Employment opportunities within the specified aircraft manufacturer encompass a broad spectrum of roles, ranging from engineering and design to manufacturing, maintenance, and administrative support. These positions facilitate the creation, upkeep, and operational management of high-end business jets. For example, a prospective employee might find openings for avionics technicians, structural engineers, or marketing specialists.
Securing a position with this company can offer competitive salaries, comprehensive benefits packages, and opportunities for professional development within a technologically advanced environment. The manufacturers historical significance in the aviation industry and its reputation for innovation can provide employees with a sense of stability and pride in their work. Furthermore, these roles often contribute directly to advancements in aircraft technology and customer satisfaction.
The following sections will delve into specific departments and required skills, application processes, and overall employee experience within this renowned organization, providing a clearer understanding of what to expect when pursuing a career there.
The following guidance aims to assist prospective candidates in maximizing their potential when seeking employment at the aforementioned aerospace corporation. Careful consideration of these points can improve the likelihood of a successful application and integration into the organization.
Tip 1: Target Relevant Skillsets: Focus applications on roles aligning with demonstrable skills and experience. For instance, candidates with backgrounds in composite materials should explore manufacturing roles involving these materials.
Tip 2: Highlight Technical Proficiency: Emphasize expertise in relevant software and technologies. Examples include CAD/CAM software for engineering roles or specific aircraft maintenance diagnostic tools for technician positions.
Tip 3: Showcase Industry Awareness: Demonstrate an understanding of the aerospace industry and the company’s position within it. This may involve referencing recent developments in business aviation or the company’s latest aircraft models.
Tip 4: Quantify Achievements: Whenever possible, use data to illustrate accomplishments in previous roles. For example, detailing improvements in production efficiency or cost reductions achieved through specific projects.
Tip 5: Tailor Application Materials: Customize resumes and cover letters to each specific job posting. Generic applications are less effective than those directly addressing the requirements outlined in the job description.
Tip 6: Prepare for Technical Interviews: Expect rigorous technical assessments during the interview process. Review fundamental engineering principles, manufacturing processes, or relevant software applications depending on the targeted role.
Tip 7: Research the Company Culture: Gain insights into the company’s values and work environment. Resources such as employee reviews and industry publications can provide valuable information.
Adhering to these guidelines can enhance a candidate’s competitiveness and increase the probability of securing a fulfilling and impactful career. These preparatory steps reflect a commitment to excellence and a genuine interest in contributing to the organization’s success.
The subsequent sections will explore career paths and the application procedures in more detail.
1. Engineering
Engineering disciplines form the bedrock of this aerospace manufacturer’s operations. These specialized roles drive aircraft design, development, testing, and certification. A direct correlation exists between the availability of proficient engineers and the company’s capacity to innovate and produce cutting-edge business jets. Mechanical, electrical, aerospace, and software engineering expertise are all critical components, working synergistically to ensure airworthiness, performance, and passenger comfort. For instance, engineers are directly responsible for designing aerodynamic structures, developing advanced avionics systems, and optimizing fuel efficiency.
The practical application of engineering principles extends to the continuous improvement of manufacturing processes and the resolution of technical challenges that arise during production. Engineers are involved in material selection, stress analysis, and the implementation of quality control measures. They collaborate closely with manufacturing teams to streamline workflows, reduce costs, and ensure adherence to stringent safety regulations. A specific example is the development of new composite materials that enhance aircraft strength while reducing weight, directly improving performance characteristics.
In summary, engineering is an indispensable function within the company’s ecosystem. The success of the organization hinges on the expertise and ingenuity of its engineering workforce. While challenges related to technological advancements and regulatory compliance persist, a strong engineering foundation enables the company to maintain its competitive edge and deliver innovative products to the market, ensuring the continuity of opportunities for engineering professionals.
2. Manufacturing
The manufacturing division constitutes a significant segment of the overall employment landscape within this aerospace corporation. These roles are directly responsible for the physical construction and assembly of aircraft, encompassing a range of specialized skills and trades. Efficient manufacturing processes are fundamental to meeting production targets, maintaining quality standards, and ultimately, delivering finished aircraft to customers. A disruption in manufacturing can, therefore, have cascading effects on the entire organization, impacting delivery schedules, revenue, and customer satisfaction. Real-life examples include roles such as aircraft assemblers, composite technicians, and machinists, each playing a critical part in the creation of a finished aircraft. Understanding the importance of manufacturing within the context of job opportunities reveals the company’s reliance on skilled labor and adherence to rigorous production protocols.
