Opportunities within the aerospace sector in the Atlanta, Georgia, metropolitan area encompass positions focused on the design, development, testing, and manufacturing of aircraft, spacecraft, and related systems. These roles often require a strong foundation in engineering principles, mathematics, and physics, and can range from entry-level positions to specialized roles requiring advanced degrees and experience. Examples include propulsion engineers, structural analysts, avionics specialists, and project managers overseeing aerospace initiatives.
The presence of major corporations, government facilities, and academic institutions with aerospace programs contributes to the significance of this job market. These jobs fuel innovation in areas such as air transportation, defense, and space exploration. The availability of these positions supports economic growth and technological advancement in the region and nationally. Historically, the evolution of aviation and the growth of related industries have been central to the expansion of this sector in the area.
The following sections will detail the specific types of roles available, the skills and qualifications generally sought by employers, the major companies and organizations involved, and the factors contributing to the region’s appeal for aerospace professionals.
Successfully pursuing opportunities in the aerospace sector in the Atlanta, Georgia, metropolitan area requires a focused and strategic approach. The following tips are intended to guide individuals seeking such positions.
Tip 1: Cultivate a strong foundation in core engineering principles. Employers often prioritize candidates with a solid understanding of fundamental concepts in areas such as thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, structural analysis, and control systems.
Tip 2: Tailor resumes and cover letters to specifically highlight relevant skills and experience. Generic applications are less likely to gain traction. Demonstrate how qualifications align with the specific requirements of each position.
Tip 3: Proactively network with professionals in the field. Attend industry events, join relevant professional organizations (e.g., AIAA), and connect with individuals on platforms such as LinkedIn. Informational interviews can provide valuable insights and connections.
Tip 4: Research companies and organizations actively involved in aerospace activities within the region. Identify companies that align with career interests and proactively monitor their job postings. Direct applications can be more effective than relying solely on job boards.
Tip 5: Consider obtaining relevant certifications and professional licenses. Certifications such as those offered by the FAA or professional engineering (PE) licensure can enhance credentials and demonstrate expertise.
Tip 6: Develop proficiency in industry-standard software and tools. Familiarity with software packages used for CAD, CAE, CFD, and project management can significantly increase employability. Examples include MATLAB, SolidWorks, ANSYS, and relevant programming languages.
Tip 7: Be prepared to showcase technical expertise during interviews. Employers often use technical questions, problem-solving exercises, and portfolio reviews to assess candidates’ capabilities. Practice articulating technical knowledge clearly and concisely.
These strategies will help individuals improve their chances of securing a position within the competitive aerospace job market. Thorough preparation and targeted efforts are essential for success.
The subsequent sections will explore the specific skills and qualifications employers prioritize, providing further guidance for aspiring aerospace professionals in the Atlanta region.
1. Skills and Qualifications
A strong correlation exists between the requisite skills and qualifications and the available aerospace engineering opportunities within the Atlanta metropolitan area. Possessing the specific competencies sought by employers significantly enhances a candidate’s prospects. A thorough understanding of these requirements is critical for both career planning and professional development.
- Technical Proficiency
Technical proficiency encompasses a deep understanding of engineering principles, mathematical modeling, and the application of relevant software tools. For instance, a structural analysis engineer role necessitates proficiency in finite element analysis (FEA) software such as ANSYS or Abaqus. Similarly, a propulsion engineer requires expertise in thermodynamics and fluid mechanics, along with experience in software used for simulating engine performance. A lack of these technical skills will hinder the ability to contribute effectively to projects and may disqualify candidates from consideration.
- Problem-Solving Abilities
Aerospace engineering projects often involve complex challenges requiring innovative solutions. Strong problem-solving abilities are essential for identifying, analyzing, and resolving technical issues that arise during the design, testing, and manufacturing phases. Consider a scenario where a design flaw is discovered during wind tunnel testing. The engineer must be able to diagnose the root cause, propose alternative designs, and implement modifications to address the problem. Candidates should be prepared to demonstrate their problem-solving skills through examples from previous projects.
- Communication and Collaboration
Aerospace projects are rarely undertaken in isolation. Effective communication and collaboration skills are crucial for working within multidisciplinary teams, coordinating with stakeholders, and conveying technical information clearly and concisely. For example, an engineer may need to present design proposals to management, collaborate with manufacturing teams to ensure manufacturability, and communicate with suppliers to resolve technical issues. Failure to communicate effectively can lead to misunderstandings, delays, and errors.
