The most advantageous urban centers for individuals seeking careers within the aeronautics and space industry are characterized by a confluence of factors. These locations typically feature a strong presence of aerospace companies, government research facilities, educational institutions offering specialized programs, and a generally supportive economic climate. For example, a concentration of engineering firms, coupled with a readily available skilled workforce, contributes to a city’s desirability.
Access to plentiful career opportunities, potential for high earning, and the chance to contribute to technological advancements are significant benefits associated with residing in these prime locations. Historically, government investment in research and development has played a crucial role in establishing these hubs. Moreover, the growth of commercial space exploration is further influencing the prominence of certain areas.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific locations demonstrating these characteristics, examining the factors contributing to their standing and outlining the opportunities available to professionals in this field. Consideration will be given to aspects such as major employers, educational infrastructure, and cost of living.
Strategic career planning is essential for individuals targeting premier aerospace locations. Awareness of industry trends and tailored preparation significantly enhance the likelihood of success.
Tip 1: Research Key Employers: Identify major aerospace companies and government agencies operating within the target city. Understanding their core activities, recent projects, and hiring patterns allows for focused application efforts.
Tip 2: Tailor Resumes and Cover Letters: Generic applications are unlikely to succeed. Customize resumes and cover letters to align with the specific requirements and values of each employer, highlighting relevant skills and experiences.
Tip 3: Network Strategically: Attend industry conferences, career fairs, and online forums to connect with professionals in the field. Networking provides valuable insights and potential leads.
Tip 4: Pursue Relevant Education and Certifications: Advanced degrees, specialized certifications, and technical training enhance competitiveness. Align educational pursuits with the demands of the target job market.
Tip 5: Consider Internship Opportunities: Internships provide valuable experience and exposure to the industry. Actively seek out internship programs offered by aerospace companies and research institutions.
Tip 6: Develop Strong Technical Skills: Proficiency in relevant software, programming languages, and engineering principles is crucial. Continuously update technical skills to remain competitive in a rapidly evolving field.
Tip 7: Understand the Local Cost of Living: Research the cost of housing, transportation, and other expenses in the target city. Consider salary expectations and financial planning accordingly.
Adopting these strategies improves chances of securing a fulfilling career in prominent aerospace centers. Proactive planning and targeted efforts are key to navigating a competitive job market.
The following section will present a concluding overview, reinforcing the core principles discussed in this article.
1. Job Market Size
The magnitude of the aerospace job market within a metropolitan area serves as a primary indicator of its desirability for industry professionals. A substantial job market typically signifies a robust and dynamic sector, presenting a higher probability of employment opportunities and career progression.
- Number of Aerospace Companies
The sheer quantity of aerospace firms, ranging from large multinational corporations to smaller specialized businesses, directly influences the number of available positions. Cities hosting numerous established companies, like those in Southern California or the Seattle metropolitan area, tend to exhibit larger job markets. For instance, a city with multiple aircraft manufacturers, satellite developers, and component suppliers provides a diverse range of employment prospects.
- Government and Military Presence
The presence of government research facilities, military bases, and defense contractors significantly contributes to the overall aerospace job market. Locations with a substantial federal footprint, such as Huntsville, Alabama (NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center), or Colorado Springs, Colorado (U.S. Space Command), often feature a high concentration of aerospace-related jobs. Government investment and defense spending drive demand for engineers, scientists, and technicians.
- Economic Growth and Investment
A city’s overall economic health and its level of investment in aerospace research and development correlate directly with job market expansion. Cities experiencing economic growth, fueled by technological innovation and venture capital funding, tend to attract and retain aerospace companies. Investment in infrastructure and research institutions stimulates job creation and fosters a competitive environment.
The size of the job market directly dictates the career opportunities available to aerospace professionals. Major corporations like Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and Blue Origin, all have headquarters or satellite locations that offer a large number of potential employment areas. Thus, a large number of aerospace companies, a significant government and military presence, coupled with robust economic growth and investment create a magnet that attracts the best in the aerospace field.
