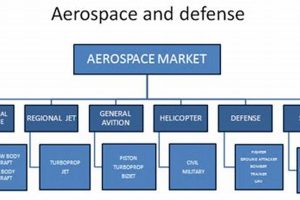
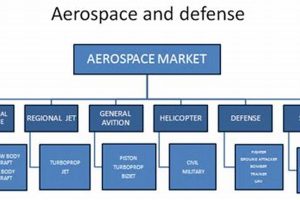
Activities encompassing the research, development, production, and deployment of aerial vehicles and related technologies for national security purposes are a critical component of modern military strategy. These activities include the creation of advanced aircraft, unmanned systems, and associated support infrastructure designed to maintain air superiority and project power globally. The technologies developed in this sector often have dual-use applications, benefiting both military and civilian domains.
Investment in this specialized field yields significant returns through enhanced national security, technological innovation, and economic growth. Historically, advancements in this area have led to breakthroughs in materials science, propulsion systems, and communications technologies, all of which have found applications in commercial aviation, space exploration, and other industries. This ongoing cycle of innovation provides a strategic advantage and strengthens a nation’s overall competitiveness.
Further discussion will delve into specific technological advancements driving progress, explore the current geopolitical landscape influencing development priorities, and analyze the economic impact of governmental and private sector investment in this multifaceted domain. A look at the workforce development and the future technologies on the horizon will also be examined.
Key Considerations for Strategic Investment and Development
The following points highlight crucial aspects for stakeholders involved in the advancement and utilization of specialized aerial technologies for national defense:
Tip 1: Prioritize Research and Development: Consistent investment in fundamental research is essential for maintaining technological superiority. This includes exploring novel propulsion systems, advanced materials, and autonomous control algorithms. For example, funding research into hypersonic flight and directed energy weapons can significantly enhance offensive and defensive capabilities.
Tip 2: Foster Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration between government agencies and private sector entities accelerates innovation and reduces development costs. Sharing expertise and resources through joint ventures can lead to more efficient and effective solutions. An example is the development of new sensor technologies spearheaded by a collaborative effort.
Tip 3: Focus on Cybersecurity: Protecting sensitive data and critical infrastructure from cyber threats is paramount. Robust cybersecurity measures must be integrated into all aspects of design, development, and deployment. The vulnerability of unmanned aerial systems to hacking requires continuous improvement in security protocols.
Tip 4: Emphasize Pilot Training and Proficiency: Highly skilled personnel are crucial for the effective operation and maintenance of sophisticated aerial systems. Comprehensive training programs and realistic simulation environments are essential for developing and sustaining the necessary expertise. Increased investment in advanced pilot training programs is key.
Tip 5: Promote International Cooperation: Collaborating with allies on defense-related aerial projects can enhance interoperability and burden-sharing. Joint development and procurement initiatives can lead to more cost-effective solutions and strengthen strategic alliances. Participating in multinational exercises and technology sharing programs is an example.
Tip 6: Adapt to Evolving Threats: Continuous monitoring of the global security landscape is necessary to anticipate and adapt to emerging threats. Investing in counter-drone technologies and developing strategies to address asymmetric warfare are crucial for maintaining a defensive edge. A focus on adaptive and flexible defense strategies is essential.
Tip 7: Consider Ethical Implications: As aerial technologies become more autonomous, ethical considerations must be addressed. Developing clear guidelines and regulations for the use of lethal autonomous weapons systems is essential to ensure responsible innovation. A focus on responsible and ethical development is paramount.
Adherence to these considerations fosters effective strategic planning, efficient resource allocation, and the development of robust and secure aerial defense capabilities. This enables nations to safeguard their interests and maintain a competitive advantage in an increasingly complex global environment.
The subsequent sections of this article will further elaborate on these critical areas and provide a comprehensive overview of the current state and future trends.
1. Technological Superiority Imperative
The pursuit of technological dominance constitutes a foundational principle within specialized aerial activities for national defense. Maintaining a decisive advantage in air and space capabilities is not merely desirable, but an operational requirement for ensuring national security and projecting global influence. This imperative shapes investment strategies, research and development priorities, and procurement decisions within the sector.
- Advanced Materials and Aerostructures
The development and implementation of advanced materials, such as high-strength alloys and composites, are critical for enhancing aircraft performance, reducing weight, and improving durability. Examples include the use of carbon fiber composites in advanced fighter aircraft and the development of heat-resistant materials for hypersonic vehicles. These innovations directly translate into increased speed, maneuverability, and operational lifespan of aerial assets.
