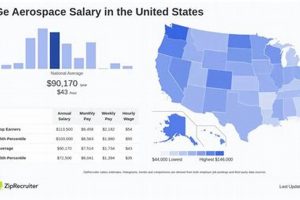
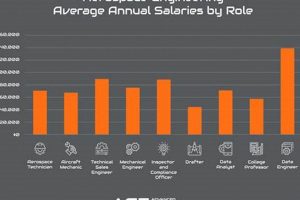
Compensation for professionals designing, developing, and testing aircraft, spacecraft, and related systems in the Golden State varies based on factors such as experience, education, location within the state, and the employing company. Entry-level positions typically offer lower pay scales, while senior roles requiring specialized expertise command higher remuneration.
Understanding the financial prospects in this field is crucial for career planning and informed decision-making. It allows prospective and current aerospace engineers to gauge their market value, negotiate salaries effectively, and assess the long-term financial viability of their career paths. The earning potential reflects the demand for skilled professionals in this technologically advanced sector and underscores the region’s prominent role in aerospace innovation.
The following sections will delve into specific salary ranges based on experience level, explore regional variations within California, and provide insights into the factors that most significantly influence the earnings of these specialized engineers.
Insights Regarding Remuneration for Aerospace Engineers in California
The following considerations are provided to assist individuals in understanding and navigating compensation expectations within the aerospace engineering field in California.
Tip 1: Research Prevailing Market Rates: Conduct thorough research using salary surveys from reputable sources, such as professional engineering organizations and industry-specific databases. This provides a benchmark for evaluating offered compensation packages.
Tip 2: Account for Cost of Living: California’s cost of living varies significantly by region. Adjust salary expectations based on the specific location of the job, factoring in housing, transportation, and other expenses.
Tip 3: Highlight Relevant Experience: Quantify accomplishments and demonstrate how past experience directly translates to the requirements of the target role. This strengthens the case for a higher compensation offer.
Tip 4: Emphasize Specialized Skills: Certifications, proficiency in specific software, or expertise in niche areas of aerospace engineering can command a premium. Clearly articulate these skills during the negotiation process.
Tip 5: Understand the Employer’s Financial Situation: Publicly traded companies often have salary bands and compensation structures that are more transparent. Private companies may have more flexibility, but research their financial health before negotiating.
Tip 6: Negotiate the Entire Package: Consider benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, stock options, and paid time off as part of the overall compensation package. These benefits can significantly impact the total value of the offer.
Tip 7: Consider Long-Term Career Growth: Evaluate the potential for career advancement and salary increases within the organization. A lower starting salary may be acceptable if the company offers opportunities for rapid growth and development.
By incorporating these strategies, professionals can effectively assess and advocate for fair and competitive earnings, aligning their compensation with their skills, experience, and the realities of the California aerospace engineering job market.
The subsequent section will conclude the discussion, summarizing the key points and offering final thoughts on navigating the complexities of compensation within this dynamic field.
1. Experience
Experience is a primary determinant of compensation for aerospace engineers in California. A direct correlation exists between years of relevant professional experience and earning potential. Entry-level positions, typically requiring a Bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering or a related field and minimal practical experience, command the lowest salaries. As engineers accumulate experience, their ability to independently manage complex projects, troubleshoot technical issues, and contribute to innovative solutions increases. This enhanced skill set translates directly to higher remuneration.
For instance, an engineer with 1-3 years of experience might focus on supporting senior engineers in specific tasks, such as design analysis or testing. Compensation reflects this role, typically falling within a defined range for early-career professionals. Conversely, an engineer with 10+ years of experience may lead entire projects, mentor junior engineers, and contribute to strategic decision-making. Their salary will be significantly higher, reflecting their increased responsibilities and expertise. The progression in compensation is not linear; steeper increases are often observed at key career milestones, such as reaching the level of senior engineer or principal engineer.