2. Industry Cluster Density
The concentration of aerospace firms, research institutions, and related support services within a specific geographic region, termed “Industry Cluster Density,” significantly impacts a city’s standing as a prime location for aerospace careers. A high density fosters collaboration, innovation, and knowledge spillover, creating a dynamic and attractive environment for professionals.
- Proximity and Collaboration
Close proximity between companies and institutions facilitates collaboration on projects, knowledge sharing, and the development of new technologies. For instance, the concentration of aerospace firms in Southern California allows for easy interaction between engineers, scientists, and researchers, fostering innovation and accelerating project timelines. This collaborative environment enhances the attractiveness of the region to skilled professionals.
- Supply Chain Optimization
A dense industry cluster optimizes supply chains by reducing transportation costs and lead times. The presence of numerous component suppliers, manufacturers, and service providers in close proximity streamlines operations and improves efficiency. This efficient ecosystem attracts companies seeking to minimize costs and maximize productivity, subsequently creating more job opportunities.
- Talent Pool and Recruitment
High industry cluster density attracts a skilled talent pool. Professionals are drawn to areas with ample job opportunities and a vibrant aerospace community. This concentrated talent pool makes recruitment easier for companies and provides professionals with greater career mobility within the region. Educational institutions also tend to establish specialized programs to cater to the needs of local industry, further enhancing the talent pipeline.
- Knowledge Spillovers and Innovation
Proximity facilitates the transfer of knowledge and the exchange of ideas, leading to innovation. Informal interactions, conferences, and workshops within the cluster promote the dissemination of information and the development of new technologies. This dynamic environment fosters creativity and attracts individuals seeking to be at the forefront of aerospace advancements.
The benefits of industry cluster density are evident in regions like the Seattle metropolitan area, home to Boeing and numerous aerospace suppliers. The close proximity of these companies fosters collaboration, optimizes supply chains, attracts talent, and promotes innovation, making the region highly desirable for aerospace professionals. Therefore, regions with a high degree of “Industry Cluster Density” represent prime locations for aerospace careers due to the convergence of collaboration, streamlined supply chains, talent availability, and the accelerated pace of technological advancement they foster.
3. Research & Development
Investment in research and development (R&D) is a critical driver for aerospace innovation and, consequently, a defining characteristic of premier cities for related employment. The concentration of R&D activities signifies a commitment to future growth and technological advancement, attracting both established companies and skilled professionals.
- Government Funding and Initiatives
Federal funding for aerospace research, often channeled through agencies like NASA and the Department of Defense, plays a vital role in shaping urban landscapes. Cities that host major research centers or benefit from substantial government grants experience significant job creation in engineering, science, and technology. For example, Huntsville, Alabama, benefits immensely from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center, a hub for propulsion research. Government initiatives also incentivize private sector investment, further expanding R&D activities and bolstering the local job market.
- University-Industry Partnerships
Collaborative research projects between universities and aerospace companies are essential for translating theoretical advancements into practical applications. Cities with strong universities that have established partnerships with local aerospace firms witness accelerated innovation and a steady stream of skilled graduates entering the workforce. For instance, partnerships between MIT and companies in the Boston area have fueled advancements in areas like robotics and artificial intelligence for aerospace applications.
- Private Sector Investment in Innovation
The willingness of private companies to invest in internal R&D programs is a strong indicator of a city’s potential for aerospace job growth. Companies that prioritize innovation are more likely to expand their operations, create new products, and hire specialized personnel. For example, the significant investments in R&D made by companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin in locations like Los Angeles and Seattle contribute to the dynamism of the local aerospace industry and attract highly skilled engineers and scientists.
- Incubator and Startup Ecosystems
A thriving ecosystem of incubators and startups focused on aerospace technologies signals a forward-looking urban environment. These entities often drive disruptive innovation and create specialized job opportunities in areas such as advanced materials, propulsion systems, and autonomous flight. Cities that actively support these ecosystems, through funding, mentorship programs, and access to facilities, are more likely to emerge as leaders in aerospace innovation and employment. Examples are found around Boulder, Colorado where a number of smaller innovative companies thrive.
In conclusion, robust R&D activity, driven by government funding, university partnerships, private sector investment, and a supportive startup ecosystem, directly translates to increased job opportunities and career advancement in the aerospace industry. This makes cities that prioritize and foster R&D particularly attractive to professionals seeking fulfilling and impactful careers in this dynamic field.