- Next-Generation Propulsion Systems
Investment in cutting-edge propulsion technologies, including advanced jet engines, ramjets, and electric propulsion systems, is essential for achieving superior speed, range, and fuel efficiency. The development of variable cycle engines and hybrid-electric propulsion systems offers the potential to significantly improve the performance characteristics of military aircraft and unmanned aerial vehicles. These advancements contribute to enhanced operational reach and reduced logistical burdens.
- Autonomous Systems and Artificial Intelligence
The integration of autonomous systems and artificial intelligence (AI) into aerial platforms is transforming the landscape of specialized aerial defense. Autonomous capabilities, such as autonomous flight control, target recognition, and decision-making, enable unmanned systems to perform complex missions in contested environments. AI-powered systems also enhance situational awareness, improve decision-making speed, and reduce the cognitive load on human operators. This translates into more effective and efficient utilization of aerial assets.
- Advanced Sensors and Communication Technologies
The deployment of advanced sensors, including high-resolution radar systems, electro-optical/infrared sensors, and electronic warfare systems, is crucial for maintaining situational awareness and detecting threats. Secure and robust communication networks are essential for enabling seamless data exchange and command and control across distributed aerial assets. Examples include the development of advanced radar systems capable of detecting stealth aircraft and the implementation of secure data links for unmanned aerial vehicle operations. These technologies enhance the ability to identify, track, and engage targets in all weather conditions and across vast distances.
These facets of technological superiority, exemplified through continuous innovation and strategic investment, are intrinsically linked to the overall effectiveness of aerial defense. Maintaining a technological edge is paramount for deterring potential adversaries, protecting national interests, and ensuring the success of military operations in the increasingly complex global security environment.
2. Strategic Deterrence Capability
The relationship between strategic deterrence and specialized aerial activities constitutes a critical element of national security. A credible strategic deterrence posture relies significantly on the ability to project power and maintain air superiority, both of which are direct outputs of a robust aerial defense infrastructure. The possession of advanced aircraft, long-range strike capabilities, and effective air defense systems communicates a nation’s resolve and capacity to respond to aggression, thereby discouraging potential adversaries from initiating hostile actions. For instance, the deployment of strategic bombers capable of delivering conventional or nuclear payloads serves as a tangible demonstration of a nation’s commitment to defending its interests. This demonstrable capability dissuades potential aggressors by raising the stakes associated with any contemplated attack.
The effectiveness of strategic deterrence is further enhanced by the integration of diverse aerial assets and advanced technologies. Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) provide persistent surveillance and reconnaissance capabilities, enabling early detection of potential threats and facilitating rapid response. Furthermore, the development and deployment of hypersonic weapons systems creates a strategic advantage by reducing response times and increasing the penetration capabilities of offensive forces. Real-world examples include the U.S. Air Force’s deployment of B-2 Spirit stealth bombers for strategic deterrence missions and the ongoing development of hypersonic cruise missiles by various nations. These initiatives underscore the direct link between advanced aerial technology and the enhancement of strategic deterrence.
Understanding the intrinsic link between strategic deterrence and aerial capabilities is crucial for policymakers and defense strategists. Challenges include maintaining technological superiority in the face of rapid advancements by potential adversaries and adapting to evolving threat landscapes. Ultimately, a well-funded and technologically advanced aerial defense force serves as a cornerstone of strategic deterrence, contributing to regional stability and preventing large-scale conflicts. Continuous investment in research, development, and deployment of cutting-edge aerial technologies is, therefore, essential for maintaining a credible and effective strategic deterrence posture.
3. Global Power Projection
Global power projection, in the context of specialized aerial activities for national defense, represents a nation’s capacity to extend its influence and military capabilities beyond its immediate borders. This capability is inextricably linked to its aerial assets and the technologies that underpin them.
- Strategic Airlift Capabilities
The ability to rapidly deploy troops, equipment, and supplies to distant locations is a cornerstone of global power projection. Strategic airlift aircraft, such as the C-17 Globemaster III and the C-5 Galaxy, enable the swift transportation of personnel and materiel across vast distances. These aircraft facilitate the establishment of forward operating bases, support humanitarian aid operations, and enable rapid response to emerging crises, thereby extending a nation’s influence and ability to intervene in global events.
