Positions focused on designing, developing, testing, and manufacturing aircraft, spacecraft, satellites, and related systems are available within the designated geographical region. These opportunities span a range of specializations, including aerodynamics, propulsion, structural analysis, and avionics, among others. An engineer working in this field might, for example, be involved in designing a new type of composite wing for a commercial airliner or developing guidance systems for space exploration vehicles.
The concentration of such roles in this area reflects the historical significance and continued presence of major aerospace companies and government research institutions. Benefits of pursuing such a career path can include competitive salaries, opportunities for professional growth, and the chance to contribute to cutting-edge advancements in technology. The sector’s history in this region dates back to the early days of aviation and has been instrumental in shaping the technological landscape of the United States.
This article will explore specific industry sectors, key employers, required qualifications, and current trends shaping the employment landscape for professionals in this specialized area of engineering within the specified region. Further sections will delve into educational pathways and resources available for individuals seeking to enter or advance within this field.
Guidance for Pursuing Professional Opportunities in the Aerospace Sector
The following insights are intended to assist individuals seeking to navigate the competitive environment of the aerospace industry within the designated geographical area. Emphasis is placed on strategic planning and proactive skill development.
Tip 1: Prioritize development of expertise in high-demand specializations. Areas such as advanced materials, autonomous systems, and cybersecurity are experiencing significant growth and require specialized skills.
Tip 2: Cultivate a strong understanding of regulatory frameworks and industry standards. Familiarity with FAA regulations, ISO standards, and other relevant guidelines is essential for compliance and project success.
Tip 3: Actively engage in networking within the aerospace community. Attend industry conferences, join professional organizations, and connect with established professionals to expand professional reach.
Tip 4: Tailor resumes and cover letters to specifically address the requirements outlined in job postings. Highlight relevant experience, skills, and accomplishments that demonstrate a strong fit for each role.
Tip 5: Prepare thoroughly for technical interviews. Expect questions related to engineering principles, problem-solving methodologies, and specific technologies relevant to the position.
Tip 6: Consider pursuing advanced degrees or certifications to enhance qualifications and demonstrate commitment to professional development. A master’s degree or specialized certifications can provide a competitive advantage.
Tip 7: Research companies and their specific projects. Demonstrating knowledge of a company’s work and contributions to the industry illustrates genuine interest and initiative.
Adhering to these recommendations can enhance an applicant’s prospects for securing a desirable position within the aerospace sector. A strategic approach, combined with continuous skill development, is crucial for long-term success.
The next section of this article will examine specific employers and their contributions to this region’s aerospace landscape.
1. Qualifications
Qualifications serve as a foundational determinant for accessing positions in the aerospace engineering sector within this region. The attainment of specific academic degrees, certifications, and demonstrated experience directly impacts an applicant’s eligibility and competitiveness. Aerospace firms in this area typically require a minimum of a bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering or a closely related field, such as mechanical or electrical engineering. Advanced degrees, such as a Master’s or Ph.D., are often prerequisites for research and development roles or specialized engineering positions. Furthermore, specific certifications, like those related to project management or systems engineering, may be required depending on the specific role and company.
The demand for specialized expertise in areas such as composite materials, autonomous systems, and computational fluid dynamics underscores the importance of continuous professional development. For example, an engineer seeking a role in designing advanced aircraft wings might require certification in finite element analysis software and a thorough understanding of composite material properties. Similarly, those working on space-based systems often need extensive knowledge of orbital mechanics, spacecraft propulsion systems, and mission operations. Several prominent companies in the region have specific training programs aimed at enhancing employee skill sets in these critical areas, acknowledging the evolving technological landscape. Practical examples of required qualifications could include demonstrating proficiency in CAD software, a deep comprehension of aerodynamics, and experience with testing and simulation methodologies.
In summary, qualifications act as gatekeepers to opportunities in aerospace engineering within the area. The investment in appropriate education, relevant certifications, and continuous skill development is crucial for gaining entry into this sector. A deficiency in these areas can significantly hinder career advancement. Thus, aspiring professionals should carefully assess the required qualifications of target positions and proactively pursue the necessary training and experience to meet these demands, thereby maximizing their chances of securing meaningful employment in this competitive field.
2. Competition
The aerospace engineering job market within Southern California is characterized by intense competition. This stems from a confluence of factors, including a high concentration of aerospace companies, a strong presence of top-tier engineering universities, and the region’s overall desirability as a place to live and work. Consequently, the supply of qualified engineers often exceeds the available positions, leading to a selective hiring process and a heightened demand for exceptional candidates. Graduates entering the field, experienced engineers seeking advancement, and individuals relocating to the region all contribute to this competitive environment. Securing a position often requires not only a strong academic record and relevant experience but also demonstrated skills, a proactive approach to networking, and a compelling personal brand.
