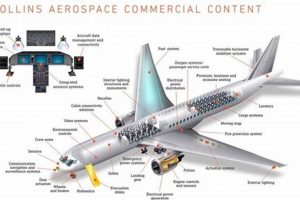
This refers to the business operations and presence of a major aerospace and defense company within the Russian Federation. It encompasses activities such as the sales, support, and potential manufacturing of aircraft components and related services offered within that specific geographic market.
Prior to geopolitical shifts and sanctions, such a presence facilitated access to the Russian aviation market, including collaborations with local manufacturers and airlines. This allowed for participation in the growth of the region’s aerospace industry and the provision of necessary maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) services. Moreover, it enabled the company to establish relationships with key stakeholders in the Russian aviation sector, influencing technology adoption and industry standards.
The following sections will examine the operational scope, market impact, and the implications of recent international events on this aspect of the broader aerospace industry.
Strategic Considerations for Aerospace Operations in the Russian Federation
The following offers key strategic considerations pertaining to aerospace business activities within Russia, based on historical context and evolving geopolitical factors. These insights are intended for informational purposes and do not constitute financial or legal advice.
Tip 1: Conduct Thorough Due Diligence: Prior to any investment or operational expansion, comprehensive due diligence is crucial. This includes assessing geopolitical risks, understanding the regulatory environment, and evaluating the financial stability of potential partners.
Tip 2: Prioritize Compliance: Adherence to international sanctions and export control regulations is paramount. Maintaining a robust compliance program mitigates the risk of legal and financial penalties.
Tip 3: Cultivate Local Partnerships: Establishing strong relationships with local aerospace companies and government entities can facilitate market access and navigate complex regulatory landscapes. However, always assess the potential risks associated with such partnerships.
Tip 4: Adapt Product Offerings: Tailor product offerings to meet the specific needs and requirements of the Russian aviation market. This may involve localization of technology or the provision of specialized maintenance services.
Tip 5: Monitor Geopolitical Developments: The geopolitical landscape is subject to rapid change. Continuous monitoring of political and economic developments is essential for informed decision-making.
Tip 6: Evaluate Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: Analyze the reliance on global supply chains and identify potential vulnerabilities in accessing critical components and materials. Diversification of suppliers may be necessary to mitigate disruptions.
Tip 7: Implement Robust Risk Management: A comprehensive risk management framework should be in place to address potential threats such as economic downturns, political instability, and supply chain disruptions. Contingency plans are essential for navigating unforeseen circumstances.
These strategic considerations emphasize the importance of careful planning, compliance, and adaptation when operating in a dynamic and complex environment. A proactive and risk-aware approach is crucial for navigating the challenges and capitalizing on opportunities within the Russian aerospace sector.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific aspects of market access, regulatory compliance, and risk mitigation strategies for aerospace businesses operating in the Russian Federation.
1. Market Access Strategies
Market access strategies, in the context of the business operations inside Russia, are paramount for maintaining a competitive edge and ensuring sustainable growth. These strategies encompass a range of activities designed to facilitate the entry and expansion of products and services within the Russian aerospace market, while adhering to legal and geopolitical constraints.
- Regulatory Navigation
Effective navigation of Russian aviation regulations is essential for market access. This involves understanding certification processes, import/export controls, and compliance with local standards. Failure to adhere to these regulations can result in delays, penalties, or even market exclusion. Previously, the certification of aircraft components, for example, required close collaboration with Russian aviation authorities and adherence to specific technical standards.
- Partnership Development
Establishing strategic partnerships with local aerospace companies and government entities can significantly enhance market access. These partnerships provide valuable insights into the Russian market, facilitate access to distribution channels, and foster relationships with key stakeholders. Joint ventures with Russian manufacturers, for instance, can enable technology transfer and the localization of production, thereby improving competitiveness. However, the risk of intellectual property infringement must be carefully considered.
- Localization of Products and Services
Adapting products and services to meet the specific needs and requirements of the Russian aerospace market is crucial for success. This may involve modifying designs, incorporating local components, or providing specialized training and support services in the Russian language. Aircraft maintenance services, for instance, often require localization to comply with Russian safety standards and operational procedures. Before sanctions, this allowed for more competitive bids on government contracts.
