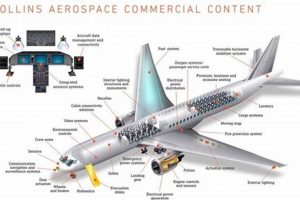
A key player in the aviation and aerospace industry, this Wisconsin-based division specializes in the design, manufacture, and service of a wide array of technologically advanced systems and components. These products cater to commercial, military, and business aviation sectors, contributing to safer and more efficient air travel. Their portfolio includes avionics, aerostructures, and interior systems, among others.
The presence of this facility in Wisconsin provides significant economic benefits to the region through job creation, technological innovation, and workforce development. Its long-standing history within the state underscores its commitment to local communities and its role as a vital partner in advancing aerospace capabilities. The organization’s activities contribute to national defense, global connectivity, and the overall advancement of aerospace technologies.
The following sections will delve into specific aspects of the company’s operations, including its product lines, technological innovations, contributions to the aerospace industry, and impact on the Wisconsin economy. These explorations will further illuminate the multifaceted nature of its contributions and the significance of its presence.
Best Practices in Aviation Technology
The following recommendations are informed by the operational expertise and engineering rigor of a leading aerospace entity located in Wisconsin. These guidelines promote safety, efficiency, and innovation within the aviation sector.
Tip 1: Prioritize System Integration Testing: Comprehensive testing of integrated systems is crucial before deployment. This minimizes unforeseen interactions and ensures optimal performance of all interconnected components. For instance, avionics systems should be rigorously tested with flight control software before installation.
Tip 2: Emphasize Human Factors Engineering: Design interfaces and systems with a strong emphasis on usability and human factors. This reduces pilot workload, minimizes errors, and enhances overall safety. Consider ergonomic design of cockpit controls and intuitive display layouts.
Tip 3: Invest in Predictive Maintenance: Utilize data analytics and sensor technology to predict potential failures and schedule maintenance proactively. This reduces downtime, minimizes maintenance costs, and enhances operational reliability. Implement condition-based monitoring for critical engine components.
Tip 4: Adhere to Stringent Quality Control: Implement rigorous quality control processes throughout the manufacturing and assembly stages. This minimizes defects, ensures component reliability, and enhances overall system performance. Employ statistical process control and rigorous inspection protocols.
Tip 5: Foster Continuous Innovation: Encourage research and development activities to advance aerospace technologies and improve existing systems. This ensures competitiveness, enhances capabilities, and drives industry progress. Invest in advanced materials, additive manufacturing, and autonomous systems research.
Tip 6: Implement Robust Cybersecurity Measures: Integrate robust cybersecurity protocols to protect critical aerospace systems from cyber threats. This protects against data breaches, system compromise, and potential safety hazards. Employ encryption, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits.
Tip 7: Promote Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing: Foster collaboration between engineers, technicians, and other stakeholders to share knowledge and best practices. This facilitates innovation, improves problem-solving, and enhances overall performance. Organize regular technical workshops and knowledge-sharing sessions.
By adhering to these practices, organizations can enhance the safety, efficiency, and reliability of their aerospace operations, ultimately contributing to the advancement of the industry as a whole.
The subsequent sections will explore related topics, providing further insights into advancements and best practices within the aerospace domain.
1. Manufacturing Excellence
Manufacturing excellence is a cornerstone of the operations within this Wisconsin-based division. It represents a commitment to high-quality production processes, advanced technological integration, and a skilled workforce. The organization’s reputation is fundamentally linked to its ability to consistently deliver aerospace components and systems that meet stringent industry standards and performance requirements. For example, the flawless execution of aerostructure manufacturing directly impacts the safety and efficiency of aircraft utilizing these components.
The pursuit of manufacturing excellence translates into tangible benefits, including reduced production costs, enhanced product reliability, and improved customer satisfaction. This emphasis drives the adoption of lean manufacturing principles, automation technologies, and advanced quality control measures. The fabrication of sophisticated avionics systems, for instance, necessitates meticulous adherence to precision engineering and rigorous testing protocols. The commitment to efficiency and precision ensures the operational longevity and effectiveness of their products.