- Project Management Skills
Many aerospace engineering roles involve managing projects, whether it’s leading a design team, overseeing a testing program, or coordinating the manufacturing of a component. Project management skills include planning, organizing, budgeting, and tracking progress to ensure projects are completed on time and within budget. For instance, a project manager responsible for developing a new aircraft system must be able to create a project schedule, allocate resources effectively, and monitor progress against milestones. Ineffective project management can result in cost overruns, schedule delays, and compromised product quality.
These skills and qualifications collectively represent the foundational requirements for successful employment in the aerospace sector within the Atlanta metropolitan area. Demonstrating proficiency in these areas significantly increases a candidate’s competitiveness and ability to contribute meaningfully to aerospace engineering projects.
2. Industry Growth Projections
The projected expansion of the aerospace industry significantly influences the availability and nature of aerospace engineering positions in the Atlanta, Georgia, area. Understanding these projections is crucial for anticipating future job market trends and aligning career development with industry demands.
- Increased Demand for Commercial Aircraft
Forecasts indicate a sustained increase in air travel, leading to a heightened demand for new and more efficient commercial aircraft. This necessitates the expansion of engineering teams focused on design, manufacturing, and maintenance. Atlanta’s proximity to major aerospace manufacturers and suppliers positions it as a key location for supporting these growth initiatives. For example, companies may increase hiring of structural engineers, aerodynamicists, and avionics specialists to meet the demand for next-generation aircraft development.
- Expansion of the Space Sector
The burgeoning private space sector, driven by companies involved in satellite technology, space tourism, and exploration, is creating new opportunities for aerospace engineers. Atlanta’s research institutions and existing aerospace infrastructure provide a foundation for supporting this expanding market. Anticipate greater demand for engineers with expertise in propulsion systems, orbital mechanics, and spacecraft design. This also includes engineers capable of addressing the unique challenges of operating in the space environment.
- Advancements in Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS)
The increasing adoption of unmanned aerial systems across various sectors, including agriculture, delivery services, and infrastructure inspection, fuels the demand for engineers specializing in UAS design, control systems, and regulatory compliance. Atlanta’s strategic location and growing technology sector make it an attractive hub for UAS development and operations. Expect increased demand for engineers focused on autonomous flight control, sensor integration, and the development of safe and reliable UAS platforms.
- Focus on Sustainable Aviation
Growing environmental concerns are driving innovation in sustainable aviation technologies, including electric propulsion, alternative fuels, and lightweight materials. This shift towards greener aviation creates opportunities for engineers with expertise in these areas. Atlanta’s research institutions and aerospace companies are increasingly investing in sustainable aviation technologies, creating a demand for engineers with skills in areas such as battery technology, fuel cell design, and the application of composite materials.
In summary, industry growth projections point toward a robust demand for aerospace engineers in Atlanta, Georgia. The expansion of commercial aviation, the burgeoning space sector, the increasing adoption of UAS, and the focus on sustainable aviation are all contributing to this growth. Individuals seeking careers in this field should align their skills and education with these emerging trends to maximize their career prospects.
3. Major Employers Location
The geographic distribution of major aerospace employers in the Atlanta metropolitan area is a primary determinant of the accessibility and concentration of engineering positions. The presence of these entities serves as a central factor in shaping the regional job market for aerospace professionals.
- Proximity to Key Transportation Hubs
The location of aerospace firms near Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport and major transportation corridors provides logistical advantages, facilitating the efficient movement of personnel, materials, and finished products. This proximity often translates to a higher concentration of aerospace-related operations and subsequently, engineering jobs. For instance, companies specializing in aircraft maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) services typically locate near airports to minimize downtime and transportation costs, generating demand for skilled engineers in those areas.
- Strategic Clustering Around Research Institutions
The presence of prominent universities and research institutions, such as the Georgia Institute of Technology, influences the location decisions of aerospace employers. These institutions serve as talent pipelines and centers for innovation, attracting companies seeking access to skilled graduates and cutting-edge research. Areas surrounding these institutions often become hubs for aerospace startups and established firms engaged in research and development, creating a demand for engineers with advanced degrees and specialized expertise. This clustering fosters collaboration and knowledge sharing, further enhancing the region’s appeal as a center for aerospace activity.
- Influence of Government and Military Installations
The presence of federal facilities and military installations also plays a significant role in shaping the geographic distribution of aerospace employers. These installations often require specialized engineering services for aircraft maintenance, modernization, and research projects. Companies providing these services tend to locate near government facilities to facilitate collaboration and responsiveness to client needs. This concentration of government-related aerospace activity can create a stable and predictable demand for engineering positions, particularly those requiring security clearances or specialized expertise in defense-related technologies.