- Long-Range Strike Capabilities
The capacity to conduct precision strikes against targets located thousands of miles away is a critical component of global power projection. Long-range bombers, such as the B-2 Spirit and the B-52 Stratofortress, equipped with advanced munitions, provide a credible deterrent and enable a nation to project its military force globally. These capabilities are essential for deterring aggression, responding to threats, and safeguarding national interests in distant regions.
- Carrier-Based Aviation
Aircraft carriers serve as mobile airbases, enabling a nation to project its air power to virtually any location on the globe. Carrier-based aircraft, including fighter jets, strike aircraft, and airborne early warning and control (AEW&C) aircraft, provide a flexible and adaptable means of maintaining air superiority, conducting maritime patrols, and supporting ground operations. The presence of an aircraft carrier strike group in a region sends a clear message of a nation’s commitment to defending its interests and maintaining stability.
- Air Refueling Capabilities
The ability to extend the range and endurance of aerial assets through in-flight refueling is a critical enabler of global power projection. Air refueling tankers, such as the KC-46 Pegasus and the KC-135 Stratotanker, allow aircraft to travel greater distances, remain on station for longer periods, and conduct more complex missions. These capabilities are essential for projecting power to distant locations, supporting long-range strike operations, and maintaining a persistent presence in strategically important regions.
The confluence of these aerial capabilities, supported by advanced technologies and skilled personnel, forms the backbone of global power projection. These assets enable a nation to extend its influence, respond to crises, and safeguard its interests across the globe. Investment in these capabilities is paramount for maintaining a credible deterrent and ensuring the ability to project power effectively in an increasingly complex and contested world.
4. Resource Allocation Efficiency
Optimal resource allocation is paramount within specialized aerial vehicle activities related to national security. Efficiency in this context directly impacts operational readiness, technological advancement, and the overall sustainability of a nation’s air defense capabilities. Suboptimal allocation can lead to critical capability gaps, delayed technological innovation, and reduced cost-effectiveness.
- Lifecycle Cost Management
Effective lifecycle cost management requires a comprehensive approach to budgeting and resource allocation, considering the total cost of ownership for aerial assets from procurement to disposal. Examples include investing in durable and easily maintainable aircraft designs to minimize long-term maintenance expenses, implementing predictive maintenance programs to reduce unscheduled downtime, and optimizing supply chain logistics to ensure timely availability of spare parts. Efficient lifecycle cost management maximizes the operational availability of aerial assets while minimizing overall expenditures.
- Prioritized Investment in Emerging Technologies
Strategic allocation of resources toward the development and integration of emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence, autonomous systems, and advanced materials, is critical for maintaining a competitive edge. Examples include funding research and development programs focused on next-generation propulsion systems, advanced sensor technologies, and cyber warfare capabilities. Prioritizing investment in these areas ensures that a nation’s aerial defense force remains at the forefront of technological innovation.
- Streamlined Procurement Processes
Efficient procurement processes are essential for acquiring aerial assets and related equipment in a timely and cost-effective manner. This includes streamlining bureaucratic procedures, fostering competition among suppliers, and leveraging economies of scale through joint procurement initiatives with allied nations. Minimizing delays and reducing administrative overhead in the procurement process ensures that aerial defense capabilities are acquired efficiently and without unnecessary expense.
- Optimized Personnel Management
Effective personnel management is crucial for maximizing the productivity and effectiveness of the workforce supporting aerial defense activities. This includes providing adequate training and development opportunities, implementing performance-based compensation systems, and promoting a culture of continuous improvement. Optimizing personnel management ensures that the available talent is utilized effectively and that the workforce remains motivated and engaged.
These facets of resource allocation efficiency are intrinsically linked to the overall effectiveness of specialized aerial activities for national defense. By prioritizing lifecycle cost management, investing in emerging technologies, streamlining procurement processes, and optimizing personnel management, nations can maximize the return on their investment in aerial defense and maintain a sustainable and effective air force. Such efficiency contributes directly to enhanced operational readiness, technological superiority, and a stronger strategic posture.
5. Interoperability Enhancement
Interoperability enhancement is a critical element within the sphere of specialized aerial activities for national security, acting as a force multiplier for defense capabilities. The ability of various aerial platforms, communication systems, and data networks to seamlessly exchange information and operate in a coordinated manner directly impacts mission effectiveness and reduces operational risks. For example, disparate aircraft types from different branches of the military, or even different nations, must be able to communicate securely and share targeting data in real-time to execute complex joint operations effectively. Failure to achieve sufficient interoperability can lead to delays, miscommunications, and even mission failure. This emphasis has caused various countries to adopt standardized communication protocols.