In conclusion, manufacturing excellence is not merely a procedural aspect, but a core strategic objective that directly influences the success and sustainability of the Wisconsin-based operation. This dedication ensures a continuous output of high-performance products, and reinforces its position as a key contributor within the aerospace sector. Overcoming the challenges of high-precision manufacturing requires ongoing investments in technology and workforce training. This ongoing commitment strengthens its ability to contribute to the overarching goals of safety, reliability, and technological advancement in the field of aerospace.
2. Engineering Innovation
Engineering innovation is a critical driving force behind this aerospace division’s success, shaping its product development, operational efficiency, and overall competitiveness within the global aerospace market. It represents a constant pursuit of novel solutions and advancements within the engineering domain, resulting in tangible improvements to existing technologies and the creation of entirely new capabilities.
- Advanced Materials Research
The division engages in extensive research and development concerning advanced materials, seeking to enhance the strength, durability, and weight characteristics of aerospace components. This research leads to the incorporation of composites, alloys, and other innovative materials into aircraft structures and systems, improving fuel efficiency and overall performance. An example includes the development and implementation of lightweight composite materials in aircraft interiors, reducing aircraft weight and thus, fuel consumption.
- Avionics Systems Development
The company is a significant contributor to the advancement of avionics systems, focusing on developing innovative solutions for flight control, navigation, communication, and surveillance. These developments include enhanced flight management systems, improved display technologies, and advanced sensor integration, enhancing pilot situational awareness and overall flight safety. An instance is the development and integration of advanced head-up displays (HUDs) providing pilots with critical flight information directly within their line of sight.
- Aerostructures Optimization
Engineering innovation drives the optimization of aerostructures, focusing on enhancing aerodynamic performance, reducing drag, and improving structural integrity. Through computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and finite element analysis (FEA), engineers refine aircraft wing designs, fuselage structures, and other aerodynamic components. An illustration involves the application of winglet technologies on aircraft wings, minimizing induced drag and improving fuel efficiency.
- Sustainable Technologies Integration
The integration of sustainable technologies is another key area of engineering innovation, reflecting a commitment to environmental responsibility and reducing the environmental impact of air travel. These efforts involve the development of more efficient engine technologies, the use of sustainable aviation fuels, and the implementation of energy-efficient systems within aircraft. This is demonstrated by the research into and implementation of hybrid-electric propulsion systems for smaller aircraft, minimizing emissions and noise pollution.
These facets of engineering innovation collectively contribute to the Wisconsin-based operation’s reputation as a leader in aerospace technology. The commitment to continuous improvement and the pursuit of groundbreaking advancements reinforces its position as a key innovator in the industry, fostering enhanced safety, efficiency, and sustainability in air travel. These advancements further contribute to the state’s economic vitality by attracting skilled talent and fostering technological development.
3. Avionics Expertise
Avionics expertise forms a critical and integral component of the operations conducted by this Wisconsin-based division. The division’s standing in the aerospace industry is fundamentally dependent on its proficiency in designing, manufacturing, and maintaining advanced avionics systems. These systems encompass a wide array of technologies, including flight management systems, communication systems, navigation systems, and surveillance systems. The expertise in these areas directly impacts the safety, efficiency, and overall performance of aircraft across various sectors, including commercial, military, and business aviation. For instance, the development and integration of advanced flight control systems contributes directly to reduced pilot workload and enhanced aircraft stability.
The practical application of avionics expertise within this division is evident in its contributions to various aircraft platforms and programs. The company designs and produces critical components for aircraft, supporting a wide array of functionalities, such as automated flight control, precise navigation, and seamless communication. This contribution is not limited to new aircraft; it also extends to the modernization and upgrade of existing aircraft fleets, improving their capabilities and extending their operational lifespans. The integration of advanced weather radar systems is an example of how expertise enhances situational awareness, thus improving flight safety in adverse weather conditions.
In summary, avionics expertise is not just a capability but a defining characteristic that shapes the operations and contributions of the Wisconsin division. The facility’s success is inextricably linked to its ability to innovate and excel in the avionics domain. Maintaining and advancing this expertise requires continuous investment in research and development, workforce training, and collaboration with industry partners. Any challenges to this commitment could directly impact the division’s competitive edge and its contribution to the aerospace industry. This expertise plays a vital role in the overall advancement of aerospace technologies and in supporting safe and efficient air travel.
