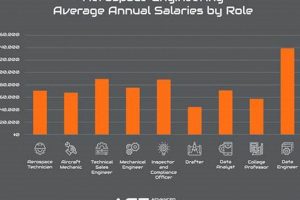
Positions within the Canadian aeronautics and space sector encompass a wide spectrum of roles, from engineering and design to manufacturing, maintenance, and research. These opportunities are concentrated in areas with significant aerospace activity, and reflect the diverse needs of both established companies and emerging ventures in the field. The availability of such roles is impacted by technological advancements, government investments, and the overall economic climate.
The Canadian aerospace industry contributes substantially to the nation’s economy, driving innovation and creating high-skilled employment. Its historical development is rooted in Canada’s strategic location for air travel and its early involvement in aircraft manufacturing. Benefits extend beyond direct employment, fostering technological advancements in related sectors and enhancing Canada’s international competitiveness. Factors such as government funding for research and development significantly shape the trajectory and growth of this sector.
This article will further explore the specific types of available positions, the skills and qualifications typically required for success, the key geographical locations where these opportunities are most prevalent, and the outlook for future growth and career pathways within this dynamic and evolving industry. Understanding these elements is crucial for individuals seeking to enter or advance within this field.
The following provides key considerations for those seeking employment within the Canadian aerospace sector. Adhering to these guidelines can increase the likelihood of securing a suitable position.
Tip 1: Acquire Relevant Education and Training. Possessing a degree in aerospace engineering, mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, or a related scientific field is fundamental. Completion of specialized training programs, such as those offered by colleges and technical institutes, can further enhance employability.
Tip 2: Develop Specialized Skills. Proficiency in areas such as CAD/CAM software, computational fluid dynamics (CFD), structural analysis, and avionics is highly valued. Obtaining certifications in relevant software or technical disciplines demonstrates a commitment to professional development.
Tip 3: Gain Practical Experience. Internships, co-op placements, and entry-level positions within aerospace companies provide invaluable hands-on experience. Participation in industry-related projects and competitions can also showcase practical skills and knowledge.
Tip 4: Network Strategically. Attending industry conferences, career fairs, and networking events provides opportunities to connect with potential employers and industry professionals. Engaging with relevant professional organizations can facilitate valuable connections.
Tip 5: Tailor Applications to Specific Positions. Carefully review job descriptions and tailor resumes and cover letters to highlight relevant skills and experience. Emphasize accomplishments and contributions that align with the specific requirements of the role.
Tip 6: Research Potential Employers. Thoroughly research the company’s history, products, services, and culture. Understanding the organization’s values and strategic goals demonstrates a genuine interest in the opportunity.
Tip 7: Prepare for Technical Interviews. Technical interviews often involve problem-solving exercises and questions related to engineering principles and industry practices. Practice answering common interview questions and be prepared to demonstrate technical proficiency.
By prioritizing education, skills development, practical experience, and strategic networking, individuals can significantly improve their prospects of securing fulfilling and rewarding careers within the Canadian aeronautics and space sector. A proactive approach to career planning is essential for success in this competitive field.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific career paths and future trends shaping the industry, offering further insights into navigating this dynamic landscape.
1. Engineering Expertise
Engineering expertise forms the bedrock of the Canadian aerospace sector, directly influencing the types and quality of available roles. A skilled engineering workforce is essential for innovation, design, and the overall competitiveness of Canadian aerospace companies. Without this foundation, the sector’s capacity for growth and technological advancement would be severely limited.
- Aerodynamic Design and Analysis
This facet encompasses the design and analysis of aircraft and spacecraft structures to optimize performance and efficiency. Engineers specializing in aerodynamics utilize computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and wind tunnel testing to refine designs, ensuring flight stability and minimizing drag. Within “aerospace jobs canada”, roles in aerodynamic design are crucial for developing fuel-efficient aircraft and advanced propulsion systems, impacting flight safety and operational costs.
- Structural Integrity and Materials Science
Aerospace engineers specializing in structural integrity ensure that aircraft and spacecraft can withstand the extreme stresses and environmental conditions encountered during flight. This involves selecting appropriate materials, conducting stress analyses, and implementing rigorous testing protocols. Opportunities within “aerospace jobs canada” related to structural engineering are vital for maintaining aircraft safety and extending service life, particularly with the increasing use of composite materials and advanced alloys.
- Avionics and Control Systems
Avionics engineers design and develop the electronic systems that control and monitor aircraft operations, including navigation, communication, and flight control. These systems are increasingly complex, incorporating advanced sensors, computer algorithms, and data processing techniques. For “aerospace jobs canada”, expertise in avionics is essential for developing autonomous flight systems, improving air traffic management, and enhancing the overall safety and efficiency of air travel.
