Opportunities in the field relating to the design, development, and testing of aircraft and spacecraft, situated within the Spanish economy, constitute a specialized employment sector. These positions encompass a broad range of roles, from research and development to manufacturing and maintenance, all located within Spanish territory. As an illustration, an individual might secure a position designing aerodynamic components for a Spanish aerospace manufacturer or working on the integration of satellite systems at a research facility in Spain.
This sector’s significance stems from its contribution to technological advancement, economic growth, and national security within Spain. Historically, Spain has invested in its aerospace industry, leading to the creation of specialized educational programs and research institutions. This investment has fostered a skilled workforce and attracted international collaborations, strengthening the nation’s position in the global aerospace market and contributing to its overall technological prowess.
The following sections will delve into the specific types of roles available, the skills and qualifications typically required, the key companies operating in this arena, and the overall outlook for career advancement within this dynamic sector of the Spanish economy.
Strategies for Securing Employment in the Spanish Aerospace Sector
The subsequent recommendations are intended to enhance the prospects of individuals seeking to enter or advance within the field, specifically within the Spanish context.
Tip 1: Develop Specialized Skills: Obtain expertise in areas highly valued by Spanish aerospace companies. This may include proficiency in computational fluid dynamics (CFD), finite element analysis (FEA), or specific aerospace software packages commonly used in Spain.
Tip 2: Acquire Relevant Certifications: Pursue certifications recognized within the European aerospace industry. Examples include those related to aircraft maintenance, quality assurance, or project management, demonstrating adherence to industry standards.
Tip 3: Master the Spanish Language: Fluency in Spanish is frequently a prerequisite for successful integration into Spanish workplaces and collaboration with local teams. Language proficiency demonstrates commitment and facilitates effective communication.
Tip 4: Target Relevant Companies: Research and identify key aerospace companies operating within Spain. Tailor applications to align with the specific needs and projects of these organizations, showcasing relevant skills and experience.
Tip 5: Network Strategically: Attend industry events and conferences held in Spain to connect with professionals in the field. Building relationships can provide valuable insights into available positions and facilitate introductions.
Tip 6: Consider Postgraduate Studies: Obtain a Master’s degree or PhD from a reputable Spanish university specializing in aerospace engineering. Advanced education demonstrates a deep commitment to the field and provides specialized knowledge.
Tip 7: Gain International Experience: Seek internships or research opportunities with aerospace organizations outside of Spain, particularly within Europe. International experience broadens perspectives and demonstrates adaptability.
Adherence to these recommendations should significantly enhance an individual’s competitiveness and chances of securing a suitable position within this specialized field.
The following sections will further expand on the resources and pathways available to those seeking a career in this demanding yet rewarding sector of the Spanish economy.
1. Qualifications
Required qualifications directly dictate access to roles within Spanish aerospace engineering. A foundational degree in aerospace engineering, mechanical engineering, or a closely related field is typically a prerequisite. Furthermore, many advanced positions, especially those involving research, development, or design, necessitate a Master’s degree or a doctorate. The specific coursework and specializations pursued during academic studies are directly linked to the types of offered in Spain. For instance, an engineer with a specialization in aerodynamics may find roles in aircraft design, while expertise in propulsion systems may lead to engine development.
The relationship between qualifications and sector opportunities extends beyond academic degrees. Practical experience, often gained through internships or co-op programs, is crucial. Knowledge of industry-standard software, such as CATIA, ANSYS, or MATLAB, is frequently required by companies. Moreover, certain positions may demand specific certifications, such as those related to aircraft maintenance or airworthiness regulations mandated by the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA). The absence of these desired qualifications can effectively limit access to certain career paths.
Ultimately, the accumulation of relevant qualifications, encompassing both academic achievements and practical skill sets, determines an individual’s eligibility for and success within this sector of the Spanish economy. A continuous commitment to professional development and the acquisition of new skills are essential for maintaining competitiveness in a dynamic and technologically advanced environment.