The practical application of manufacturing principles translates into the day-to-day tasks of assembling fuselage sections, installing wiring harnesses, and fitting interior components. Employees in these positions must adhere to strict tolerances and quality control guidelines, often utilizing specialized tools and equipment. Further, the manufacturing division continually adopts new technologies and processes to improve efficiency and reduce waste. For example, the implementation of automated drilling systems or the use of 3D printing for prototyping components can streamline production timelines and enhance the precision of manufactured parts. These advancements require manufacturing employees to undergo continuous training and adapt to evolving industry standards.
In conclusion, manufacturing is an integral component of the organizations operational success. The demand for skilled manufacturing professionals remains a key factor in the company’s ability to meet market demands and maintain its position as a leader in the business aviation sector. While challenges such as supply chain disruptions and increasing production costs persist, a strong focus on efficient manufacturing processes and workforce development enables the company to navigate these obstacles effectively, reinforcing the long-term significance of manufacturing jobs within the organization.
3. Maintenance
Aircraft maintenance represents a critical and substantial aspect of employment opportunities within this aerospace organization. The longevity, safety, and operational efficiency of the aircraft fleet are directly dependent on the expertise and diligence of maintenance personnel. This division encompasses roles ranging from routine inspections and preventative maintenance to complex repairs and overhauls. Failure to maintain aircraft to the prescribed standards can result in compromised safety, regulatory non-compliance, and significant financial losses due to grounded aircraft and potential legal ramifications. For instance, experienced airframe and powerplant (A&P) technicians are essential for diagnosing mechanical issues, performing engine repairs, and ensuring that all systems operate within designated parameters.
The practical application of maintenance protocols involves adhering to stringent FAA regulations and company-specific maintenance manuals. Technicians utilize specialized tools and diagnostic equipment to identify potential problems and implement corrective actions. Furthermore, the maintenance division is often at the forefront of implementing service bulletins and airworthiness directives issued by regulatory authorities or the manufacturer. For example, a maintenance team might be tasked with retrofitting an entire fleet of aircraft with upgraded avionics systems or reinforcing wing structures to address fatigue concerns. The meticulous execution of these procedures requires a high degree of technical proficiency and attention to detail.
In summary, aircraft maintenance is a cornerstone of the company’s operational model. The continued demand for skilled maintenance technicians and engineers underscores the critical role this division plays in ensuring the airworthiness and reliability of the aircraft fleet. While challenges such as aging aircraft, increasing maintenance costs, and a shortage of qualified technicians persist, a proactive approach to maintenance training, technological innovation, and adherence to regulatory standards enables the company to mitigate these risks and maintain its commitment to safety and operational excellence, further emphasizing the significance of related employment positions.
4. Administration
Administrative functions are essential for the efficient operation of this aerospace manufacturer, directly impacting the productivity and efficacy of all departments, including engineering, manufacturing, and maintenance. These roles provide the necessary support to ensure that technical personnel can focus on their specialized tasks, ultimately contributing to the overall success of the organization.
- Human Resources
This facet involves recruiting, hiring, and managing employees. It includes creating job descriptions, conducting interviews, processing payroll, administering benefits, and ensuring compliance with labor laws. In the context of jobs at this company, Human Resources plays a critical role in attracting and retaining top talent in highly competitive fields. For instance, HR professionals are responsible for developing competitive compensation packages and career development programs to incentivize skilled engineers and technicians to join and remain with the company.
- Finance and Accounting
This department oversees the financial health of the organization, managing budgets, tracking expenses, preparing financial reports, and ensuring compliance with accounting regulations. Within an aerospace context, finance and accounting professionals are involved in managing large-scale capital expenditures for aircraft development, negotiating contracts with suppliers, and analyzing the profitability of various product lines. Their expertise ensures the financial stability and sustainability of the company.
- Legal and Compliance
This facet focuses on ensuring that the company operates within the bounds of all applicable laws and regulations. This includes drafting and reviewing contracts, managing intellectual property, and ensuring compliance with aviation safety regulations. In the aerospace industry, legal and compliance professionals are instrumental in navigating complex regulatory frameworks, such as those imposed by the FAA, and mitigating legal risks associated with aircraft design, manufacturing, and operation.
- Information Technology
The IT department manages the company’s computer systems, networks, and data infrastructure. This includes providing technical support, ensuring data security, and developing and implementing IT solutions to improve efficiency and productivity. Given the increasing reliance on technology in aerospace manufacturing and design, IT professionals are crucial for maintaining the integrity of critical data, supporting engineering simulations, and facilitating communication and collaboration across different departments.
These administrative facets are inextricably linked to all functions within this aerospace corporation. Opportunities within these departments support the manufacturing, engineering, and management efforts vital to delivering high-quality, safe, and technologically advanced aircraft. The effectiveness of these administrative components directly impacts the company’s ability to compete and thrive in the global aerospace market. For example, efficiently managing supply chain logistics through effective IT solutions, and maintaining a legally compliant and safe work environment contribute to its operational excellence.
