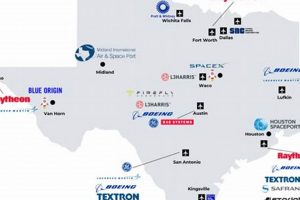
Opportunities within the aerospace sector at Lee Aerospace involve various roles contributing to aircraft component manufacturing, maintenance, and related services. These positions often encompass engineering, production, quality control, and administrative functions, supporting the company’s operations. Examples include aircraft painters, engineers specializing in avionics or structural design, and quality assurance inspectors.
Employment at such entities can offer individuals career development within a technically advanced field, potentially providing competitive compensation and benefits packages. The aerospace industry has a long history of innovation and skilled labor demand, and companies like Lee Aerospace contribute to both local economies and the global aviation supply chain. These organizations often foster a culture of precision, safety, and continuous improvement.
The following sections will elaborate on specific career paths, required qualifications, and the overall employment landscape within this specialized segment of the aerospace industry, providing a deeper understanding of the potential opportunities available.
The following guidance is provided to assist individuals seeking employment within the aerospace sector, particularly at entities like Lee Aerospace. Adherence to these recommendations can improve the likelihood of securing a suitable position.
Tip 1: Target Relevant Skills: Focus on developing skills directly applicable to aerospace manufacturing and maintenance, such as aircraft painting, sheet metal work, or avionics repair. Certifications and training programs in these areas are highly valued.
Tip 2: Emphasize Quality Assurance Experience: Highlight any experience with quality control procedures, inspections, or regulatory compliance relevant to the aviation industry. Familiarity with AS9100 standards is advantageous.
Tip 3: Network Within the Industry: Attend industry events, join professional organizations, and connect with individuals working in aerospace manufacturing. Networking can provide valuable insights and potential job leads.
Tip 4: Tailor Resumes and Cover Letters: Customize application materials to match the specific requirements of each position, emphasizing relevant experience and qualifications. Generic applications are less likely to be successful.
Tip 5: Prepare for Technical Interviews: Expect technical interviews that assess practical knowledge and problem-solving abilities. Review fundamental concepts related to aircraft structures, systems, and manufacturing processes.
Tip 6: Research the Company: Demonstrate a thorough understanding of Lee Aerospace’s products, services, and company culture. This shows genuine interest and commitment.
Tip 7: Highlight Safety Consciousness: Emphasize a strong commitment to safety protocols and procedures. The aerospace industry prioritizes safety above all else.
By focusing on relevant skills, demonstrating quality assurance expertise, and actively networking, individuals can significantly increase their chances of securing a fulfilling career in this dynamic field.
The subsequent sections will delve further into specific roles and the overall outlook for individuals pursuing careers within this sector.
1. Manufacturing Expertise
Manufacturing expertise is fundamentally connected to employment opportunities at Lee Aerospace. It constitutes a core requirement across various roles, shaping the skills and knowledge expected of employees and influencing the organization’s operational capabilities.
- Precision Fabrication and Assembly
This involves the accurate cutting, shaping, and joining of materials to create aircraft components. Proficiency in techniques such as sheet metal forming, welding, and composite material layup is crucial. For example, manufacturing winglets requires precise measurements, adherence to stringent tolerances, and meticulous assembly to ensure aerodynamic performance. Such fabrication expertise directly contributes to the quality and reliability of aircraft parts produced.
- Process Optimization and Efficiency
The ability to streamline manufacturing processes, reduce waste, and improve production efficiency is highly valued. This encompasses lean manufacturing principles, statistical process control, and the implementation of automation technologies. For instance, optimizing the painting process for aircraft interiors can minimize material usage, reduce drying time, and enhance the consistency of the finish. These improvements directly impact the cost-effectiveness and competitiveness of Lee Aerospace’s operations.
- Quality Control and Inspection
Ensuring that manufactured components meet stringent quality standards and regulatory requirements is paramount. This requires expertise in nondestructive testing methods, dimensional metrology, and visual inspection techniques. For example, inspecting aircraft windows for scratches, blemishes, or structural defects using specialized equipment ensures compliance with aviation safety regulations. Effective quality control safeguards the integrity of the final product and prevents potential failures in service.
