Positions that offer significant opportunities for growth, advancement, and contribution within the aerospace sector are highly desirable for graduates and experienced professionals. These roles often involve challenging projects, competitive compensation, and a positive work-life balance. An example includes roles in design and development of next-generation aircraft or spacecraft.
The selection of suitable careers within this technical field is crucial for individual success and the continued advancement of the aerospace industry. Focusing on areas that align with personal strengths and interests can lead to increased job satisfaction and professional fulfillment. Historically, access to specific roles has been determined by education, experience, and demonstrated skills.
The following sections will explore specific career paths in aerospace engineering, including design engineering, research and development, project management, and systems engineering, providing insights into the responsibilities, required skills, and potential career progression for each.
Guidance for Aspiring Aerospace Professionals
The following recommendations are designed to aid individuals in identifying and securing optimal career paths within the field. Careful consideration of these points can enhance prospects for professional success and long-term career satisfaction.
Tip 1: Develop a Strong Foundation in Core Engineering Principles: A comprehensive understanding of fundamental concepts in mathematics, physics, and engineering is essential. This foundation allows for adaptability and problem-solving capabilities across various aerospace sub-disciplines.
Tip 2: Gain Proficiency in Relevant Software and Tools: Mastery of industry-standard software for CAD, simulation, and analysis is critical. Familiarity with tools like MATLAB, ANSYS, and SolidWorks enhances employability and on-the-job performance.
Tip 3: Pursue Internships and Co-op Opportunities: Practical experience gained through internships or co-op programs provides invaluable insight into the industry and allows for the application of theoretical knowledge to real-world problems. These experiences also facilitate networking opportunities.
Tip 4: Specialize in a Niche Area of Aerospace Engineering: Focusing on a specific area, such as propulsion systems, avionics, or structural analysis, can increase expertise and make individuals more competitive for specialized positions. Deep knowledge in a particular domain is highly valued by employers.
Tip 5: Cultivate Strong Communication and Teamwork Skills: Aerospace projects are inherently collaborative, requiring effective communication and teamwork. Developing these skills is crucial for successful project execution and career advancement. Clear and concise communication is vital in a complex engineering environment.
Tip 6: Consider Advanced Education or Certifications: Pursuing a master’s degree or relevant certifications can enhance technical skills and demonstrate a commitment to professional development. Advanced qualifications can open doors to more specialized and higher-level positions.
Tip 7: Network with Industry Professionals: Attending industry conferences, joining professional organizations, and connecting with individuals in the field can provide valuable insights and networking opportunities. Building relationships with experienced professionals can lead to mentorship and career guidance.
Implementing these strategies enhances preparedness for navigating the complexities of the aerospace job market and ultimately contributes to securing a fulfilling and impactful career.
The subsequent sections will delve into the long-term outlook for aerospace engineering roles and offer final thoughts on navigating a successful career.
1. Innovation
Positions facilitating significant innovation are often considered highly desirable. The ability to contribute to the creation of new technologies, designs, or processes directly correlates with professional satisfaction and impact within the aerospace field. Roles that stagnate, failing to offer opportunities for pioneering work, may diminish in appeal over time. A prime example is the development of electric propulsion systems for aircraft; engineers involved in this type of project directly contribute to a more sustainable future for aviation, increasing the perceived value of such positions. Further, work on novel materials and manufacturing techniques directly leads to increases in performance and efficiency.
The importance of innovation extends beyond individual satisfaction; it directly affects the competitiveness of organizations. Companies that prioritize research and development often attract and retain top talent by offering the chance to work on cutting-edge projects. These firms are better positioned to adapt to changing market demands and technological advancements. For instance, the race to develop reusable rocket technology has spurred significant innovation in areas such as propulsion, aerodynamics, and autonomous control systems. The practical significance of this drive is evident in the reduced cost of space access and increased accessibility to space-based services.
In summary, innovation is a critical component of what defines desirable roles in aerospace engineering. The opportunity to contribute to the field’s evolution drives professional satisfaction and contributes directly to an organization’s success. While challenges in innovation always exist, the rewards, both professional and societal, are substantial. Prioritizing positions that foster innovation ensures continued advancement and helps to shape the future of the aerospace industry.
2. Impact
The degree to which a position directly contributes to tangible advancements in aerospace technology or societal well-being is a critical determinant of its desirability. Roles with demonstrable, positive impact are inherently more appealing to many engineers seeking fulfilling careers. This stems from a desire to contribute to solutions for complex problems, improve existing systems, or create entirely new capabilities. This effect results in higher rates of employee retention and increased rates of success due to employee satisfaction.
An illustrative example can be found in the field of sustainable aviation. Engineers working on the development of more fuel-efficient engines or alternative fuel sources are directly addressing concerns related to climate change and environmental sustainability. This positions these roles as highly impactful, as their work directly contributes to a more environmentally responsible aerospace industry. Similarly, engineers who design and implement safety enhancements for commercial aircraft play a vital role in protecting human lives. The significance of this contribution cannot be overstated, and it elevates the appeal of positions focused on safety-critical systems. Work within the field of space exploration has high rates of employee satisfaction because it can be extremely impactful as well.