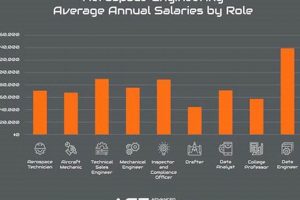
2. Salary Expectations
Compensation within Spanish aerospace engineering is contingent upon a variety of factors. Years of experience constitutes a primary determinant, with entry-level positions naturally commanding lower salaries than those offered to seasoned professionals. The specific role also plays a significant role; design engineers, for instance, may earn differently than quality control specialists. Geographical location within Spain further influences remuneration, as metropolitan areas such as Madrid or Barcelona typically offer higher compensation packages compared to less urbanized regions due to differing costs of living and demand for skilled labor. For instance, an entry-level engineer in Seville might expect a starting salary in the lower range, while a senior project manager in Madrid could command a considerably higher figure.
Industry demand and the presence of international companies also have an effect. As Spain’s aerospace sector grows and attracts foreign investment, competition for qualified engineers intensifies, potentially driving salaries upward. Specific skill sets, such as proficiency in advanced simulation software or expertise in composite materials, command premium compensation due to their scarcity. Collective bargaining agreements negotiated by unions can also establish minimum wage standards for certain positions within larger companies, ensuring a baseline level of compensation for engineers within those organizations. The general economic climate in Spain can also influence the financial scope of the field.
Therefore, understanding salary expectations in Spain requires a nuanced approach. Prospective engineers should research average salaries for comparable roles in similar locations, factor in their individual skills and experience, and consider the overall economic conditions to accurately assess their potential earning power. Thorough research and negotiation are crucial for securing fair compensation commensurate with the value they bring to the industry.
3. Company Landscape
The presence and nature of specific companies within Spain directly shape the availability and character of its aerospace engineering sector jobs. The “Company Landscape” acts as a primary driver, determining the types of roles offered, the required skill sets, and the geographical distribution of these opportunities. Major international players, such as Airbus, maintain a significant presence, offering positions in design, manufacturing, and maintenance of commercial aircraft. Smaller, specialized firms often focus on niche areas, such as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or satellite technology, generating employment requiring distinct technical expertise. The strategic decisions of these organizations, including investments in research and development or expansion of production facilities, have a direct and measurable effect on the number and type of positions available. For instance, an Airbus facility expansion in Seville would inevitably lead to the creation of related engineering opportunities in that region.
The composition of the “Company Landscape” extends beyond large multinational corporations. A network of smaller suppliers, subcontractors, and research institutions contributes significantly to the sector. These entities often require engineers with specialized skills in areas such as materials science, avionics, or software development. Furthermore, government agencies involved in space exploration and defense contribute to the demand for engineers with expertise in propulsion systems, satellite communications, and related fields. The competitive dynamics among these organizations also affect employment conditions, including salary levels, benefits packages, and opportunities for professional advancement. The emergence of new companies focused on sustainable aviation technologies, for example, could create increased demand for engineers with expertise in electric propulsion or alternative fuels.
In conclusion, understanding the “Company Landscape” is crucial for anyone seeking to enter or advance within the Spanish aerospace engineering sector. It provides valuable insights into the types of roles available, the skills in demand, and the potential for career growth. By analyzing the strategies and activities of key companies and organizations, individuals can make informed decisions about their education, training, and career paths, thereby maximizing their chances of success in this dynamic and technologically advanced field. This knowledge enables a more strategic and targeted approach to job searching and career development within Spain.
4. Regional Opportunities
The availability of aerospace engineering positions within Spain is not uniform; rather, it is geographically concentrated, directly influencing the “Regional Opportunities” component of the broader employment landscape. Certain regions have established themselves as centers for aerospace activity, attracting companies, investment, and talent. This concentration is frequently due to historical factors, existing infrastructure, or government initiatives aimed at fostering the industry in specific areas. Consequently, job seekers must recognize these geographical disparities to strategically target their efforts. For example, Andalusia, particularly around Seville, hosts significant aerospace manufacturing and assembly operations. Madrid, as the capital and a major economic hub, is home to numerous research institutions and corporate headquarters related to the sector. Understanding this spatial distribution is paramount for those seeking relevant employment in Spain.