- Equipment Operation and Maintenance
Operating and maintaining specialized manufacturing equipment, such as CNC machines, paint booths, and autoclaves, is essential for smooth production. This demands technical proficiency in equipment setup, troubleshooting, and preventative maintenance procedures. For example, calibrating a CNC milling machine to precise specifications ensures accurate machining of aircraft components. Proper equipment management minimizes downtime and maximizes productivity.
The facets of manufacturing expertise directly impact the nature and availability of positions at Lee Aerospace. From skilled technicians to process engineers, the organization relies on individuals with a strong foundation in manufacturing principles and practices to maintain its position as a provider of aerospace solutions. The demand for skilled professionals in these areas is expected to remain robust as the company continues to innovate and expand its operations.
2. Engineering Innovation
Engineering innovation is a critical driver of opportunities at Lee Aerospace. It underpins the company’s ability to develop advanced products and solutions, attracting talent and shaping the skills required across various employment roles.
- Design Optimization for Performance and Efficiency
This involves leveraging engineering principles and simulation tools to optimize aircraft component designs for improved aerodynamic performance, reduced weight, and enhanced structural integrity. For example, Lee Aerospace might employ computational fluid dynamics (CFD) to refine the shape of a winglet, minimizing drag and maximizing lift. Such optimization directly translates into tangible benefits for airline operators, such as lower fuel consumption and increased payload capacity.
- Materials Science and Application
The selection and application of advanced materials, such as composites and lightweight alloys, are pivotal for enhancing aircraft performance and durability. Engineers must possess a thorough understanding of material properties, manufacturing processes, and structural analysis techniques. For instance, the adoption of carbon fiber reinforced polymers (CFRP) for aircraft interior components can significantly reduce weight compared to traditional materials, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and passenger comfort.
- Systems Integration and Automation
Integrating complex systems, such as avionics, lighting, and environmental control, requires expertise in electrical engineering, software development, and systems engineering principles. Furthermore, the implementation of automation technologies, such as robotics and automated inspection systems, can improve manufacturing efficiency and product quality. For example, integrating LED lighting systems into aircraft cabins requires careful consideration of power consumption, heat dissipation, and electromagnetic compatibility. Automated inspection systems can detect subtle defects in manufactured components that might be missed by human inspectors.
- Research and Development (R&D) for Future Technologies
Investing in R&D is essential for driving innovation and maintaining a competitive edge in the aerospace industry. This encompasses exploring emerging technologies, conducting feasibility studies, and developing prototypes for new products and services. For example, Lee Aerospace might invest in researching advanced window technologies, such as electrochromic windows that automatically adjust tint in response to sunlight. Successful R&D efforts can lead to the creation of new markets and the expansion of the company’s product portfolio.
These facets of engineering innovation directly influence the demand for skilled engineers and technicians at Lee Aerospace. From design engineers to materials scientists to systems integrators, the organization relies on individuals with a strong foundation in engineering principles and a passion for innovation to drive its growth and success. The continued emphasis on R&D ensures that Lee Aerospace remains at the forefront of aerospace technology, creating exciting opportunities for talented individuals seeking to contribute to the future of aviation.
3. Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is integral to operations and subsequently, employment opportunities, at Lee Aerospace. It encompasses a systematic approach to ensuring that products and services meet predetermined standards and regulatory requirements, thereby influencing the skills and expertise sought in prospective employees.
- Inspection and Testing Protocols
This facet involves rigorous examination of materials, components, and finished products to identify defects or deviations from specifications. Certified inspectors utilize specialized equipment and techniques, such as nondestructive testing (NDT) methods, to assess structural integrity and performance. For example, x-ray inspection of composite materials detects internal flaws that could compromise aircraft safety. Adherence to these protocols is a non-negotiable requirement for production personnel.
- Documentation and Record Keeping
Meticulous documentation of all quality-related activities, including inspection results, corrective actions, and process changes, is essential for traceability and accountability. Detailed records demonstrate compliance with industry standards and facilitate continuous improvement efforts. For example, maintaining a comprehensive audit trail of raw material sourcing, manufacturing processes, and final product testing provides evidence of adherence to aviation regulations. This rigorous record-keeping necessitates personnel with strong attention to detail and organizational skills.
- Compliance with Regulatory Standards
The aerospace industry is subject to stringent regulatory oversight by agencies such as the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA). Lee Aerospace must adhere to these regulations to ensure the safety and reliability of its products. This requires a thorough understanding of applicable standards, such as AS9100, and the implementation of processes to ensure compliance. For example, documenting and validating all design changes to meet airworthiness requirements is critical. Personnel involved in these activities must possess a deep understanding of aviation regulations and quality management systems.