Understanding the impact of experience is crucial for both aerospace engineers seeking to maximize their earning potential and for companies seeking to attract and retain top talent. Engineers should actively seek opportunities to expand their skill set and take on increasingly challenging roles to accelerate their career progression and corresponding salary growth. Employers must recognize and reward experience appropriately to maintain a competitive workforce and foster innovation within the aerospace sector. Failing to acknowledge the value of experience can lead to employee attrition and a loss of valuable institutional knowledge.
2. Education
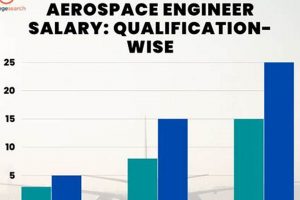
Academic qualifications significantly influence the compensation trajectory of aerospace engineers in California. The attainment of advanced degrees and specialized certifications can substantially impact earning potential within the profession.
- Bachelor’s Degree as a Foundation
A Bachelor of Science degree in Aerospace Engineering or a closely related field (e.g., Mechanical Engineering, Physics) serves as the baseline educational requirement for entry-level positions. While a bachelor’s degree enables initial employment, salary expectations are generally lower compared to candidates possessing graduate-level qualifications. The curriculum provides foundational knowledge in aerodynamics, propulsion, structures, and control systems.
- Master’s Degree for Specialization and Advancement
Pursuing a Master of Science degree allows for specialization in a particular area of aerospace engineering, such as propulsion, structural analysis, or astrodynamics. This advanced knowledge is highly valued by employers and often translates into higher starting salaries and faster career progression. A master’s degree demonstrates a commitment to in-depth understanding and research capabilities.
- Doctoral Degree for Research and Leadership Roles
A Ph.D. in Aerospace Engineering is typically pursued by individuals seeking research-intensive positions in academia or industry, or leadership roles requiring advanced analytical skills. Doctoral graduates are often involved in developing cutting-edge technologies and pushing the boundaries of aerospace knowledge. This level of expertise commands the highest salaries within the profession.
- Certifications and Continuing Education
Obtaining professional certifications (e.g., Professional Engineer (PE) license) and engaging in continuing education activities can also positively impact earnings. These credentials demonstrate a commitment to professional development and can enhance an engineer’s credibility and marketability. Specific certifications relevant to specialized areas, such as project management or systems engineering, may also lead to salary increases.
In summary, while a Bachelor’s degree is the foundational requirement, advanced degrees and professional certifications demonstrably increase the “california aerospace engineer salary”. Employers often prioritize candidates with specialized knowledge and advanced analytical skills, recognizing the value of higher education in driving innovation and problem-solving within the aerospace industry. Therefore, investment in advanced education represents a strategic pathway to enhanced earning potential for aerospace engineers in California.
3. Location
Geographic location within California exerts a substantial influence on compensation for aerospace engineers. This impact is primarily attributable to variations in cost of living and the concentration of aerospace industry employers across different regions. Areas with a higher cost of living, such as the San Francisco Bay Area and Los Angeles County, typically offer higher salaries to offset increased expenses related to housing, transportation, and other essential goods and services. The presence of major aerospace companies, research institutions, and government facilities in specific regions creates a competitive job market, further driving up compensation levels.
For instance, aerospace engineers working in Silicon Valley, where numerous technology companies and aerospace startups are located, often receive higher salaries compared to their counterparts in less densely populated areas of the state. This difference reflects the intense competition for skilled engineers and the premium placed on innovation and technological expertise. Similarly, the presence of large aerospace contractors in Southern California, particularly in Los Angeles and San Diego counties, contributes to a higher average compensation for aerospace engineers in that region. These examples illustrate how the concentration of aerospace-related activity and the associated cost of living directly impact the “california aerospace engineer salary”.