The connection between “Regional Opportunities” and “aerospace engineering positions” operates on several levels. First, the presence of established companies directly translates into job creation within a given region. Second, regional government policies, such as tax incentives or infrastructure improvements, can attract aerospace businesses, further stimulating job growth. Third, the availability of specialized training programs and universities in certain regions enhances the local talent pool, making those areas more attractive to employers. For instance, the Polytechnic University of Madrid offers renowned aerospace engineering programs, contributing to the concentration of talent and opportunities in the Madrid region. Furthermore, the development of aerospace clusters, where related companies and institutions are located in close proximity, creates synergistic effects that drive innovation and job creation. The absence of these regional advantages can limit opportunities for engineers in other parts of Spain.
In summary, “Regional Opportunities” constitutes a critical factor in navigating the Spanish aerospace engineering jobs market. The geographical concentration of activity necessitates a targeted approach, requiring job seekers to identify and prioritize regions with a strong aerospace presence. Factors such as the presence of major companies, government support, and the availability of specialized training programs all contribute to the creation of these regional hubs. By understanding and leveraging these geographical dynamics, engineers can significantly enhance their prospects of securing employment in this dynamic sector of the Spanish economy.
5. Skill Demands
The specific “Skill Demands” represent a critical determinant of success in securing “aerospace engineering jobs spain”. The Spanish aerospace sector, like its global counterparts, requires a highly specialized and technically proficient workforce. A direct correlation exists between the skills an engineer possesses and the types of positions for which they qualify within Spain. Demand for expertise in areas such as computational fluid dynamics (CFD), finite element analysis (FEA), and advanced materials is consistently high. Companies seeking to develop next-generation aircraft components, for instance, require engineers with a deep understanding of aerodynamics and structural mechanics. Similarly, the growing importance of sustainable aviation technologies necessitates skills in areas such as electric propulsion and alternative fuels. The inability to demonstrate competence in these areas significantly limits access to opportunities within this sector.
The importance of specific “Skill Demands” is amplified by the increasing complexity of aerospace systems and the growing reliance on digital technologies. Proficiency in industry-standard software, such as CATIA, ANSYS, or MATLAB, is frequently a prerequisite for positions involving design, analysis, or simulation. Furthermore, expertise in areas such as systems engineering, project management, and quality assurance is essential for ensuring the successful development and delivery of aerospace products and services. The ability to work effectively in multidisciplinary teams, communicate technical information clearly, and adapt to evolving technologies is also highly valued by employers. Consider, for example, the requirements for integrating autonomous systems into UAVs; this task necessitates a combination of skills in robotics, control theory, and software engineering. A lack of these necessary skill sets reduces an engineer’s competitive edge in the Spanish job market.
In summary, an understanding of the precise “Skill Demands” is essential for individuals pursuing “aerospace engineering jobs spain”. By proactively developing expertise in areas valued by Spanish aerospace companies and continuously updating their skill sets to reflect technological advancements, engineers can significantly enhance their prospects for success. The Spanish aerospace sector is dynamic and competitive, demanding a workforce equipped with both specialized knowledge and practical skills. Therefore, a strategic focus on acquiring and demonstrating relevant skills is paramount for navigating this challenging yet rewarding field.
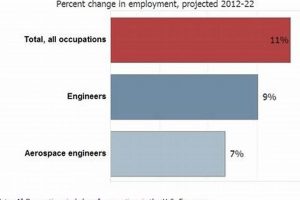
6. Growth Potential
The “Growth Potential” inherent within “aerospace engineering jobs spain” is directly correlated with broader trends in the Spanish and European aerospace industries. Increased investment in research and development, expansion of existing aerospace facilities, and the emergence of new companies and technologies contribute to a positive growth trajectory. This growth translates directly into the creation of new positions and the advancement of existing employees within the sector. For example, Spain’s participation in European Space Agency (ESA) programs generates demand for engineers specializing in satellite technology and space exploration, subsequently fueling career advancement opportunities. The practical significance of understanding this connection lies in enabling individuals to make informed decisions regarding their career paths and to acquire the skills and qualifications most relevant to future industry needs.