4. Aerostructures Production
Aerostructures production constitutes a significant operational facet of the organization located in Wisconsin, reflecting its capabilities in the design, fabrication, and assembly of critical aircraft structural components. These components directly influence aircraft performance, safety, and overall operational efficiency. The proficiency in this area is a defining element of its contribution to the aerospace sector.
- Wing Component Manufacturing
The manufacturing of wing components, including spars, ribs, and skin panels, represents a key area of aerostructures production. This involves utilizing advanced materials, such as aluminum alloys and composite materials, to achieve optimal strength-to-weight ratios. Precise manufacturing processes are crucial to ensure aerodynamic efficiency and structural integrity. An example is the production of wing components for regional jets, requiring adherence to stringent tolerances and quality control standards to maintain flight stability and fuel efficiency.
- Fuselage Section Assembly
The assembly of fuselage sections, including the integration of frames, stringers, and outer skin, is another critical aspect of aerostructures production. This process demands precise alignment and secure fastening techniques to ensure structural integrity and passenger safety. The assembly of composite fuselage sections for business aircraft exemplifies the integration of advanced materials and manufacturing processes to reduce weight and enhance aircraft performance.
- Empennage Manufacturing
The manufacturing of empennage components, including the horizontal and vertical stabilizers, requires specialized expertise in aerodynamic design and structural analysis. These components play a crucial role in aircraft stability and control. An example is the production of empennage assemblies for military transport aircraft, necessitating the ability to withstand extreme aerodynamic loads and environmental conditions.
- Control Surface Fabrication
The fabrication of control surfaces, such as ailerons, elevators, and rudders, involves intricate manufacturing processes to ensure precise aerodynamic control and responsiveness. These surfaces are critical for pilot maneuvering and aircraft stability. The production of advanced control surfaces with integrated actuators for commercial airliners highlights the integration of mechanical and electronic systems to enhance flight control precision and safety.
These facets of aerostructures production underscore the significance of the Wisconsin operation’s role in the aerospace supply chain. These activities directly support aircraft manufacturers and operators globally. The organization’s capabilities in this area are integral to the broader aerospace industry and contribute significantly to the state’s economy through job creation and technological innovation. Sustained investment in advanced manufacturing technologies and workforce development are critical to maintaining and enhancing its competitive edge in this domain.
5. Regional Economy
The presence of a significant aerospace operation in Wisconsin has a multifaceted and substantial impact on the regional economy. Its influence spans job creation, supply chain dynamics, tax revenue generation, and the attraction of specialized talent to the region, all contributing to the area’s economic vitality.
- Direct Job Creation
The operation directly employs a substantial number of individuals in engineering, manufacturing, administrative, and management roles. These positions provide stable income for families and contribute to the local tax base. For example, the creation of hundreds of manufacturing jobs directly increases consumer spending in the local community, supporting retail businesses and service providers.
- Supply Chain Stimulation
The aerospace facility relies on a network of suppliers for raw materials, components, and services. This demand stimulates economic activity throughout the supply chain, benefiting smaller businesses and creating additional indirect employment opportunities. For instance, the need for specialized tooling and machining services creates opportunities for local machine shops, fostering their growth and expansion.
- Tax Revenue Generation
The operation contributes significantly to local and state tax revenues through property taxes, income taxes, and sales taxes. These revenues support public services, infrastructure improvements, and educational programs within the region. The payment of property taxes on large manufacturing facilities allows local municipalities to invest in essential community resources, such as schools and public safety services.
- Talent Attraction and Retention
The presence of a major aerospace employer attracts skilled engineers, technicians, and managers to the region, enhancing the overall workforce quality and fostering innovation. This influx of talent can lead to the development of new technologies and the creation of spin-off companies. The availability of challenging and rewarding aerospace careers encourages qualified professionals to relocate to and remain in Wisconsin, strengthening the state’s intellectual capital.
In summary, the aerospace operation acts as a significant economic engine for the region, generating employment, supporting local businesses, and contributing to the overall prosperity of the community. Its continued success and expansion are vital to maintaining and enhancing the region’s economic competitiveness and quality of life. The operation’s investment in local partnerships and community engagement activities further reinforces its positive economic impact and its commitment to the region’s long-term well-being.
