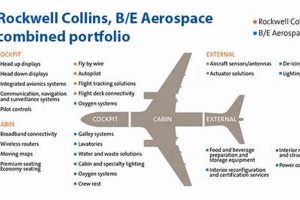
The entity in question represents a significant player in the aviation and high-technology sectors. It functions as a provider of technologically advanced systems and services. These offerings span diverse domains including avionics, aerostructures, aircraft interiors, and mission systems, playing a crucial role in the design, manufacture, and support of commercial, military, and business aircraft.
Its importance lies in its contribution to enhanced aircraft performance, safety, and passenger experience. The company’s history is characterized by innovation and a dedication to advancing the capabilities of flight. This translates into substantial benefits for airlines, aerospace manufacturers, and ultimately, the traveling public through more efficient, reliable, and comfortable air travel.
The following sections will delve into specific areas where its technologies and solutions are particularly impactful, examining the evolution of its product lines and the future trends it is helping to shape within the global aerospace industry.
Strategic Approaches in Aerospace Technology
The following outlines key considerations when leveraging advanced technologies within the aerospace industry, drawing upon established practices from a leading systems and service provider. These points serve as guidelines for enhancing operational efficiency and ensuring technological superiority.
Tip 1: Prioritize System Integration: A holistic approach to system design is critical. Ensuring seamless interoperability between avionics, communication systems, and aircraft structures maximizes performance and reduces potential failure points.
Tip 2: Invest in Advanced Materials: Lightweight, high-strength materials are crucial for fuel efficiency and structural integrity. Research and implement advanced composites and alloys to enhance aircraft performance characteristics.
Tip 3: Emphasize Cybersecurity Measures: Implement robust cybersecurity protocols throughout all aircraft systems. Protecting data and ensuring system integrity are paramount in an increasingly interconnected aerospace environment.
Tip 4: Focus on Predictive Maintenance: Utilize data analytics to predict component failures and schedule maintenance proactively. This reduces downtime, extends component lifespan, and lowers overall operational costs.
Tip 5: Streamline Communication Systems: Establish clear and reliable communication channels between pilots, ground control, and maintenance personnel. Effective communication is essential for safe and efficient operations.
Tip 6: Optimize Flight Path Efficiency: Leverage advanced navigation systems and weather data to optimize flight paths for reduced fuel consumption and shorter travel times. Enhanced route planning contributes to cost savings and environmental sustainability.
Tip 7: Implement Advanced Cabin Management Systems: Integrate sophisticated cabin management systems to enhance passenger comfort and entertainment. A positive passenger experience contributes to brand loyalty and airline profitability.
Adherence to these approaches fosters a culture of innovation, safety, and efficiency, leading to improved operational outcomes and sustained competitive advantage within the aerospace sector.
The next section explores the future of aerospace technology and emerging trends that will shape the industry in the coming years.
1. Advanced Avionics Systems
Advanced Avionics Systems are a core element of capabilities, contributing significantly to aircraft performance, safety, and operational efficiency. These systems encompass a wide array of technologies designed to enhance situational awareness, navigation, and overall flight management.
- Flight Management Systems (FMS)
The FMS integrates navigation, performance, and guidance functions to optimize flight profiles. This allows aircraft to fly more efficiently, reducing fuel consumption and emissions. An example includes the utilization of Required Navigation Performance (RNP) procedures, enhancing precision during approaches, particularly in challenging environments. The FMS ensures optimal resource utilization and compliance with airspace regulations.
- Communication, Navigation, and Surveillance (CNS) Systems
CNS systems are critical for maintaining communication with ground control, navigating accurately, and monitoring aircraft position. ADS-B (Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast) is an example of a CNS technology that provides enhanced surveillance capabilities. This enhances safety and enables more efficient air traffic management.
- Electronic Flight Instrument Systems (EFIS)
EFIS replaces traditional analog instruments with digital displays, providing pilots with a consolidated and intuitive presentation of flight data. Head-Up Displays (HUDs) are an advanced form of EFIS that project critical flight information onto the pilot’s line of sight. This reduces workload and improves situational awareness, particularly during critical phases of flight such as takeoff and landing.
- Weather Radar Systems
Advanced weather radar systems provide pilots with real-time information about weather conditions along the flight path. This allows them to avoid hazardous weather, such as thunderstorms and turbulence, ensuring passenger safety and minimizing flight disruptions. Doppler radar technology enhances the accuracy and range of weather detection.
The continuous development and integration of these Advanced Avionics Systems solidify’s position as a leader in providing comprehensive solutions for the aerospace industry. The advancements in avionics technology enable safer, more efficient, and more reliable air travel, contributing to the overall growth and sustainability of the sector.
2. Aerospace Structural Components
Aerospace structural components form a critical part of any aircraft, directly influencing its performance, safety, and longevity. These components, ranging from fuselage sections to wing assemblies, are designed, manufactured, and maintained to meet stringent aerospace standards. Their integrity is paramount, reflecting directly on aircraft reliability and operational efficiency. As such, expertise in the design and production of such components is a crucial aspect of an aerospace entity.
