Positions within the aeronautics and astronautics fields located within the state represent a significant portion of the regional employment landscape. These roles encompass a wide range of specializations, including engineering, manufacturing, maintenance, and research, all contributing to the design, development, and operation of aircraft, spacecraft, and related systems. Examples include aircraft mechanics, aerospace engineers, and quality control specialists.
This sector offers substantial economic advantages to the state through job creation, attraction of investment, and technological advancement. Historically, the area’s central location and relatively lower cost of living have made it an attractive hub for aerospace activities. The presence of military installations and related defense contractors further strengthens this industry, contributing to a stable and growing job market.
The following sections will delve deeper into specific areas of opportunity, required skill sets, educational pathways, and prominent employers within the state, providing a detailed overview of the professional landscape for individuals seeking careers in this dynamic and vital sector.
The following recommendations are designed to assist individuals seeking employment in the aeronautics and astronautics fields within the state. A strategic approach to education, skill development, and networking is crucial for success.
Tip 1: Target Specific Skills: Identify areas of high demand, such as composite materials, avionics, or cybersecurity, and pursue relevant training or certifications. Demonstrable proficiency in these specialized areas will significantly enhance employability.
Tip 2: Leverage Educational Resources: Explore programs at state universities and technical colleges that offer degrees and certifications in aerospace engineering, aviation maintenance, and related fields. Consider pursuing advanced degrees to increase competitiveness.
Tip 3: Network Strategically: Attend industry conferences, job fairs, and networking events to connect with potential employers and learn about unadvertised opportunities. Actively engage with professional organizations, such as the Oklahoma Aeronautics Commission.
Tip 4: Tailor Application Materials: Customize resumes and cover letters to align with the specific requirements of each position. Highlight relevant skills, experience, and accomplishments using action verbs and quantifiable results.
Tip 5: Consider Internships and Apprenticeships: Gain practical experience through internships and apprenticeships with aerospace companies in the state. These opportunities provide valuable hands-on training and can lead to full-time employment.
Tip 6: Research Key Employers: Identify major aerospace companies operating within the state, such as Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and Northrop Grumman, and understand their specific hiring needs and company culture.
Tip 7: Prepare for Technical Interviews: Practice answering technical questions and demonstrate problem-solving skills. Be prepared to discuss previous projects, relevant coursework, and technical challenges overcome.
By focusing on targeted skills, strategic networking, and meticulous preparation, individuals can significantly increase their chances of securing rewarding positions within this thriving sector.
The subsequent sections will provide further insights into specific employers and career pathways within the Oklahoma aeronautics industry.
1. Engineering Roles
Engineering roles form a cornerstone of the broader “aerospace jobs in oklahoma” landscape. These positions directly contribute to the design, development, testing, and production of aircraft, spacecraft, and related systems. The demand for skilled engineers is a primary driver of growth within the state’s aeronautics sector. For example, mechanical engineers are crucial for designing airframes and propulsion systems, while electrical engineers focus on avionics and control systems. The presence of these roles is not merely ancillary; it is fundamental to the existence and advancement of the industry.
The practical significance of engineering talent within Oklahoma is evident in the operations of major aerospace employers. Companies involved in aircraft maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) require engineers to ensure safety and compliance with regulatory standards. Similarly, research and development initiatives rely heavily on engineers to innovate and develop new technologies. The concentration of engineering expertise in the state makes it an attractive location for aerospace companies seeking to expand their operations or establish new facilities.
The availability of qualified engineers directly affects the state’s ability to compete in the global aerospace market. Addressing the need for continuous skill development and attracting engineering graduates to Oklahoma are crucial for sustaining long-term growth. Challenges include competing with other states that offer higher salaries or more attractive lifestyle options. However, the growing aerospace sector in Oklahoma presents opportunities for career advancement and professional fulfillment, attracting talent and contributing to the overall economic health of the state.
2. Manufacturing Demand
The demand for manufactured aerospace components and systems is a critical driver of positions within Oklahoma’s aeronautics industry. This demand directly translates into employment opportunities across various skill levels, from skilled technicians and machinists to production managers and quality control specialists. Increased manufacturing activity necessitates a larger workforce to meet production targets, thereby expanding the number of “aerospace jobs in oklahoma”. For instance, a contract to produce aircraft components for a major airline will lead to the hiring of additional workers to operate machinery, assemble parts, and ensure adherence to stringent quality standards.
The geographic concentration of aerospace manufacturers within the state amplifies the importance of this demand. Companies specializing in areas such as composite materials, precision machining, and specialized electronics contribute significantly to the overall employment figures. Furthermore, government contracts related to defense and military aviation play a vital role, as these agreements often involve substantial manufacturing requirements. The ability of Oklahoma-based manufacturers to secure and fulfill these contracts directly influences the availability of jobs and the economic stability of the region. Investment in advanced manufacturing technologies and workforce training programs is essential to maintaining competitiveness and attracting further manufacturing demand to the state.
