Institutions offering exceptional education and research opportunities within the field of flight and space vehicle design, development, and testing, located across the globe, represent a significant source of innovation and talent. These programs typically feature rigorous curricula, advanced laboratory facilities, and close collaborations with industry leaders. An example would be a university known for its contributions to spacecraft propulsion and aeronautical design.
The significance of these specialized institutions lies in their ability to produce highly skilled engineers and researchers crucial for advancements in aviation, space exploration, and related technologies. Their research output contributes significantly to economic growth and national security. Historically, their emergence has been closely tied to periods of rapid technological progress, particularly during the Cold War era and the ongoing space race.
This analysis will explore factors contributing to the perceived excellence of these institutions, examining their academic structure, research focus, and industrial partnerships. Furthermore, a discussion of key programs and recent advancements stemming from these institutions will be provided.
Strategies for Aspiring Aerospace Engineers
Pursuing a career in aerospace engineering requires rigorous preparation and a strategic approach to academic and professional development. The following insights, distilled from the attributes of leading aerospace engineering programs worldwide, are designed to guide prospective students and early-career professionals.
Tip 1: Cultivate a Strong Foundation in Mathematics and Physics: A solid understanding of calculus, differential equations, linear algebra, classical mechanics, thermodynamics, and fluid dynamics is essential. Mastery of these subjects is the cornerstone of all advanced aerospace engineering coursework. For example, the design of aircraft control systems relies heavily on control theory, which in turn depends on advanced mathematical concepts.
Tip 2: Focus on Hands-On Project Experience: Participate in extracurricular activities such as rocketry clubs, drone design competitions, and model airplane building. These experiences provide invaluable practical skills and demonstrate a passion for the field. Many top programs value candidates with demonstrable project experience.
Tip 3: Develop Proficiency in Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Simulation Software: Familiarize oneself with industry-standard software packages such as CATIA, ANSYS, and MATLAB. These tools are integral to the design, analysis, and simulation of aerospace systems. Proficiency in these programs can significantly enhance career prospects.
Tip 4: Seek Internship Opportunities at Aerospace Companies or Research Institutions: Internships provide real-world experience and networking opportunities, offering exposure to the challenges and rewards of the profession. Securing internships at reputable organizations is a significant advantage when applying for full-time positions.
Tip 5: Specialize in a Specific Area of Aerospace Engineering: Identify a sub-discipline that aligns with individual interests and career goals, such as aerodynamics, propulsion, structures, or astrodynamics. Focused specialization allows for the development of deep expertise and increases competitiveness in the job market.
Tip 6: Network with Professionals in the Aerospace Industry: Attend industry conferences, join professional organizations like the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA), and connect with aerospace engineers on professional networking platforms. Building a strong professional network can open doors to internships, mentorships, and job opportunities.
Tip 7: Emphasize Communication and Teamwork Skills: Aerospace engineering is a collaborative field. Develop strong communication, presentation, and teamwork skills. The ability to effectively communicate technical information and work collaboratively with diverse teams is highly valued by employers.
These recommendations provide a roadmap for individuals seeking to excel in the field of aerospace engineering. By focusing on a strong technical foundation, practical experience, and professional development, aspiring engineers can position themselves for success in this demanding yet rewarding profession.
These principles will serve as a solid basis for the detailed information about leading academic institutions presented in the subsequent sections of this analysis.
1. Reputation
An institution’s reputation, particularly concerning aerospace engineering programs, directly influences its ability to attract high-caliber students, secure substantial research funding, and forge strategic partnerships with industry leaders and government agencies. A strong reputation is often built upon a history of groundbreaking research, distinguished faculty, and successful alumni who have made significant contributions to the field. The cause-and-effect relationship is clear: a history of excellence leads to enhanced recognition, which in turn attracts further talent and resources, perpetuating a cycle of achievement. The prominence of a university within the aerospace sector serves as a signal of quality and rigor to prospective students and employers alike.