In conclusion, geographic location serves as a critical determinant of compensation for aerospace engineers in California. Understanding regional variations in cost of living and the distribution of aerospace industry employers is essential for effectively evaluating job offers and making informed career decisions. The concentration of aerospace-related activities in specific areas creates a competitive job market, driving up salaries to attract and retain qualified professionals. Ignoring the impact of location can lead to unrealistic salary expectations and potentially limit career opportunities.
4. Company Size
The size of the employing organization exerts a discernible influence on compensation levels for aerospace engineers in California. Larger companies, often characterized by established revenue streams, extensive project portfolios, and comprehensive benefits packages, typically offer higher salaries compared to smaller firms or startups. This differential is primarily attributable to the financial capacity of larger organizations to invest in talent acquisition and retention strategies, including competitive compensation and comprehensive benefits.
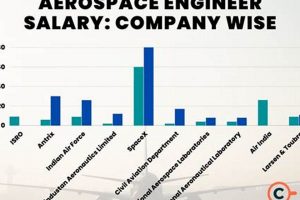
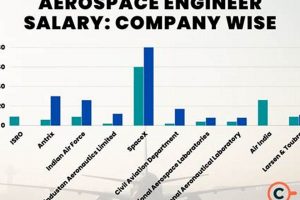
For instance, a multinational aerospace corporation with thousands of employees and billions of dollars in annual revenue is more likely to provide higher salaries and more extensive benefits (e.g., robust health insurance, generous retirement plans, stock options) than a smaller startup focused on a niche area of aerospace technology with limited funding. Larger companies often have well-defined salary bands based on experience, education, and performance, providing a structured framework for compensation. Conversely, smaller companies may offer more flexibility in terms of roles and responsibilities but may face constraints in offering salaries comparable to those of larger organizations. Real-world examples include companies like Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and Northrop Grumman, which, due to their size and scope, often set the benchmark for “california aerospace engineer salary”.
Understanding the relationship between company size and compensation is essential for aerospace engineers in California seeking to maximize their earning potential. While smaller companies may offer unique opportunities for professional growth and innovation, larger organizations generally provide greater financial stability and higher salaries. Consequently, individuals should carefully consider the trade-offs between these factors when evaluating job offers and making career decisions. This aspect constitutes a significant component influencing remuneration, especially when juxtaposed with elements like role specialization and location within the state.
5. Specialization
Specialization within aerospace engineering exerts a demonstrable influence on compensation levels in California. The acquisition of expertise in specific areas of this diverse field often commands a premium, reflecting the market demand for specialized skill sets and the perceived value of focused knowledge.
- Propulsion Systems
Engineers specializing in propulsion systems, encompassing jet engines, rocket engines, and alternative propulsion technologies, are often highly sought after. This demand stems from the critical role propulsion systems play in aircraft and spacecraft performance. Real-world examples include the development of advanced rocket engines for space exploration and the optimization of jet engine efficiency for commercial aviation. Consequently, expertise in propulsion systems generally leads to higher earning potential compared to more general aerospace engineering roles. The design, testing, and maintenance of these complex systems require specialized knowledge, translating into a higher market value.
- Structural Analysis and Design
Specialists in structural analysis and design are crucial for ensuring the integrity and safety of aerospace vehicles. Their expertise involves analyzing stress, strain, and fatigue characteristics of aircraft and spacecraft structures. Examples of this specialization include designing lightweight yet robust airframes for commercial airliners and developing heat shields for spacecraft re-entry. This specialization typically commands higher compensation due to the critical nature of ensuring structural integrity and the complexity of the required analyses. A deep understanding of materials science and structural mechanics is essential, further contributing to the value of these specialists.
- Avionics and Control Systems
Avionics and control systems engineers are responsible for the electronic and software components that govern aircraft and spacecraft operation. This specialization includes designing flight control systems, navigation systems, and communication systems. The increasing complexity of modern aerospace vehicles, driven by advanced automation and connectivity, has fueled demand for these specialists. Consequently, expertise in avionics and control systems is generally associated with higher salaries. The integration of software, electronics, and mechanical systems requires a broad skill set, making these engineers highly valuable to aerospace companies.