- Propulsion Systems Engineering
This area focuses on the design, development, and testing of aircraft and spacecraft propulsion systems, ranging from jet engines and rocket motors to electric propulsion technologies. Engineers in this field work to improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and increase thrust capabilities. Roles within “aerospace jobs canada” focused on propulsion are key to developing sustainable aviation technologies and enabling future space exploration missions, contributing to environmental responsibility and scientific advancement.
In summary, engineering expertise is not merely a desirable attribute but a fundamental requirement for success within the Canadian aerospace sector. From aerodynamic design to propulsion systems, specialized engineering skills are essential for driving innovation, ensuring safety, and maintaining the competitiveness of “aerospace jobs canada” in a global market. Continued investment in engineering education and training is crucial for supporting the future growth and sustainability of this vital industry.
2. Manufacturing Roles
Manufacturing roles form a critical segment of “aerospace jobs canada,” directly impacting the production, assembly, and maintenance of aircraft, spacecraft, and related components. The presence of robust manufacturing capabilities within Canada’s aerospace sector is essential for maintaining a competitive edge and fostering economic growth. These roles encompass a diverse range of activities, from precision machining and composite fabrication to final assembly and quality control. Without a skilled manufacturing workforce, Canada’s ability to innovate and produce cutting-edge aerospace technologies would be significantly hampered. For instance, companies like Bombardier and Pratt & Whitney Canada rely heavily on their manufacturing divisions to produce aircraft and engines, respectively, demonstrating the vital link between manufacturing jobs and the overall health of the aerospace industry.
Further analysis reveals that the types of manufacturing roles available within “aerospace jobs canada” are closely tied to advancements in manufacturing technologies. The adoption of automation, robotics, and additive manufacturing techniques necessitates a workforce with specialized skills in areas such as CNC programming, robotic maintenance, and 3D printing. These evolving demands require ongoing investment in training and education programs to ensure that Canadian workers possess the expertise needed to operate and maintain advanced manufacturing equipment. Moreover, the shift towards lighter, more durable materials, such as carbon fiber composites, has created a demand for skilled technicians and engineers with expertise in composite fabrication and repair. This signifies a need for specialized vocational training and apprenticeship programs to support the continued growth of manufacturing capabilities within the Canadian aerospace sector.
In conclusion, understanding the significance of manufacturing roles within “aerospace jobs canada” is paramount for both job seekers and policymakers. These roles are not merely ancillary to engineering and design; they are integral to translating innovative concepts into tangible products and ensuring the long-term sustainability of the Canadian aerospace industry. While challenges such as global competition and the need for continuous technological upgrades exist, addressing these issues through strategic investments in workforce development and infrastructure will be crucial for maintaining Canada’s position as a leading aerospace manufacturing nation.
3. Regulatory Compliance
Adherence to stringent regulatory standards is paramount within the Canadian aerospace sector. This framework, governed by organizations such as Transport Canada, directly influences the nature and availability of positions and is intrinsically linked to “aerospace jobs canada.”
- Certification and Airworthiness
Aircraft certification and airworthiness regulations mandate rigorous testing, inspection, and documentation processes. Engineers, technicians, and inspectors specializing in these areas ensure that aircraft designs meet safety standards and that aircraft are maintained in airworthy condition throughout their operational life. Within “aerospace jobs canada”, roles related to certification are vital for ensuring public safety and upholding Canada’s reputation for aerospace excellence.
- Manufacturing Standards and Quality Control
Aerospace manufacturing is subject to strict quality control standards, including AS9100 and Nadcap certifications. Quality control engineers and technicians are responsible for implementing and monitoring quality management systems, ensuring that components and assemblies meet stringent specifications. These positions within “aerospace jobs canada” are essential for maintaining product integrity and preventing defects, impacting operational efficiency and reducing the risk of safety incidents.
- Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) Regulations
MRO activities are heavily regulated to ensure that aircraft are maintained to the highest safety standards. Licensed aircraft maintenance engineers (AMEs) and technicians are responsible for performing inspections, repairs, and overhauls in accordance with approved maintenance schedules and procedures. These roles within “aerospace jobs canada” are critical for extending the lifespan of aircraft and ensuring their continued airworthiness, contributing to the overall safety and reliability of air travel.
- Environmental Regulations and Compliance
Increasingly, aerospace operations are subject to environmental regulations aimed at reducing emissions and noise pollution. Engineers and environmental specialists are responsible for developing and implementing strategies to minimize the environmental impact of aircraft operations, including the use of alternative fuels and noise abatement procedures. The demand for these skills within “aerospace jobs canada” reflects the growing emphasis on sustainable aviation and corporate social responsibility.