Moreover, the “Growth Potential” is inextricably linked to Spain’s strategic position within the global aerospace market. Its established manufacturing capabilities, skilled workforce, and participation in international collaborations position the country as a key player in the industry. Airbus’s significant presence in Spain, for instance, provides a foundation for sustained growth and employment opportunities. Furthermore, the increasing focus on sustainable aviation technologies, such as electric and hybrid propulsion systems, presents new avenues for innovation and career advancement. Engineers with expertise in these emerging fields are particularly well-positioned to capitalize on the “Growth Potential” within the Spanish aerospace sector. The impact of these opportunities creates a knock-on effect in the economy of Spain.
In conclusion, understanding the “Growth Potential” is crucial for individuals seeking “aerospace engineering jobs spain.” The sector’s future prospects are tied to broader trends in the industry, Spain’s strategic position, and the emergence of new technologies. While challenges such as economic fluctuations and global competition exist, the overall outlook for career advancement remains positive. By aligning their skills and aspirations with the identified growth areas, engineers can maximize their potential for success within this dynamic and strategically important sector of the Spanish economy. An informed understanding of these dynamics contributes to more effective career planning and greater professional fulfillment.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding employment within the aerospace engineering sector in Spain. The information provided aims to offer clarity and guidance for prospective professionals.
Question 1: What are the fundamental academic prerequisites for securing a position in Spanish aerospace engineering?
A bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering, or a closely related discipline such as mechanical or electrical engineering, constitutes the minimum educational requirement. Advanced positions often necessitate a master’s degree or doctorate.
Question 2: Is fluency in the Spanish language a mandatory requirement for employment in this sector?
While not always explicitly stated, proficiency in Spanish is highly advantageous and often considered a significant asset. Communication with local teams and integration into Spanish workplaces are facilitated by language skills.
Question 3: Which specific software proficiencies are most valued by Spanish aerospace employers?
Competency in industry-standard software packages such as CATIA, ANSYS, MATLAB, and similar tools used for design, analysis, and simulation is frequently expected.
Question 4: In which regions of Spain are the majority of aerospace engineering positions concentrated?
Aerospace activity is primarily concentrated in Andalusia (Seville area), Madrid, and Catalonia. These regions host major aerospace companies, research institutions, and government facilities.
Question 5: Are there specific certifications that enhance an applicant’s competitiveness in the Spanish aerospace job market?
Certifications related to aircraft maintenance, airworthiness regulations (EASA), project management, and quality assurance can significantly strengthen an application.
Question 6: What are the key sectors within the Spanish aerospace industry offering employment opportunities?
Opportunities exist in commercial aviation, space exploration, defense, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), and related support services. Each sector demands unique skill sets and expertise.
In summary, preparation for a career in Spanish aerospace engineering involves acquiring relevant academic qualifications, developing in-demand skills, and understanding the regional dynamics of the industry.
The subsequent section will explore the challenges and rewards associated with this career path.
Conclusion
This exploration has addressed the multifaceted nature of opportunities in the design, development, and maintenance of aircraft and spacecraft within the Spanish economy. Key aspects examined include essential qualifications, salary expectations, the relevant company landscape, regional concentrations of opportunities, critical skill demands, and the overall growth potential within the sector. The convergence of these factors shapes the realities for those seeking entry or advancement within this specialized professional area.
The information presented should empower prospective engineers to make informed decisions regarding career pathways and skill development. The Spanish aerospace sector, while presenting significant challenges, offers substantial rewards for those with the requisite expertise and dedication. Continued vigilance and strategic adaptation to the evolving needs of the industry remain paramount for sustained success in this demanding yet vital field.