The impact of reputation is evident in recruitment practices. Major aerospace corporations often prioritize graduates from universities with established aerospace engineering programs. These institutions frequently benefit from on-campus recruiting events, exclusive internship opportunities, and collaborative research projects co-led by university faculty and industry professionals. For example, a university known for its contributions to hypersonic flight research might attract funding for specialized laboratories and scholarships for students pursuing advanced degrees in that area. The reputation extends beyond domestic borders, influencing international collaborations and the global standing of the institution. A high-ranking university often attracts collaborative agreements from other international colleges and researchers.
In summary, the reputation of an institution is not merely a superficial attribute but a critical indicator of its overall quality and effectiveness in aerospace engineering education and research. It reflects a legacy of achievement and serves as a powerful magnet for talent, resources, and partnerships. Understanding the significance of reputation is essential for prospective students seeking to maximize their career opportunities and for institutions striving for excellence in this demanding and rapidly evolving field.
2. Faculty Expertise
Faculty expertise is a critical component determining the stature of leading aerospace engineering colleges globally. The depth and breadth of knowledge possessed by professors directly influence the quality of education, research output, and the overall intellectual environment within the department. The presence of renowned experts in specialized fields, such as aerodynamics, propulsion, or structural analysis, attracts high-caliber students and funding opportunities, creating a synergistic effect that elevates the institution’s standing. For instance, a professor recognized for seminal work in computational fluid dynamics can attract research grants, establish advanced simulation laboratories, and mentor doctoral students who subsequently make significant contributions to the field. Therefore, the presence of such faculty directly elevates the program’s profile.
The practical significance of faculty expertise extends beyond academic research. Experienced professors often maintain strong connections with industry partners, facilitating internships, collaborative projects, and technology transfer. This exposure to real-world engineering challenges enhances the practical skills of students and prepares them for successful careers in the aerospace sector. Moreover, faculty with industry experience can provide invaluable insights into current trends and future directions, shaping the curriculum to meet the evolving needs of the profession. As an example, faculty actively involved in the development of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) can integrate relevant coursework and research projects into the curriculum, ensuring students are well-versed in this rapidly growing area of aerospace engineering.
In summary, faculty expertise is a cornerstone of top-tier aerospace engineering programs. It drives innovation, attracts talent and resources, and prepares students for successful careers. The dedication and skill set of the professors is a significant factor in defining the character and quality of the academic program. Evaluating the expertise and experience of faculty members is thus crucial for prospective students and for institutions aspiring to achieve excellence in aerospace engineering education and research.
3. Research Funding
Research funding constitutes a critical lifeline for institutions aspiring to rank among the leading aerospace engineering colleges globally. It directly impacts the capacity to conduct cutting-edge research, attract and retain top-tier faculty, and provide students with access to state-of-the-art facilities and equipment. Without robust financial support, advancements in aerospace technology would be significantly hampered, hindering an institution’s ability to contribute meaningfully to the field.
- Infrastructure Development and Maintenance
Sufficient funding enables the construction and upkeep of specialized laboratories, wind tunnels, flight simulators, and advanced manufacturing facilities. These resources are essential for conducting experimental research, validating theoretical models, and training students in practical skills. For example, research into hypersonic flight requires access to high-speed wind tunnels, the construction and maintenance of which are exceptionally expensive, requiring significant financial investment. Without this infrastructure, colleges simply can’t compete with the top players.
- Faculty Recruitment and Retention
Competitive salaries, research grants, and endowed professorships are essential for attracting and retaining leading researchers and educators in aerospace engineering. Funding allows institutions to offer competitive packages, luring talented individuals from industry and other academic institutions. For example, a well-funded college can offer a higher salary to a distinguished professor, attracting them to leave their current position and bring their expertise and research to the new institution. It also ensures that existing experts remain incentivised to continue researching at that institution.
- Student Research Opportunities and Scholarships
Research funding facilitates the creation of undergraduate and graduate research opportunities, allowing students to participate in cutting-edge projects under the guidance of experienced faculty. Furthermore, it enables the provision of scholarships and fellowships, attracting talented students who might otherwise be unable to afford the cost of education. For example, government-funded research grants can provide stipends for graduate students, enabling them to focus on their research without needing to seek external employment. This attracts top students and allows current students to dedicate more time and thought to the work, increasing the output.