The influence of competition extends beyond initial job placement. It also affects career progression within the aerospace sector. Engineers must continually enhance their skills, adapt to evolving technologies, and pursue advanced education to remain competitive for promotions and leadership roles. Companies benefit from this competition by having access to a highly skilled and motivated workforce, driving innovation and productivity. However, it also necessitates that companies offer competitive compensation packages, professional development opportunities, and a stimulating work environment to attract and retain top talent. Examples of companies that thrive on intense competition are SpaceX, Boeing, and Northrop Grumman. Each company is constantly innovating, developing and creating, because if they stop, they might not stay competitive. All these companies are located in Southern California.
In summary, competition is an integral component of the aerospace engineering job landscape in Southern California. Understanding its dynamics is essential for both job seekers and employers. For aspiring engineers, recognizing the competitive nature of the market necessitates a strategic approach to career planning, emphasizing continuous learning and proactive networking. For companies, it highlights the importance of fostering a culture of innovation and providing opportunities for employee growth to attract and retain the best talent. While challenging, this competitive environment ultimately contributes to the region’s status as a hub for aerospace innovation and technological advancement.
3. Specializations
The diversity of specialized fields within aerospace engineering significantly influences the landscape of opportunities available in Southern California. This region, renowned for its concentration of aerospace industries, requires engineers with specific skills and knowledge across a spectrum of disciplines. The demand for particular specializations directly correlates with the technological advancements and strategic priorities of companies operating within the area. For example, the increased focus on sustainable aviation fuels has created a surge in the need for engineers specializing in chemical propulsion and alternative fuel technologies. Similarly, the development of advanced unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) has generated a high demand for expertise in areas like autonomous systems, sensor integration, and control algorithms. Understanding these specialization trends is crucial for job seekers aiming to align their skills with industry needs.
The practical significance of recognizing the relationship between specializations and regional job markets is manifold. Engineers who possess in-demand skills are more likely to secure employment, negotiate favorable compensation packages, and experience accelerated career growth. Furthermore, targeted specialization enables engineers to contribute meaningfully to specific projects and innovations that directly impact the aerospace industry. Consider the instance of an engineer specializing in computational fluid dynamics (CFD). Their expertise is highly valued in optimizing aircraft designs, improving aerodynamic performance, and ensuring structural integrity. Their contributions directly enhance the efficiency and safety of aerospace systems, highlighting the practical value of their specialized knowledge. Moreover, the geographic concentration of specific specializations creates specialized ecosystems and clusters that facilitate collaboration and knowledge sharing among professionals in related fields.
In conclusion, specializations are not merely academic distinctions within aerospace engineering; they are critical components that shape the dynamics of the job market in Southern California. The demand for specific expertise is driven by technological advancements and industry priorities, creating a dynamic and competitive environment. Aspiring aerospace engineers can maximize their career prospects by identifying high-demand specializations, acquiring relevant skills and knowledge, and actively engaging with the regional aerospace community. By focusing on specialization, candidates increase their employability and make a meaningful impact on the ongoing evolution of the aerospace industry.
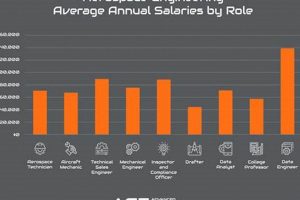
4. Compensation
Compensation represents a critical consideration for individuals pursuing opportunities within the aerospace engineering sector in Southern California. It influences talent attraction, retention, and overall job satisfaction. The following facets highlight key factors influencing compensation packages within the region.
- Experience Level
Entry-level positions typically offer lower salaries compared to those requiring extensive experience. A recent graduate may earn significantly less than an engineer with ten or more years of experience in a specialized area such as propulsion systems or structural analysis. The difference in compensation reflects the value placed on practical knowledge and demonstrated ability to solve complex engineering challenges. For instance, a senior engineer overseeing a project involving the design of a new aircraft wing may command a significantly higher salary due to their proven track record of success.
- Level of Education
Educational attainment impacts compensation levels. Possessing a Master’s or Ph.D. degree often translates to higher earning potential, especially in research and development roles. The additional expertise gained through advanced studies is valued by employers seeking to innovate and push the boundaries of aerospace technology. An individual with a doctorate specializing in computational fluid dynamics, for example, may be sought after for roles involving the design and optimization of aerodynamic surfaces, leading to increased compensation.