- Distribution and Logistics Optimization
Establishing efficient distribution and logistics networks is essential for delivering products and services to customers in a timely and cost-effective manner. This involves selecting appropriate transportation modes, managing inventory levels, and complying with customs regulations. The vastness of the Russian territory and the complexity of its transportation infrastructure necessitate careful planning and execution. A robust logistics network previously ensured timely delivery of spare parts and maintenance equipment to Russian airlines.
The efficacy of market access strategies directly impacts the company’s ability to operate effectively within the Russian Federation. By navigating regulatory hurdles, cultivating strategic partnerships, localizing products and services, and optimizing distribution networks, the aerospace manufacturer can maximize its market penetration and achieve long-term sustainable growth. The ongoing geopolitical instability however, significantly complicates the implementation and viability of these strategies.
2. Regulatory Compliance Adherence
Regulatory compliance adherence constitutes a critical component of business activities. Its presence within the Russian Federation necessitates a rigorous framework to ensure operations align with both international standards and local legislation. Failure to maintain compliance can result in severe penalties, reputational damage, and potential disruptions to the supply chain. Prior to escalating international tensions, the entity was required to navigate complex export control regulations, sanctions regimes, and Russian aviation standards. This involved meticulous documentation, internal audits, and ongoing monitoring of evolving legal landscapes. For example, the export of certain aircraft components necessitated obtaining specific licenses from relevant authorities, a process demanding detailed technical specifications and end-user verification.
The importance of adherence extends beyond simply avoiding penalties. It also plays a vital role in maintaining relationships with international partners and building trust with Russian customers. Compliance with international ethical standards and anti-corruption laws is essential for safeguarding the company’s reputation and ensuring sustainable business practices. For instance, the company’s interactions with Russian government officials and local contractors required strict adherence to anti-bribery regulations, necessitating robust compliance training programs and due diligence procedures. Furthermore, adapting to evolving sanctions regimes imposed by various countries has been a continuous challenge, requiring constant monitoring and adjustments to operational procedures.
In summary, regulatory compliance adherence represents a complex and dynamic challenge for operation within the Russian Federation. A proactive and robust approach is essential for navigating the intricate legal and geopolitical landscape. The long-term success hinges on its ability to maintain unwavering compliance standards, thereby mitigating risks, upholding its reputation, and fostering sustainable growth in a challenging environment. Current circumstances have dramatically increased the difficulty and complexity of maintaining such adherence.
3. Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
Supply chain vulnerabilities represent a significant consideration for the presence within the Russian Federation. Geopolitical instability, sanctions, and logistical challenges can disrupt the flow of components, materials, and finished goods, impacting production schedules and customer service capabilities.
- Geopolitical Risks and Sanctions
International sanctions imposed on Russia following geopolitical events have created substantial disruptions. These sanctions restrict the export of certain technologies and materials to Russia, limiting the availability of crucial components required for manufacturing and maintenance operations. For instance, restrictions on the export of advanced avionics or specialized alloys necessitate the identification of alternative suppliers or the development of substitute materials, potentially increasing costs and lead times.
- Logistical Constraints and Infrastructure Limitations
Russia’s vast geography and infrastructure limitations present logistical challenges to supply chain management. Transportation bottlenecks, customs delays, and inadequate warehousing facilities can impede the efficient movement of goods, increasing transit times and costs. For example, transporting aircraft components from manufacturing facilities in Europe or the United States to maintenance hubs in remote regions of Russia can be time-consuming and expensive, particularly during winter months when weather conditions are severe.
- Dependency on Foreign Suppliers
Reliance on foreign suppliers for critical components and materials exposes the supply chain to potential disruptions. If key suppliers are located in countries that impose sanctions or experience political instability, the availability of essential inputs may be jeopardized. For example, if a primary supplier of aircraft engines or landing gear is unable to fulfill orders due to geopolitical factors, the aircraft manufacturer may face production delays or even operational shutdowns.