- Spacecraft Systems Engineering
Spacecraft systems engineering encompasses the design, development, and integration of all subsystems within a spacecraft, including power, communication, thermal control, and attitude control. This specialization requires a broad understanding of aerospace engineering principles and specialized knowledge of the space environment. With the growing interest in space exploration and commercial space activities, demand for spacecraft systems engineers is increasing. Consequently, individuals with expertise in this area often command higher salaries, reflecting the specialized knowledge and critical role they play in mission success.
In summary, specialization demonstrably influences the “california aerospace engineer salary” in California. The demand for specialized skill sets, driven by technological advancements and industry trends, leads to higher compensation for engineers with expertise in propulsion systems, structural analysis and design, avionics and control systems, and spacecraft systems engineering. Acquisition of specialized knowledge represents a strategic pathway to enhanced earning potential in the dynamic aerospace engineering job market.
6. Market Demand
The prevailing market demand for aerospace engineers in California exerts a substantial influence on compensation levels. When demand exceeds supply, employers are compelled to offer more competitive salaries to attract and retain qualified professionals. This dynamic is particularly evident in regions with a high concentration of aerospace companies and research institutions. Increased hiring activity driven by industry growth, technological advancements, and government contracts creates upward pressure on compensation, benefiting individuals seeking employment or advancement within the field. The inverse is also true; a downturn in the aerospace sector, resulting in layoffs or hiring freezes, can lead to a decrease in salary offers and reduced bargaining power for job seekers. For example, periods of increased defense spending or heightened commercial space activity often correlate with a surge in demand for aerospace engineers and a corresponding increase in the “california aerospace engineer salary.”
The specific skills and expertise in demand further refine the relationship between market forces and remuneration. Areas such as electric propulsion, autonomous systems, and advanced materials engineering are currently experiencing rapid growth, resulting in a premium for engineers possessing these skill sets. Employers are willing to pay higher salaries to secure talent capable of contributing to these cutting-edge technologies. Furthermore, the geographic distribution of aerospace companies within California impacts market demand. Regions with a higher concentration of aerospace employers, such as Southern California and the San Francisco Bay Area, typically exhibit greater demand for aerospace engineers and higher corresponding salary levels. Understanding these geographic and skill-based nuances is essential for effectively navigating the job market and maximizing earning potential.
In summary, market demand serves as a fundamental driver of compensation for aerospace engineers in California. Fluctuations in industry activity, technological advancements, and geographic concentrations of employers directly influence salary levels. Staying abreast of these trends is crucial for both job seekers and employers to ensure competitive compensation and maintain a skilled workforce. Ignoring the impact of market demand can lead to missed opportunities for engineers and difficulty in attracting and retaining talent for companies, highlighting the practical significance of understanding this dynamic.
7. Negotiation Skills
Effective negotiation skills are directly correlated with the earning potential of aerospace engineers in California. While factors such as experience, education, and specialization establish a baseline for compensation, the ability to articulate one’s value proposition and strategically negotiate salary and benefits significantly influences the final outcome. A candidate with superior negotiation skills can often secure a higher starting salary, more favorable benefits packages, and enhanced opportunities for future salary increases, even when compared to peers with similar qualifications but weaker negotiation abilities. The causal relationship is straightforward: proficient negotiation translates into a more advantageous compensation agreement. This proficiency encompasses the ability to research prevailing market rates, confidently articulate one’s skills and accomplishments, and effectively counter offers that do not align with expectations. The “california aerospace engineer salary” is not a fixed entity; rather, it is a negotiable range within which skilled individuals can maximize their financial returns.
