Organizations designing, manufacturing, and operating aircraft, spacecraft, rockets, and related systems within the United States constitute a significant sector of the national economy. These entities contribute substantially to both defense and civilian endeavors. As an example, a firm specializing in the production of commercial airliners falls under this classification.
The contributions of these organizations are vital to national security, technological innovation, and economic growth. They drive advancements in materials science, propulsion systems, and automation, resulting in tangible benefits for various industries beyond aerospace. Historically, government initiatives and investments have played a crucial role in fostering the development and expansion of this sector.
The following sections will explore key players in this field, examining their respective areas of expertise, contributions to the industry, and recent developments that are shaping the future of flight and space exploration.
Achieving and sustaining a leading position within the competitive aerospace landscape demands a multifaceted approach encompassing technological superiority, operational efficiency, and a proactive engagement with evolving market dynamics. The subsequent insights distill key principles observed among prominent U.S. aerospace entities.
Tip 1: Prioritize Research and Development Investment: Maintaining a competitive edge necessitates consistent and substantial investment in research and development. Organizations should allocate resources to explore emerging technologies, such as advanced materials, autonomous systems, and sustainable propulsion, to secure future market share.
Tip 2: Cultivate Strategic Partnerships: Collaboration with universities, government agencies, and other industry players can accelerate innovation and expand access to specialized expertise. Forming strategic alliances allows organizations to share resources, mitigate risks, and collectively address complex challenges.
Tip 3: Emphasize Operational Excellence: Streamlining manufacturing processes, optimizing supply chains, and implementing rigorous quality control measures are crucial for enhancing efficiency and reducing costs. Organizations should adopt Lean methodologies and Six Sigma principles to improve operational performance.
Tip 4: Foster a Culture of Innovation: Creating an environment that encourages experimentation, risk-taking, and continuous improvement is essential for driving innovation. Organizations should empower employees to contribute ideas and reward innovative solutions.
Tip 5: Focus on Talent Acquisition and Retention: Attracting and retaining skilled engineers, scientists, and technicians is critical for sustaining a competitive advantage. Organizations should offer competitive compensation packages, professional development opportunities, and a supportive work environment.
Tip 6: Proactively Adapt to Regulatory Changes: The aerospace industry is subject to stringent regulatory oversight. Organizations must remain vigilant in monitoring regulatory changes and proactively adapt their operations to ensure compliance. This includes adhering to evolving safety standards and environmental regulations.
Tip 7: Embrace Digital Transformation: The integration of digital technologies, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics, can enhance decision-making, improve operational efficiency, and unlock new business opportunities. Organizations should invest in digital infrastructure and develop strategies to leverage these technologies effectively.
By adhering to these principles, organizations can strengthen their position within the aerospace sector and contribute to the continued advancement of aviation and space exploration.
The ensuing discussion will delve into the challenges and opportunities facing the industry, providing a forward-looking perspective on the future of aerospace.
1. Innovation Drivers
The capacity for innovation is central to the sustained success and global competitiveness of leading aerospace organizations in the United States. These entities consistently generate groundbreaking technologies and methodologies, propelled by a confluence of internal and external factors. These innovation drivers not only enhance their market position but also contribute significantly to national security and economic progress.
- Research and Development Investment
Substantial financial commitment to research and development is a fundamental driver of innovation. Top aerospace firms allocate significant portions of their revenue to exploring novel materials, propulsion systems, and digital technologies. For instance, investments in advanced composite materials have led to lighter and more fuel-efficient aircraft, while research into autonomous systems has paved the way for unmanned aerial vehicles and more sophisticated flight control systems. This consistent investment fuels a cycle of technological advancement, allowing these companies to maintain a competitive edge.
- Government Partnerships and Funding
Collaborative relationships with government agencies, particularly the Department of Defense and NASA, are crucial for fostering innovation. Government funding and contracts provide resources for developing cutting-edge technologies with applications in both defense and civilian sectors. Examples include the development of advanced jet engines and hypersonic vehicles, which often originate from government-sponsored research programs. These partnerships also facilitate the transfer of knowledge and expertise between government and industry, accelerating the pace of innovation.
- Talent Acquisition and Development
Attracting and retaining top engineering and scientific talent is essential for driving innovation. Leading aerospace companies actively recruit graduates from top universities and invest in training and development programs to cultivate expertise in specialized fields. These companies foster a culture of innovation by encouraging employees to experiment, take risks, and challenge conventional thinking. The presence of highly skilled and motivated personnel is a critical factor in generating new ideas and translating them into tangible products and services.