- Collaboration and Partnerships
Adequate funding enables institutions to forge partnerships with industry, government agencies, and other universities, fostering collaborative research projects and knowledge sharing. These partnerships provide access to external expertise, resources, and funding opportunities, further enhancing an institution’s research capabilities. For example, collaborations between universities and aerospace companies can lead to joint research ventures, technology transfer agreements, and the development of new aerospace products and services. In this way, research funding facilitates collaboration.
In conclusion, research funding is not merely a financial input but a catalyst for innovation and excellence in aerospace engineering education and research. It enables top institutions to develop state-of-the-art facilities, attract and retain leading faculty, provide students with exceptional research opportunities, and forge strong partnerships with industry and government. These factors collectively contribute to an institution’s ability to produce highly skilled engineers, conduct groundbreaking research, and maintain its position among the leading aerospace engineering colleges worldwide.
4. Industry Connections
The prominence of industry connections serves as a defining characteristic of leading aerospace engineering colleges globally. A reciprocal relationship exists: successful colleges cultivate strong ties with aerospace companies and government agencies, and these connections, in turn, enhance the institution’s educational and research capabilities. The presence of robust industry relationships contributes to the overall ranking and recognition of these academic programs. It is this relationship that allows the institution to hold its high ranking in the list of top aerospace engineering colleges in the world.
These connections manifest in several forms, including collaborative research projects, internship programs, guest lectures by industry professionals, and advisory boards comprised of industry leaders. Such collaborations provide students with invaluable real-world experience, exposing them to current industry practices and challenges. For example, a university working closely with a major aircraft manufacturer might involve students in the design and testing of new aircraft components. This not only provides practical experience but also increases the likelihood of graduates being hired by that company. Furthermore, industry partnerships facilitate technology transfer, enabling universities to translate research findings into commercial applications, thereby driving innovation within the aerospace sector. The impact is direct and consequential: stronger connections result in better-prepared graduates and more relevant research.
In summary, industry connections are not merely an ancillary benefit but a fundamental component of top-tier aerospace engineering education. These relationships provide students with essential practical experience, facilitate technology transfer, and ensure that curricula remain aligned with industry needs. Consequently, institutions that prioritize and cultivate strong industry connections are better positioned to produce highly skilled engineers and researchers, contributing to advancements in the aerospace field and solidifying their place among the world’s leading institutions.
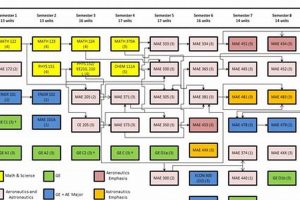
5. Curriculum Rigor
Curriculum rigor forms a cornerstone of academic excellence within top aerospace engineering colleges globally. It’s not just about difficulty; it’s about depth, breadth, and the cultivation of critical thinking skills necessary for solving complex aerospace challenges. A demanding curriculum pushes students beyond rote memorization, fostering innovation and problem-solving capabilities essential for future aerospace engineers.
- Emphasis on Fundamental Principles
A rigorous curriculum emphasizes a deep understanding of fundamental scientific and engineering principles, including advanced mathematics, physics, fluid dynamics, thermodynamics, and materials science. These principles serve as the foundation for all subsequent aerospace engineering coursework. For example, a thorough grounding in fluid dynamics is essential for understanding aerodynamics and designing efficient aircraft wings. Colleges often incorporate comprehensive theoretical work, as well as extensive practical lab work.
- Integration of Advanced Topics
Top programs integrate advanced topics such as computational fluid dynamics, finite element analysis, control systems, and space mission design into the curriculum. These subjects expose students to the cutting-edge technologies and techniques used in modern aerospace engineering. An example would be including modules on the latest advancements in composite materials, which are critical for designing lightweight and strong aircraft structures, as well as assignments relating to cutting-edge fields such as rocket design.
- Focus on Design and Project-Based Learning
A hallmark of rigorous aerospace engineering programs is a strong emphasis on design and project-based learning. Students are challenged to apply their knowledge to solve real-world engineering problems, often working in teams to design, build, and test aerospace systems. For example, students might be tasked with designing a small satellite, a drone, or a rocket engine, requiring them to integrate knowledge from multiple disciplines and develop essential teamwork and project management skills.