4. Educational Infrastructure
A robust educational infrastructure is a cornerstone of any city recognized as a prime location for aerospace careers. The presence of reputable universities, vocational schools, and research institutions specializing in aerospace engineering, aeronautics, and related fields directly impacts the availability of a skilled workforce. These institutions serve as talent pipelines, supplying companies with graduates possessing the necessary technical knowledge and practical skills. The correlation is direct: a strong educational base attracts aerospace companies seeking qualified employees, which in turn, fuels further economic growth and solidifies the city’s position as an industry hub. For example, the concentration of aerospace firms around the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in Boston and Stanford University in the Silicon Valley is a direct consequence of the skilled graduates these institutions produce.
The quality and relevance of aerospace-related programs within these institutions are also critical. Programs that emphasize hands-on experience, industry collaborations, and exposure to cutting-edge technologies are particularly valuable. Cities that actively promote partnerships between educational institutions and aerospace companies create a synergistic environment that benefits both students and employers. These partnerships often involve internships, research collaborations, and curriculum development, ensuring that graduates are well-prepared for the demands of the industry. The Colorado School of Mines’ proximity to aerospace facilities around Denver exemplifies this advantage. It offers highly specialized education and collaborative research that directly serve and improve from the local economy.
In summary, educational infrastructure is not merely a supporting element but an integral component of the foundation upon which thriving aerospace hubs are built. Cities aiming to attract and retain aerospace companies must invest in and foster strong educational institutions that can consistently produce a skilled and adaptable workforce. The ongoing challenge lies in ensuring that educational programs evolve to meet the ever-changing demands of the industry, requiring continuous dialogue and collaboration between educational institutions and aerospace employers. The presence of those connections are key in determining the “best cities for aerospace jobs”.
5. Cost of Living
The cost of living is a significant factor influencing the attractiveness of any city as a prime location for aerospace employment. It directly affects the quality of life for professionals and their families and plays a critical role in determining whether a particular location is financially sustainable for a long-term career.
- Housing Affordability
Housing, including both rental and purchase options, typically constitutes the largest portion of a household budget. Cities with inflated housing costs, such as those in California’s Bay Area, can offset the benefits of high salaries in the aerospace industry. Conversely, cities with more affordable housing markets, even if salaries are slightly lower, may offer a higher overall standard of living. The availability of diverse housing options, ranging from apartments to single-family homes, also influences the attractiveness of a location.
- Taxation and Income
State and local tax rates can significantly impact disposable income. Areas with high income taxes or property taxes reduce the amount of money available for discretionary spending and savings. While some cities may offer high salaries, the net income after taxes may be less appealing compared to locations with lower tax burdens. Consideration must be given to the overall tax climate when evaluating the financial viability of a city.
- Transportation Costs
Transportation expenses, including vehicle ownership, public transportation, and commuting costs, contribute substantially to the cost of living. Cities with well-developed public transportation systems can reduce the need for personal vehicles, lowering overall expenses. Proximity to work and the availability of alternative transportation options, such as cycling or walking, can also impact transportation costs. Areas with significant traffic congestion or long commute times can also indirectly increase the cost of living due to lost productivity.
- Goods and Services Expenses
The prices of everyday goods and services, such as groceries, utilities, healthcare, and entertainment, influence the overall cost of living. Cities with higher price levels for these essential items require higher salaries to maintain a comparable standard of living. Regional variations in price levels can be significant, and prospective employees must consider these differences when evaluating potential locations.
The interplay between these elements determines the ultimate feasibility of a city as a long-term residence for aerospace professionals. While some cities may boast high salaries and numerous job opportunities, the cost of living can erode the benefits. Evaluating these factors and comparing them to potential earnings is crucial for making informed career decisions in the aerospace industry. Balancing career prospects with financial sustainability is essential for a successful and fulfilling career in prime aerospace hubs.