- Competitive Market Dynamics
The intensely competitive nature of the aerospace industry serves as a powerful catalyst for innovation. Companies are constantly striving to develop superior products and services to gain market share and attract customers. This competitive pressure incentivizes firms to invest in R&D, improve manufacturing processes, and explore new business models. The pursuit of efficiency and cost-effectiveness also drives innovation, leading to the development of more affordable and sustainable aerospace solutions.
These multifaceted innovation drivers are interconnected and mutually reinforcing. The combined effect of robust R&D investment, government partnerships, talent acquisition, and competitive pressures ensures that top aerospace firms in the United States remain at the forefront of technological advancement. This continuous cycle of innovation not only benefits these individual organizations but also strengthens the overall aerospace ecosystem and contributes to broader societal goals.
2. Market Dominance
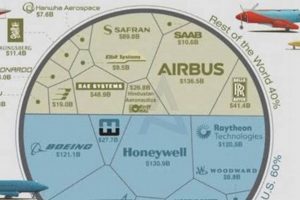
Market dominance, a defining characteristic of leading United States aerospace entities, is not merely a result of chance but a consequence of sustained technological innovation, strategic partnerships, and effective execution. These organizations secure and maintain their prominent positions through a combination of factors, including substantial government contracts, intellectual property portfolios, and expansive distribution networks. This dominance manifests as a significant market share, pricing influence, and the capacity to set industry standards. For example, a company holding a large proportion of military aircraft production demonstrates this characteristic. The influence enables reinvestment in research, perpetuating a cycle of innovation and further solidifying market leadership.
The importance of market dominance extends beyond financial metrics. It signifies the trust and reliability these companies have established with government agencies, commercial clients, and international partners. This trust is earned through consistent performance, adherence to rigorous safety standards, and the ability to deliver complex projects on time and within budget. Moreover, it fosters collaboration and provides opportunities to shape regulatory frameworks, ensuring a stable operating environment. Understanding this connection provides insights into the competitive advantages of these firms and their long-term sustainability. Organizations seek to emulate these strategies, while governments recognize the importance of nurturing these capabilities for national security and economic prosperity.
In summary, market dominance is both a consequence and a driver of success for prominent aerospace firms in the U.S. It reflects a commitment to innovation, operational excellence, and strategic partnerships. This position confers significant advantages, including influence over industry standards, access to resources, and the ability to shape the future of aerospace technology. Recognizing this interplay is crucial for stakeholders seeking to understand the dynamics of the aerospace sector and for policymakers aiming to support its continued growth.
3. Technological Prowess
Technological prowess is a cornerstone of competitive advantage for leading aerospace organizations within the United States. This encompasses a comprehensive range of capabilities, from advanced materials science to sophisticated software engineering, and serves as a critical differentiator in a rapidly evolving global market.
- Advanced Materials Science and Engineering
The development and application of advanced materials, such as carbon fiber composites, titanium alloys, and high-temperature ceramics, are crucial for enhancing aircraft performance, reducing weight, and improving fuel efficiency. Leading aerospace companies in the U.S. invest heavily in materials research to create lighter, stronger, and more durable components. For example, the extensive use of carbon fiber in Boeing’s 787 Dreamliner significantly reduced its weight and improved its fuel economy compared to previous generation aircraft. This materials expertise directly translates to improved performance and cost-effectiveness, providing a competitive edge in the commercial and military aviation sectors.
- Propulsion Systems and Aerodynamics
The design and development of advanced propulsion systems, including jet engines, rocket engines, and electric propulsion, are fundamental to aerospace innovation. U.S. aerospace companies are at the forefront of developing more efficient, powerful, and environmentally friendly engines. For instance, General Electric’s LEAP engine, used in many commercial airliners, incorporates advanced technologies to reduce fuel consumption and emissions. Similarly, companies like SpaceX are pushing the boundaries of rocket propulsion with reusable rocket technology, dramatically lowering the cost of space access. These advancements in propulsion systems and aerodynamics are essential for maintaining U.S. leadership in both air and space domains.
- Avionics and Embedded Systems
The integration of sophisticated avionics and embedded systems is critical for modern aircraft and spacecraft. These systems include flight control computers, navigation systems, radar systems, and electronic warfare systems. Top aerospace companies in the U.S. possess deep expertise in developing and integrating these complex systems, ensuring safe and efficient operation of aircraft and spacecraft. For example, Lockheed Martin’s F-35 fighter jet incorporates advanced sensor fusion and electronic warfare capabilities, providing a significant advantage in air combat. The ability to design and integrate these complex systems is a key factor in the competitiveness of U.S. aerospace companies.