Ultimately, sustained manufacturing demand is not only a source of present-day employment but also a predictor of future growth in Oklahoma’s aeronautics sector. A decline in this demand could lead to job losses and economic downturn, highlighting the need for strategic initiatives to support and expand the manufacturing base. These initiatives include fostering innovation, attracting foreign investment, and promoting collaboration between industry, government, and educational institutions to ensure a resilient and thriving “aerospace jobs in oklahoma” landscape.
3. Maintenance Specialists
The presence of maintenance specialists is an indispensable element of “aerospace jobs in oklahoma.” These skilled technicians are responsible for the inspection, repair, and overhaul of aircraft and related systems, ensuring their continued airworthiness and operational safety. The demand for maintenance specialists is directly proportional to the volume of aviation activity within the state, including commercial airlines, military operations, and private aviation. Consequently, a robust cohort of maintenance specialists is critical for sustaining a viable aerospace sector. A grounded aircraft generates no revenue; maintenance specialists directly mitigate this loss by rapidly diagnosing and rectifying mechanical and electronic faults.
Oklahoma’s strategic geographic location and the presence of major aviation hubs and military installations create a significant and consistent need for qualified maintenance personnel. For example, Tinker Air Force Base, a major maintenance and logistics center for the U.S. Air Force, employs a substantial number of aircraft mechanics, avionics technicians, and related specialists. The economic impact of these jobs extends beyond direct employment, supporting local businesses and contributing to the state’s tax revenue. Furthermore, the rigorous training and certification requirements for maintenance specialists, such as FAA Airframe and Powerplant (A&P) licenses, ensure a high level of competence and professionalism within the workforce.
The long-term viability of “aerospace jobs in oklahoma” hinges, in part, on addressing the challenges associated with recruiting and retaining qualified maintenance specialists. These challenges include competition from other industries, the need for ongoing training and skill upgrades, and the requirement to comply with evolving safety regulations. Successful strategies involve fostering partnerships between educational institutions and industry, providing competitive compensation and benefits, and promoting a culture of safety and continuous improvement. Failing to address these challenges could ultimately hinder the growth and competitiveness of Oklahoma’s aerospace industry.
4. Defense Contractors
Defense contractors operating within Oklahoma constitute a substantial component of the state’s aeronautics employment sector. These companies, engaged in the development, production, and maintenance of military aircraft, missiles, and related defense systems, generate a significant number of high-skill positions. The presence of facilities such as Tinker Air Force Base and associated contractor operations creates a concentrated demand for engineers, technicians, logisticians, and program managers. The ebb and flow of defense spending directly affects the number of available “aerospace jobs in oklahoma” tied to these contractors.
The relationship is one of interdependence. Oklahoma’s favorable regulatory environment, central geographic location, and relatively low cost of living attract defense contractors. In turn, these contractors provide economic stimulus through direct employment and indirect support of local businesses. For example, a major contract award for aircraft modernization at Tinker Air Force Base necessitates the hiring of additional personnel by the prime contractor and its subcontractors, expanding the scope of available “aerospace jobs in oklahoma”. This expansion cascades through the local economy, benefiting suppliers and service providers.
Understanding the dynamics between defense contractors and “aerospace jobs in oklahoma” is crucial for policymakers and workforce development professionals. Strategic investments in education and training programs aligned with the needs of the defense industry can ensure a pipeline of qualified workers, mitigating the risk of skills gaps and attracting further investment. The long-term stability of this sector, however, is contingent on adapting to evolving defense priorities and technological advancements. Diversification into adjacent commercial aerospace markets can provide a buffer against fluctuations in defense spending, further strengthening the resilience of Oklahoma’s aeronautics industry.
5. Research Opportunities
Research activities form a critical link in the chain that sustains and expands the availability of “aerospace jobs in oklahoma”. These opportunities, spanning fundamental science to applied engineering, fuel innovation, attract investment, and cultivate a skilled workforce capable of meeting the evolving demands of the industry. The pursuit of advancements in aerospace technology is inextricably tied to the creation of specialized roles within the state.
- Basic Science Exploration
Fundamental research, often conducted at universities and research institutions, lays the groundwork for future technological breakthroughs. Areas like aerodynamics, materials science, and propulsion systems are subject to ongoing investigation. For example, the development of new composite materials for aircraft structures requires extensive laboratory testing and theoretical modeling, creating positions for research scientists, engineers, and technicians. The insights gained from these studies eventually translate into improved designs and manufacturing processes, enhancing the competitiveness of Oklahoma’s aerospace sector.