Ultimately, the perceived impact of a role within aerospace engineering is a subjective but crucial consideration. While compensation and career progression are important, the ability to make a meaningful contribution to the advancement of technology, the betterment of society, or the exploration of the universe often serves as a primary motivator for engineers seeking optimal career opportunities. Recognizing and prioritizing roles with significant positive impact are essential for attracting and retaining top talent within the aerospace sector.
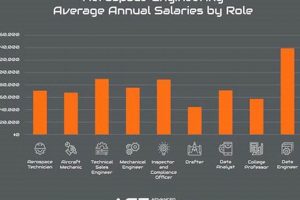
3. Compensation
Financial remuneration is a significant factor when evaluating the desirability of positions within the aerospace engineering field. Competitive compensation packages are essential for attracting and retaining qualified professionals, particularly in a highly specialized and competitive industry.
- Base Salary
The starting point for most compensation discussions is the base salary. This figure reflects the core value an employer places on an engineer’s skills and experience. Aerospace engineers often possess advanced degrees and specialized expertise, which command higher salaries compared to other engineering disciplines. Geographic location and the specific industry sector (e.g., government, defense, commercial aviation) also influence base salary levels.
- Benefits Packages
Beyond the base salary, comprehensive benefits packages contribute significantly to overall compensation. These packages typically include health insurance (medical, dental, vision), life insurance, disability insurance, and retirement plans (e.g., 401(k) with employer matching). Generous benefits packages can substantially increase the value of a position, making it more attractive to prospective employees. The quality and extent of these benefits play a crucial role in employee satisfaction and retention.
- Performance-Based Bonuses
Many aerospace engineering positions offer performance-based bonuses as an incentive for achieving specific goals or exceeding expectations. These bonuses can be tied to individual performance metrics, project milestones, or overall company profitability. Performance-based bonuses provide an opportunity for engineers to earn additional income based on their contributions and achievements, further enhancing the attractiveness of a role.
- Equity and Stock Options
In some cases, particularly within startup companies or high-growth aerospace firms, equity or stock options may be offered as part of the compensation package. This provides engineers with a stake in the company’s success and the potential for significant financial gains if the company performs well. Equity and stock options align the interests of employees with the company’s long-term growth and can be a powerful tool for attracting and retaining talent.
In conclusion, compensation encompasses more than just the base salary. It includes a comprehensive package of benefits, performance-based incentives, and potential equity opportunities. A well-structured compensation package is critical for attracting and retaining skilled aerospace engineers, ensuring that companies remain competitive in a demanding industry. Assessing the entire compensation package is crucial when evaluating the merits of a career opportunity.
4. Growth Potential
The availability of opportunities for professional advancement and skill development constitutes a critical factor in defining optimal career paths within aerospace engineering. Positions characterized by limited upward mobility or negligible opportunities for learning new skills may be less desirable, even if offering competitive initial compensation. The connection is causal: a lack of growth potential directly limits long-term career prospects and overall professional fulfillment. These positions are thus less likely to be considered among the most advantageous careers.
The aerospace sector, driven by technological innovation and demanding engineering standards, necessitates continuous learning and adaptation. Career paths that enable engineers to expand their expertise in emerging technologies, such as advanced materials, autonomous systems, or sustainable propulsion, contribute to long-term career resilience and increased earning potential. For instance, engineers who initially focus on structural analysis and subsequently develop skills in computational fluid dynamics become more versatile and are better positioned for leadership roles in design and development. In the face of rapid technological change, engineers must continue to demonstrate learning and new skills to maintain relevancy in the field.
In conclusion, growth potential represents a key determinant for aerospace engineers when evaluating prospective roles. The promise of advancement, skill enhancement, and exposure to novel technologies significantly enhances the attractiveness of a position. Organizations that prioritize employee development and offer clear career progression pathways are more likely to attract and retain top talent in this competitive industry.
5. Location
Geographic location exerts a significant influence on the perceived desirability of aerospace engineering positions. The concentration of aerospace companies, government agencies, and research institutions in specific regions directly impacts the availability of opportunities and the overall career landscape. Proximity to major aerospace hubs often translates to a greater density of potential employers, fostering increased competition for talent and, consequently, potentially higher compensation and more diverse career paths.
For example, regions such as Southern California, Seattle, and the Space Coast of Florida have historically served as epicenters of aerospace activity. These areas benefit from established infrastructure, a skilled workforce, and a network of supporting industries. This concentration can lead to a more dynamic job market, offering engineers exposure to a broader range of projects and technologies. However, these locations may also present challenges, such as higher costs of living and increased competition for desirable positions. Conversely, emerging aerospace hubs might offer lower costs of living but potentially fewer immediate opportunities. The choice of location should therefore align with individual career goals and lifestyle preferences.