- Cybersecurity Threats and Data Breaches
Cybersecurity threats pose a growing risk to supply chain security. Data breaches, ransomware attacks, and other cyber incidents can compromise sensitive information, disrupt logistics operations, and damage critical infrastructure. For example, a cyberattack targeting a major transportation company could disrupt the movement of goods across Russia, causing widespread supply chain disruptions and economic losses.
These supply chain vulnerabilities highlight the need for robust risk mitigation strategies. Diversifying suppliers, building strategic partnerships with local manufacturers, and investing in cybersecurity defenses are essential for ensuring supply chain resilience and mitigating the impact of disruptions. Ultimately, addressing these vulnerabilities is critical for maintaining operational continuity and supporting the long-term sustainability within the Russian aerospace market. Alternative sourcing and strategic stockpiling of key parts would be essential.
4. Geopolitical Risk Mitigation
Geopolitical risk mitigation is integral to the operational viability of the business activities within the Russian Federation. The Russian aerospace sector, due to its strategic importance and close ties to the Russian government, is particularly susceptible to geopolitical influences. International sanctions, trade restrictions, and political instability directly impact market access, supply chain integrity, and financial transactions. Therefore, proactive identification and mitigation of these risks are essential for maintaining business continuity. For example, the imposition of sanctions targeting specific Russian entities requires immediate adjustments to contractual agreements, sourcing strategies, and financial compliance procedures to avoid legal repercussions and maintain operational efficiency.
Effective risk mitigation necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the geopolitical landscape and the ability to anticipate potential disruptions. This involves continuous monitoring of political developments, regulatory changes, and international relations, coupled with scenario planning to prepare for various contingencies. A key element is diversification of supply chains to reduce reliance on single sources and establishing robust compliance programs to ensure adherence to international sanctions and export control regulations. Furthermore, engaging with government relations and industry associations can provide valuable insights into emerging risks and opportunities. The suspension of cooperation on certain aerospace projects with Western entities demonstrates the tangible impact of geopolitical shifts, underscoring the need for adaptability and alternative business models.
In conclusion, geopolitical risk mitigation is not merely a compliance exercise but a strategic imperative for the companys long-term sustainability within the Russian aerospace market. The ability to navigate the complexities of the geopolitical environment, adapt to unforeseen events, and maintain operational resilience is crucial for mitigating potential losses and capitalizing on available opportunities. As geopolitical tensions persist, this aspect of the business demands unwavering attention and proactive management.
5. Technology Transfer Limitations
Technology transfer limitations present a complex challenge to aerospace operations within Russia. These restrictions, imposed by international regulations and national security concerns, significantly affect the scope and nature of collaborative projects and the ability to deploy advanced technologies.
- Export Control Regulations
Export control regulations implemented by various countries restrict the transfer of sensitive technologies to Russia. These regulations are designed to prevent the acquisition of technologies that could be used for military purposes or to undermine national security. Aerospace technologies, including advanced avionics, propulsion systems, and materials science, are often subject to stringent export controls, requiring licenses and certifications that can be difficult to obtain. The implications of these limitations include restricted access to cutting-edge technologies, hindering innovation and limiting the ability to offer competitive products and services. For example, obtaining export licenses for advanced aircraft components can be a lengthy and uncertain process, impacting project timelines and increasing costs.
- Intellectual Property Protection
Weak intellectual property protection in Russia presents another limitation to technology transfer. Concerns over the potential for unauthorized copying or reverse engineering of proprietary technologies deter companies from sharing their most valuable innovations. This lack of confidence can lead to reluctance in establishing joint ventures or licensing agreements, limiting the potential for technology transfer. For instance, aerospace companies may hesitate to transfer proprietary manufacturing processes or design specifications to Russian partners, fearing that their intellectual property rights may not be adequately protected. The risk of intellectual property theft can significantly impact investment decisions and collaborative opportunities.
- Sanctions and Trade Restrictions
Economic sanctions and trade restrictions imposed on Russia by various countries have further curtailed technology transfer. These measures limit the transfer of goods, services, and technology to specific Russian entities or sectors, including the aerospace industry. The impact of sanctions can be far-reaching, affecting access to financing, limiting trade opportunities, and disrupting supply chains. For example, sanctions targeting Russian defense companies may prohibit the transfer of technology used in the production of aircraft components, forcing them to rely on less advanced technologies or seek alternative suppliers. This environment significantly constrains innovation and competitiveness.