- Applied Engineering Projects
Applied research focuses on translating scientific discoveries into practical applications. This includes the development of new aircraft designs, the improvement of existing systems, and the integration of advanced technologies. For example, research into unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) necessitates expertise in areas such as autonomous control, sensor technology, and data analysis. These projects not only generate specific jobs related to the research itself but also create a demand for skilled professionals capable of implementing and maintaining these technologies in real-world scenarios. The presence of robust applied research programs signals a commitment to innovation, attracting aerospace companies and further expanding “aerospace jobs in oklahoma”.
- Government-Sponsored Research
Government agencies, particularly the Department of Defense and NASA, fund a significant portion of aerospace research. These projects address national security concerns and explore new frontiers in space exploration. For example, research into hypersonics or advanced propulsion systems generates opportunities for scientists and engineers to work on cutting-edge technologies. Furthermore, government-sponsored research often involves partnerships with private companies, fostering collaboration and knowledge transfer. The ability of Oklahoma-based institutions and companies to secure government research contracts is a key indicator of the strength and competitiveness of its aerospace sector.
- Technology Transfer and Commercialization
The ultimate goal of many research efforts is to translate new technologies into commercial products and services. This process, known as technology transfer, involves licensing patents, creating spin-off companies, and forming strategic alliances. For example, a new sensor technology developed at a university could be licensed to an aerospace manufacturer, leading to the creation of new products and new “aerospace jobs in oklahoma”. Successful technology transfer requires a supportive ecosystem that includes venture capital, business incubators, and access to expertise in areas such as intellectual property law and marketing. A strong commitment to technology transfer ensures that research investments translate into tangible economic benefits for the state.
In summation, research opportunities are not merely academic pursuits; they are integral to the vitality and growth of “aerospace jobs in oklahoma”. A thriving research ecosystem attracts talent, stimulates innovation, and positions the state at the forefront of aerospace technology. Sustained investment in research is essential for ensuring a competitive and prosperous future for Oklahoma’s aeronautics industry.
6. Technical Education
Technical education serves as the foundational pillar for the “aerospace jobs in oklahoma” market. The presence of qualified personnel, equipped with the skills required to operate and maintain sophisticated aeronautical systems, is directly contingent upon robust technical training programs. This encompasses institutions offering certifications, associate degrees, and specialized training in areas such as aircraft maintenance, avionics, and precision manufacturing. Without such programs, the availability of skilled labor diminishes, creating a bottleneck that impedes industry growth. For example, the existence of FAA-approved Part 147 aviation maintenance technician schools within the state directly supports the maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) sector, supplying a continuous stream of certified mechanics capable of ensuring aircraft airworthiness. Failure to adequately invest in these training programs precipitates a skills gap, potentially forcing companies to relocate to regions with a more readily available workforce.
The practical applications of technical education are far-reaching within Oklahoma’s aerospace industry. Technicians trained in composite materials are vital to the manufacturing of lightweight aircraft components, while electronics specialists are essential for maintaining complex avionics systems. The effectiveness of these technical programs is gauged by their ability to align curricula with industry needs, ensuring that graduates possess the specific competencies demanded by employers. Cooperative programs and apprenticeships, where students gain hands-on experience working alongside experienced professionals, are particularly valuable in bridging the gap between classroom learning and real-world application. The success of these initiatives hinges on maintaining close collaborations between educational institutions and aerospace companies, allowing for continuous feedback and curriculum refinement.
In summary, technical education is not merely an ancillary element but a vital prerequisite for a thriving “aerospace jobs in oklahoma” landscape. The challenges lie in anticipating future skill requirements, adapting curricula to emerging technologies, and ensuring equitable access to training opportunities across the state. A proactive approach to technical education, one that prioritizes industry collaboration and responsiveness to changing demands, is essential for sustaining the long-term growth and competitiveness of Oklahoma’s aeronautics sector. The continued investment in and enhancement of technical education directly translates to a more skilled workforce and a more prosperous economic future for the state.
7. Economic Impact
The financial consequences stemming from the availability of positions within the aeronautics and astronautics fields are considerable for the state. These ramifications extend beyond direct employment, influencing various sectors and contributing to overall economic stability and growth.
- Direct Employment and Wages
The primary economic benefit arises from direct employment within aerospace companies. These positions, often requiring specialized skills and training, tend to offer higher-than-average wages, injecting significant income into the local economy. For example, an aerospace engineer earning a substantial salary contributes to the tax base, supports local businesses, and stimulates consumer spending. The aggregate effect of these salaries across the entire aerospace workforce creates a significant economic multiplier effect.
- Supply Chain and Indirect Effects
The aeronautics sector relies on a complex supply chain, encompassing manufacturers of components, providers of specialized services, and distributors of raw materials. The demand generated by aerospace companies sustains a network of businesses, creating indirect employment opportunities and further economic activity. For example, an aircraft manufacturer in Oklahoma may source parts from local machine shops, generating revenue and jobs for those businesses. This ripple effect extends throughout the economy, amplifying the initial economic impact.