Ultimately, the optimal location for an aerospace engineer depends on a complex interplay of factors, including job availability, compensation levels, cost of living, proximity to desired lifestyle amenities, and the specific area of specialization. A thorough evaluation of these considerations is essential for making informed decisions about career prospects and long-term professional satisfaction. While the allure of established aerospace centers is undeniable, emerging regions offer the potential for unique opportunities and career growth.
6. Work-Life Balance
The concept of work-life balance holds significant relevance when considering optimal career choices within the aerospace engineering field. Achieving equilibrium between professional responsibilities and personal well-being directly impacts job satisfaction, productivity, and long-term career sustainability. Therefore, the integration of personal and professional life must be strongly assessed.
- Flexible Work Arrangements
The availability of flexible work arrangements, such as telecommuting, compressed workweeks, or flextime, significantly influences work-life balance. These arrangements allow engineers to better manage personal commitments and reduce commute times, leading to decreased stress and improved overall well-being. Organizations offering flexible work options are often perceived as more employee-centric and attract a wider pool of talent. A practical example includes a design engineer who can adjust work hours to accommodate family responsibilities while still meeting project deadlines.
- Vacation and Leave Policies
Generous vacation and leave policies are crucial for enabling engineers to disconnect from work and recharge. Adequate time off allows for travel, personal pursuits, and spending time with family and friends. Companies that prioritize employee well-being through robust vacation and leave programs tend to experience higher levels of employee engagement and reduced burnout. For instance, parental leave policies provide essential support for engineers balancing career and family life.
- Company Culture and Management Support
A supportive company culture that values work-life balance and encourages open communication plays a vital role. Management should foster an environment where employees feel comfortable discussing their personal needs and are provided with the resources and support necessary to manage their workloads effectively. When management explicitly promotes a healthy integration of work and personal life, employees feel more valued and are more likely to thrive. When workers see that management supports personal development, they tend to be more successful.
- Workload Management and Project Deadlines
Realistic workload management and reasonable project deadlines are essential for preventing overwork and burnout. Unrealistic expectations and excessive workloads can lead to increased stress levels and decreased job satisfaction. Organizations that prioritize efficient project planning and resource allocation are more likely to promote a sustainable work-life balance for their employees. Clear, measurable, attainable project goals are helpful in maintaining a healthy balance. When these projects are designed with employee considerations in mind, higher rates of success are observed.
Integrating these factors enhances the appeal of aerospace engineering positions. Organizations committed to fostering a healthy work-life balance are more likely to attract and retain top talent, leading to increased productivity, innovation, and long-term success. Consequently, when assessing career opportunities, prospective aerospace engineers should prioritize companies that demonstrate a genuine commitment to employee well-being and the integration of personal and professional life.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries related to pursuing careers within aerospace engineering, providing concise answers to key concerns.
Question 1: What educational qualifications are essential for securing positions?
A bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering or a closely related field (e.g., mechanical engineering, physics) is generally considered a minimum requirement. Advanced degrees (master’s or doctoral) are often necessary for research-oriented roles or specialized positions.
Question 2: Which skills are highly valued by employers?
Proficiency in CAD software, finite element analysis, computational fluid dynamics, and programming languages is essential. Strong communication, teamwork, and problem-solving skills are equally important.
Question 3: How significant are internships in securing careers?
Internships provide invaluable practical experience and networking opportunities. They demonstrate a commitment to the field and allow students to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world problems, significantly enhancing employability.
Question 4: What are the primary factors influencing compensation levels?
Experience, education, specialization, geographic location, and the specific industry sector (e.g., government, defense, commercial aviation) all contribute to determining compensation.
Question 5: What career paths are available beyond traditional design roles?
Opportunities extend to areas such as research and development, project management, systems engineering, testing and evaluation, sales, and consulting, offering a diverse range of career options.
Question 6: How can I stay current with industry trends and technological advancements?
Membership in professional organizations (e.g., AIAA), attendance at industry conferences, and continuous learning through online courses or professional development programs are essential for staying informed.
In conclusion, proactive engagement, continuous skill development, and strategic career planning are crucial for navigating the complexities of the aerospace engineering job market.
The following section provides a summary of key insights and final advice for aspiring aerospace engineers.
Concluding Remarks on Optimal Aerospace Engineering Careers
This exploration of optimal aerospace engineering careers has illuminated various factors influencing their desirability. Innovation, impact, compensation, growth potential, location, and work-life balance have been presented as critical determinants. These considerations provide a framework for evaluating opportunities and making informed decisions about career paths within the industry.
The aerospace field continues to evolve, demanding adaptable and skilled professionals. By carefully weighing the aforementioned factors and prioritizing continuous learning, aspiring aerospace engineers can position themselves for fulfilling and impactful careers, contributing to the advancement of technology and the exploration of new frontiers.