- Continuous Improvement Initiatives
Quality assurance is not a static process; it involves ongoing efforts to identify areas for improvement and implement changes to enhance product quality and process efficiency. This requires a culture of continuous learning and a commitment to data-driven decision-making. For example, analyzing customer feedback to identify recurring defects and implementing corrective actions to prevent future occurrences is essential. Employees at all levels are expected to contribute to these initiatives, requiring a proactive and problem-solving mindset.
These interconnected facets of quality assurance directly impact the types of employment opportunities available at Lee Aerospace. The company seeks individuals with the technical skills, attention to detail, and commitment to regulatory compliance necessary to uphold the highest standards of quality. This emphasis on quality not only ensures the safety and reliability of its products but also contributes to the company’s reputation and long-term success.
4. Aircraft Components
The manufacture, maintenance, and distribution of aircraft components are central to the existence and operation of companies such as Lee Aerospace. Therefore, a direct correlation exists between the demand for skilled labor in the production of these components and the nature of employment opportunities within the organization. Without the production, repair, and distribution of aircraft parts, the fundamental business model of such companies would cease to exist. For example, if Lee Aerospace specializes in aircraft windows and interior components, its workforce must include individuals skilled in glass cutting, shaping, polishing, and installation, as well as those familiar with the materials science and engineering principles applicable to interior design and functionality. The practical significance is that the specific types of aircraft components a company focuses on directly define the skills and positions it requires.
The interplay between aircraft components and employment is also influenced by regulatory frameworks and technological advancements. Stringent aviation safety regulations necessitate highly trained quality control personnel who can ensure that all manufactured or repaired components meet exacting standards. Furthermore, technological advancements in materials, manufacturing processes, and design software require continual training and adaptation of the workforce. As an example, the increasing use of composite materials in aircraft structures requires engineers and technicians skilled in composite layup, curing, and inspection techniques. This dynamic environment means that the jobs available are not static but evolve in response to changing industry demands and technological innovations.
In summary, the connection between aircraft components and employment opportunities within companies like Lee Aerospace is undeniable. The specific types of components handled, the regulatory environment, and technological advancements all contribute to the skills and expertise demanded of the workforce. Challenges arise in the need for continuous training and adaptation to new technologies, but the understanding of this link is crucial for both companies seeking to fill positions and individuals looking to pursue careers in this segment of the aerospace industry. The ability to produce and maintain high-quality aircraft components forms the bedrock of these businesses and defines the scope and nature of their employment needs.
5. Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is an indispensable element influencing the landscape of opportunities within companies like Lee Aerospace. Adherence to stringent aviation regulations mandates specific expertise and dictates the scope and nature of numerous roles. Positions directly involved in ensuring compliance are critical for the continued operation and success of the organization.
- FAA Compliance Officer/Specialist
This role involves interpreting and implementing Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) regulations related to aircraft component manufacturing, maintenance, and repair. Duties include developing compliance programs, conducting internal audits, and acting as a liaison with regulatory agencies. For example, this specialist would ensure all manufacturing processes adhere to FAA guidelines regarding materials, fabrication techniques, and safety protocols. The necessity for this role is borne out of strict adherence to aviation safety standards.
- Quality Assurance Engineer
Quality Assurance Engineers play a crucial role in ensuring that all products and processes meet regulatory and company standards. They develop and implement quality control procedures, conduct inspections, and analyze data to identify areas for improvement. For example, a quality assurance engineer might oversee the non-destructive testing of aircraft windows to verify structural integrity and compliance with safety regulations. This requires detailed knowledge of engineering principles and regulatory requirements.
- Documentation Specialist
This position focuses on the creation and maintenance of documentation required for regulatory compliance, including technical manuals, inspection reports, and certification paperwork. Accurate and complete documentation is essential for demonstrating adherence to industry standards and facilitating audits. For example, the specialist must ensure all materials used in aircraft interiors are properly documented and certified as flame-resistant, as required by aviation regulations. This role demands strong organizational and writing skills.