- Impact of State and Local Economic Incentives
State and local governments often offer economic incentives, such as tax breaks, infrastructure improvements, and workforce development programs, to attract aerospace companies to specific regions. These incentives can influence location decisions and result in a concentration of aerospace activity in designated areas. Companies may choose to locate in areas with favorable business climates and access to skilled labor, leading to a higher concentration of engineering jobs in those locations. Therefore, understanding the interplay between government incentives and corporate location decisions is crucial for comprehending the spatial distribution of aerospace engineering opportunities.
In conclusion, the location of major aerospace employers within the Atlanta metropolitan area is not arbitrary. It is driven by factors such as proximity to transportation hubs, research institutions, government installations, and the availability of economic incentives. These factors collectively shape the regional job market for aerospace engineers and influence the accessibility of career opportunities in this field.
4. Job Market Demand
Job market demand serves as a critical indicator of the opportunities and challenges within the aerospace engineering sector in the Atlanta metropolitan area. Fluctuations in demand directly impact hiring trends, salary expectations, and the overall career prospects for engineers in this field. Understanding the factors influencing this demand is essential for both job seekers and employers.
- Technological Advancements
Innovations in areas such as advanced materials, autonomous systems, and sustainable propulsion directly fuel the demand for specialized aerospace engineers. For example, the increasing use of composite materials in aircraft manufacturing necessitates engineers with expertise in their design, testing, and integration. Similarly, the development of electric propulsion systems for aircraft requires engineers with knowledge of electric motors, battery technology, and power electronics. Companies actively engaged in these technological advancements often experience increased hiring activity to support their research and development efforts. The pace of technological change subsequently dictates the need for continual professional development among engineers.
- Government Spending and Defense Contracts
Government investment in aerospace programs, particularly those related to defense and space exploration, exerts a considerable influence on job market demand. Contracts awarded to aerospace companies for the development and production of military aircraft, satellites, and launch vehicles typically lead to an increase in engineering positions. Fluctuations in government spending priorities and defense budgets can create volatility in the job market. For example, a major contract awarded to a local company for the development of a new missile system would result in a surge in demand for engineers with expertise in missile design, guidance systems, and aerodynamics.
- Economic Conditions and Commercial Aviation
The overall health of the economy and the performance of the commercial aviation industry are closely linked to the demand for aerospace engineers. Economic growth typically leads to increased air travel, driving demand for new aircraft and maintenance services. Conversely, economic downturns can result in reduced air travel and decreased aircraft orders, leading to layoffs and hiring freezes. Airlines and aircraft manufacturers adjust their workforce based on projected demand for air travel and the financial performance of the industry. The ability of the commercial aviation sector to adapt to economic fluctuations is therefore a critical factor influencing the stability of the aerospace engineering job market.
- Regional Infrastructure and Industry Ecosystem
The presence of a well-developed aerospace industry ecosystem in the Atlanta metropolitan area, including suppliers, research institutions, and government agencies, supports sustained job market demand. This ecosystem fosters collaboration, innovation, and the development of a skilled workforce. The availability of specialized training programs and the presence of strong professional networks attract aerospace companies and engineers to the region. A robust infrastructure, including airports, research facilities, and transportation networks, is essential for supporting the growth of the aerospace sector. The ongoing development and maintenance of this infrastructure contribute to the sustained demand for aerospace engineers in the area.
In summary, the demand for aerospace engineers in Atlanta, Georgia, is shaped by a complex interplay of technological advancements, government spending, economic conditions, and the strength of the regional industry ecosystem. A comprehensive understanding of these factors is essential for individuals seeking to navigate the job market and for companies seeking to attract and retain top talent.
5. Educational Requirements
The attainment of specific academic qualifications represents a foundational prerequisite for securing aerospace engineering positions within the Atlanta metropolitan area. Employers consistently prioritize candidates demonstrating a robust theoretical understanding and practical application of engineering principles acquired through formal education.
- Bachelor’s Degree in Aerospace Engineering or a Closely Related Field
A bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering, or a closely related field such as mechanical engineering or electrical engineering, serves as the standard entry-level educational requirement. This curriculum provides a comprehensive foundation in core engineering principles, including fluid mechanics, thermodynamics, structural analysis, and control systems. Curricula should be accredited by ABET (Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology) to ensure the program meets industry standards. For example, graduates from Georgia Tech’s aerospace engineering program are consistently sought after by employers in the region due to the program’s rigor and industry relevance. Failure to possess this foundational degree significantly limits career opportunities in the field.