- Specific Skills and Specialization
Compensation is influenced by specific skills and specialization areas within aerospace engineering. High-demand skills, such as expertise in autonomous systems, cybersecurity, or advanced materials, command premium salaries. This reflects the limited supply of qualified professionals in these fields and the critical role these skills play in driving innovation and addressing emerging challenges within the industry. A software engineer specializing in cybersecurity for aerospace systems, may command a higher salary than a general software developer due to the specialized nature of their skill set and its importance in protecting critical infrastructure.
- Company Size and Type
Company size and type impact compensation packages. Large aerospace corporations typically offer more competitive salaries and benefits compared to smaller firms or startups. However, smaller companies may offer other advantages, such as greater opportunities for advancement and a more flexible work environment. Furthermore, government contractors may have different compensation structures compared to commercial aerospace companies, with variations in benefits packages and long-term incentives. An engineer working for a major aerospace corporation may receive a comprehensive benefits package including health insurance, retirement plans, and stock options, whereas an engineer at a smaller firm may have more limited benefits but greater flexibility in their work schedule.
These facets collectively influence the compensation landscape for aerospace engineering positions in Southern California. Aspiring and experienced engineers should carefully consider these factors when evaluating job opportunities and negotiating salary packages. Recognizing the value of experience, education, specialized skills, and the type of employer can lead to greater financial success in this competitive industry.
5. Innovation
Innovation forms a cornerstone of the aerospace industry, and its influence on engineering positions in Southern California is substantial. The region’s concentration of aerospace companies and research institutions necessitates continuous advancements in technology, creating a demand for engineers capable of driving and implementing these innovations. This requirement for perpetual evolution directly impacts the skills sought after by employers and the nature of work performed by engineers.
- Advanced Materials Development
The pursuit of lighter, stronger, and more heat-resistant materials is a constant driver of innovation. Engineers are required to develop, test, and implement these new materials in aircraft and spacecraft design. For instance, the development of carbon fiber composites has revolutionized aircraft construction, demanding engineers with expertise in material science, structural analysis, and manufacturing processes. The application of such materials in projects like advanced aircraft or spacecraft necessitates a highly skilled workforce adept at the latest materials technologies.
- Autonomous Systems Integration
The integration of autonomous systems into both aircraft and spacecraft represents a significant area of innovation. This requires engineers proficient in robotics, artificial intelligence, sensor fusion, and control systems. The development of autonomous drones for surveillance or delivery services, or the creation of self-navigating spacecraft, directly relies on engineers capable of designing, programming, and testing these complex systems. This area is actively influencing hiring practices, with a premium being placed on candidates with experience in machine learning and autonomous control algorithms.
- Sustainable Propulsion Technologies
Addressing environmental concerns requires innovation in propulsion systems, focusing on reducing emissions and improving fuel efficiency. Engineers are actively working on developing electric propulsion systems, hybrid engines, and alternative fuel sources. The creation of more fuel-efficient jet engines or the development of electric propulsion for urban air mobility vehicles demands a workforce familiar with the latest advancements in thermodynamics, combustion, and energy storage. Companies are actively seeking engineers with expertise in these areas to meet regulatory requirements and consumer demands for environmentally friendly technologies.
- Digitalization and Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE)
The digitalization of aerospace engineering processes, including the use of MBSE, has become crucial for efficiency and accuracy. Engineers are needed who can implement digital design tools, create virtual prototypes, and conduct simulations to optimize system performance. The use of such technologies allows for faster development cycles, reduced costs, and improved product reliability. The implementation of MBSE and digitalization strategies necessitates engineers with expertise in software development, data analytics, and systems integration, making these skills increasingly valuable in the Southern California aerospace job market.
These examples illustrate how innovation directly translates into specific skill requirements for engineering positions in Southern California. Companies are actively seeking engineers who can contribute to these advancements, creating a dynamic and competitive job market. This emphasis on innovation not only drives the aerospace industry forward but also shapes the career paths and skill development of engineers within the region.
6. Regulation
Regulation exerts a significant influence on aerospace engineering positions in Southern California. Aerospace activities, due to their potential impact on public safety and national security, are subject to stringent oversight. These regulatory requirements impact the types of work performed, the necessary qualifications for engineers, and the overall operational environment within the industry.
- Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) Compliance
The FAA regulates all aspects of civil aviation, including aircraft design, manufacturing, and maintenance. Aerospace engineers working in Southern California must adhere to FAA regulations in their work. This encompasses ensuring that aircraft designs meet safety standards, developing maintenance procedures that comply with FAA guidelines, and participating in certification processes. Non-compliance can lead to significant penalties, including project delays, fines, and reputational damage. For instance, engineers involved in designing aircraft control systems must rigorously adhere to FAA standards to ensure the safety and reliability of these systems.