- Environmental Compliance Manager
With increased focus on environmental sustainability, this role ensures that operations comply with environmental regulations related to emissions, waste disposal, and hazardous materials handling. Responsibilities include developing environmental management plans, conducting audits, and implementing corrective actions. For instance, the environmental compliance manager would ensure that paint booths and other manufacturing processes meet air quality standards and that waste materials are disposed of properly. This position necessitates knowledge of environmental regulations and sustainable practices.
These examples demonstrate how regulatory compliance shapes the spectrum of employment opportunities at entities such as Lee Aerospace. The demand for professionals equipped with the knowledge and skills to navigate complex regulatory frameworks and ensure adherence to industry standards is expected to remain robust as the aviation industry continues to prioritize safety, quality, and environmental responsibility. Those possessing applicable certifications and experience are likely to be in high demand within this sector.
6. Technical Skills
Technical skills are the bedrock of the workforce at Lee Aerospace, directly influencing the organization’s operational capabilities and shaping the opportunities available to prospective employees. These skills are not merely desirable; they are essential for ensuring the precision, safety, and reliability demanded by the aerospace industry.
- CAD/CAM Proficiency
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) skills are paramount for engineers and technicians involved in the design, modeling, and manufacturing of aircraft components. For example, CAD software is utilized to create detailed blueprints of aircraft windows, ensuring accurate dimensions and adherence to specifications. CAM software translates these designs into instructions for CNC machines, automating the manufacturing process. This proficiency directly impacts efficiency, precision, and the ability to innovate new designs.
- Materials Science and Engineering Expertise
A deep understanding of materials science and engineering principles is essential for selecting appropriate materials for aircraft components, ensuring their strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. For example, knowledge of composite materials is crucial for manufacturing lightweight yet strong aircraft interiors. Engineers must be able to analyze material properties, conduct stress tests, and select appropriate manufacturing processes to ensure the structural integrity of components. This expertise directly affects the safety and longevity of aircraft components.
- Avionics and Electrical Systems Knowledge
Technicians and engineers working on aircraft avionics and electrical systems must possess a thorough understanding of electrical circuits, wiring diagrams, and troubleshooting techniques. For instance, diagnosing and repairing faulty wiring in an aircraft lighting system requires precise testing equipment and a deep understanding of electrical principles. This knowledge is crucial for ensuring the safe and reliable operation of essential aircraft systems.
- Quality Control and Inspection Techniques
Implementing and conducting quality control and inspection procedures require comprehensive knowledge of industry standards, metrology equipment, and testing methodologies. The application of non-destructive testing (NDT) methods, such as ultrasonic testing or radiography, is vital for detecting hidden flaws in aircraft components without causing damage. Proper execution of these techniques ensures that all components meet stringent safety and performance requirements, minimizing the risk of failures during operation.
These technical skills are not isolated competencies, but rather interconnected elements that contribute to the overall quality and efficiency of operations at Lee Aerospace. The demand for individuals possessing these skills is consistently high, reflecting the organization’s commitment to excellence and its position as a provider of advanced aerospace solutions. As technology advances and the aerospace industry evolves, the need for continuous learning and skill development will remain paramount for those seeking to advance their careers within this dynamic sector.
7. Career Advancement
Career advancement within entities such as Lee Aerospace represents a tangible incentive and outcome of dedicated service, skill acquisition, and performance. The trajectory of an employee’s career is shaped by factors intrinsic to both the individual and the organization.
- Internal Promotion Policies
Organizations often prioritize internal candidates for higher-level positions, particularly those demonstrating consistent performance and a commitment to professional development. Lee Aerospace, for instance, may have established policies that favor promoting from within, providing employees with a clear pathway for advancement. An aircraft mechanic demonstrating exceptional skills and leadership potential could be promoted to a supervisory role, overseeing a team of technicians and ensuring the quality of maintenance operations. Such internal promotion policies create a culture of loyalty and incentivize employees to invest in their long-term career growth within the company.
- Skill Enhancement Opportunities
The availability and utilization of skill enhancement opportunities directly impact an employee’s potential for career progression. Companies investing in training programs, certifications, and educational resources empower employees to acquire new skills and knowledge, making them more competitive for advancement opportunities. For example, Lee Aerospace might offer employees access to specialized training in composite materials, avionics repair, or quality assurance, enhancing their expertise and preparing them for roles with greater responsibility. The continuous development of technical expertise is a hallmark of career growth in technically demanding fields.