- Advanced Degrees (Master’s or Doctorate) for Specialized Roles
Certain specialized roles, particularly those in research and development or advanced design, typically require a Master’s or Doctorate degree. These advanced degrees allow for in-depth study of specific areas within aerospace engineering, such as propulsion, aerodynamics, or composite materials. Employers often seek candidates with advanced degrees for positions requiring expertise in emerging technologies or novel engineering solutions. For instance, a researcher developing new hypersonic propulsion systems would likely require a doctorate in aerospace engineering with a specialization in combustion and fluid dynamics. Acquiring an advanced degree enhances career prospects and opens doors to leadership positions.
- Relevant Coursework and Specializations
Specific coursework and specializations within an engineering degree program can significantly enhance a candidate’s competitiveness for particular aerospace engineering positions. For example, coursework in avionics and control systems is highly relevant for positions involving the design and development of aircraft navigation and guidance systems. Similarly, coursework in composite materials and structural analysis is essential for positions focused on aircraft structural design. Selecting coursework that aligns with desired career paths demonstrates a commitment to developing specialized expertise and increases employability. The more focused and relevant the coursework, the better prepared a candidate will be for the technical challenges of the role.
- Internships and Co-op Experiences
Practical experience gained through internships and co-op programs is highly valued by employers in the aerospace sector. These experiences provide students with opportunities to apply their academic knowledge to real-world engineering problems and develop valuable technical skills. Internships and co-op programs also allow students to network with industry professionals and gain insights into the aerospace industry. For instance, an internship at a major aerospace manufacturer could involve working on a team designing and testing new aircraft components. This hands-on experience significantly enhances a candidate’s resume and demonstrates their ability to contribute effectively to a team. Employers often prioritize candidates with relevant internship or co-op experience.
In summary, specific educational qualifications are critical for gaining entry into and advancing within the aerospace engineering field in the Atlanta metropolitan area. Possessing the appropriate degrees, relevant coursework, and practical experience gained through internships or co-op programs significantly enhances a candidate’s competitiveness and ability to succeed in this demanding profession. Aligning educational pursuits with the specific needs of the aerospace industry is essential for achieving long-term career goals.
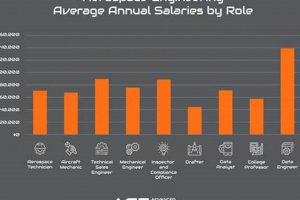
6. Salary and Benefits
Compensation packages for aerospace engineering positions within metropolitan Atlanta are influenced by multiple factors, including experience level, educational attainment, specialization, and the specific employer. Salary and benefits represent a significant component of the overall value proposition for prospective employees and play a crucial role in attracting and retaining qualified professionals. For instance, entry-level aerospace engineers in Atlanta may expect a starting salary within a defined range, while those with advanced degrees and specialized skills, such as computational fluid dynamics or structural analysis, command higher compensation. Benefits packages typically include health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and potentially stock options or performance-based bonuses. The attractiveness of these packages directly impacts an organization’s ability to compete for talent in the competitive aerospace job market.
Geographic location also contributes to salary considerations. Atlanta’s cost of living, while lower than some major metropolitan areas, is factored into compensation structures. Employers balance the need to offer competitive salaries with the economic realities of the region. Furthermore, the presence of major aerospace corporations and government facilities in the area drives competition for talent, potentially leading to increased salary offers and enhanced benefits packages. As an example, positions requiring security clearances or specialized expertise in defense-related technologies may offer premium compensation due to the limited pool of qualified candidates. Collective bargaining agreements, where applicable, also influence salary scales and benefit provisions for unionized employees within the aerospace sector.
In summary, salary and benefits are inextricably linked to aerospace engineering positions in the Atlanta metropolitan area. They act as a key determinant for attracting and retaining qualified personnel. Understanding the interplay of experience, education, specialization, geographic location, and employer type is crucial for individuals navigating the job market and for organizations seeking to maintain a competitive edge. The ability to offer comprehensive and attractive compensation packages remains a vital factor in ensuring the long-term success of the aerospace industry in the region.
7. Regional Cost of Living
The regional cost of living in metropolitan Atlanta significantly influences the attractiveness and sustainability of aerospace engineering positions located within the area. This factor interacts with salary levels and overall quality of life, impacting both recruitment and retention of qualified professionals.
- Housing Affordability
Housing costs, whether renting or purchasing, constitute a substantial portion of an individual’s expenses. While Atlanta’s housing market is generally more affordable compared to major coastal cities, variations exist within the metropolitan area. The availability of reasonably priced housing near major aerospace employers directly affects the net disposable income of engineers. If housing costs are disproportionately high relative to salaries, attracting and retaining talent becomes more challenging. For example, an engineer accepting a position in an area with rapidly increasing housing costs may find their purchasing power diminished, potentially leading to job dissatisfaction and attrition.