- Attraction of Investment and Talent
A thriving aerospace industry attracts investment from both domestic and foreign sources. Companies seeking to expand or relocate often consider the availability of a skilled workforce, a favorable regulatory environment, and the presence of a strong support infrastructure. The promise of “aerospace jobs in oklahoma” can serve as a magnet for talent, drawing skilled professionals to the state. The influx of investment and talent further strengthens the industry, creating a virtuous cycle of growth and innovation.
- Technological Innovation and Spin-off Industries
The aerospace industry is a catalyst for technological innovation, driving advancements in materials science, engineering, and manufacturing processes. These innovations often have applications beyond the aerospace sector, leading to the development of new products and services in other industries. For example, technologies developed for aircraft engines may find applications in energy production or transportation. The creation of spin-off industries further diversifies the economy and generates additional economic opportunities.
In conclusion, the economic impact of “aerospace jobs in oklahoma” is multifaceted and far-reaching. From direct employment and wages to supply chain effects, investment attraction, and technological innovation, the aeronautics sector plays a pivotal role in driving economic growth and prosperity within the state. Strategic investments in education, infrastructure, and workforce development are essential to sustaining and expanding these economic benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Aerospace Employment in Oklahoma
The following section addresses common inquiries related to career opportunities in the aeronautics and astronautics sectors within the state. The information provided aims to offer clarity and guidance to prospective applicants and interested parties.
Question 1: What are the primary types of positions available within the Oklahoma aerospace industry?
The industry encompasses a broad spectrum of roles, including aerospace engineers, aircraft mechanics, avionics technicians, manufacturing specialists, quality control inspectors, and program managers. These positions support various activities, from aircraft design and production to maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) operations.
Question 2: What level of education or training is typically required for entry-level aerospace jobs in Oklahoma?
Educational requirements vary depending on the specific position. Engineering roles generally require a bachelor’s or master’s degree in aerospace, mechanical, or electrical engineering. Technical positions, such as aircraft mechanics, typically require certification from an FAA-approved Part 147 school or equivalent training.
Question 3: Which companies are the major employers within the state’s aeronautics sector?
Key employers include Boeing, Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, and various MRO facilities operating at Tinker Air Force Base and other locations. A comprehensive list of aerospace companies can be obtained from the Oklahoma Department of Commerce and the Oklahoma Aeronautics Commission.
Question 4: What is the salary range for aerospace jobs in Oklahoma?
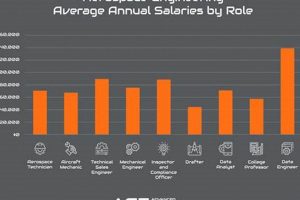
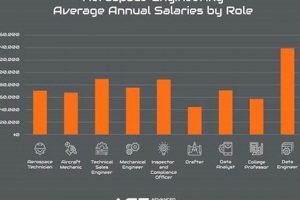
Salaries vary significantly based on experience, education, and specific job responsibilities. Entry-level positions may offer salaries in the $40,000 to $60,000 range, while experienced engineers and managers can earn upwards of $100,000 annually. Salary data can be obtained from industry surveys and online compensation databases.
Question 5: Are there specific skills or certifications that are particularly valuable in the Oklahoma aerospace job market?
Skills in areas such as composite materials, avionics systems, lean manufacturing, and quality assurance are highly sought after. Certifications such as FAA Airframe and Powerplant (A&P) licenses, Six Sigma Black Belt, and project management professional (PMP) credentials can significantly enhance employability.
Question 6: What are the prospects for long-term growth within the Oklahoma aerospace industry?
The outlook for the industry is generally positive, driven by factors such as increasing air travel, growing demand for military aircraft, and the state’s favorable business climate. However, the industry is subject to cyclical fluctuations in the global economy and changes in government spending. Long-term success depends on continuous innovation and a commitment to workforce development.
This FAQ section provides a general overview of key considerations for individuals seeking careers in the aeronautics industry within the state. Further research and networking are encouraged to gain more specific information and insights.
The subsequent section will present a summary of key resources for pursuing “aerospace jobs in oklahoma”.
In Summary
This exploration has detailed the scope and significance of “aerospace jobs in oklahoma,” emphasizing the diversity of roles, the importance of technical education, and the considerable economic impact on the state. From engineering and manufacturing to maintenance and research, a robust network of opportunities exists for skilled professionals. The stability and growth of this sector are inextricably linked to strategic investments in workforce development and technological advancement.
The continued prosperity of Oklahoma’s aeronautics industry hinges on proactive adaptation to evolving global demands and unwavering support for local talent. By fostering innovation and promoting strategic partnerships, the state can ensure its position as a prominent hub for aerospace activity, creating a lasting legacy of economic prosperity and technological leadership.