- Mentorship and Sponsorship Programs
Mentorship and sponsorship programs provide valuable guidance and support for employees seeking to advance their careers. Experienced leaders can offer insights into organizational dynamics, career planning strategies, and skill development opportunities. For example, a senior engineer at Lee Aerospace might mentor a junior engineer, providing advice on project management, technical problem-solving, and professional networking. These programs often help employees navigate the complexities of the organization and identify opportunities for growth that might otherwise be overlooked. Mentorship programs are especially beneficial for individuals from underrepresented groups, facilitating their career advancement and promoting diversity within the leadership ranks.
- Performance Recognition and Rewards
Formal recognition of employee achievements and contributions can be a powerful motivator for career advancement. Companies implementing performance-based reward systems, such as bonuses, promotions, and increased responsibilities, incentivize employees to strive for excellence and demonstrate their value to the organization. For example, an employee who consistently exceeds performance targets in aircraft window production might receive a bonus or be promoted to a lead technician role, recognizing their contributions and providing opportunities for further career development. Recognition of performance is a strong incentive for dedicated and ambitious employees.
These facets underscore the multifaceted relationship between career advancement and employment within organizations like Lee Aerospace. The existence and active promotion of internal promotion pathways, skill development, mentorship opportunities, and performance recognition are key components for career progress.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Lee Aerospace Jobs
The following section addresses common inquiries related to employment opportunities at Lee Aerospace. The information is intended to provide clarity for potential applicants.
Question 1: What types of positions are typically available at Lee Aerospace?
Lee Aerospace offers a range of positions spanning manufacturing, engineering, quality assurance, and administrative functions. Specific roles may include aircraft painters, avionics technicians, structural engineers, quality inspectors, and customer service representatives. Open positions will vary based on the current needs of the organization.
Question 2: What qualifications are generally required for manufacturing roles?
Manufacturing roles often require a high school diploma or equivalent, along with vocational training or certification in a relevant field, such as aircraft mechanics, sheet metal fabrication, or welding. Experience in a manufacturing environment, particularly within the aerospace industry, is generally preferred. Certain positions may require specific certifications, such as FAA Airframe and Powerplant licenses.
Question 3: What education and experience are necessary for engineering positions?
Engineering positions typically require a bachelor’s degree in a relevant engineering discipline, such as aerospace, mechanical, or electrical engineering. Experience in aircraft design, structural analysis, or avionics systems is often required. Advanced degrees and professional certifications may be preferred for senior engineering roles.
Question 4: How does Lee Aerospace ensure quality and safety?
Lee Aerospace adheres to stringent quality control processes and complies with all applicable aviation regulations, including those set forth by the FAA. The company maintains a comprehensive quality management system and employs certified quality inspectors to ensure that all products and services meet the highest standards of safety and reliability.
Question 5: What opportunities for professional development are offered to employees?
Lee Aerospace recognizes the importance of employee development and provides opportunities for training, certification, and continuing education. The company may offer tuition reimbursement programs, in-house training sessions, and access to external workshops and conferences to enhance employee skills and knowledge.
Question 6: How does one apply for a position at Lee Aerospace?
Applicants can typically find current job openings on the Lee Aerospace website or through online job boards. Applications generally require a resume, cover letter, and completion of an online application form. Candidates are encouraged to carefully review the job descriptions and tailor their application materials to highlight relevant skills and experience.
These answers provide a general overview of common questions regarding employment at Lee Aerospace. For the most up-to-date information, prospective applicants should consult the company’s official website or contact the human resources department directly.
The subsequent section will provide final thoughts and conclusions regarding the topic of Lee Aerospace Jobs.
Conclusion
This exploration of employment opportunities within Lee Aerospace has highlighted several key aspects: the diverse range of positions available, the critical importance of technical skills and regulatory compliance, and the potential for career advancement. The demand for skilled professionals in manufacturing, engineering, and quality assurance remains a consistent theme, reflecting the company’s commitment to high standards and its role in the aerospace industry. A robust understanding of these facets is vital for any individual considering a career at this organization.
The future of Lee Aerospace, and indeed the broader aerospace sector, depends on a workforce equipped with the knowledge and adaptability to meet evolving challenges. Prospective employees are encouraged to carefully consider their skills and qualifications against the specific requirements of available positions, and to pursue continuous learning to remain competitive in a demanding field. The opportunities within aerospace are significant, and thoughtful preparation can pave the way for a rewarding and impactful career.