- Transportation Expenses
Transportation costs encompass expenses related to commuting, vehicle maintenance, and public transportation. Atlanta’s reliance on automobiles necessitates consideration of fuel costs, insurance premiums, and potential traffic congestion. The availability and efficiency of public transportation options can mitigate these costs. Engineers working in areas with limited public transportation may incur higher transportation expenses, impacting their overall financial well-being. Proximity to public transit corridors and employer-provided transportation benefits can alleviate this burden. These factors influence the net compensation and perceived value of aerospace engineering positions in different locations within the metropolitan area.
- Tax Burden
State and local taxes, including income tax and property tax, contribute to the overall cost of living. Variations in tax rates across different counties within the Atlanta metropolitan area can influence the net income available to aerospace engineers. Lower tax burdens translate to increased disposable income and enhance the attractiveness of positions in those areas. Conversely, higher tax burdens may necessitate higher salaries to maintain a competitive compensation package. The tax environment is therefore a crucial consideration for both employers seeking to attract talent and engineers evaluating job offers in different locations.
- Access to Amenities and Services
The availability and affordability of essential amenities and services, such as healthcare, childcare, education, and recreation, contribute to the overall quality of life and influence the perceived cost of living. Access to quality schools and healthcare facilities is particularly important for engineers with families. The cost of childcare and private education can be substantial and significantly impact the financial well-being of working parents. The presence of cultural and recreational amenities enhances the attractiveness of the region and can offset higher costs in other areas. The availability of these resources influences the overall appeal of aerospace engineering positions in Atlanta and their long-term sustainability for employees and their families.
In summary, the regional cost of living is an integral factor influencing the desirability of aerospace engineering jobs in Atlanta, Georgia. Balancing competitive salaries with the realities of housing costs, transportation expenses, tax burdens, and access to amenities is essential for both attracting and retaining a skilled workforce in the region’s aerospace sector.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common inquiries and concerns regarding aerospace engineering opportunities within the Atlanta metropolitan area.
Question 1: What is the typical educational background required for aerospace engineering positions in Atlanta?
A bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering or a closely related field (e.g., mechanical engineering, electrical engineering) is generally considered the minimum requirement. Advanced degrees (Master’s or Ph.D.) may be necessary for specialized research or leadership roles.
Question 2: Which are the major employers of aerospace engineers in the Atlanta area?
Prominent employers include Lockheed Martin, Delta Air Lines (for maintenance and engineering), various aerospace suppliers, and research institutions such as the Georgia Institute of Technology. Government facilities in the region also offer aerospace-related employment opportunities.
Question 3: What specific skills are most sought after by aerospace engineering employers in Atlanta?
Technical proficiency in areas such as computational fluid dynamics, structural analysis, control systems, and aerospace materials is highly valued. Strong problem-solving, communication, and project management skills are also essential.
Question 4: How does the cost of living in Atlanta compare to other major metropolitan areas with aerospace industries?
Atlanta generally offers a lower cost of living compared to cities like Los Angeles, Seattle, or Boston, which also have significant aerospace presences. This can make Atlanta an attractive option for engineers seeking a balance between career opportunities and affordability.
Question 5: What is the outlook for job growth in the aerospace engineering sector in Atlanta?
The aerospace industry in Atlanta is expected to experience moderate growth due to factors such as the expansion of the commercial aviation sector, increasing investment in unmanned aerial systems, and ongoing research and development efforts at local universities.
Question 6: Are internships and co-op experiences beneficial for securing aerospace engineering positions in Atlanta?
Yes, internships and co-op experiences are highly valued by employers. These experiences provide practical skills, industry knowledge, and networking opportunities that significantly enhance a candidate’s competitiveness.
These responses provide a concise overview of key considerations for individuals pursuing aerospace engineering careers in the Atlanta metropolitan area.
The subsequent section will summarize the key points discussed in this article, offering a consolidated perspective on aerospace engineering opportunities in the region.
Aerospace Engineering Jobs in Atlanta, GA
This article has explored the landscape of aerospace engineering opportunities in Atlanta, Georgia. The investigation encompassed crucial aspects, including the requisite skills and qualifications, industry growth projections, the location of major employers, job market demand, educational requirements, salary expectations, and the regional cost of living. These elements collectively shape the career prospects for aerospace engineers within the metropolitan area.
The information presented provides a foundation for informed decision-making regarding career planning and professional development in the aerospace engineering field. The sustained growth of the industry and the strategic location of Atlanta within the national aerospace landscape suggest continued opportunities for qualified professionals. Further investigation and proactive engagement with the industry are encouraged for those seeking to advance or establish their careers in aerospace engineering jobs in Atlanta, GA.