In conclusion, regulatory compliance permeates every facet of the Canadian aerospace sector, directly shaping the roles and responsibilities of numerous positions within “aerospace jobs canada”. From ensuring airworthiness to minimizing environmental impact, adherence to these regulations is essential for maintaining safety, upholding quality, and promoting sustainable growth within the industry. A strong understanding of regulatory requirements is therefore a highly valued asset for individuals seeking to pursue careers in Canadian aerospace.
4. Research & Development
Research and development (R&D) forms a crucial pillar within the Canadian aerospace sector, directly influencing the demand for specialized positions and the overall advancement of the industry. Innovation driven by R&D efforts creates a ripple effect, leading to the emergence of new technologies, products, and processes, which subsequently necessitate a skilled workforce to design, develop, and implement these advancements. The presence of a robust R&D ecosystem within Canadas aerospace sector serves as a catalyst for economic growth, enhancing competitiveness on a global scale. Without sustained investment in R&D, the long-term viability and growth prospects of “aerospace jobs canada” would be significantly diminished. For example, the development of new aircraft materials and propulsion systems requires extensive research, ultimately leading to the creation of specialized engineering roles focused on these cutting-edge technologies.
The types of R&D roles available within “aerospace jobs canada” are diverse, encompassing areas such as aerodynamics, avionics, materials science, and propulsion systems. Each of these domains requires specialized expertise and a deep understanding of scientific principles. University research labs, government research institutions (like the National Research Council Canada), and private sector companies all contribute to the R&D landscape, offering a range of opportunities for researchers, engineers, and technicians. Furthermore, government funding programs and tax incentives play a vital role in supporting R&D activities, creating a conducive environment for innovation and attracting skilled professionals to “aerospace jobs canada.” Successful outcomes from these research efforts, such as the development of more fuel-efficient engines or advanced flight control systems, not only benefit the aerospace sector but also contribute to broader societal goals, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving air traffic safety.
In summary, the symbiotic relationship between R&D and “aerospace jobs canada” is undeniable. Investment in R&D fuels innovation, which in turn creates demand for a highly skilled workforce. While challenges such as funding constraints and international competition exist, continued support for R&D initiatives is essential for maintaining Canada’s position as a leading aerospace nation and ensuring the long-term growth and sustainability of “aerospace jobs canada.” A strategic focus on fostering innovation will be paramount in navigating the evolving landscape of the global aerospace industry and capitalizing on emerging opportunities.
5. Technical Skills
The Canadian aerospace sector demands a highly skilled workforce, rendering specific technical competencies indispensable for securing and performing effectively in available positions. A deficiency in these skills directly impacts an individual’s prospects within “aerospace jobs canada”. The following highlights critical technical skills necessary for success.
- CAD/CAM Proficiency
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) skills are fundamental for designing and manufacturing aerospace components. Mastery of software such as CATIA, SolidWorks, or NX is essential for creating detailed models, generating manufacturing instructions, and simulating performance. Within “aerospace jobs canada”, these skills are utilized daily for designing aircraft structures, engine components, and interior systems, ensuring precision and efficiency in the manufacturing process. An example is the design of complex wing structures requiring precise CAD modeling for aerodynamic efficiency and structural integrity.
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA) Expertise
FEA involves simulating the behavior of aerospace structures under various loads and environmental conditions. This skill is critical for predicting stress, strain, and deformation, ensuring structural integrity and safety. Engineers within “aerospace jobs canada” employ FEA software such as ANSYS or Abaqus to analyze aircraft wings, fuselage sections, and engine components, identifying potential failure points and optimizing designs for performance and durability. For instance, FEA is used to assess the impact of bird strikes on aircraft windshields, ensuring they can withstand significant impact forces.
- Programming and Software Development Skills
Programming skills are increasingly vital in aerospace, particularly for developing embedded systems, control algorithms, and data analysis tools. Proficiency in languages such as C++, Python, or MATLAB is highly valued. Within “aerospace jobs canada”, these skills are applied in developing flight control software, simulating aircraft performance, and analyzing flight data. A practical example is the development of autonomous navigation systems for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), requiring sophisticated programming and algorithm development.
- Materials Science Knowledge
Understanding the properties and behavior of aerospace materials, including metals, composites, and ceramics, is crucial for selecting appropriate materials for specific applications. Knowledge of material testing techniques, failure analysis, and corrosion prevention is also essential. Within “aerospace jobs canada”, materials scientists and engineers play a vital role in selecting materials for aircraft structures, engine components, and thermal protection systems. An example is the selection of lightweight composite materials for aircraft fuselages to reduce weight and improve fuel efficiency, requiring in-depth knowledge of material properties and manufacturing processes.