The importance of negotiation extends beyond the initial salary offer. Regular performance reviews and discussions regarding promotions provide opportunities to leverage negotiation skills to advocate for merit-based increases and expanded responsibilities. Engineers who can effectively demonstrate their contributions to the company’s success and justify their value are more likely to receive favorable consideration during these evaluations. Furthermore, understanding the nuances of benefit packages, including health insurance, retirement plans, and stock options, allows for a more comprehensive assessment of the overall compensation and enables strategic negotiation to optimize the value proposition. For example, an engineer might negotiate for increased contributions to a retirement plan in lieu of a slightly higher salary, depending on their individual financial goals. It’s also useful to remember that sometimes, a new company may offer perks to lure an engineer from their former employ and a careful evaluation of these benefits are in order.
In conclusion, negotiation skills represent a critical and often underestimated component of the aerospace engineer’s earning potential in California. While technical expertise and academic credentials provide a foundation for a successful career, the ability to effectively advocate for one’s value and strategically negotiate compensation packages is essential for maximizing financial rewards. The challenges lie in developing and honing these skills through practice, research, and a clear understanding of market dynamics. Recognizing the practical significance of negotiation skills empowers aerospace engineers to proactively shape their career trajectory and secure compensation that accurately reflects their contributions and value to the organization. These are the “california aerospace engineer salary” determining factors beyond the base figures.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common inquiries and misconceptions regarding financial compensation for professionals within the aerospace engineering field in California.
Question 1: What is the typical entry-level compensation for an aerospace engineer in California?
Entry-level remuneration varies based on the employer and location. However, a general range for individuals with a Bachelor’s degree and limited experience typically falls between $70,000 and $90,000 annually. This figure is subject to change based on market demand and the specific skill sets required by the employing organization.
Question 2: How does possessing a Master’s or Ph.D. degree impact compensation?
Advanced degrees generally lead to higher earning potential. A Master’s degree can increase starting salaries by 10-20%, while a Ph.D. can command even higher remuneration, particularly for research-oriented positions. The precise impact depends on the specific area of specialization and the employer’s valuation of advanced academic qualifications.
Question 3: Does location within California significantly affect earnings?
Yes, location plays a crucial role. Areas with a high cost of living, such as the San Francisco Bay Area and Los Angeles County, typically offer higher salaries to offset increased expenses. Compensation in these regions can be significantly higher than in more rural or less densely populated areas of the state.
Question 4: How do compensation packages compare between large aerospace corporations and smaller startups?
Large aerospace corporations often provide higher base salaries and more comprehensive benefits packages due to their greater financial resources. Smaller startups may offer lower initial salaries but potentially provide opportunities for equity ownership and faster career advancement.
Question 5: What specialized skills command the highest salaries in the current aerospace engineering job market?
Skills in high demand include expertise in electric propulsion, autonomous systems, advanced materials, and cybersecurity for aerospace applications. Professionals possessing these specialized skills are often highly sought after and can command premium compensation.
Question 6: How important are negotiation skills in determining an aerospace engineer’s salary?
Negotiation skills are essential for maximizing earning potential. The ability to effectively articulate one’s value proposition, research market rates, and strategically negotiate salary and benefits can significantly impact the final compensation package.
In summary, numerous factors influence the compensation of aerospace engineers in California. Understanding these factors enables professionals to make informed career decisions and advocate for fair remuneration.
The concluding section will synthesize the key insights presented throughout this article and offer final recommendations for navigating the complexities of aerospace engineering compensation in California.
“california aerospace engineer salary”
This exploration has illuminated the multifaceted determinants of compensation for aerospace engineers in California. Factors ranging from experience and education to specialization, company size, market demand, and negotiation skills collectively shape earning potential. A comprehensive understanding of these dynamics is paramount for both aspiring and established professionals within this field.
The trajectory of remuneration for these highly skilled individuals reflects not only their individual capabilities but also the economic forces and technological advancements that define the aerospace industry. Continued vigilance regarding market trends, proactive skill development, and strategic negotiation will be critical for navigating the evolving landscape of “california aerospace engineer salary” and ensuring sustained career prosperity.