Opportunities in the field related to designing, developing, and testing aircraft and spacecraft within a specific North Carolina metropolitan area are considered a career path sought by qualified professionals. These positions encompass a broad spectrum of roles, from research and development to manufacturing and testing, all located in or near a particular city known for its financial and logistical infrastructure.
The significance of this regional employment sector lies in its contribution to technological advancement, economic growth, and national security. Historically, the presence of these roles has indicated a region’s commitment to innovation and its ability to attract and retain highly skilled talent. This specific location benefits from a strong manufacturing base and access to a skilled workforce, making it an attractive destination for aerospace companies.
The subsequent sections will delve into the types of available roles, the qualifications typically required, the major employers in this area, and the overall job market outlook within this specialized sector.
The following tips offer guidance for professionals seeking opportunities related to the aerospace field within the Charlotte metropolitan area. These suggestions aim to improve application strategies and enhance career prospects within this competitive market.
Tip 1: Targeted Resume Customization: Adapt application materials to explicitly reflect the requirements outlined in particular role descriptions. Highlight relevant skills and experiences that align with the specific demands of the aerospace engineering position.
Tip 2: Emphasize Relevant Software Proficiency: Demonstrate expertise in industry-standard software applications, such as CAD, CAE, and CFD tools. Specific examples of projects where these tools were utilized to achieve tangible results will strengthen candidacy.
Tip 3: Highlight Specific Aerospace Knowledge: Articulate a deep understanding of core aerospace principles, including aerodynamics, propulsion, and materials science. Cite specific examples of projects or coursework where these principles were applied.
Tip 4: Showcase Project Management Skills: Aerospace projects often require meticulous planning and coordination. Demonstrate experience in project management methodologies, including scheduling, budgeting, and risk assessment.
Tip 5: Network Strategically: Attend industry events and connect with professionals working in the aerospace sector in the Charlotte area. Utilize online platforms, such as LinkedIn, to expand the professional network and identify potential opportunities.
Tip 6: Consider Relevant Certifications: Pursue certifications relevant to specific areas of aerospace engineering, such as FAA certifications or professional engineering licenses. These credentials can demonstrate a commitment to professional development and enhance credibility.
Tip 7: Research Local Aerospace Companies: Identify key companies operating in or near Charlotte that specialize in aerospace engineering. Understand their core competencies, projects, and technologies to tailor applications effectively.
These strategies emphasize preparation, focused skill development, and proactive networking to increase the likelihood of securing fulfilling career opportunities. The next section will discuss resources that may be helpful in career advancement.
1. Job Role Diversity
The breadth of available positions constitutes a significant aspect of opportunities for those in Charlotte. This variety stems from the multifaceted nature of the industry and the range of operations conducted within the metropolitan area.
- Design Engineer
Design engineers are responsible for creating and refining the blueprints for aircraft and spacecraft components. Their role requires a deep understanding of aerodynamics, materials science, and structural integrity. In the context of Charlotte, these engineers might work on optimizing fuel efficiency for commercial airliners or developing advanced composite materials for high-performance aircraft. The implications include contributing to safer, more efficient, and more environmentally friendly aerospace technologies.
- Manufacturing Engineer
Manufacturing engineers focus on optimizing the production processes involved in building aerospace components. This includes selecting appropriate manufacturing techniques, designing tooling and fixtures, and ensuring quality control throughout the production line. Within Charlotte, manufacturing engineers may oversee the production of specialized aircraft parts or manage the assembly of entire systems. Their work directly impacts the efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and reliability of aerospace manufacturing.
- Test Engineer
Test engineers design and execute tests to validate the performance and safety of aerospace systems. They use sophisticated equipment and methodologies to simulate real-world conditions and identify potential weaknesses or failures. In Charlotte, test engineers might conduct wind tunnel testing on scale models of aircraft or perform structural tests on composite materials. Their role is critical in ensuring the airworthiness and reliability of aerospace products.
- Research and Development Engineer
Research and development engineers are involved in the exploration of new technologies and concepts that can advance the aerospace industry. They conduct experiments, develop prototypes, and analyze data to identify promising areas for innovation. Within Charlotte, R&D engineers might work on developing advanced propulsion systems, exploring new materials for lightweight structures, or designing autonomous flight control systems. Their work drives long-term advancements in aerospace technology and capabilities.
The availability of these diverse positions within Charlotte reflects the region’s multifaceted involvement in the aerospace sector. This variety offers professionals the opportunity to specialize in specific areas of interest or to broaden their skill sets across different disciplines, contributing to a vibrant and dynamic professional environment.