- Software Engineering and Artificial Intelligence
Software engineering plays an increasingly important role in modern aerospace, with applications ranging from flight control systems to mission planning and data analysis. The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning is further transforming the industry, enabling autonomous flight, predictive maintenance, and more efficient operations. Prominent U.S. aerospace firms are investing heavily in software development and AI research to enhance the capabilities of their products and services. An example is the development of autonomous drones for surveillance and delivery, which rely on advanced algorithms for navigation and obstacle avoidance. Expertise in software engineering and AI is becoming a critical factor in determining the long-term success of aerospace companies.
These diverse areas of technological prowess are interconnected and mutually reinforcing. The ability to excel in materials science, propulsion systems, avionics, and software engineering enables U.S. aerospace companies to develop cutting-edge products and services that meet the evolving needs of both commercial and military customers. The continuous pursuit of technological advancement is essential for maintaining U.S. leadership in the global aerospace industry.
4. Defense Contracts
The allocation of defense contracts is a pivotal factor shaping the composition and operational scope of leading aerospace organizations within the United States. These contracts, awarded by the Department of Defense and related agencies, provide significant revenue streams, enabling firms to sustain research and development initiatives, expand manufacturing capabilities, and maintain a skilled workforce. A direct consequence of securing such contracts is the ability to undertake projects of national importance, ranging from advanced weapons systems to sophisticated surveillance technologies. Lockheed Martin’s sustained role as a primary contractor for the F-35 fighter jet program exemplifies the scale and duration of these engagements. The magnitude of the financial investment and the technological requirements serve as both a driver of innovation and a barrier to entry for smaller firms. Securing a defense contract enhances prestige of these aerospace company.
Beyond the immediate financial benefits, defense contracts foster long-term strategic partnerships between government and industry. These relationships facilitate the transfer of knowledge, the standardization of technologies, and the development of secure supply chains. The contractual obligations often mandate adherence to stringent quality control measures, cybersecurity protocols, and ethical standards, which contribute to the overall reliability and integrity of the aerospace sector. This synergy between public and private entities has historically fueled technological advancements that extend beyond military applications, contributing to civilian aerospace innovations and broader economic growth.
In conclusion, defense contracts are a critical component of the business model for many top-tier aerospace companies in the United States. The revenue generated, the strategic partnerships forged, and the technological advancements spurred by these contracts collectively shape the industry landscape. Challenges remain in balancing defense priorities with commercial opportunities, ensuring fair competition, and adapting to evolving geopolitical realities. However, the fundamental link between defense spending and aerospace innovation remains a defining characteristic of this sector.
5. Space Exploration
Space exploration serves as both a technological frontier and a significant business driver for leading United States aerospace organizations. These entities play a vital role in designing, manufacturing, and operating the spacecraft, launch vehicles, and associated infrastructure necessary for missions beyond Earth’s atmosphere. Their involvement spans a broad range of activities, from scientific research to commercial ventures.
- Design and Manufacturing of Spacecraft
Top aerospace companies possess the engineering expertise and manufacturing capabilities required to produce spacecraft tailored to specific mission requirements. These craft include satellites for communication, Earth observation, and scientific study, as well as crewed vehicles for human spaceflight. For example, Boeing and Lockheed Martin have been instrumental in the development of NASA’s Orion spacecraft, intended for future crewed missions to the Moon and Mars. The precision and reliability demanded by space missions necessitate advanced manufacturing processes and rigorous testing protocols.
- Development of Launch Vehicles
Access to space depends on reliable and cost-effective launch vehicles. Leading aerospace firms are involved in the design, development, and operation of rockets capable of delivering payloads into orbit. SpaceX’s Falcon series of rockets represents a prominent example of commercially developed launch vehicles used for both government and private sector missions. The pursuit of reusable launch systems, such as those pioneered by SpaceX, aims to reduce the cost of space access and enable more frequent missions.
- Satellite Operations and Management
Once in orbit, satellites require ongoing operation and management to fulfill their intended functions. Aerospace companies often provide services related to satellite control, data processing, and mission planning. These services are crucial for ensuring the continued performance and longevity of satellite assets. For example, companies like Northrop Grumman offer satellite servicing and life-extension capabilities, which can prolong the operational lifespan of existing satellites and reduce the need for costly replacements.
- Research and Development of Space Technologies
Space exploration drives innovation in a wide range of technologies, including advanced materials, propulsion systems, and robotics. Aerospace companies invest in research and development to create new technologies that can enable more ambitious space missions. For instance, the development of advanced radiation shielding for spacecraft is essential for protecting astronauts from the harmful effects of space radiation during long-duration missions. These technological advancements often have applications beyond space exploration, benefiting other industries and contributing to broader societal goals.
In summary, the connection between space exploration and leading United States aerospace organizations is multifaceted, encompassing spacecraft design, launch vehicle development, satellite operations, and technology research. These companies are critical partners in advancing the frontiers of space exploration and harnessing the benefits of space technology for scientific discovery, economic development, and national security.