- Material Selection and Engineering
The choice of materials, encompassing aluminum alloys, titanium, composites, and advanced polymers, plays a significant role in the performance of structural components. Their design leverages finite element analysis and computational fluid dynamics, ensuring structural integrity under varied flight conditions. The use of lightweight, high-strength materials to reduce weight and improve fuel efficiency aligns with broader sustainability efforts within the aerospace industry.
- Manufacturing Processes and Quality Control
Manufacturing processes for aerospace structural components involve precision machining, automated fiber placement, and advanced welding techniques. Stringent quality control measures, including non-destructive testing (NDT) and dimensional inspection, ensure adherence to design specifications and regulatory requirements. These processes directly impact the airworthiness and long-term durability of aircraft structures.
- Structural Health Monitoring (SHM)
SHM systems integrate sensors and data analytics to detect damage or degradation in structural components. Continuous monitoring enables proactive maintenance and prevents catastrophic failures. This approach extends the operational lifespan of aircraft and enhances safety by identifying potential issues before they escalate.
- Aerodynamic Design and Optimization
Aerodynamic design is essential for minimizing drag and maximizing lift, influencing aircraft performance and fuel efficiency. Structural components are designed to maintain aerodynamic profiles under various flight loads. Computational fluid dynamics simulations are used to optimize the shape and configuration of these components, reducing fuel consumption and enhancing stability.
The comprehensive approach to aerospace structural components, from material selection to manufacturing and ongoing monitoring, illustrates the commitment to delivering high-performance, safe, and reliable aircraft. The ability to innovate and apply advanced technologies in this domain contributes significantly to the overall competitiveness and sustainability of the aerospace sector.
3. Connectivity & Communication
Connectivity and communication systems represent a critical domain, supporting essential functionalities and enabling the flow of information across various operational elements. Their seamless integration is foundational to performance and efficiency, facilitating real-time data exchange and situational awareness.
- Aircraft Communication Systems
Aircraft communication systems encompass voice and data links between the aircraft, ground control, and other aircraft. These systems enable air traffic control, airline operational control, and passenger communications. Examples include VHF radios for short-range communication and satellite-based systems for long-range communication, ensuring constant connectivity regardless of location. Failure in these systems can lead to operational delays and safety concerns.
- Cabin Connectivity Solutions
Cabin connectivity solutions provide passengers with internet access and entertainment options during flights. These systems often utilize satellite communication and onboard Wi-Fi networks to deliver a seamless experience. Implementation must address bandwidth limitations and security considerations to maintain system reliability and data privacy. High-quality cabin connectivity can significantly enhance passenger satisfaction.
- Network Management and Cybersecurity
Network management and cybersecurity are essential for protecting communication systems from cyber threats and ensuring data integrity. Firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption protocols are implemented to safeguard sensitive information. Robust network management ensures the continuous availability of communication services. A breach in cybersecurity can compromise aircraft systems and data, potentially jeopardizing safety and security.
- Air Traffic Management (ATM) Integration
Integration of communication systems with ATM infrastructure enables seamless data exchange between aircraft and air traffic control centers. This integration enhances situational awareness, reduces congestion, and improves the efficiency of air traffic operations. Data links and automated communication protocols facilitate real-time coordination. Effective ATM integration is critical for ensuring safe and efficient air travel.
The role of connectivity and communication extends beyond simple data transfer. These interconnected facets support critical functionalities and enhance the overall aviation experience, contributing to the continuous improvement of safety and operational efficiency across the aerospace sector.
4. Mission Systems Integration
Mission systems integration represents a critical function within the broader operational scope. It involves the seamless incorporation of diverse technological components into a unified, functional system that meets specific mission requirements. This integration extends across multiple domains, including communication, surveillance, navigation, and weapon systems, contingent upon the nature of the mission. Failure to effectively integrate these systems can lead to compromised performance, reduced operational effectiveness, and potential safety risks. Successful mission systems integration is therefore essential for achieving mission objectives and ensuring the safety of personnel and assets.
As a provider of technologically advanced systems and services within the aerospace sector, a significant aspect of operations involves expertise in mission systems integration. Its involvement in this area encompasses the design, development, and implementation of integrated solutions for a range of applications, including military, commercial, and government projects. For example, integrating advanced sensor packages with communication systems to provide real-time situational awareness in a combat environment, or incorporating weather radar systems with flight management systems to enhance safety and efficiency for commercial airlines, are key examples. Expertise in mission systems integration allows for the tailoring of technological solutions to meet the complex and evolving requirements of clients.
In summary, mission systems integration is a fundamental aspect of aerospace capabilities. Proficiency in this area is crucial for ensuring operational effectiveness and safety across diverse missions. The ability to integrate diverse technologies into a unified system represents a core competency for companies operating in the aerospace and defense industries. Its contributions to mission systems integration significantly enhance the overall capabilities of its clients, supporting their success in demanding and dynamic operational environments. Maintaining a focus on innovation and a commitment to quality are critical for sustaining leadership in this field.