2. Required Education Levels
Educational attainment directly influences access to opportunities related to aerospace within the Charlotte metropolitan area. A bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering, mechanical engineering, or a closely related field typically serves as the foundational requirement for entry-level positions. Coursework in aerodynamics, propulsion, materials science, and structural analysis is considered fundamental knowledge for aspiring engineers. The absence of such a degree significantly restricts candidacy for roles involving design, analysis, or research and development.
For specialized positions or roles involving advanced research and development, a master’s degree or doctorate in aerospace engineering or a related discipline becomes increasingly necessary. These advanced degrees provide in-depth knowledge and specialized skills in areas such as computational fluid dynamics, advanced materials, or control systems. Companies operating in the Charlotte region, particularly those engaged in cutting-edge research, frequently seek candidates with graduate-level qualifications. For example, a company developing novel propulsion systems might require a candidate with a PhD specializing in combustion and fluid mechanics. The practical significance of this understanding lies in the need for prospective professionals to carefully align their educational pursuits with the specific requirements of their desired roles.
In summary, the required education level for aerospace engineering roles in Charlotte functions as a critical filter, influencing career progression and access to specialized opportunities. While a bachelor’s degree provides a base for entry, advanced degrees often open doors to more complex and research-oriented positions. Therefore, understanding the connection between educational qualifications and role requirements is crucial for individuals seeking to advance their careers within the aerospace sector in this geographical area.
3. Key Skill Demands
The relationship between required competencies and career opportunities in Charlotte’s aerospace sector is a direct and consequential one. Certain abilities are fundamental for professionals seeking employment in this field. For example, proficiency in CAD/CAM software is often essential for design engineers creating component blueprints. Similarly, a strong understanding of computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is frequently a prerequisite for engineers involved in aerodynamic analysis and optimization. These skill demands are not arbitrary; they reflect the specific tasks and challenges inherent in roles within the industry. An engineer lacking these skills would face significant difficulties in performing required duties, thereby limiting their employment prospects in this geographical area.
Beyond technical expertise, soft skills also play a crucial role. Project management capabilities, communication effectiveness, and teamwork aptitude are highly valued by employers. Aerospace projects often involve multidisciplinary teams working on complex systems. The ability to collaborate effectively, articulate technical concepts clearly, and manage projects efficiently is critical for success. For instance, a project engineer might need to coordinate the activities of design, manufacturing, and testing teams while adhering to strict deadlines and budget constraints. Consequently, candidates who can demonstrate a blend of technical skills and soft skills are often favored in the competitive hiring landscape. Knowledge of regulations like Federal Aviation Regulations (FAR) is also important.
The relevance of understanding these key skill demands lies in their direct impact on career advancement. Candidates who proactively develop and demonstrate these competencies significantly improve their chances of securing desired positions in the Charlotte aerospace sector. This proactive approach can involve pursuing relevant certifications, participating in professional development programs, or undertaking personal projects to gain practical experience. In summary, identifying and cultivating these specific skills is a strategic investment for anyone seeking a fulfilling and successful career within this specialized domain.
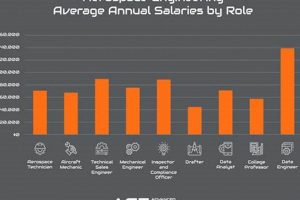
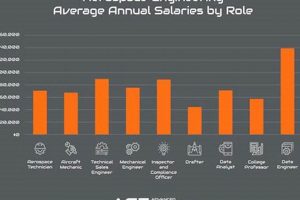
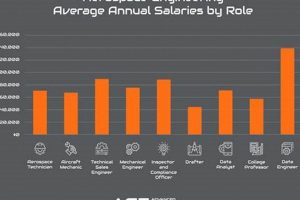
4. Salary Expectations
Compensation levels for aerospace professionals in Charlotte are influenced by a complex interplay of factors. These elements include experience, education, specialization, and the specific employer. Understanding these determinants is crucial for both prospective employees and companies operating in the region.
- Experience Level
Entry-level positions typically command lower salaries compared to those offered to experienced engineers with extensive track records. Engineers with several years of experience in the field, particularly those holding professional certifications or specialized skills, can expect significantly higher compensation. The level of experience directly correlates to the complexity of tasks and the degree of autonomy expected on the job. For opportunities in Charlotte, a lead design engineer with ten years of experience will command a considerably higher salary than a recent graduate.