- Demanding Assessment and Evaluation
Rigorous programs employ demanding assessment methods, including challenging exams, comprehensive design reports, and rigorous project evaluations, to ensure that students have mastered the required material. These assessments not only measure students’ knowledge but also their ability to apply that knowledge to solve complex engineering problems. The constant pressure of frequent assessments is also designed to prepare students for life in a challenging professional environment.
In conclusion, curriculum rigor is a defining characteristic of leading aerospace engineering programs. It equips graduates with the technical expertise, critical thinking skills, and problem-solving abilities necessary to succeed in the demanding aerospace industry. By emphasizing fundamental principles, integrating advanced topics, focusing on design and project-based learning, and implementing demanding assessment methods, these programs ensure that their graduates are well-prepared to contribute to the advancement of aerospace technology.
6. Facilities
The quality and availability of facilities represent a tangible indicator of an institution’s commitment to aerospace engineering education and research. Leading colleges worldwide prioritize investment in advanced infrastructure to foster innovation and provide students with practical learning experiences that mirror real-world industry settings.
- Advanced Wind Tunnels
Wind tunnels are essential for aerodynamic testing and the validation of aircraft designs. Top aerospace engineering programs feature a range of wind tunnels capable of simulating various flight conditions, including subsonic, transonic, supersonic, and hypersonic speeds. These facilities enable researchers and students to investigate airflow patterns, measure lift and drag forces, and optimize aircraft performance. An example is the use of a hypersonic wind tunnel to test the aerodynamic characteristics of a new spacecraft design intended for re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere. These specialised tunnels are key to advancing our understanding of air travel.
- Flight Simulators
Flight simulators provide students with a safe and controlled environment to experience the complexities of aircraft handling and navigation. Advanced simulators incorporate realistic cockpit controls, visual displays, and motion platforms to replicate the sensations of flight. These facilities are used for pilot training, aircraft design evaluation, and research into human-machine interaction. For instance, aerospace engineers can use flight simulators to test the effectiveness of new flight control systems or to train pilots to handle emergency situations.
- Materials Testing Laboratories
Materials testing laboratories are equipped with sophisticated instruments for characterizing the mechanical properties of aerospace materials, such as metals, composites, and ceramics. These facilities enable researchers to evaluate the strength, stiffness, fatigue resistance, and environmental durability of materials used in aircraft and spacecraft construction. An example is the use of high-powered microscopes and spectrometers to analyse the microstructure of advanced alloys intended for use in jet engines. Testing labs also often include 3D printing capabilities, which are used to create scaled mock ups.
- Propulsion Laboratories
Propulsion laboratories are used for the testing and development of aircraft and spacecraft propulsion systems, including jet engines, rocket engines, and electric propulsion devices. These facilities feature specialized equipment for measuring thrust, fuel consumption, exhaust emissions, and other performance parameters. Researchers use propulsion laboratories to optimize engine designs, develop new propulsion technologies, and improve the efficiency and environmental impact of aerospace transportation. For example, an engine can be tested at different altitudes and temperatures, in order to simulate conditions during flight.
These facilities collectively support the research and educational missions of leading aerospace engineering colleges. The presence of advanced infrastructure provides students with invaluable practical experience, enhances research capabilities, and contributes to the overall reputation and standing of the institution. These facilities are not just amenities but indispensable tools that drive innovation and prepare students to meet the challenges of the aerospace industry.
7. Graduation Outcomes
Graduation outcomes serve as a key metric in evaluating the efficacy of aerospace engineering colleges and identifying those that justifiably rank among the top globally. These outcomes, encompassing employment rates, starting salaries, graduate school admissions, and contributions to the aerospace sector, reflect the quality of education, research opportunities, and industry connections offered by these institutions. A direct correlation exists: superior colleges produce graduates who are highly sought after by aerospace companies, government agencies, and research institutions. For example, institutions with strong industry partnerships often boast higher placement rates as a result of internships leading to full-time job offers.