5. Innovation
Innovation is a fundamental driver of success and a core component within the employment structure of this aerospace manufacturer. Its influence extends across all departments, from engineering and design to manufacturing and customer support. The creation of novel technologies, designs, and processes directly contributes to the company’s competitive advantage and market leadership. A tangible example is the development and implementation of advanced winglet designs that improve fuel efficiency and aircraft range, directly impacting customer value and operational costs. This requires a workforce that is not only technically proficient but also possesses a mindset geared toward problem-solving, creativity, and continuous improvement. Therefore, a robust culture of innovation is inextricably linked to the availability of challenging and rewarding positions for individuals with the aptitude and drive to push technological boundaries.
The practical application of an innovative approach manifests in various ways throughout the organization. Engineers are encouraged to explore unconventional design concepts and leverage cutting-edge materials. Manufacturing teams seek ways to optimize production processes and reduce waste through the adoption of automation and advanced manufacturing techniques. Even administrative departments contribute by developing innovative solutions for streamlining operations and improving employee engagement. These multifaceted efforts necessitate the cultivation of an environment that fosters experimentation, collaboration, and the sharing of knowledge. The company’s investment in research and development, along with its commitment to supporting employee-driven innovation initiatives, underscores the importance of this principle.
In summary, innovation is not merely a buzzword but a vital engine for growth and sustainability. It significantly shapes the nature of positions within the company, attracting individuals with the skills and passion to contribute to groundbreaking advancements in business aviation. While maintaining a commitment to safety and reliability remains paramount, the ability to adapt and embrace new ideas is crucial for continued success in a rapidly evolving industry. This reinforces the critical link between a culture of innovation and the creation of fulfilling and impactful employment opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Employment Opportunities
The following section addresses common inquiries related to job prospects, application procedures, and employee expectations. The information presented aims to provide clarity and guidance for prospective candidates.
Question 1: What are the typical educational requirements for engineering positions?
Engineering roles generally necessitate a bachelor’s degree in a relevant field, such as aerospace, mechanical, electrical, or computer engineering. Advanced degrees, such as a Master’s or Doctorate, may be required for specialized research or leadership positions.
Question 2: What types of experience are considered valuable for manufacturing roles?
Experience in aircraft assembly, composite fabrication, machining, or related manufacturing processes is highly regarded. Certifications, such as those from vocational schools or apprenticeship programs, can also enhance a candidate’s qualifications.
Question 3: Are there opportunities for professional development within the organization?
The company offers a variety of training and development programs to support employee growth. These may include technical training, leadership development courses, and tuition reimbursement for advanced education.
Question 4: How competitive is the application process for sought-after positions?
The application process can be highly competitive, particularly for roles requiring specialized skills or experience. Candidates are advised to thoroughly review job descriptions, tailor their application materials, and highlight relevant accomplishments.
Question 5: What is the company’s approach to diversity and inclusion?
The organization is committed to fostering a diverse and inclusive work environment. This commitment is reflected in recruitment practices, employee training programs, and initiatives to promote equal opportunities for all individuals.
Question 6: What are the typical benefits offered to employees?
Benefits packages typically include medical, dental, and vision insurance, paid time off, retirement savings plans, and life insurance. Specific benefits may vary depending on the position and location.
The insights provided should assist in understanding the company’s employment landscape. Prospective candidates are encouraged to conduct thorough research and carefully consider their qualifications before applying.
The subsequent section will provide additional information.
Conclusion
This exposition has provided a detailed overview of employment prospects, encompassing engineering, manufacturing, maintenance, administration, and innovation. The preceding analysis has illuminated the diverse range of roles available and the skills and qualifications required for success. The company’s commitment to fostering a diverse and inclusive workplace, coupled with its emphasis on continuous improvement and technological advancement, further shapes the nature of its roles.
Potential applicants should carefully evaluate their skills and career aspirations against the opportunities described. The pursuit of positions at this organization represents not only a job search but also an engagement with a legacy of aerospace engineering and design. Interested parties are encouraged to consult the company’s official website for the most up-to-date listings and application guidelines.


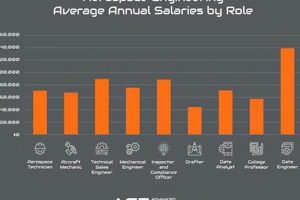

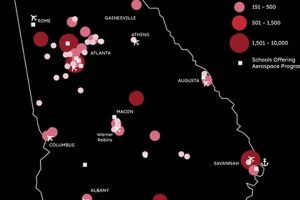
![Aerospace Jobs: Engineer Job Growth [Trends & Outlook] Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions Aerospace Jobs: Engineer Job Growth [Trends & Outlook] | Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/th-861-300x200.jpg)