These facets of technical expertise collectively contribute to the success of individuals within “aerospace jobs canada”. Continuous development and refinement of these skills are imperative for maintaining a competitive edge in this technologically advanced and demanding field. As technology continues to evolve, adaptability and a commitment to lifelong learning are crucial for individuals seeking long-term success in the Canadian aerospace sector.
6. Geographic Concentration
The distribution of opportunities within “aerospace jobs canada” is far from uniform; rather, it exhibits a pronounced geographic concentration. This phenomenon arises from a confluence of factors, including historical development, the presence of established aerospace companies, specialized infrastructure, and proximity to research institutions. Consequently, certain regions within Canada emerge as prominent aerospace hubs, attracting a disproportionate share of industry activity and employment. The location of manufacturing facilities, maintenance centers, and research facilities directly influences the availability of positions, creating regional disparities in job opportunities.
Specific examples illustrate this concentration. Montreal, Quebec, boasts a significant cluster of aerospace companies, including Bombardier and Pratt & Whitney Canada, resulting in a high concentration of engineering, manufacturing, and maintenance roles. Similarly, the Greater Toronto Area hosts a number of aerospace component manufacturers and service providers, contributing to a regional concentration of related positions. Winnipeg, Manitoba, also maintains a notable presence in the aerospace sector, particularly in aircraft maintenance and repair, creating a regional demand for skilled technicians and engineers. Understanding these geographic patterns is crucial for individuals seeking to enter or advance within the Canadian aerospace industry, as it informs strategic decisions regarding education, training, and job searching.
Ultimately, the geographic concentration of “aerospace jobs canada” reflects the complex interplay of historical factors, infrastructure investments, and industry dynamics. While this concentration presents opportunities for individuals located near these hubs, it also poses challenges for those residing in other regions. Addressing these disparities may require targeted government initiatives aimed at promoting aerospace development in underserved areas, fostering a more geographically balanced distribution of opportunities within the Canadian aerospace sector. Recognizing and understanding this concentration is therefore a critical first step for both job seekers and policymakers alike.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding employment opportunities within the Canadian aeronautics and space sector, providing informative and objective responses.
Question 1: What are the primary educational qualifications typically required for entry-level engineering positions?
A bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering, mechanical engineering, or a closely related field is generally considered the minimum educational requirement for entry-level engineering roles. Some positions may require a master’s degree or specialized certifications.
Question 2: In what geographical regions of Canada are aerospace employment opportunities most concentrated?
Aerospace employment is primarily concentrated in Quebec (particularly Montreal), Ontario (especially the Greater Toronto Area), and Manitoba (Winnipeg). These regions host major aerospace companies and related industries.
Question 3: What types of skills are most valuable for individuals seeking manufacturing roles in the aerospace sector?
Skills in CNC programming, robotics, composite materials fabrication, and quality control are highly valued for manufacturing positions. Experience with aerospace-specific manufacturing standards is also beneficial.
Question 4: How important is regulatory compliance experience for aerospace professionals?
Regulatory compliance experience is critically important, as the aerospace sector is heavily regulated. Knowledge of Transport Canada regulations, AS9100 standards, and other relevant industry certifications is highly desirable.
Question 5: What role does research and development play in shaping aerospace career opportunities?
Research and development drives innovation and creates demand for specialized positions in areas such as aerodynamics, propulsion systems, and materials science. Investment in R&D is essential for the continued growth of the sector.
Question 6: Are there specific technical skills that are consistently sought after by aerospace employers?
Proficiency in CAD/CAM software, finite element analysis (FEA), programming languages (such as C++ or Python), and materials science is consistently sought after by aerospace employers. Strong analytical and problem-solving skills are also essential.
These insights offer a foundational understanding of the landscape of opportunities. Individuals pursuing a career in this domain must prioritize acquiring relevant education, skills, and experience.
The following section will provide additional resources for those seeking further information and guidance.
Aerospace Jobs Canada
This analysis has explored critical facets of the Canadian aeronautics and space sector, emphasizing the skills, qualifications, and geographic factors that shape the landscape of “aerospace jobs canada.” From engineering expertise and manufacturing roles to regulatory compliance and research & development, each element contributes to the dynamic nature of this industry.
Sustained investment in education, workforce development, and technological advancement is essential for ensuring the continued growth and competitiveness of the Canadian aerospace sector. Future success hinges on adapting to evolving industry demands and strategically positioning Canada as a global leader in aeronautics and space technology.