The practical significance of focusing on graduation outcomes lies in their ability to inform prospective students and stakeholders about the real-world impact of an aerospace engineering program. A university with consistently high placement rates in leading aerospace firms and frequent alumni contributions to significant aerospace projects demonstrates a proven track record of preparing graduates for successful careers. Conversely, a program with lower employment rates or limited industry engagement might signal deficiencies in curriculum relevance or career support services. Institutions that produce successful entrepreneurs who create their own aerospace companies also demonstrate a focus on fostering innovation and leadership capabilities.
In summary, graduation outcomes are not merely a measure of individual student success but a reflection of the overall effectiveness of an aerospace engineering college. They provide valuable insights into the quality of education, research opportunities, and industry connections offered by the institution. While challenges exist in accurately quantifying and comparing graduation outcomes across different institutions, these metrics remain essential for assessing the value and impact of aerospace engineering education and identifying the world’s leading programs. A college can be objectively evaluated based on these tangible metrics.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Top Aerospace Engineering Colleges in World
The following section addresses common inquiries concerning institutions renowned for their aerospace engineering programs, providing objective information to aid prospective students and other interested parties.
Question 1: What criteria define an aerospace engineering program as “top tier?”
Evaluative criteria include, but are not limited to, faculty expertise, research funding, industry connections, curriculum rigor, facilities, and graduate employment outcomes. Reputational surveys and rankings often reflect a composite assessment of these factors. Further, institutions known for being innovative leaders in this field are considered to be top-tier.
Question 2: How significant are university rankings in selecting an aerospace engineering program?
Rankings can provide a general overview of institutional strengths but should not be the sole determinant. Prospective students are advised to consider program-specific attributes and align their choices with individual academic and career goals. Personal fit should also be considered; it is more important than the ranking.
Question 3: Is it essential for top aerospace engineering colleges to be located in countries with prominent aerospace industries?
Proximity to aerospace industries can enhance internship and employment opportunities, however, it is not a prerequisite. Institutions with strong industry partnerships can provide similar advantages regardless of geographical location. Some universities also partner with institutions located nearby to aerospace industries, further diversifying the institution.
Question 4: What is the relative importance of theoretical knowledge versus practical experience in aerospace engineering curricula?
A balanced approach is optimal. Top programs emphasize a strong foundation in theoretical principles coupled with hands-on experience through laboratory work, design projects, and internships. This combination creates a more holistic education.
Question 5: How crucial is research experience for undergraduate students aspiring to attend top aerospace engineering graduate programs?
Undergraduate research experience is highly valued by graduate admissions committees. It demonstrates a student’s aptitude for research, commitment to the field, and ability to contribute to scholarly endeavors. It is therefore very important to have research experience if you are planning to continue to a graduate program.
Question 6: What specific skills and attributes are most sought after by employers hiring graduates from top aerospace engineering colleges?
Employers typically seek graduates with strong analytical and problem-solving skills, proficiency in relevant software tools, the ability to work effectively in teams, and excellent communication skills. They also highly value practical experience gained through internships and design projects. Demonstrated passion for this line of work is also commonly sought.
In summary, the selection of an aerospace engineering program should be based on a comprehensive evaluation of various factors, aligning individual needs and aspirations with the strengths and opportunities offered by different institutions.
The following section transitions to a discussion of the career pathways available to graduates of top aerospace engineering colleges.
Conclusion
This exploration of top aerospace engineering colleges in world has illuminated key characteristics that define these institutions. Emphasis has been placed on faculty expertise, research funding, industry connections, curriculum rigor, facilities, and graduate outcomes as determinants of institutional quality and student success. The analysis underscores the multifaceted nature of excellence in aerospace engineering education.
The pursuit of advanced knowledge in aerospace engineering demands careful consideration and strategic planning. Aspiring engineers are encouraged to critically evaluate institutional attributes, aligning their choices with personal aspirations and the evolving landscape of the aerospace industry. The future of aerospace innovation hinges on the talent cultivated within these institutions. Those interested in this field should invest significant time into researching the best possible educational institutions.



![Top Ivy League Aerospace Engineering Programs [Year] Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions Top Ivy League Aerospace Engineering Programs [Year] | Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-123-300x200.jpg)