- International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) and Export Administration Regulations (EAR)
ITAR and EAR control the export of defense-related technologies and information. These regulations affect aerospace companies involved in the design, development, and manufacture of military aircraft, spacecraft, and related components. Engineers working on projects subject to ITAR/EAR must comply with strict export control requirements, including obtaining necessary licenses and safeguarding sensitive information. A failure to comply with these regulations can result in substantial fines, imprisonment, and loss of export privileges. For example, engineers developing missile guidance systems must adhere to ITAR regulations to prevent unauthorized access to this technology by foreign entities.
- Environmental Regulations
Aerospace activities can have significant environmental impacts, including air and noise pollution. Regulatory agencies, such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the California Air Resources Board (CARB), impose regulations to mitigate these impacts. Engineers working in Southern California must consider environmental regulations in their designs and operations. This may involve developing quieter aircraft engines, reducing emissions from manufacturing processes, and implementing sustainable aviation practices. Failure to comply with environmental regulations can result in fines, legal action, and damage to a company’s reputation. For instance, engineers designing new jet engines must strive to minimize noise pollution to comply with local noise ordinances.
- Safety Standards and Certifications
Adherence to industry safety standards and certifications is critical in the aerospace industry. Organizations like the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) and the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) develop standards that engineers must follow. Compliance with these standards helps to ensure the safety and reliability of aerospace products and services. Engineers may also need to obtain specific certifications to demonstrate their competence in certain areas. For example, structural engineers may need to obtain certifications to demonstrate their expertise in designing and analyzing aircraft structures. Upholding these safety standards and certifications contributes significantly to maintaining public trust and ensuring operational integrity.
In summary, regulation plays a pivotal role in shaping aerospace engineering positions in Southern California. Compliance with FAA regulations, ITAR/EAR, environmental standards, and safety certifications is essential for engineers working in this sector. The ability to navigate these complex regulatory requirements is a valuable skill, influencing career opportunities and the overall success of aerospace companies in the region. The integration of these regulatory requirements into the design, development, and operation of aerospace systems ensures safety, security, and environmental sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common inquiries regarding careers in aerospace engineering within the specified region. These answers are intended to provide clarity and guidance to individuals seeking opportunities in this field.
Question 1: What are the primary industries employing aerospace engineers in Southern California?
Key industries include commercial aviation, defense, space exploration, and related technology sectors. These industries encompass aircraft manufacturing, satellite development, rocket propulsion, and engineering consulting.
Question 2: What educational qualifications are typically required for entry-level aerospace engineering positions?
A minimum of a bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering or a closely related field, such as mechanical engineering or electrical engineering, is generally required. Advanced degrees, such as a Master’s or Ph.D., are often preferred for research and development roles.
Question 3: What are the most sought-after skills in the current aerospace engineering job market?
In-demand skills include expertise in computational fluid dynamics, finite element analysis, composite materials, autonomous systems, and proficiency with industry-standard software such as CAD and MATLAB.
Question 4: How does the cost of living in Southern California impact the overall compensation for aerospace engineers?
The high cost of living in Southern California is typically factored into compensation packages offered by aerospace companies. Salaries are generally adjusted to reflect the higher expenses associated with housing, transportation, and other essential goods and services.
Question 5: What are the typical career progression pathways for aerospace engineers in this region?
Career progression can include advancement to senior engineering roles, project management positions, technical leadership roles, and management positions within engineering departments. Opportunities may also exist to move into specialized areas such as research and development or consulting.
Question 6: How can aspiring aerospace engineers enhance their chances of securing a position in Southern California?
Strategic actions include obtaining relevant certifications, gaining internships or co-op experience, actively networking within the aerospace community, and tailoring resumes and cover letters to specifically address the requirements of each job posting.
These FAQs offer insights into the realities and expectations surrounding careers in aerospace engineering within Southern California. Prospective and current professionals in this field will benefit from considering these factors in their career planning.
The following section will provide resources useful for further study and engagement.
Conclusion
The preceding analysis has explored critical aspects of employment opportunities in the aerospace engineering sector within Southern California. These aspects include essential qualifications, the intensity of competition, prevalent specializations, compensation determinants, the driving force of innovation, and the pervasive influence of regulatory compliance. Each of these factors independently and collectively shapes the professional trajectory for individuals pursuing careers in this high-technology domain.
Understanding the complexities inherent in the Southern California aerospace engineering landscape is crucial for both aspiring and established professionals. Ongoing technological advancements and evolving regulatory frameworks demand continuous skill development and adaptation. Individuals and organizations alike must remain proactive to maintain competitiveness and contribute meaningfully to the ongoing advancement of the aerospace industry in this vital region. Further research into specific companies and fields is advised for optimal success.