment opportunities related to aircraft and spacecraft engineering within the San Francisco Bay Area. It aims to clarify key aspects of the job market, required qualifications, and career prospects within this specific geographic region.
Question 1: What specific engineering disciplines are most in demand within the Bay Area’s aerospace sector?
Aerospace engineering positions in bay area include areas like propulsion systems, avionics, structural analysis, and systems engineering currently experience high demand. Emerging areas such as autonomous flight systems and electric propulsion are also witnessing increasing recruitment activity.
Question 2: How does the cost of living in the Bay Area affect compensation packages for aerospace engineers?
The exceptionally high cost of living necessitates that employers offer competitive salaries and benefits packages to attract and retain qualified professionals. These packages must adequately compensate for housing, transportation, and other expenses.
Question 3: What are the most common qualifications employers seek in candidates for entry-level aerospace engineering positions?
Entry-level positions typically require a bachelor’s or master’s degree in aerospace engineering or a related field, strong academic performance, and demonstrated proficiency in relevant software tools. Internship experience and participation in aerospace-related projects are highly valued.
Question 4: What impact do government contracts and funding have on job security within the Bay Area’s aerospace industry?
Government contracts and funding play a significant role in driving employment within the sector. Fluctuations in government spending and contract awards can directly impact job security and hiring trends at companies reliant on such funding.
Question 5: What strategies can aspiring aerospace engineers employ to enhance their competitiveness in the Bay Area job market?
Targeted networking, acquisition of in-demand skills, tailoring resumes to specific job requirements, and building a strong online presence can significantly improve a candidate’s chances of success.
Question 6: How does the presence of NASA Ames Research Center influence the types of aerospace engineering jobs available in the Bay Area?
NASA Ames contributes to a consistent demand for research scientists and engineers focused on aeronautics, space exploration, and related technologies. This federal presence creates opportunities for individuals interested in research-oriented careers.
In summary, the San Francisco Bay Area offers numerous opportunities within the aerospace engineering field, but it is also a competitive market that requires specific qualifications and strategic career planning.
The next section will delve into future trends and predictions for the aerospace engineering sector in the Bay Area.
Conclusion
This exploration of aerospace engineering jobs bay area has detailed the defining characteristics of this specialized employment sector. It has addressed the requisite skills, influential employers, geographical advantages, growth dynamics, and competitive pressures inherent in securing a role within this domain. The analysis underscores the complex interplay of factors that shape both opportunities and challenges for professionals aspiring to contribute to aerospace advancement within the Bay Area.
Continued monitoring of industry trends and proactive skills development remain paramount for individuals seeking to navigate this dynamic landscape. Future success hinges on a commitment to innovation, adaptability to emerging technologies, and a comprehensive understanding of the evolving needs of the aerospace sector within the specified geographic region.