- Educational Attainment
Advanced degrees often translate into higher earning potential. Individuals holding master’s degrees or doctorates in aerospace engineering or related fields are often valued for their specialized knowledge and research capabilities. Employers in Charlotte may offer higher starting salaries to candidates with advanced degrees and recognize promotions faster, particularly for positions involving research, development, or advanced analysis. A Ph.D. in Aerospace Engineering can unlock opportunities not available to engineers with only a bachelors degree.
- Specific Skills and Specialization
Demand for expertise in certain specialized areas can drive up salaries. Engineers proficient in computational fluid dynamics (CFD), finite element analysis (FEA), or specialized software used in aerospace design and simulation may command higher compensation. Moreover, expertise in niche areas such as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or advanced composite materials may also lead to increased earning potential. In Charlotte’s competitive job market, employers may compete for candidates with niche skills, leading to salary premiums.
- Company Size and Type
Compensation packages can vary significantly depending on the size and type of company. Larger, established aerospace firms may offer more competitive salaries and benefits packages compared to smaller startups or private companies. However, smaller companies may offer other incentives such as equity or greater opportunities for advancement. Companies in Charlotte will follow this standard expectation.
Salary expectations within the aerospace sector in Charlotte are dynamic and reflect the candidate’s qualifications, the specific role, and the overall economic climate. Individuals seeking employment in the field should carefully research prevailing salary ranges, factor in their own skill sets and experience, and negotiate accordingly to secure competitive compensation.
5. Local Company Presence
The concentration of aerospace firms within the Charlotte metropolitan area constitutes a primary determinant of available career opportunities. The presence of these companies directly influences the volume and type of engineering roles accessible to qualified professionals.
- Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs)
OEMs involved in the design and manufacture of aircraft and spacecraft systems create a demand for a wide range of engineering disciplines. These companies require specialists in aerodynamics, structures, propulsion, and avionics, providing opportunities for both entry-level and experienced engineers. For example, a major OEM with a facility near Charlotte might employ engineers to design and test new aircraft components, thereby contributing to a concentration of available positions in the area. The presence of multiple OEMs leads to a competitive job market with diverse career paths.
- Tier 1 Suppliers
Tier 1 suppliers provide critical components and systems to OEMs. These suppliers often specialize in specific areas, such as engine parts, landing gear, or control systems. The presence of Tier 1 suppliers generates demand for engineers with expertise in manufacturing, quality control, and supply chain management. A Tier 1 supplier in Charlotte specializing in composite materials might employ engineers to develop and manufacture lightweight aircraft structures. The supply chain adds depth to the job pool.
- Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) Facilities
MRO facilities provide maintenance, repair, and overhaul services for existing aircraft. These facilities require engineers with expertise in aircraft maintenance, structural repair, and systems integration. An MRO facility near Charlotte might employ engineers to inspect and repair aircraft engines, avionics systems, or airframes. These facilities provide career opportunities focused on the sustainment and improvement of aircraft reliability.
- Research and Development (R&D) Firms
R&D firms focus on developing new technologies and concepts for the aerospace industry. These firms require engineers with expertise in advanced materials, propulsion systems, and autonomous flight control. An R&D firm in Charlotte might employ engineers to develop new materials for lightweight aircraft structures or to design advanced algorithms for autonomous flight. These firms drive innovation and create opportunities for engineers with a strong research background.
The combined presence of OEMs, Tier 1 suppliers, MRO facilities, and R&D firms in the Charlotte area contributes to a robust and diversified market. This concentration of aerospace companies provides a wide array of career opportunities for engineers with diverse skill sets and experience levels. Furthermore, the interactions between these companies foster a dynamic environment that encourages innovation and growth within the aerospace sector.
6. Regional Growth Potential
The sustained expansion of the Charlotte metropolitan area directly influences the availability and nature of opportunities within the aerospace engineering sector. An increase in regional economic activity, coupled with strategic investments in infrastructure and technological development, creates a favorable environment for aerospace companies to establish or expand their operations. This growth stimulates demand for qualified engineers across various disciplines, including design, manufacturing, testing, and research and development. For example, if the region attracts a new aircraft component manufacturing facility, there would be a corresponding need for aerospace engineers to oversee production processes, quality control, and supply chain management.
The importance of regional growth potential lies in its capacity to foster a dynamic and competitive job market. A thriving regional economy attracts skilled professionals from across the country, increasing the talent pool available to aerospace companies. Furthermore, regional growth often leads to increased investment in education and training programs, ensuring a steady supply of qualified engineers to meet the evolving needs of the industry. The availability of these jobs is particularly enhanced by Charlotte’s geographical situation and access to significant infrastructure.