The significance of interoperability extends beyond tactical scenarios. At the strategic level, it facilitates collaboration between allied forces, promoting burden-sharing and strengthening collective defense capabilities. International military exercises, such as those conducted by NATO, hinge on the ability of participating nations to integrate their aerial assets seamlessly. These exercises identify areas for improvement in interoperability and drive the development of common standards and protocols. Furthermore, it requires standardized data formats and secure communication links.
In conclusion, interoperability enhancement is not merely a desirable feature but a fundamental requirement for modern aerial defense. Addressing the technical and logistical challenges associated with achieving seamless integration across diverse systems is essential for maximizing the effectiveness of aerial operations and strengthening international partnerships. The continued investment in interoperability-focused technologies and protocols remains a strategic imperative for all nations committed to maintaining a robust and responsive aerial defense posture. It involves continuous improvement of communication, data sharing, and command and control systems.
Frequently Asked Questions About Specialized Aerial Activities
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding the specialized activities related to aerial vehicles employed for national defense purposes. These answers aim to provide clarity and foster a better understanding of this critical domain.
Question 1: What distinguishes this specialized field from commercial aviation?
The primary distinction lies in the mission objectives and operational environment. Commercial aviation focuses on the safe and efficient transport of passengers and cargo, while specialized aerial activities prioritize national security objectives, often operating in contested and hazardous environments. The aircraft employed, technologies utilized, and regulatory frameworks governing these activities differ substantially.
Question 2: How does investment in specialized aerial activities contribute to economic growth?
Investment in this sector stimulates technological innovation, creates high-skilled jobs, and generates export opportunities. The development of advanced aircraft and related technologies often leads to breakthroughs that have applications in other sectors of the economy, such as materials science, propulsion systems, and communications technologies. Furthermore, the industry supports a large supply chain of manufacturers and service providers.
Question 3: What are the key challenges facing the sector?
Challenges include maintaining technological superiority in the face of rapid advancements by potential adversaries, adapting to evolving threat landscapes, managing the rising costs of development and procurement, and addressing ethical concerns related to autonomous weapons systems. Securing cyberspace and supply chain vulnerabilities are also paramount challenges.
Question 4: How does the government ensure the responsible use of aerial capabilities?
The government establishes strict guidelines and regulations governing the use of these aerial assets. These guidelines address issues such as targeting protocols, rules of engagement, and the protection of civilian populations. Independent oversight bodies and international treaties also play a role in ensuring responsible utilization.
Question 5: What role do international collaborations play in advancing specialized aerial activities?
International collaborations enable the sharing of expertise, resources, and technologies, leading to more efficient and cost-effective development and procurement. Joint research and development initiatives, technology transfer agreements, and cooperative security arrangements enhance interoperability and strengthen alliances.
Question 6: What are some emerging trends shaping the future?
Emerging trends include the increasing adoption of unmanned systems, the integration of artificial intelligence, the development of hypersonic weapons, the proliferation of counter-drone technologies, and the growing importance of cybersecurity. These trends are driving innovation and transforming the landscape of aerial defense.
In summary, the field of specialized aerial activities is characterized by constant innovation, significant investment, and strategic importance for national security. Effective oversight, ethical considerations, and robust international collaboration are crucial for ensuring its responsible and sustainable development.
The next section will delve into the future of the industry and explore the technologies and strategies that are poised to shape its evolution in the years to come.
Concluding Remarks on Defense Flight Aerospace
This examination has illuminated the multifaceted nature of defense flight aerospace activities, emphasizing their critical role in national security. Key aspects explored include the necessity of technological superiority, the function of strategic deterrence, the impact of global power projection, the imperatives of resource allocation efficiency, and the benefits of interoperability enhancement. These interconnected elements collectively shape a nation’s capacity to maintain air dominance, protect its interests, and project influence in an increasingly complex global environment.
Sustained vigilance and proactive adaptation are paramount. The continued advancement of defense flight aerospace technologies, coupled with strategic international partnerships and a commitment to ethical considerations, will be essential for navigating future challenges and ensuring the long-term security and stability of nations. It is imperative that decision-makers, researchers, and industry leaders remain dedicated to responsible innovation and effective resource management in this vital sector.