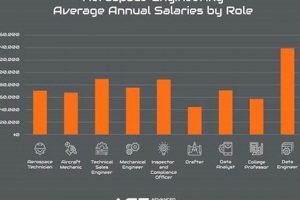
6. Average Salary
Average salary serves as a critical indicator when evaluating the most advantageous urban centers for aerospace employment. While not the sole determinant, compensation levels reflect the demand for specific skills, the cost of living, and the overall economic health of the aerospace sector within a given metropolitan area.
- Market Demand and Skill Valuation
Higher average salaries in specific aerospace roles often signal a strong demand for those skill sets within a particular city. Locations with a concentration of cutting-edge aerospace activities, such as advanced propulsion systems or satellite technology, are likely to offer premium compensation to attract and retain qualified engineers and scientists. For example, roles requiring expertise in specialized areas like quantum computing for aerospace applications or advanced materials engineering may command significantly higher salaries in cities with a high concentration of related industries. This correlation underlines the relationship between regional specialization and earnings potential.
- Cost of Living Adjustment
Nominal salary figures must be interpreted in the context of the local cost of living. A high average salary in a city with an exceptionally high cost of housing, transportation, and other essential expenses may not translate to a higher quality of life compared to a location with a lower average salary but a more affordable living environment. Therefore, aspiring aerospace professionals should consider the purchasing power parity (PPP) of their potential earnings when evaluating different urban centers. Adjusting the salary based on the area’s cost of living provides a more accurate reflection of the financial advantages of employment.
- Company Size and Structure
Average salaries can vary significantly based on the size and organizational structure of aerospace companies operating in a particular city. Large multinational corporations, with established compensation structures and extensive benefits packages, may offer higher average salaries compared to smaller, more agile startups. However, startups may provide unique opportunities for rapid career advancement and equity ownership, which can offset lower initial salaries. Understanding the composition of the aerospace industry within a city the balance between large corporations and startups is essential for interpreting average salary data.
- Experience and Education Premium
Average salary data often reflects the premium placed on experience and advanced education within a specific aerospace sector. Cities that prioritize innovation and technological leadership tend to reward individuals with advanced degrees and extensive experience in highly specialized fields. Therefore, aerospace professionals with advanced qualifications can expect to command higher salaries in locations where their expertise aligns with the needs of the local industry. Analyzing average salary data in conjunction with educational attainment and years of experience provides a more nuanced understanding of earning potential.
In conclusion, average salary is a crucial yet multifaceted element in identifying prime urban centers for aerospace careers. While it provides a general benchmark for compensation levels, it must be considered in conjunction with factors such as market demand, cost of living, company size, and experience premiums. A thorough evaluation of these interconnected factors enables aerospace professionals to make informed decisions that align with their career goals and financial aspirations.
7. Quality of Life
Quality of life, while subjective, represents a critical consideration when evaluating premier urban centers for aerospace careers. It encompasses various tangible and intangible factors influencing an individual’s overall well-being and satisfaction, impacting talent attraction and retention within the industry.
- Access to Recreation and Culture
The availability of recreational activities, cultural institutions, and entertainment options contributes significantly to a location’s desirability. Cities offering diverse opportunities for outdoor recreation, such as hiking, skiing, and water sports, attract individuals seeking an active lifestyle. A vibrant arts and culture scene, including museums, theaters, and music venues, enhances the overall appeal. The presence of these amenities influences the attractiveness of a city and positively impacts employee satisfaction. For example, Denver, Colorado, with its proximity to the Rocky Mountains and a thriving arts community, appeals to aerospace professionals seeking a balanced lifestyle.
- Healthcare and Well-being Services
Access to quality healthcare services and resources promotes the physical and mental well-being of residents. Cities with reputable hospitals, specialized medical facilities, and comprehensive wellness programs offer a sense of security and contribute to a higher quality of life. The availability of mental health services and support networks is also increasingly important, particularly in high-pressure industries like aerospace. A city’s commitment to public health initiatives and access to affordable healthcare options are key considerations.
- Education for Dependents
For professionals with families, the quality of local schools and educational opportunities for children is a paramount concern. Cities with highly rated public schools, diverse private school options, and access to quality childcare services attract families and enhance their overall well-being. The availability of specialized educational programs, such as STEM-focused schools or language immersion programs, can also be a significant draw. Furthermore, access to higher education institutions within the city provides opportunities for continuing education and professional development.