Conversely, a lack of regional growth can stifle the aerospace engineering job market. If the local economy stagnates or declines, aerospace companies may be forced to reduce their workforce or relocate to more promising areas. This can lead to a decrease in opportunities and a loss of skilled professionals from the region. Therefore, fostering a vibrant and sustainable regional economy is crucial for maintaining a healthy and thriving aerospace engineering sector. Challenges remain, however, in ensuring that the region maintains its competitivity in terms of salary levels and other facilities.
7. Industry Sector Focus
The specific industry sector focus operating in and around Charlotte directly shapes the opportunities available to aerospace engineers. Whether a company primarily engages in commercial aviation, defense, space exploration, or a combination thereof dictates the types of skills and expertise in demand. For instance, a concentration of firms supporting commercial aviation necessitates engineers specializing in aircraft maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO), as well as those focused on optimizing fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. Conversely, a strong defense sector presence creates opportunities for engineers with expertise in military aircraft design, weapons systems integration, and secure communications. A firm that makes drones for the space industry will require specialization.
This concentration on a particular focus significantly impacts the career paths and skillsets that are most advantageous within the region. For example, Charlotte’s proximity to military installations may result in a higher demand for engineers with security clearances and experience in defense-related aerospace applications. This scenario would benefit engineers with backgrounds in areas like radar systems, electronic warfare, or cybersecurity for aircraft. An individual seeking employment should therefore carefully evaluate the dominant sector to align professional development efforts and job search strategies with the prevailing needs of the local industry. The defense industry could also lead to an enhanced cybersecurity presence in the city.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the industry sector focus within the Charlotte aerospace landscape is crucial for engineers seeking to maximize their career prospects. This involves identifying the dominant sectors, tailoring skillsets to meet specific demands, and targeting companies operating within these areas. Recognizing this relationship between industry focus and career opportunities is a fundamental step toward securing fulfilling and long-term employment. It is also crucial to understanding the presence of NASA in the area.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding career opportunities within the aerospace sector in the Charlotte metropolitan area. The information presented aims to provide clarity and insight into prevailing employment conditions and expectations.
Question 1: What are the primary prerequisites for securing entry-level opportunities?
A bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering or a closely related field is generally considered a foundational requirement. Practical experience gained through internships or co-op programs enhances a candidate’s appeal. Strong communication and teamwork abilities are also crucial attributes.
Question 2: Which software proficiencies are highly valued by employers?
Expertise in industry-standard software packages, such as CATIA, ANSYS, and MATLAB, is frequently sought. Proficiency in these tools enables engineers to perform design, analysis, and simulation tasks efficiently.
Question 3: How significant is prior experience in a related industry?
While not always mandatory, previous experience in aviation, manufacturing, or defense sectors provides a distinct advantage. Such experience demonstrates familiarity with industry standards, regulatory requirements, and common engineering practices.
Question 4: What is the typical salary range for an aerospace engineer with 5 years of experience?
Compensation is contingent upon factors such as specialization, skill set, and employer. However, a rough estimate for an engineer with five years of experience falls within a competitive range reflecting prevailing market rates.
Question 5: Which are the prominent companies offering employment opportunities?
Several major aerospace firms and suppliers operate within the Charlotte area. Researching these companies and aligning skillsets with their specific needs can greatly enhance job search effectiveness.
Question 6: Are there opportunities for career advancement and professional development?
The aerospace sector in Charlotte provides avenues for professional growth through ongoing training, certifications, and leadership development programs. Pursuing advanced degrees or specialized certifications can accelerate career progression.
In summary, success within Charlotte’s aerospace domain necessitates a blend of technical skills, practical experience, and continuous learning. Prospective professionals should focus on acquiring relevant qualifications and aligning their career goals with the evolving demands of the industry.
The next section will provide a concluding perspective on navigating career opportunities in the aerospace sector in Charlotte.
Conclusion
This exploration has illuminated several crucial facets of “aerospace engineering jobs charlotte.” Key takeaways include understanding the diverse roles available, the significance of tailored skills and education, the influence of local company presence, and the impact of regional growth. The analysis demonstrates a direct correlation between preparation, targeted skill development, and heightened prospects for career success.
Success in securing “aerospace engineering jobs charlotte” demands a proactive approach, characterized by continuous learning and strategic alignment with the evolving industry landscape. Prospective professionals are encouraged to leverage the insights provided to inform their career development and maximize their opportunities within this dynamic sector. The ability to adapt to technological advancements and evolving industry needs will remain paramount for long-term success.