- Geopolitical Considerations
Geopolitical tensions influence technology transfer limitations. Political considerations often override purely economic factors, leading to restrictions on technology transfer based on national security or foreign policy objectives. Bilateral agreements and strategic partnerships between countries can either facilitate or impede technology transfer, depending on the prevailing political climate. For example, a deterioration in relations between Russia and a major aerospace technology provider could result in stricter controls on technology transfer, limiting access to essential innovations and hindering collaborative projects.
In conclusion, the various facets of technology transfer limitations significantly impact operations within the Russian Federation. Export control regulations, intellectual property concerns, sanctions, and geopolitical considerations collectively constrain access to advanced technologies and limit collaborative opportunities. Addressing these limitations requires a strategic approach that balances commercial interests with compliance obligations and geopolitical realities, ultimately shaping the scope and nature of business in the Russian aerospace sector.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding operations within the Russian Federation, providing clarity on key aspects of its presence and activities.
Question 1: What were the primary activities of the enterprise within Russia prior to recent geopolitical changes?
The primary activities encompassed the sale, maintenance, and support of aircraft components and systems to Russian airlines and aerospace manufacturers. This included providing aftermarket services, technical support, and training programs, along with participating in collaborative projects with Russian aerospace entities.
Question 2: How did international sanctions impact the company’s operations in Russia?
International sanctions imposed limitations on the export of certain technologies and materials to Russia, disrupting supply chains and restricting access to critical components. Sanctions also complicated financial transactions and required adjustments to contractual agreements to ensure compliance with international regulations.
Question 3: What measures were taken to ensure compliance with export control regulations?
Compliance with export control regulations involved meticulous documentation, internal audits, and ongoing monitoring of evolving legal landscapes. Specific licenses were obtained for the export of controlled items, requiring detailed technical specifications and end-user verification. Robust compliance training programs were implemented to ensure adherence to regulations.
Question 4: How were supply chain vulnerabilities addressed in the context of operations in Russia?
Supply chain vulnerabilities were addressed through diversification of suppliers, building strategic partnerships with local manufacturers, and implementing robust risk management strategies. Alternative sourcing was explored for critical components, and contingency plans were developed to mitigate the impact of potential disruptions.
Question 5: What role did local partnerships play in facilitating market access?
Local partnerships facilitated market access by providing valuable insights into the Russian market, fostering relationships with key stakeholders, and navigating complex regulatory landscapes. Joint ventures with Russian manufacturers enabled technology transfer and the localization of production, enhancing competitiveness. However, these partnerships also required careful assessment of potential risks.
Question 6: What strategies were employed to mitigate geopolitical risks?
Geopolitical risks were mitigated through continuous monitoring of political developments, scenario planning, and establishing robust compliance programs. Diversification of supply chains and engagement with government relations helped to navigate the complexities of the geopolitical environment and adapt to unforeseen events.
These responses provide a general overview of key considerations related to this specific business activity. Actual operations and strategies may have varied depending on specific circumstances and evolving geopolitical conditions.
The following section will explore potential future scenarios and alternative business strategies.
Conclusion
This examination of collins aerospace russia has outlined the operational considerations, strategic challenges, and evolving geopolitical landscape that defined its activities. The analysis highlighted the importance of regulatory compliance, supply chain resilience, and geopolitical risk mitigation. Additionally, technology transfer limitations posed persistent challenges. These factors, while historically significant, have been superseded by the current volatile international environment.
The future of collins aerospace russia, and similar ventures, remains uncertain. Ongoing geopolitical instability necessitates a reassessment of strategic priorities and a consideration of alternative business models. The industry must adapt to the evolving realities, focusing on responsible and compliant practices, while remaining cognizant of the long-term implications of these turbulent times.




![Collins Aerospace Wisconsin: [Benefits/Innovations] & More Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions Collins Aerospace Wisconsin: [Benefits/Innovations] & More | Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/th-878-300x200.jpg)