6. Global Reach
The operational scope of prominent aerospace organizations headquartered in the United States extends far beyond national borders, impacting international economies and geopolitical landscapes. This global reach is not merely a consequence of successful domestic operations but a strategically cultivated component of their overall business model. Factors contributing to this expansive influence include participation in international joint ventures, establishment of foreign subsidiaries, and the export of aerospace technologies and services. For instance, a U.S.-based aerospace firm might collaborate with a European partner to develop a new generation of commercial aircraft, illustrating the interdependence of these organizations on a global scale. The ability to secure contracts from foreign governments and commercial entities is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge and diversifying revenue streams.
The importance of a global presence also stems from the need to access specialized skills, resources, and manufacturing capabilities distributed across various countries. Establishing facilities in foreign markets enables companies to leverage local expertise, reduce production costs, and navigate regulatory complexities. Furthermore, it allows them to respond more effectively to the needs of international customers and tailor products to specific regional requirements. Exporting aerospace technologies and services not only generates revenue but also strengthens diplomatic ties and promotes technological standards worldwide. The global network of suppliers, distributors, and partners enhances resilience and facilitates adaptation to changing market conditions. For example, the establishment of a manufacturing plant in Asia can significantly reduce lead times and improve responsiveness to the demands of that region.
In conclusion, a significant global presence is an indispensable characteristic of leading U.S. aerospace entities. It is driven by the pursuit of market share, access to resources, and the need to navigate complex international regulatory environments. Maintaining and expanding this global reach requires ongoing investments in infrastructure, partnerships, and skilled personnel. While it presents challenges related to cultural differences, geopolitical risks, and supply chain management, the benefits of a globally integrated operation are essential for long-term sustainability and leadership in the aerospace sector.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Premier Aerospace Organizations in the United States
The following questions address common inquiries and misconceptions surrounding leading entities within the U.S. aerospace sector, offering concise and factual responses.
Question 1: What criteria define a “top” aerospace company in the U.S.?
A company’s position as a “top” aerospace organization is typically determined by a combination of factors, including annual revenue, market share, technological innovation, government contracts, and overall contribution to the aerospace industry. A firm’s reputation and influence within the sector are also considered.
Question 2: What are the primary activities undertaken by these organizations?
These companies engage in a wide range of activities, including the design, development, manufacturing, and operation of aircraft, spacecraft, satellites, and related systems. They also provide engineering services, research and development, and maintenance and support services to both government and commercial clients.
Question 3: How significant is government funding to these entities?
Government funding, particularly through defense contracts and NASA programs, constitutes a substantial portion of the revenue for many top aerospace companies. These contracts enable them to undertake large-scale projects, develop advanced technologies, and maintain a skilled workforce.
Question 4: What impact do these organizations have on technological innovation?
Leading aerospace companies are significant drivers of technological innovation, consistently pushing the boundaries of engineering and materials science. Their research and development efforts lead to advancements in areas such as propulsion systems, avionics, and composite materials, benefiting both the aerospace industry and other sectors.
Question 5: What are the educational and skill requirements for employment within these companies?
Employment typically requires a strong foundation in engineering, science, or related technical fields. Advanced degrees, such as master’s degrees or doctorates, are often preferred for research and development positions. Strong analytical skills, problem-solving abilities, and a capacity for teamwork are also essential.
Question 6: What are the major challenges facing these organizations in the future?
Major challenges include increasing global competition, adapting to evolving regulatory requirements, managing supply chain disruptions, addressing cybersecurity threats, and developing sustainable aerospace technologies. The need to attract and retain skilled talent is also a significant concern.
In summary, prominent aerospace companies in the U.S. play a crucial role in national security, technological innovation, and economic growth. Their activities are shaped by government funding, technological advancements, and evolving global challenges.
The following section will provide a case study analysis of a top aerospace company, highlighting key strategies, challenges, and future prospects.
Concluding Remarks on Leading Aerospace Organizations in the United States
The preceding analysis has explored the multifaceted nature of the top aerospace companies in the US. These organizations are characterized by their commitment to innovation, their reliance on government contracts, their technological prowess, their involvement in space exploration, and their global reach. Their activities significantly impact national security, economic growth, and technological advancement, both domestically and internationally.
Continued monitoring of these entities is essential for understanding the trajectory of the aerospace industry. Their strategic decisions, technological breakthroughs, and responses to evolving global challenges will shape the future of flight and space exploration. Furthermore, their influence on policy and technological standards necessitates informed public discourse and responsible corporate governance.





![Top Michigan Aerospace Companies: [Your Company] & More Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions Top Michigan Aerospace Companies: [Your Company] & More | Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-289-300x200.jpg)