6. Workforce Development
Workforce development is an indispensable component of the operational framework for this Wisconsin-based aerospace entity. The specialized nature of aerospace manufacturing and engineering necessitates a highly skilled workforce capable of meeting the demands of precision manufacturing, advanced technology integration, and rigorous quality control. The organization’s success is directly contingent upon its ability to cultivate and maintain a pipeline of qualified personnel. This is achieved through a variety of initiatives, including apprenticeships, training programs, and partnerships with educational institutions. For example, collaborations with local technical colleges provide students with hands-on experience and industry-specific training, preparing them for careers within the aerospace sector.
The importance of workforce development extends beyond meeting immediate staffing needs; it also contributes to long-term innovation and competitiveness. By investing in employee training and skill enhancement, the organization fosters a culture of continuous improvement and technological advancement. This proactive approach ensures that employees possess the expertise required to implement new technologies, optimize manufacturing processes, and develop innovative solutions to complex engineering challenges. One practical application involves the implementation of advanced manufacturing techniques, such as additive manufacturing, which require specialized training for engineers and technicians to effectively operate and maintain the associated equipment.
In conclusion, workforce development is not merely a peripheral activity but a core strategic imperative for the aerospace operation in Wisconsin. It is essential for ensuring operational efficiency, maintaining product quality, and driving technological innovation. Challenges related to skills gaps and labor shortages require ongoing investment in training and education programs to meet the evolving demands of the aerospace industry. This commitment to workforce development is a critical factor in the organization’s sustained success and its contribution to the broader aerospace ecosystem.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding the aerospace division located in Wisconsin. The responses aim to provide clarity on its operations, contributions, and impact.
Question 1: What are the primary products manufactured by this division?
The division specializes in the design, manufacturing, and servicing of a wide range of aerospace systems and components. This includes avionics, aerostructures, interiors, and mission systems for commercial, military, and business aviation sectors.
Question 2: How does the presence of this aerospace operation benefit the Wisconsin economy?
The facility contributes significantly to the Wisconsin economy through job creation, tax revenue generation, and the stimulation of local supply chains. It also attracts skilled talent and fosters technological innovation within the region.
Question 3: What types of engineering expertise are prevalent within the organization?
The division employs a diverse range of engineers specializing in areas such as aerospace, mechanical, electrical, and materials engineering. Expertise includes aerodynamics, structural analysis, avionics systems development, and advanced materials research.
Question 4: Does the company have partnerships with local educational institutions?
The organization maintains partnerships with local technical colleges and universities to provide training opportunities, internships, and research collaborations. These partnerships help cultivate a skilled workforce and support the development of aerospace technologies.
Question 5: What quality control measures are implemented in the manufacturing processes?
The division adheres to stringent quality control standards throughout its manufacturing processes. This includes rigorous inspection protocols, statistical process control, and compliance with industry certifications to ensure product reliability and performance.
Question 6: How does the operation contribute to advancements in aerospace technology?
The division invests in research and development activities focused on advanced materials, avionics systems, aerostructures optimization, and sustainable technologies. These efforts contribute to improved safety, efficiency, and environmental sustainability within the aerospace industry.
These responses provide a concise overview of key aspects relating to the aerospace operation located in Wisconsin. The information highlights its role as a significant contributor to both the aerospace industry and the local economy.
Subsequent discussions will delve into specific advancements, challenges, and future directions relevant to the division and the broader aerospace domain.
Conclusion
This exposition has illuminated the multifaceted significance of Collins Aerospace Wisconsin. Its activities in manufacturing excellence, engineering innovation, avionics expertise, and aerostructures production substantially contribute to both the aerospace industry and the regional economy. The operation’s role in workforce development and its impact on local communities underscore its importance as a key stakeholder.
Continued investment in technology, workforce training, and strategic partnerships is essential to ensure the sustained success of this operation and its ongoing contributions to the aerospace sector. The future viability of aerospace in Wisconsin hinges upon a commitment to innovation and a proactive approach to addressing the evolving demands of the global market.