- Community and Social Environment
The sense of community, social cohesion, and the presence of strong social networks contribute significantly to an individual’s quality of life. Cities with active community organizations, volunteer opportunities, and a welcoming atmosphere foster a sense of belonging and connection. Low crime rates, safe neighborhoods, and a sense of security enhance the overall quality of life. The diversity and inclusiveness of the community also play a crucial role, fostering a welcoming environment for individuals from diverse backgrounds.
Ultimately, the interconnectedness of these elements determines a location’s overall appeal as a “best city for aerospace jobs.” Professionals evaluate career opportunities in tandem with their holistic well-being, making a location’s dedication to recreation, health, education, and community crucial for attracting and retaining talent in this competitive sector.
Frequently Asked Questions About Prime Locations for Aerospace Careers
The following addresses common inquiries regarding the selection of optimal urban centers for professionals seeking to advance their careers within the aeronautics and space industry.
Question 1: What factors most significantly influence a city’s ranking as a top location for aerospace jobs?
The ranking is determined by a confluence of factors including the concentration of aerospace companies, the presence of government research facilities, investment in research and development, the strength of educational institutions offering relevant programs, cost of living considerations, and the overall quality of life available to professionals in the field.
Question 2: How crucial is the presence of major aerospace employers to a city’s attractiveness?
The presence of major corporations, such as Boeing, Lockheed Martin, or SpaceX, is highly significant. These companies provide a large number of job opportunities, drive innovation, and attract smaller businesses and suppliers to the region, creating a robust ecosystem. Their presence generally correlates with more opportunities and higher potential salaries.
Question 3: Does the cost of living significantly impact the desirability of a city, even if salaries are high?
Indeed. A high cost of living can substantially offset the benefits of a higher salary. Factors such as housing affordability, transportation expenses, and the cost of goods and services must be carefully considered to determine the true financial advantages of residing in a particular location. A lower cost of living may, in some instances, make a city with a moderately lower salary a more attractive overall option.
Question 4: How important is educational infrastructure, including universities and technical schools, to a city’s status?
Educational infrastructure is paramount. Reputable universities and technical schools specializing in aerospace engineering and related fields provide a pipeline of skilled graduates, attracting aerospace companies and fostering innovation. Partnerships between these institutions and industry further enhance the quality of education and ensure that graduates are well-prepared for the workforce.
Question 5: What role does government funding and investment play in establishing a city as a prime aerospace hub?
Government investment, particularly through agencies such as NASA and the Department of Defense, is a major catalyst. Funding for research and development, the establishment of government research facilities, and defense contracts stimulate economic growth and job creation in the aerospace sector. This investment often attracts private sector companies and fosters a vibrant ecosystem.
Question 6: Beyond purely economic factors, how does quality of life influence a city’s appeal to aerospace professionals?
Quality of life factors, including access to recreation, cultural amenities, healthcare, education for dependents, and a sense of community, are increasingly important considerations. These elements contribute to overall well-being and job satisfaction, influencing a professional’s decision to relocate to or remain in a particular location. A balance between career opportunities and a desirable lifestyle is often a key factor.
In conclusion, selecting a prime location for an aerospace career requires a comprehensive assessment of economic, educational, and lifestyle factors. The ideal city offers a combination of abundant job opportunities, a reasonable cost of living, a strong educational infrastructure, and a high quality of life.
The subsequent section of this document provides a concluding summary of the key principles discussed.
Conclusion
The preceding analysis has explored the multifaceted criteria defining “best cities for aerospace jobs”. The convergence of robust job markets, dense industry clusters, substantial research and development investment, comprehensive educational infrastructures, manageable costs of living, competitive average salaries, and a high quality of life establishes optimal locations for professionals within the aeronautics and space sectors.
Careful consideration of these intertwined factors empowers individuals to make informed career decisions, aligning professional aspirations with environments conducive to both economic prosperity and personal well-being. The strategic selection of a location can significantly impact career trajectory and contribute to the advancement of the aerospace industry as a whole. Further, cities themselves can use this as a yardstick to attract more talents in aerospace jobs.