5. Global Service Network
The Global Service Network is an integral component of operations, facilitating the continued airworthiness and operational readiness of its products worldwide. This network ensures that clients receive timely and effective support, regardless of their geographic location. Its existence directly impacts the reliability and lifecycle management of systems and equipment.
- Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) Services
The MRO services constitute a significant aspect of the Global Service Network, providing comprehensive support for avionics, engines, and other critical aircraft components. The network includes strategically located service centers equipped with specialized tools and trained technicians. For instance, a commercial airline experiencing an avionics malfunction in a remote location can rely on the Global Service Network to provide rapid diagnosis and repair services, minimizing aircraft downtime and ensuring the continuity of flight operations. This capability is crucial for maintaining the operational efficiency of airlines globally.
- Spare Parts Availability and Logistics
A reliable supply chain for spare parts is vital for minimizing aircraft downtime and supporting maintenance activities. The Global Service Network maintains a distributed inventory of spare parts, ensuring that critical components are readily available when and where they are needed. This includes managing logistics and transportation to expedite the delivery of parts to service centers and customer locations. The ability to quickly source and deliver spare parts is essential for supporting the operational needs of airlines and other aviation customers. For example, an aircraft on the ground (AOG) situation can be rapidly resolved with the assistance of its global network.
- Technical Support and Training
Technical support and training services are essential for enabling customers to effectively operate and maintain equipment. The Global Service Network provides access to a team of technical experts who can provide guidance and assistance on troubleshooting and maintenance procedures. The network also offers training programs for technicians and engineers, ensuring they have the knowledge and skills necessary to maintain equipment to the highest standards. Skilled technicians are essential for servicing advanced technology, which underscores its commitment to maintaining a technically proficient workforce.
- Field Service Representatives and On-Site Support
The Global Service Network deploys field service representatives to provide on-site support to customers. These representatives can assist with installation, commissioning, and maintenance activities, ensuring that equipment is operating correctly and meeting performance expectations. On-site support is particularly valuable for customers who lack the resources or expertise to perform complex maintenance tasks. For instance, field service engineers might assist a military customer with the integration of systems into a new aircraft platform, providing on-site training and technical assistance. This proximity enhances the overall customer experience.
These facets of the Global Service Network are instrumental in supporting the long-term reliability and performance of systems and equipment. The ability to provide comprehensive support services, regardless of location, is a key differentiator and contributor to customer satisfaction. The Global Service Network directly supports ongoing operations by providing responsive, dependable service that ensures continuous airworthiness.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions and answers address common inquiries regarding operations and products within the aerospace sector. This information aims to provide clear and concise explanations of core concepts and functionalities.
Question 1: What is the scope of activities in the aerospace domain?
The scope encompasses design, manufacture, and service of a wide array of systems and components for commercial, military, and business aviation. These range from avionics and aerostructures to aircraft interiors and mission systems.
Question 2: How are aircraft safety standards upheld through product offerings?
Stringent adherence to industry regulations and internal quality control processes is maintained throughout the design, manufacturing, and testing phases. Redundancy and fail-safe mechanisms are incorporated into critical systems to mitigate potential risks.
Question 3: What measures are taken to ensure cybersecurity within aircraft systems?
Robust cybersecurity protocols are implemented at multiple levels, including hardware and software security measures. Encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems are utilized to protect against cyber threats.
Question 4: How does contribute to sustainability in the aviation industry?
Investment is made in the development of fuel-efficient technologies, lightweight materials, and optimized flight management systems. These innovations reduce fuel consumption and emissions, contributing to a more sustainable aviation sector.
Question 5: What is the procedure for obtaining technical support for systems?
Technical support is available through a global network of service centers and field service representatives. Customers can access online resources, contact technical support teams, or request on-site assistance as needed.
Question 6: How are innovations integrated into existing product lines?
A continuous process of research and development drives innovation, with new technologies and features integrated into existing product lines through upgrades, retrofits, and next-generation designs. This ensures that customers benefit from the latest advancements.
These FAQs offer a concise overview of key aspects. The ongoing commitment to safety, innovation, and customer support underscores the operational philosophy.
The subsequent segment will delve into emerging trends and potential future developments within the aerospace industry.
Conclusion
This exploration has presented a comprehensive overview of the role and impact of a significant entity within the aerospace sector. From its contributions to advanced avionics and structural components to its emphasis on connectivity, mission systems integration, and global service networks, the discussion has illuminated the multifaceted nature of its operations and its influence on the aviation landscape.
The future of aerospace demands continuous innovation and adaptation. Remaining at the forefront of technological advancements and maintaining a steadfast commitment to safety and reliability will be paramount in addressing the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. The ongoing pursuit of excellence is essential for sustained leadership within this dynamic industry.



![Understanding Collins Aerospace Market Cap [Insights] Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions Understanding Collins Aerospace Market Cap [Insights] | Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/th-112-300x200.jpg)

![U.S. Hubs: Collins Aerospace US Locations Guide [2024] Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions U.S. Hubs: Collins Aerospace US Locations Guide [2024] | Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/th-97-300x200.jpg)